Wartime sexual violence
Wartime sexual violence is rape or other forms of sexual violence committed by combatants during armed conflict, war, or military occupation often as spoils of war; but sometimes, particularly in ethnic conflict, the phenomenon has broader sociological motives. Wartime sexual violence may also include gang rape and rape with objects. It is distinguished from sexual harassment, sexual assaults, and rape committed amongst troops in military service.[1][2][3]

During war and armed conflict, rape is frequently used as a means of psychological warfare in order to humiliate the enemy. Wartime sexual violence may occur in a variety of situations, including institutionalized sexual slavery, wartime sexual violence associated with specific battles or massacres, and individual or isolated acts of sexual violence.
Rape can also be recognized as genocide or ethnic cleansing when committed with the intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a targeted group; however, rape remains widespread in conflict zones. There are other international legal instruments to prosecute perpetrators but this has occurred as late as the 1990s.[4] However, these legal instruments have so far only been used for international conflicts, thus putting the burden of proof in citing the international nature of conflict in order for prosecution to proceed.
Definition of rape
The terms rape, sexual assault and sexual violence are frequently used interchangeably.[5] There is no universally accepted definition of "war rape". The Explanatory Note of the Rome Statute, which binds the International Criminal Court, defines rape as follows:
The perpetrator invaded the body of a person by conduct resulting in penetration, however slight, of any part of the body of the victim or of the perpetrator with a sexual organ, or of the anal or genital opening of the victim with any object or any other part of the body.[6]
and
The invasion was committed by force, or by threat of force or coercion, such as that caused by fear of violence, duress, detention, psychological oppression or abuse of power, against such person or another person, or by taking advantage of a coercive environment, or the invasion was committed against a person incapable of giving genuine consent.[6]
The concept of "invasion" is intended to be broad enough to be gender-neutral and the definition is understood to include situations where the victim may be incapable of giving genuine consent if affected by natural, induced or age-related incapacity.[7]
Causes
Lawlessness during wars and civil conflicts can create a culture of impunity towards human rights abuses of civilians. Among some armies, looting of civilian areas is considered a way for soldiers to supplement their often meager income, which can be unstable if soldiers are not paid on time. Some militias that cannot afford to adequately pay their troops promote pillaging as a compensation for victory, and rape of civilians can be seen as a reward for winning battles.[5][8]
According to UNICEF, "systematic rape is often used as a weapon of war in ethnic cleansing," having been used in various armed conflicts throughout the twentieth century alone, including Bosnia and Herzegovina, Cambodia, Uganda, and Vietnam.[9] In 2008, the United Nations Security Council argued that "women and girls are particularly targeted by the use of sexual violence, including as a tactic of war to humiliate, dominate, instil fear in, disperse and/or forcibly relocate civilian members of a community or ethnic group."[10]
Dara Kay Cohen argues that some military groups use gang rape to bond soldiers and create a sense of cohesion within units, particularly when troops are recruited by force.[11] Amnesty International argues that in modern conflicts rape is used deliberately as a military strategy.[12] Amnesty International describes war rape as a "weapon of war" or a "means of combat"[7] used for the purpose of conquering territory by expelling the population therefrom, decimating remaining civilians by destroying their links of affiliations, by the spread of AIDS, and by eliminating cultural and religious traditions. Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak characterizes "group rape perpetrated by the conquerors" as "a metonymic celebration of territorial acquisition".[13]
Evidence provided by Cohen also suggests that some militaries that use child soldiers use rape as a maturation ritual to increase the tolerance of troops for violence, especially in patriarchal societies that equate masculinity with dominance and control. Some refugees and internally displaced people experience human trafficking for sexual or labour exploitation due to the breakdown of economies and policing in conflict regions.[10] In some conflicts, rape is used as a means of extracting information to force women and girls to give up the location of arms caches. In discussing gang rape as a means of bonding among soldiers, Cohen discusses the viewpoint of "combatant socialization", in which military groups use gang rape as a socialization tactic during armed conflict. By using gang rape during armed conflict, militia group members:
- Prompt feelings of power and achievement
- Establish status and a reputation for aggressiveness
- Create an enhanced feeling of masculinity through bonding and bragging
- Demonstrate dedication to the group and a willingness to take risks
While war rape may not be an apparent tool or weapon of war, it does serve as a primary tool to create a cohesive military group.[11]
Gender
Rape of women
Susan Brownmiller was the first historian to attempt an overview of rape in war with documentation and theory.[14] Brownmiller's thesis is that "War provides men with the perfect psychological backdrop to give vent to their contempt for women. The maleness of the military—the brute power of weaponry exclusive to their hands, the spiritual bonding of men at arms, the manly discipline of orders given and orders obeyed, the simple logic of the hierarchical command—confirms for men what they long suspect—that women are peripheral to the world that counts." She writes that rape accompanies territorial advance by the winning side in land conflicts as one of the spoils of war, and that "Men who rape are ordinary Joes, made unordinary by entry into the most exclusive male-only club in the world."
