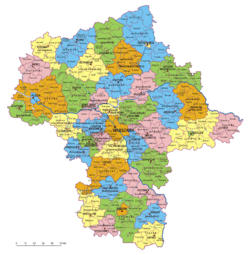
Masovian Voivodeship
Mazovian Voivodeship or Mazovia Province[4] (Polish: województwo mazowieckie [vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ mazɔˈvʲɛtskʲɛ]) is the largest and most populous of the 16 Polish provinces, or voivodeships, created in 1999. It occupies 35,579 square kilometres (13,737 sq mi) of east-central Poland, and has 5,324,500 inhabitants.[1] Its principal cities are Warsaw (1.749 million) in the centre of the Warsaw metropolitan area, Radom (226,000) in the south, Płock (127,000) in the west, Siedlce (77,000) in the east, and Ostrołęka (55,000) in the north. The capital of the voivodeship is the national capital, Warsaw.
The province was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Warsaw, Płock, Ciechanów, Ostrołęka, Siedlce and Radom Voivodeships, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998. The province's name recalls the traditional name of the region, Mazowsze (sometimes rendered in English as "Mazovia"), with which it is roughly coterminous. However, southern part of the voivodeship, with Radom, historically belongs to Lesser Poland, while Łomża and its surroundings, even though historically part of Mazovia, now is part of Podlaskie Voivodeship.
It is bordered by six other voivodeships: Warmian-Masurian to the north, Podlaskie to the north-east, Lublin to the south-east, Świętokrzyskie to the south, Łódź to the south-west, and Kuyavian-Pomeranian to the north-west.
Mazovia is the centre of science, research, education, industry and infrastructure in the country.[5] It currently has the lowest unemployment rate in Poland and is classified as a very high income province.[5] Moreover, it is popular among holidaymakers due to the number of historical monuments and greenery; forests cover over 20% of the voivodeship's area, where pines and oaks predominate in the regional landscape.[6] Additionally, the Kampinos National Park located within Masovia is a UNESCO-designated biosphere reserve.
Administrative division
Masovian Voivodeship is divided into 42 counties (powiats): 5 city counties (miasto na prawach powiatu) and 37 "land counties" (powiat ziemski). These are subdivided into 314 gminas, which include 85 "urban gminas".
.jpg)




- The counties, shown on the numbered map, are described in the table below.
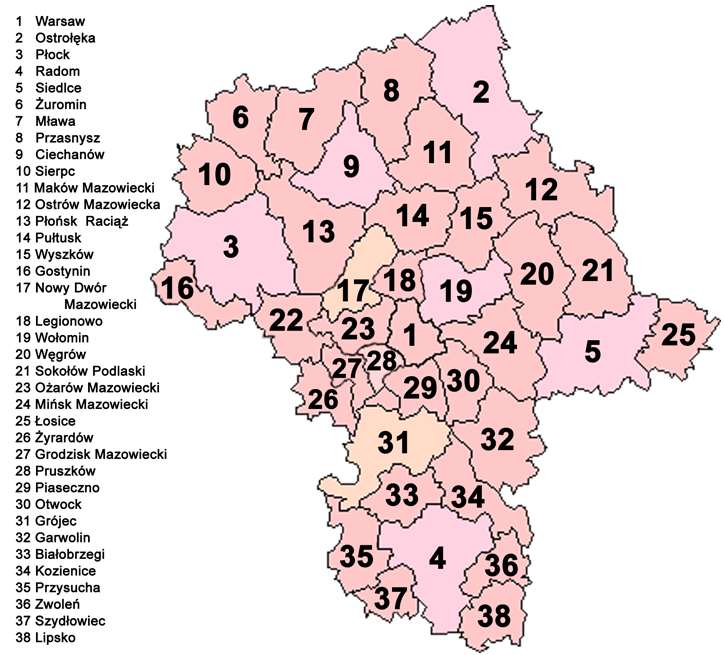 | |||||||
| Map ref. |
English and Polish names |
Area | Population (2017) |
Seat | Other towns | Total gminas | |
| (km²) | (sq mi) | ||||||
| City counties | |||||||
| 1 | Warsaw Warszawa |
517 | 200 | 1,764,615 | 1 | ||
| (2) | Ostrołęka | 29 | 11 | 52,215 | 1 | ||
| (3) | Płock | 88 | 34 | 120,787 | 1 | ||
| (4) | Radom | 112 | 43 | 214,566 | 1 | ||
| (5) | Siedlce | 32 | 12 | 77,653 | 1 | ||
| Land counties | |||||||
