Chonan languages
The Chonan languages were a family of indigenous American languages spoken in Tierra del Fuego and Patagonia. Two Chon languages are well attested: Selk'nam (or Ona), spoken by the people of the same name who occupied territory in the northeast of Tierra del Fuego; and Tehuelche spoken by the people of the same name who occupied territory north of Tierra del Fuego. The name 'Chon', or Tshon, is a blend of 'Tehuelche' and 'Ona'.
| Chonan | |
|---|---|
| Patagonian | |
| Geographic distribution | Patagonia |
| Extinct | 2019 |
| Linguistic classification | Mosetén–Chonan ?
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | chon1288[1] |
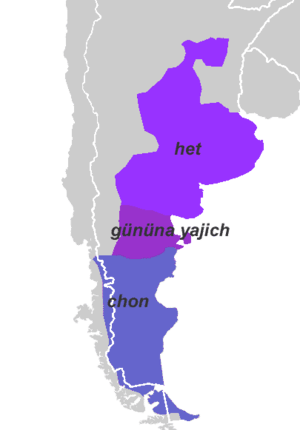 Het, Gününa Yajich (Puelche), and Chon proper. | |
Previous studies
The Selk'nam people were widely studied by anthropologists such as Martin Gusinde and Anne Chapman throughout the 20th century. However, their language became extinct in the 1970s.
History and demographics
The northern Tehuelche were conquered and later assimilated by the Mapuche during the Araucanization of Patagonia. Some 1.7 million Mapuche continue to live in Chile and Argentina. Further south they traded peacefully with y Wladfa, the colony of Welsh settlers. Some Tehuelche learnt Welsh and left their children with the settlers for their education. A solid photographic record was made of this people. However, they were later nearly exterminated in the late 19th-century government-sponsored genocides of Patagonia.[2] Of some 5000 speakers in 1900, as of 2005 there were about 20 speakers left. Tehuelche language is now extinct as of 2019
Classification
The Haush spoke a language similar to Ona. Some scholars also add to the family the Teushen language —once spoken by the Teushen, located between the Tehuelche and Puelche —though it is poorly attested.
Viegas Barros (2005) attempts to demonstrate that Puelche to the north is related to the Chon languages and would constitute one branch of an extended Chonan family. This proposal has been picked up by Lyle Campbell.[3] Based on the scanty evidence that is available, the Het peoples (or at least the Didiuhet) might be speakers of languages within the proposed Puelche branch.
If this is correct, the Chon family would be as follows:
| Chonan |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vocabulary
Loukotka (1968) lists the following basic vocabulary items for the Patagon (Chonan) languages.[4]
gloss Selknam Mánekenkn Téuesh Péeneken Áoniken one shórsh setaul xáuken háuke chochä two shóki aim xaukáya xoxieg xánkä ear shün shunó shán shaʔa shán tooth orx ánktn korr urr hor hand chen shakut chan kʔchen chen foot yul halié kel kel kel sun kren anián sheuen sheuen sheuen moon kre anim teruch kenginkon kängünkon dog uéshn ishna xelxénoe shamehuen xälänuü
References
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Chonan". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Brenzinger, 2007. Language diversity endangered. Walter de Gruyter.
- Campbell, Lyle. (in preparation) "The classification of South American languages. In Campbell & Grondona (eds.), South America. Mouton de Gruyter.
- Loukotka, Čestmír (1968). Classification of South American Indian languages. Los Angeles: UCLA Latin American Center.