Visa policies of Overseas France
Although the European portion of France is part of the Schengen Area, its overseas departments, collectivities and other territories apply their own visa policies, which have some additional exemptions or restrictions compared to the visa policy of the Schengen Area.
- Single territorial collectivity with the competences of a department and a region.
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of France |
|---|
 |
|
|
|
Related topics
|
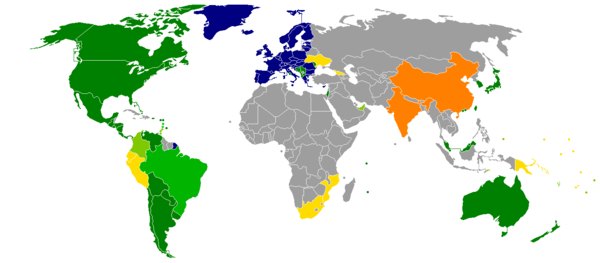
Visa-free access to:






Visa exemptions
Nationals of the following countries can enter and reside for an unlimited period without a visa in Overseas France. They may use their national identity card instead of their passport as a travel document as long as they travel directly. A passport, however, is mostly necessary because most flights from Europe connect through a foreign territory, e.g. the Paris-Papeete flights stop over in Los Angeles, which does necessarily require a USA travel authorisation. A notable exeption was the Air Tahit Nui TN64 flight on the 15th of March 2020, which flew directly to Paris from Papeete as it was not allowed to stop over in Los Angeles due to the Coronavirus pandemic. In theory, European passengers on this flight could have had taken it without a passport, but that was only an exception. [1][2][3][4][5][6]
- British citizens (except those connected only to the Crown dependencies), British subjects with right of abode in the United Kingdom, and British Overseas Territories citizens of Gibraltar.
For stays of up to 3 months in a 6-month period, visa-free entry is granted to nationals of the following countries and territories (except as otherwise noted):[1][2][3][4][5][6]
- With biometric passport.
- For French Guiana, Brazilian citizens may enter without a visa only in the following cases: up to 15 days for trips organized by an approved travel agency; up to 3 days when in transit to France (including all territories) or Brazil; local residents of Oiapoque who are holders of a special card authorising cross-border travel (in which case they can visit Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock only visa-free for up to 72 hours); or members of the emergency services.
- Except for Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin.
- For French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin, visa-free entry of up to 15 days for each stay, as long as the visa-free short stays do not total more than 120 days over a 12-month period.
- Except with passport issued by the Serbian Coordination Directorate.
- With passport bearing identity card number.
- For Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin, only British Nationals (Overseas) and British Overseas Territories citizens of Anguilla (only for Saint Martin), Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Montserrat and Turks and Caicos Islands. For other territories, British citizens connected only to the Crown dependencies, British subjects without right of abode in the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories citizens other than of Gibraltar, British Nationals (Overseas), British Overseas citizens, and British protected persons.
This exemption also applies to:
- Holders of a long-stay visa or residence permit issued by France or another Schengen country
- Nationals of the following countries holding a multiple-entry visa issued by France with validity between 6 months and 5 years:
Additional exemptions for specific territories
For specific territories, nationals of the following countries are also granted visa-free stays of up to 3 months in a 6-month period (except as otherwise noted).
For French Guiana, Guadeloupe and Martinique:[1]
For Saint Martin:[2]
|
For Saint Pierre and Miquelon:[1]
For Réunion:[1]
- Visa-free entry of up to 15 days for each stay, for trips organized by an approved travel agency.
For Mayotte:[3]
For New Caledonia, Wallis and Futuna, and French Polynesia:[4][5][6]
- Visa-free entry of up to 15 days for each stay, for trips organized by an approved travel agency. Only for New Caledonia and French Polynesia.
- Only for New Caledonia.
- With biometric passport.
