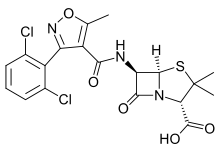
Dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.[1] It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible (non-resistant) Gram-positive bacteria.[1] It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, which would otherwise be resistant to most penicillins. Dicloxacillin is available under a variety of trade names including Diclocil (BMS).[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a685017 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60 to 80% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 0.7 hours |
| Excretion | Renal and biliary |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.535 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H17Cl2N3O5S |
| Molar mass | 470.32 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
It was patented in 1961 and approved for medical use in 1968.[3]
Medical uses
Dicloxacillin is used to treat mild-to-moderate staphylococcal infections.[4] To decrease the development of resistance, dicloxacillin is recommended to treat infections that are suspected or proven to be caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria.[4]
Dicloxacillin is similar in pharmacokinetics, antibacterial activity, and indications to flucloxacillin, and the two agents are considered interchangeable.[5] It is believed to have lower incidence of severe hepatic adverse effects than flucloxacillin, but a higher incidence of renal adverse effects.[5]
Dicloxacillin is used for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible bacteria. Specific approved indications include:[5]
- Staphylococcal skin infections and cellulitis – including impetigo, otitis externa, folliculitis, boils, carbuncles, and mastitis
- Pneumonia (adjunct)
- Osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, throat infections, streptococcus
- Septicaemia
- Empirical treatment for endocarditis
- Surgical prophylaxis
Contraindications
Dicloxacillin is contraindicated in those with a previous history of allergy (hypersensitivity/anaphylactic reaction) to any penicillins.[1][7]
Adverse effects
Common adverse drug reactions (ADRs) associated with the use of dicloxacillin include: diarrhoea, nausea, rash, urticaria, pain and inflammation at injection site, superinfection (including candidiasis), allergy, and transient increases in liver enzymes and bilirubin.[5]
On rare occasions, cholestatic jaundice (also referred to as cholestatic hepatitis) has been associated with dicloxacillin therapy. The reaction may occur up to several weeks after treatment has stopped, and takes weeks to resolve. The estimated incidence is 1 in 15,000 exposures, and is more frequent in people over 55 years old, females, and those with treatment longer than 2 weeks.[5]
It should be used with caution and monitored in the elderly, particularly with intravenous administration, due to a risk of thrombophlebitis.[1]
Dicloxacillin can also lower the effectiveness of birth control pills and pass into breast milk. [8].
Resistance
Despite dicloxacillin being insensitive to beta-lactamases, some organisms have developed resistance to other narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotics including methicillin. Such organisms include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).[12]
Mechanism of action
Like other β-lactam antibiotics, dicloxacillin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. It inhibits cross-linkage between the linear peptidoglycan polymer chains that make up a major component of the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria.
Medicinal chemistry
Dicloxacillin is insensitive to beta-lactamase (also known as penicillinase) enzymes secreted by many penicillin-resistant bacteria. The presence of the isoxazolyl group on the side chain of the penicillin nucleus facilitates the β-lactamase resistance, since they are relatively intolerant of side-chain steric hindrance. Thus, it is able to bind to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) and inhibit peptidoglycan crosslinking, but is not bound by or inactivated by β-lactamase
See also
- Beta-lactam antibiotic
- Flucloxacillin
References
- Product Information: DICLOXACILLIN SODIUM-dicloxacillin sodium capsule. Teva Pharmaceuticals USA Inc, Revised 8/2015
- Miranda-Novales G, Leaños-Miranda BE, Vilchis-Pérez M, Solórzano-Santos F (October 2006). "In vitro activity effects of combinations of cephalothin, dicloxacillin, imipenem, vancomycin and amikacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. strains". Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials. 5: 25. doi:10.1186/1476-0711-5-25. PMC 1617116. PMID 17034644.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 491. ISBN 9783527607495.
- Dicloxacillin. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012.
- Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006
- "Dicloxacillin". MedlinePlus Drug Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine, Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health.
- "DICLOXACILLIN SODIUM- dicloxacillin sodium capsule". DailyMed. National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Health & Human Services.
- "Dicloxacillin - Side Effects, Dosage, Interactions - Drugs - Everyday Health". EverydayHealth.com.
- Lacey CS (May 2004). "Interaction of dicloxacillin with warfarin". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 38 (5): 898. doi:10.1345/aph.1d484. PMID 15054148.
- Ronchera CL, Hernández T, Peris JE, Torres F, Granero L, Jiménez NV, Plá JM (October 1993). "Pharmacokinetic interaction between high-dose methotrexate and amoxycillin". Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. 15 (5): 375–9. doi:10.1097/00007691-199310000-00004. PMID 8249043.
- Moellering RC (August 1983). "Rationale for use of antimicrobial combinations". The American Journal of Medicine. 75 (2A): 4–8. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(83)90088-8. PMID 6351605.
- Rosdahl VT, Frimodt-Møller N, Bentzon MW (August 1989). "Resistance to dicloxacillin, methicillin and oxacillin in methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus detected by dilution and diffusion methods". APMIS. 97 (8): 715–22. doi:10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00467.x. PMID 2669854.