Galanin receptor 1
Galanin receptor 1 (GAL1) is a G-protein coupled receptor encoded by the GALR1 gene.[5]
Function
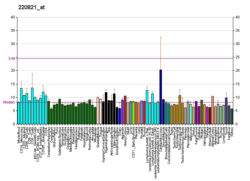
The neuropeptide galanin elicits a range of biological effects by interaction with specific G-protein-coupled receptors. Galanin receptors are seven-trans membrane proteins shown to activate a variety of intracellular second-messenger pathways. GALR1 inhibits adenylyl cyclase via a G protein of the GI/GO family. GALR1 is widely expressed in the brain and spinal cord, as well as in peripheral sites such as the small intestine and heart.[5]
gollark: Oh no. Initiating emergency heavdrones.
gollark: If it's changed, they *will* be able to.
gollark: However, it *is* only forbidden because andrewdrone is a horrible name.
gollark: Don't worry. The PotatOS privacy policy forbids it from harming you.
gollark: So I've created a useful* IRC bot for APIONET.
See also
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166573 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024553 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: GALR1 galanin receptor 1".
Further reading
- Habert-Ortoli E, Amiranoff B, Loquet I, Laburthe M, Mayaux JF (Oct 1994). "Molecular cloning of a functional human galanin receptor". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 91 (21): 9780–3. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.21.9780. PMC 44900. PMID 7524088.
- Walli R, Schäfer H, Morys-Wortmann C, Paetzold G, Nustede R, Schmidt WE (Dec 1994). "Identification and biochemical characterization of the human brain galanin receptor". Journal of Molecular Endocrinology. 13 (3): 347–56. doi:10.1677/jme.0.0130347. PMID 7534460.
- Kask K, Berthold M, Kahl U, Nordvall G, Bartfai T (Jan 1996). "Delineation of the peptide binding site of the human galanin receptor". The EMBO Journal. 15 (2): 236–44. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00354.x. PMC 449938. PMID 8617199.
- Lorimer DD, Benya RV (May 1996). "Cloning and quantification of galanin-1 receptor expression by mucosal cells lining the human gastrointestinal tract". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 222 (2): 379–85. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.0752. PMID 8670213.
- Nicholl J, Kofler B, Sutherland GR, Shine J, Iismaa TP (Dec 1995). "Assignment of the gene encoding human galanin receptor (GALNR) to 18q23 by in situ hybridization". Genomics. 30 (3): 629–30. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1292. PMID 8825658.
- Sullivan KA, Shiao LL, Cascieri MA (Apr 1997). "Pharmacological characterization and tissue distribution of the human and rat GALR1 receptors". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 233 (3): 823–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6542. PMID 9168941.
- Jacoby AS, Webb GC, Liu ML, Kofler B, Hort YJ, Fathi Z, Bottema CD, Shine J, Iismaa TP (Nov 1997). "Structural organization of the mouse and human GALR1 galanin receptor genes (Galnr and GALNR) and chromosomal localization of the mouse gene". Genomics. 45 (3): 496–508. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4960. PMID 9367674.
- Lorimer DD, Matkowskj K, Benya RV (Dec 1997). "Cloning, chromosomal location, and transcriptional regulation of the human galanin-1 receptor gene (GALN1R)". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 241 (2): 558–64. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7838. PMID 9425310.
- Fitzgerald LW, Patterson JP, Conklin DS, Horlick R, Largent BL (Nov 1998). "Pharmacological and biochemical characterization of a recombinant human galanin GALR1 receptor: agonist character of chimeric galanin peptides". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 287 (2): 448–56. PMID 9808667.
- Henson BS, Neubig RR, Jang I, Ogawa T, Zhang Z, Carey TE, D'Silva NJ (Jun 2005). "Galanin receptor 1 has anti-proliferative effects in oral squamous cell carcinoma". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (24): 22564–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.M414589200. PMID 15767248.
- Schäuble N, Reichwald K, Grassl W, Bechstein H, Müller HC, Scherag A, Geller F, Utting M, Siegfried W, Goldschmidt H, Blundell J, Lawton C, Alam R, Whybrow S, Stubbs J, Platzer M, Hebebrand J, Hinney A (Jun 2005). "Human galanin (GAL) and galanin 1 receptor (GALR1) variations are not involved in fat intake and early onset obesity". The Journal of Nutrition. 135 (6): 1387–92. doi:10.1093/jn/135.6.1387. PMID 15930442.
- Belfer I, Hipp H, Bollettino A, McKnight C, Evans C, Virkkunen M, Albaugh B, Max MB, Goldman D, Enoch MA (Jul 2007). "Alcoholism is associated with GALR3 but not two other galanin receptor genes". Genes, Brain, and Behavior. 6 (5): 473–81. doi:10.1111/j.1601-183X.2006.00275.x. PMID 17083333.
External links
- "Galanin Receptors: GAL1". IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.