| 2 | Ostrołęka County powiat ostrołęcki |
2,099 | 810 | 88,240 | Ostrołęka * | Myszyniec | 11 |
| 3 | Płock County powiat płocki |
1,799 | 695 | 111,067 | Płock * | Gąbin, Drobin, Wyszogród | 15 |
| 4 | Radom County powiat radomski |
1,530 | 591 | 145,232 | Radom * | Pionki, Iłża, Skaryszew | 13 |
| 5 | Siedlce County powiat siedlecki |
1,603 | 619 | 81,685 | Siedlce * | Mordy | 13 |
| 6 | Żuromin County powiat żuromiński |
805 | 311 | 39,885 | Żuromin | Bieżuń | 6 |
| 7 | Mława County powiat mławski |
1,182 | 456 | 73,919 | Mława | 10 | |
| 8 | Przasnysz County powiat przasnyski |
1,218 | 470 | 53,448 | Przasnysz | Chorzele | 7 |
| 9 | Ciechanów County powiat ciechanowski |
1,063 | 410 | 90,823 | Ciechanów | Glinojeck | 9 |
| 10 | Sierpc County powiat sierpecki |
853 | 329 | 53,215 | Sierpc | 7 | |
| 11 | Maków County powiat makowski |
1,065 | 411 | 46,435 | Maków Mazowiecki | Różan | 10 |
| 12 | Ostrów Mazowiecka County powiat ostrowski |
1,218 | 470 | 74,464 | Ostrów Mazowiecka | Brok | 11 |
| 13 | Płońsk County powiat płoński |
1,384 | 534 | 88,612 | Płońsk | Raciąż | 12 |
| 14 | Pułtusk County powiat pułtuski |
829 | 320 | 51,409 | Pułtusk | 7 | |
| 15 | Wyszków County powiat wyszkowski |
876 | 338 | 73,929 | Wyszków | 6 | |
| 16 | Gostynin County powiat gostyniński |
616 | 238 | 46,345 | Gostynin | 5 | |
| 17 | Nowy Dwór Mazowiecki County powiat nowodworski |
692 | 267 | 79,290 | Nowy Dwór Mazowiecki | Nasielsk, Zakroczym | 6 |
| 18 | Legionowo County powiat legionowski |
390 | 151 | 115,384 | Legionowo | Serock | 5 |
| 19 | Wołomin County powiat wołomiński |
955 | 369 | 241,890 | Wołomin | Ząbki, Marki, Kobyłka, Zielonka, Radzymin, Tłuszcz | 12 |
| 20 | Węgrów County powiat węgrowski |
1,219 | 471 | 67,490 | Węgrów | Łochów | 9 |
| 21 | Sokołów County powiat sokołowski |
1,131 | 437 | 55,511 | Sokołów Podlaski | Kosów Lacki | 9 |
| 22 | Sochaczew County powiat sochaczewski |
731 | 282 | 85,103 | Sochaczew | 8 | |
| 23 | Warsaw West County powiat warszawski zachodni |
533 | 206 | 115,466 | Ożarów Mazowiecki | Łomianki, Błonie | 7 |
| 24 | Mińsk County powiat miński |
1,164 | 449 | 152,945 | Mińsk Mazowiecki | Sulejówek, Halinów, Kałuszyn | 13 |
| 25 | Łosice County powiat łosicki |
772 | 298 | 32,046 | Łosice | 6 | |
| 26 | Żyrardów County powiat żyrardowski |
533 | 206 | 76,413 | Żyrardów | Mszczonów | 5 |
| 27 | Grodzisk Mazowiecki County powiat grodziski |
367 | 142 | 92,847 | Grodzisk Mazowiecki | Milanówek, Podkowa Leśna | 6 |
| 28 | Pruszków County powiat pruszkowski |
246 | 95 | 162,922 | Pruszków | Piastów, Brwinów | 6 |
| 29 | Piaseczno County powiat piaseczyński |
621 | 240 | 182,082 | Piaseczno | Konstancin-Jeziorna, Góra Kalwaria, Tarczyn | 6 |
| 30 | Otwock County powiat otwocki |
615 | 237 | 122,661 | Otwock | Józefów, Karczew | 8 |
