Zand dynasty
The Zand dynasty (Persian: سلسله زندیه, Selseleye Zandiye; ![]()
Zand dynasty سلسله زندیه | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1751–1794 | |||||||||||
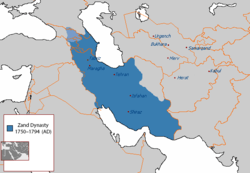 The Zand dynasty at its zenith under Karim Khan. Light-blue shows the Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti, which was de jure under Zand rule, but de facto autonomous. Present day state boundaries overlaid in orange for comparison. | |||||||||||
| Capital | Shiraz | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Persian (official) | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Shah | |||||||||||
• 1751–1779 | Karim Khan Zand (first) | ||||||||||
• 1789–1794 | Lotf Ali Khan Zand (last) | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 1751 | ||||||||||
• Qajar conquest | 1794 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
Karim Khan Zand

The dynasty was founded by Karim Khan Zand, chief of the Zand tribe, which is a tribe of Laks,[2][5] a branch of Lurs[2] who may have been originally Kurdish.[2][5] Nader Shah moved the Zand tribe from their home in Lakestan to the eastern steppes of Khorasan. After Nader's death, the Zand tribe, under the guidance of Karim Khan, went back to their original land.[6] After Adil Shah was made king Karim Khan and his soldiers defected from the army and along with Ali Morad Khan Bakhtiari and Abolfath Khan Haft Lang, two other local chiefs, became a major contender but was challenged by several adversaries.[7] Abolfath Khan was the Vizier, Karim Khan became the army chief commander and Ali Morad Khan became the regent.[7]
Karim Khan declared Shiraz his capital, and in 1778 Tehran became the second capital. He gained control of central and southern parts of Iran. In order to add legitimacy to his claim, Karim Khan placed the infant Shah Ismail III, the grandson of the last Safavid king, on the throne in 1757. Ismail was a figurehead king and real power was vested in Karim Khan. Karim Khan chose to be the military commander and Alimardan Khan was the civil administrator. Soon enough Karim Khan managed to eliminate his partner as well as the puppet king and in 1760, founded his own dynasty. He refused to accept the title of the king and instead named himself Vakilol Ro'aya (Advocate of the People).
By 1760, Karim Khan had defeated all his rivals and controlled all of Iran except Khorasan, in the northeast, which was ruled by Shah Rukh. His foreign campaigns against Azad Khan in Azerbaijan and against the Ottomans in Mesopotamia brought Azerbaijan and the province of Basra into his control. But he never stopped his campaigns against his arch-enemy, Mohammad Hassan Khan Qajar, the chief of the Qoyunlu Qajars. The latter was finally defeated by Karim Khan and his sons, Agha Mohammad Khan and Hossein Qoli Khan Qajar, were brought to Shiraz as hostages.
Karim Khan's monuments in Shiraz include the famous Arg of Karim Khan, Vakil Bazaar, and several mosques and gardens. He is also responsible for building of a palace in the town of Tehran, the future capital of the Qajar dynasty.
Decline and fall
Karim Khan's death in 1779 left his territory vulnerable to threats from his enemies. His son and successor Abu al-Fath was an incompetent ruler who was heavily influenced by his half uncle (and Karim Khan's commander), Zaki Khan. Other rulers such as Ali Morad and Jafar Khan also failed to follow the policies of Karim Khan and soon enough, the country was under attack from all sides.
The biggest enemies of the Zands, the Qajar chiefs, led by the former hostage, Agha Mohammad Khan, were advancing fast against the declining kingdom. Finally, in 1789, Lotf Ali Khan, a grand-nephew of Karim Khan, declared himself the new king. His reign (until 1794) was spent mostly in war with the Qajar khan. He was finally captured and brutally killed in the fortress of Bam, putting an effective end to the Zand Dynasty.
Politically, it is also important that the Zands, especially Karim Khan, chose to call themselves Vakilol Ro'aya (Advocate of the People) instead of kings. Other than the obvious propaganda value of the title, it can be a reflection of the popular demands of the time, expecting rulers with popular leanings instead of absolute monarchs who were totally detached from the population, like the earlier Safavids.
Culture
The Zand era was an era of relative peace and economic growth for the country. Many territories that were once captured by the Ottomans in the late Safavid era were retaken, and Iran was once again a coherent and prosperous country. After Iranian painting reached its height at the end of the 17th century, a special school of painting took shape during the Zand era in the 17th and 18th centuries.[8] The art of this era is remarkable and, despite the short length of the dynasty, a distinct Zand art had the time to emerge. Many Qajar artistic traits were copied from the Zand examples.
In foreign policy, Karim Khan attempted to revive the Safavid era trade by allowing the British to establish a trading post in the port of Bushehr. This opened the hands of the British East India company in Iran and increased their influence in the country.[9] The taxation system was reorganized in a way that taxes were levied fairly. The judicial system was fair and generally humane. Capital punishment was rarely implemented.
Legacy