Summary of short-stay visa exemptions
| Country or territory | France (Schengen) | French Guiana | Guadeloupe and Martinique | Réunion | Mayotte | Saint Pierre and Miquelon | Wallis and Futuna | French Polynesia | New Caledonia | Saint Martin | Saint Barthélemy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Schengen 'Annex II'[lower-alpha 1] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | organized trips or in transit | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | |
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | |
| No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | |
| No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| No | No | No | organized trips | No | No | No | organized trips | organized trips | No | No | |
| No | No | No | organized trips | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
- Except Brazil, Colombia, East Timor, Georgia, Grenada, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Palau, Peru, Saint Vincent and the Greandines, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tuvalu, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, Vanuatu, and British nationals without freedom of movement other than British Nationals (Overseas).
Obtaining a visa
Foreign nationals who require a visa for a part of Overseas France can obtain one by lodging an application at a French embassy or consulate in their country of residence (or, in the case of foreign nationals already in metropolitan France, the local prefecture)[7] for a fee of up to €99 (depending on the destination, length of stay, and age of applicant).[8]
Schengen short-stay visas are not valid for Overseas France (except for nationals of certain countries as listed above), and vice versa. A visa with the designation "départements français d'Amérique" (DFA) allows visiting the French overseas departments in the Americas (French Guiana, Guadeloupe and Martinique) as well as Saint Pierre and Miquelon.[1]
Visitor statistics
| Country/territory | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67,908 | 63,913 | 62,278 | 53,656 | |
| 39,086 | 35,765 | 34,887 | 32,946 | |
| 12,174 | 11,447 | 12,527 | 13,175 | |
| 9,757 | 9,167 | 9,315 | 9,167 | |
| 7,888 | 7,993 | 7,887 | 8,103 | |
| 7,221 | 7,315 | 7,136 | 6,477 | |
| 6,326 | 8,402 | 9,279 | 7,206 | |
| 5,987 | 5,555 | 3,268 | 1,876 | |
| 4,206 | 4,185 | 4,111 | 3,826 | |
| 3,980 | 4,711 | 4,834 | 3,255 | |
| 3,951 | 3,538 | 4,028 | 3,477 | |
| Total | 192,495 | 183,831 | 180,602 | 164,393 |
| Country/territory | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36,725 | 37,245 | 36,545 | 39,183 | |
| 22,809 | 20,926 | 18,065 | 15,722 | |
| 21,151 | 20,056 | 19,087 | 15,674 | |
| 9,143 | 8,529 | 6,780 | 6,334 | |
| 6,128 | 6,329 | 6,128 | 6,763 | |
| 3,648 | 3,520 | 3,616 | 3,950 | |
| 3,453 | 3,552 | 3,371 | 3,946 | |
| 1,045 | 1,104 | 832 | 718 | |
| Total | 115,676 | 113,951 | 107,187 | 107,753 |
See also
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for French Guiana. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for French Polynesia. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Lesser Antilles. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Mayotte. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for New Caledonia. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Reunion. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Saint Pierre and Miquelon. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Wallis and Futuna. |
References
- Ruling of 26 July 2011 regarding the documents and visas required for the entry of foreigners in the territory of Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Martinique, Réunion and the collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Légifrance, consolidated version of 15 August 2020. (in French)
- Ruling of 18 April 2012 regarding the documents and visas required for the entry of foreigners in the territory of the collectivities of Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin, Légifrance, consolidated version of 15 August 2020. (in French)
- Ruling of 4 February 2015 regarding the documents and visas required for the entry of foreigners in the territory of Mayotte, Légifrance, consolidated version of 15 August 2020. (in French)
- Ruling of 22 July 2011 regarding the documents and visas required for the entry of foreigners in the territory of New Caledonia, Légifrance, consolidated version of 15 August 2020. (in French)
- Ruling of 26 July 2011 regarding the documents and visas required for the entry of foreigners in the territory of Wallis and Futuna, Légifrance, consolidated version of 15 August 2020. (in French)
- Ruling of 29 December 2011 regarding the documents and visas required for the entry of foreigners in the territory of French Polynesia, Légifrance, consolidated version of 15 August 2020. (in French)
- "Voyage en outre-mer : de quel visa a besoin un étranger ?". service-public.fr.
- Visa fees, Ministry of Foreign Affairs of France. (in French)
- "Données détaillées". www.ispf.pf.
- "Touristes selon le lieu de résidence". isee.nc.