| 31 | Grójec County powiat grójecki |
1,269 | 490 | 98,692 | Grójec | Warka, Nowe Miasto nad Pilicą, Mogielnica | 10 |
| 32 | Garwolin County powiat garwoliński |
1,284 | 496 | 108,551 | Garwolin | Łaskarzew, Pilawa, Żelechów | 14 |
| 33 | Białobrzegi County powiat białobrzeski |
639 | 247 | 33,669 | Białobrzegi | Wyśmierzyce | 6 |
| 34 | Kozienice County powiat kozienicki |
917 | 354 | 61,874 | Kozienice | 7 | |
| 35 | Przysucha County powiat przysuski |
801 | 309 | 42,869 | Przysucha | 8 | |
| 36 | Zwoleń County powiat zwoleński |
571 | 220 | 36,892 | Zwoleń | 5 | |
| 37 | Szydłowiec County powiat szydłowiecki |
452 | 175 | 40,340 | Szydłowiec | 5 | |
| 38 | Lipsko County powiat lipski |
748 | 289 | 35,426 | Lipsko | 6 | |
| * seat not part of the county | |||||||
Cities and towns
The voivodeship contains 85 cities and towns. These are listed below in descending order of population (according to official figures for 2006):[7]
- Warsaw (1,764,615)
- Radom (214,566)
- Płock (120,787)
- Siedlce (77,653)
- Pruszków (61,237)
- Legionowo (54,041)
- Ostrołęka (53,982)
- Piaseczno (47,660)
- Ciechanów (45,902)
- Otwock (43,247)
- Żyrardów (41,161)
- Mińsk Mazowiecki (40,399)
- Sochaczew (37,925)
- Wołomin (37,164)
- Ząbki (35,770)
- Marki (32,686)
- Mława (29,702)
- Nowy Dwór Mazowiecki (28,637)
- Grodzisk Mazowiecki (27,055)
- Wyszków (27,010)
- Piastów (23,273)
- Ostrów Mazowiecka (22,560)
- Płońsk (22,233)
- Józefów (20,488)
- Pionki (19,788)
- Pułtusk (19,229)
- Gostynin (19,119)
- Sierpc (18,791)
- Sulejówek (18,676)
- Kozienice (18,541)
- Sokołów Podlaski (18,419)
- Kobyłka (17,897)
- Zielonka (17,539)
- Przasnysz (17,069)
- Łomianki (16,875)
- Konstancin-Jeziorna (16,579)
- Garwolin (16,072)
- Milanówek (15,660)
- Grójec (14,990)
- Węgrów (12,606)
- Błonie (12,354)
- Szydłowiec (12,030)
- Brwinów (11,968)
- Góra Kalwaria (11,130)
- Warka (11,028)
- Karczew (10,396)
- Maków Mazowiecki (9,880)
- Żuromin (8,647)
- Ożarów Mazowiecki (8,237)
- Zwoleń (8,176)
- Tłuszcz (8,127)
- Radzymin (7,864)
- Nasielsk (7,364)
- Białobrzegi (7,320)
- Łosice (7,252)
- Łochów (6,452)
- Przysucha (6,245)
- Mszczonów (6,231)
- Lipsko (5,826)
- Iłża (5,165)
- Łaskarzew (4,908)
- Raciąż (4,752)
- Pilawa (4,196)
- Gąbin (4,137)
- Żelechów (4,016)
- Skaryszew (3,989)
- Tarczyn (3,886)
- Nowe Miasto nad Pilicą (3,832)
- Podkowa Leśna (3,824)
- Serock (3,721)
- Halinów (3,369)
- Zakroczym (3,367)
- Glinojeck (3,052)
- Myszyniec (3,014)
- Drobin (2,980)
- Kałuszyn (2,905)
- Chorzele (2,783)
- Wyszogród (2,772)
- Różan (2,661)
- Mogielnica (2,461)
- Kosów Lacki (2,135)
- Bieżuń (1,874)
- Brok (1,859)
- Mordy (1,840)
- Wyśmierzyce (889)
Protected areas

Protected areas in Masovian Voivodeship include one National Park and nine Landscape Parks. These are listed below.