John R. Perry, writes of Karim Khan Zand as a forward-thinking and popular leader, whom he credits as opening up international trade, employing a fair fiscal system and showing respect for co-existing religious institutions.[10]
Rulers/kings
- Karim Khan Zand, 1751–1779 کریم خان زند
- Mohammad Ali Khan Zand, 1779 محمدعلی خان زند
- Abol-Fath Khan Zand, 1779 ابولفتح خان زند
- Sadeq Khan Zand, 1779–1782 صادق خان زند
- Ali-Morad Khan Zand, 1782–1785 علیمراد خان زند
- Jafar Khan, 1785–1789 جعفر خان زند
- Sayed Morad Khan, 1789 سيد مراد خان زند
- Lotf Ali Khan, 1789–1794 لطفعلی خان زند
Other notable members
- Zaki Khan Zand
- Rustam Khan Zand
Family tree
Budaq Khan | Bay Agha | Inaq Khan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allah Morad Khan | Bay Agha II | Zaki Khan Zand | Karim Khan Zand 1751–1779 | Sadeq Khan Zand 1779–1781 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Koda Morad Khan | Ali-Morad Khan Zand 1782–1785 | Akbar Khan Zand | Abol-Fath Khan Zand 1779 | Mohammad Ali Khan Zand 1779 | Jafar Khan Zand 1785–1789 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sayed Morad Khan 1789 | Rostam Khan Zand | Lotf Ali Khan 1789–1794 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/iran-ii2-islamic-period-page-4
- Perry, John. "ZAND DYNASTY". www.iranicaonline.org. Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 24 March 2017.
The founder of the dynasty was Moḥammad Karim Khan b. Ināq Khan (...) of the Bagala branch of the Zand, a pastoral tribe of the Lak branch of Lors (perhaps originally Kurds; see Minorsky, p. 616) (...)
- Muhammad Karim Khan, of the Zand clan of the Lur tribe, suc- ceeded in imposing his authority on parts of the defunct Safavid empire, David Yeroushalmi, The Jews of Iran in The Nineteenth Century: Aspects of History, Community, and Culture, BRILL, 2009, ISBN 978-90-04-15288-5, p. xxxix.
- "A Brief History of Bahrain".
- ...the bulk of the evidence points to their being one of the northern Lur or Lak tribes, who may originally have been immigrants of Kurdish origin., Peter Avery, William Bayne Fisher, Gavin Hambly, Charles Melville (ed.), The Cambridge History of Iran: From Nadir Shah to the Islamic Republic, Cambridge University Press, 1991, ISBN 978-0-521-20095-0, p. 64.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 21 February 2006. Retrieved 21 February 2006.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "History of Iran". www.farhangsara.com. Retrieved 9 May 2017.
- "New Page 1". Retrieved 9 May 2017.
- "Afshar and Zand". 23 February 2013. Retrieved 9 May 2017.
- Makers of the Muslim World Series -Karim Khan Zand, by John R. Perry, Oneworld Publications October 2006, ISBN 1-85168-435-2
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zand dynasty. |
- www.iranchamber.com/history/zand/zand.php
- www.iranologie.com/history/history13.html
- www.friesian.com/iran.htm#zand
- www.zandbenevolent.com
— Royal house — House of Zand Founding year: 1760 Deposition: 1794 | ||
| Preceded by Afsharid dynasty |
Ruling house of Iran 1760–1794 |
Succeeded by House of Qâjâr |

.svg.png)