Kelly Dawn Askin observes that increasingly, the victims of war are civilians. An estimated 45 million plus civilians died during World War II. Male and female civilians may be subject to torture, but many studies show that war rape is more frequently perpetrated on women than men.[15][16] This may be due to the reluctance of men to come forward with accusations of being raped, and also an institutional bias amongst NGOs, who frequently focus resources on female victims.[17] However rape against women is also underreported.[18] Perpetrators of sexual violence against women and children "commonly include not only enemy civilians and troops but also allied and national civilians and even comrades in arms."[15]
The victims of war rape are usually "civilians", a category first recognized in the 19th century.[19] Although war rape of women is documented throughout history, laws protecting civilians in armed conflict have tended not to recognize sexual assault on women. Even when laws of war have recognized and forbidden sexual assault, few prosecutions have been brought. According to Kelly Dawn Askin, the laws of war perpetuated the attitude that sexual assaults against women are less significant crimes, not worthy of prosecution.[20] War rape has until recently been a hidden element of war, which according to Human Rights Watch is linked to the largely gender-specific character of war rape – abuse committed by men against women. This gender-specific character has contributed to war rape being "narrowly portrayed as sexual or personal in nature, a portrayal that depoliticizes sexual abuse in conflict and results in its being ignored as a war crime."[16]
"To the victor go the spoils" has been a war cry for centuries, and women classed as part of the spoils of war.[21] Furthermore, war rape has been downplayed as an unfortunate but inevitable side effect of sending men to war.[16] Also, war rape has in the past been regarded as a tangible reward to soldiers (who were paid irregularly), and as a soldier's proof of masculinity and success.[22] In reference to war rape in ancient times, Harold Washington argues that warfare itself is imaged as rape, and that the cities attacked are its victims. He argues that war rape occurs in the context of stereotypes about women and men, which are part of the basic belief that violent power belongs to men, and that women are its victims.[23]
Rape of men
The rape of men by other men is also common in war. A 2009 study by Lara Stemple[24] found that it had been documented in conflicts worldwide; for example, 76% of male political prisoners in 1980s El Salvador and 80% of concentration camp inmates in Sarajevo reported being raped or sexually tortured. Stemple concludes that the "lack of attention to sexual abuse of men during conflict is particularly troubling given the widespread reach of the problem".[17][25] Mervyn Christian of Johns Hopkins School of Nursing has found that male rape is commonly underreported.[26]
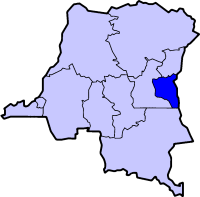
According to a survey published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2010, 30% of women and 22% of men from the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo reported that they had been subject to conflict-related sexual violence.[17] Despite the popular perception that rape during conflict is primarily targeted against women, these figures show that sexual violence committed against men is not a marginal occurrence. The lack of awareness for the magnitude of the rape of men during conflict relates to chronic underreporting. Although the physical and psychological repercussions from rape are similar for women and men, male victims tend to demonstrate an even greater reluctance to report their suffering to their families or the authorities.[27]
According to The Guardian, "Both perpetrator and victim enter a conspiracy of silence and why male survivors often find, once their story is discovered, that they lose the support and comfort of those around them. In the patriarchal societies found in many developing countries, gender roles are strictly defined. […] Often, […] wives who discover their husbands have been raped decide to leave them. They ask me: 'So now how am I going to live with him? As what? Is this still a husband? Is it a wife?' They ask, 'If he can be raped, who is protecting me?'".[17]
Gender roles within social hierarchies are concerned with the question of agency in the conduct of physical violence. Men are expected to exert violence, while women are victimized by it. In conflict situations, rape against men dissolves this relationship and puts men in the ‘receiving’ role of the victim. Similarly, the ‘penetrating’ role of men as opposed to the ‘receiving’ role of women in conventional sexual intercourse illustrates this constructed power relationship. Hence, male rape victims experience the worst possible ‘humiliation’ with regards to the ingrained social roles they are traditionally expected to fulfill. Moreover, their stigmatization takes on particularly severe dimensions within conservative social environments in which homosexual intercourse – regardless of consent – is punished harshly. For example, Ugandan male rape victims explain their choice to not speak out with the fear of being branded homosexuals.[28] As homosexuality is widely condemned in Uganda, male victims of sexual violence often struggle to get proper support because they are accused of being gay. In certain cases, gender roles concerning violence and sexual conduct are so deeply ingrained that the mere existence of male rape is denied.