- Kampinos National Park (a UNESCO-designated biosphere reserve)
- Bolimów Landscape Park (partly in Łódź Voivodeship)
- Brudzeń Landscape Park
- Bug Landscape Park
- Chojnów Landscape Park
- Górzno-Lidzbark Landscape Park (partly in Kuyavian-Pomeranian and Warmian-Masurian Voivodeships)
- Gostynin-Włocławek Landscape Park (partly in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship)
- Kozienice Landscape Park
- Masovian Landscape Park
- Podlaskie Bug Gorge Landscape Park (partly in Lublin Voivodeship)
Most popular surnames in the region
- Kowalski: 26,270
- Wiśniewski: 21,940
- Kowalczyk: 21,586
- Lukasik: 15,562
- Mazurkiewicz: Founding of Masovia Name.
Historical
Masovian Voivodeship (1526–1795)
Masovia Voivodeship, 1526–1795 (Polish: Województwo Mazowieckie) was an administrative region of the Kingdom of Poland, and of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, from the 15th century until the partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (1795). Together with Płock and Rawa Voivodeships, it formed the province (prowincja) of Masovia.
Masovian Voivodeship (1816–1837)
Masovian Voivodeship was one of the voivodeships of Congress Poland. It was formed from Warsaw Department, and transformed into Masovia Governorate.
Transportation
%2C_%C5%BBmigr%C3%B3d%2C_2015-12-05.jpg)
There are three main road routes that pass through the voivodeship: Cork–Berlin–Poznań–Warszawa–Minsk–Moscow–Omsk, Prague–Wrocław–Warsaw–Białystok–Helsinki and Pskov–Gdańsk–Warsaw–Kraków–Budapest.
Currently, there are various stretches of autostrada in the area, with the A2 autostrada connecting the region, and therefore the capital city, with the rest of Europe. The autostrada passes directly through the voivodship from west to east, connecting it with Belarus and Germany. However, the A2 is yet to be built east of Warsaw to connect Poland with Belarus. The S8 expressway connects Warsaw with Białystok in the neighboring eastern province, along with the S17 being built to connect Warsaw with Lublin.
The railroad system is based on Koleje Mazowieckie and PKP Intercity.
The main international airport in the region is Warsaw Frederic Chopin Airport.
Economy
Mazovian Voivodeship is the wealthiest province in Poland. The gross domestic product (GDP) of the province was €112.2 billion in 2018, accounting for 22.6% of the Polish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was €34,400 or 114% of the EU27 average in the same year.[8]
Unemployment
The unemployment rate stood at 4.8% in 2017 and was higher than the national and the European average.[9]
| Year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unemployment rate (in %) |
12.3 | 9.1 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.2 | 6.4 | 5.5 | 4.8 |
Gallery
 Płock Cathedral, burial site of Polish monarchs
Płock Cathedral, burial site of Polish monarchs Warsaw Old Town, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
Warsaw Old Town, a UNESCO World Heritage Site Saint Catherine of Alexandria church in Radom
Saint Catherine of Alexandria church in Radom Palace in Otwock Wielki
Palace in Otwock Wielki
 Łyszkiewicz Apartment in Warsaw, birthplace of Marie Curie, presently a museum of the Nobel Prize winner
Łyszkiewicz Apartment in Warsaw, birthplace of Marie Curie, presently a museum of the Nobel Prize winner Birthplace of Frédéric Chopin in Żelazowa Wola, presently a museum of the composer
Birthplace of Frédéric Chopin in Żelazowa Wola, presently a museum of the composer
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Masovian Voivodeship. |
- Second Polish Republic's Warsaw Voivodeship (1919–1939)
References
- www.ideo.pl, ideo -. "Urząd Statystyczny w Warszawie". Retrieved 10 April 2017.
- https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/2995521/10474907/1-05032020-AP-EN.pdf
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- Arkadiusz Belczyk, Tłumaczenie polskich nazw geograficznych na język angielski Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine [Translation of Polish Geographical Names into English], 2002-2006.
- "WHY WARSAW? - Aquatherm Warsaw". Retrieved 10 April 2017.
- Internet, JSK. "Mazowieckie Province". Retrieved 10 April 2017.
- "GUS - Główny Urząd Statystyczny - Błąd 404. Strona o podanym adresie nie istnieje" (in Polish). Stat.gov.pl. Archived from the original on 2008-05-05. Retrieved 2013-05-11.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- "Regional Unemployment by NUTS2 Region". Eurostat.


.png)