Hetacillin
Hetacillin is a beta-lactam antibiotic that is part of the aminopenicillin family. It is a prodrug and it has no antibacterial activity itself,[1] but quickly splits off acetone in the human body to form ampicillin,[2] which is active against a variety of bacteria.
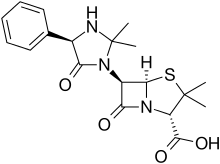 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hetacin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Veterinary Use |
| Routes of administration | Intramammary injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.466 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H23N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 389.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Administration
Hetacillin can be administered orally.[2] The potassium salt, hetacillin potassium, is administered by injection, either intravenously or intramuscularly. It is sold under the trade name Hetacin for intramammary injection in veterinary use.[3]
Hetacillin was removed from the market for human use when the discovery was made that it is actually cleaved in the gastrointestinal tract to formaldehyde and had no advantages over ampicillin.
Chemistry
Hetacillin is prepared from ampicillin and acetone. In aqueous solutions it is unstable, with a half life of 15 to 30 minutes at 37 °C (99 °F) and pH 7, quickly releasing acetone again.[1][4]
As opposed to ampicillin, hetacillin is only marginally broken down by the bacterial enzyme beta-lactamase, at least in vitro.[4]
References
- "Hetacillin". Drugbank.
- Sutherland R, Robinson OP (June 1967). "Laboratory and pharmacological studies in man with hetacillin and ampicillin". British Medical Journal. 2 (5555): 804–8. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5555.804. PMC 1843140. PMID 5182358.
- Hetacin-K Intramammary Infusion for Veterinary Use
- Faine S, Harper M (January 1973). "Independent antibiotic actions of hetacillin and ampicillin revealed by fast methods". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 3 (1): 15–8. doi:10.1128/aac.3.1.15. PMC 444353. PMID 4597707.