History of laws against sexual assault during war
Prosecution of rapists in war crime tribunals is a recent development. However, the lack of explicit recognition of war rape in international law or applicable humanitarian law may not be used as a defense by the perpetrator of war rape.[29] Laws and customs of war prohibit offenses such as "inhuman treatment" or "indecent assaults", adding to this domestic military codes and domestic civil codes (national law) may make sexual assault a crime.
More recent humanitarian law concerns the maltreatment of civilians and "any devastation not justified by military necessity".[30]
Pre-modern European era
One of the first references to the "laws of war", or "traditions of war" was by Cicero, who urged soldiers to observe the rules of war, since obeying the regulations separated the "men" from the "brutes". Conquering the riches and property of an enemy was regarded as legitimate reason for war in itself. Women were included with "property", since they were considered under the lawful ownership of a man, whether a father, husband, slave master, or guardian. In this context, the rape of a woman was considered a property crime committed against the man who owned the woman.[21]
The ancient Greeks considered war rape of women "socially acceptable behavior well within the rules of warfare", and warriors considered the conquered women "legitimate booty, useful as wives, concubines, slave labor, or battle-camp trophy".[21]
In the Middle Ages, and until the 19th century, this attitude and practice prevailed, and the legal protection of women in war time related indirectly to the legal protection women were granted in peace times. In medieval Europe, women were considered as an inferior gender by law.[31] The Catholic Church sought to prevent rape during feudal warfare through the institution of Peace and Truce of God which discouraged soldiers from attacking women and civilians in general and through the propagation of a Christianized version of chivalry ideal of a knight who protected innocents and did not engage in lawlessness.
According to Fadl, Medieval Islamic military jurisprudence laid down severe penalties for those who committed rape.[32] The punishment for such crimes were severe, including death, regardless of the political convictions and religion of the perpetrator.[32]
In 1159, John of Salisbury wrote Policraticus in an attempt to regulate the conduct of armies engaged in "justifiable" wars. Salisbury believed that acts of theft and "rapine" (property crimes) should receive the most severe punishment, but also believed that obeying a superior's commands whether legal or illegal, moral or immoral, was the ultimate duty of the soldier.[33]
In the 15th and 16th century, despite considerations and systematization of the laws of war, women remained objects available to the conquering male in any way whatsoever. The influential writer Francisco de Vitoria stood for a gradual emergence of the notion that glory or conquest were not necessarily acceptable reasons to start a war. The jurist Alberico Gentili insisted that all women, including female combatants, should be spared from sexual assault in wartime. However, in practice war rape was common.
It is suggested that one reason for the prevalence of war rape was that at the time, military circles supported the notion that all persons, including women and children, were still the enemy, with the belligerent having conquering rights over them.[19] In the late Middle Ages, the laws of war even considered war rape as an indication of a man's success in the battlefield and "opportunities to rape and loot were among the few advantages open to... soldiers, who were paid with great irregularity by their leaders....triumph over women by rape became a way to measure victory, part of a soldier's proof of masculinity and success, a tangible reward for services rendered....an actual reward of war".[22]
During this period in history, war rape took place not necessarily as a conscious effort of war to terrorize the enemy, but rather as earned compensation for winning a war. There is little evidence to suggest that superiors regularly ordered subordinates to commit acts of rape.[34] Throughout this period of history war became more regulated, specific, and regimented. The first formal prosecution for war crimes did not take place until the late Middle Ages.[34]
Early modern European era
Hugo Grotius, considered the father of the law of nations and the first to conduct a comprehensive work on systematizing the international laws of war, concluded that rape "should not go unpunished in war any more than in peace". Emmerich van Vattel emerged as an influential figure when he pleaded for the immunity of civilians against the ravages of war, considering men and women civilians as non-combatants.[35]
In the late 18th century and 19th century, treaties and war codes started to include vague provisions for the protection of women: The Treaty of Amity and Commerce (1785) specified that in case of war "women and children....shall not be molested in their persons". Article 20 of the Order No. 20 (1847), a supplement to the US Rules and Articles of war, listed the following as severely punishable "Assassination, murder, malicious stabbing or maiming, rape". The Declaration of Brussels (1874) stated that the "honours and rights of the family....should be respected" (article 38).[36]
In the 19th century, the treatment of soldiers, prisoners, the wounded, and civilians improved when core elements of the laws of war were put in place by nations who were signatories to treaties. However, while the customs of war mandated more humane treatment of soldiers and civilians, new weapons and advanced technology increased destruction and altered the methods of war.[37]
The Lieber Code (1863) was the first codification of the international customary laws of land war and an important step towards humanitarian law. The Lieber Code emphasized protection of civilians and stated that "all rape...[is] prohibited under the penalty of death", which was the first prohibition of rape in customary humanitarian law.[38]
During the 20th century, international legal procedures attempted to prevent and prosecute perpetrators of war rape. Similarly, individual states developed laws pertaining to war rape's victims and perpetrators.
Article 46 of the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 regarding Land Warfare explicitly required that "[f]amily honour and rights [and] the lives of persons...must be respected" by the occupying powers.[38]
After World War I, the Commission of Responsibilities, set up in 1919 to examine the atrocities committed by the German Empire and the other Central Powers during the war, found substantial evidence of sexual violence and subsequently included rape and forced prostitution among the violations of the laws and customs of war. Efforts to prosecute failed.[39]
World War II
The Nuremberg and Tokyo Tribunals became the first international courts of real significance. The victorious Allied powers established them in 1945 and 1946 respectively to prosecute the major war criminals of the European Axis powers (in fact only Germans) and of Japan for crimes against peace, war crimes, and crimes against humanity. The possibility of prosecuting sexual violence as a war crime was present because of the recognition of war rape as serious violation of the laws of war in the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 assertion that "[f]amily honour and rights [and] the lives of persons...must be respected."
While the Nuremberg Tribunals failed to charge Nazi war criminals with rape, witnesses testified about it occurring. Previous war crimes trials had prosecuted for sex crimes, hence war rape could have been prosecuted under customary law and/or under the IMT (International Military Tribunals) Charter's Article 6(b): "abduction of the civilian population....into slavery and for other purposes" and "abduction unjustified by military necessity." Similarly, it would have been possible to prosecute war rape as crime against humanity under Article 6(c) of the Nuremberg Charter: "other inhumane acts" and "enslavement". However, notwithstanding evidence of sexual violence in Europe during World War II, a lack of will led to rape and sexual violence not being prosecuted at the Nuremberg Tribunals.[40]
The International Military Tribunal for the Far East did convict Japanese officers "of failing to prevent rape" in the Nanking Massacre, which is known as the "Rape of Nanking".[41][42] The tribunal, in Tokyo, prosecuted cases of sexual violence and war rape as war crimes under the wording "inhumane treatment", "ill-treatment," and "failure to respect family honour and rights." According to the prosecution, in excess of 20,000 women and girls were raped during the first weeks of the Japanese occupation of the Chinese city of Nanking. The War Crimes Tribunal in Tokyo included accounts of sexual violence crimes in the trial testimonies as well as public records.[43] On a national level, a commander of the 14th Area Army, General Yamashita, was convicted for, inter alia, "rape under his command."[43] Some 35 Dutch comfort women brought a successful case before the Batavia Military Tribunal in 1948.[43]
It is well known that brutal mass rapes were committed against German women; both during and after World War II. According to some estimations over 100,000 women were raped by Soviet soldiers in Berlin during and after The Battle of Berlin.[44]
The phrase "from eight to 80" was used to describe potential victims of Soviet mass-rape. "Red Army soldiers don't believe in 'individual liaisons' with German women," wrote the playwright Zakhar Agranenko in his diary when serving as an officer of marine infantry in East Prussia. "Nine, ten, twelve men at a time – they rape them on a collective basis."[44] Rape was regarded by men in the Soviet army as a well-deserved form of punishment, whether the civilians had anything to do with the war or not. In total, historians estimate that over two million German women were raped.[45]
Marocchinate (Italian for "Moroccan' deeds") is a term applied to the mass rape and killings committed during World War II after the Battle of Monte Cassino in Italy. These were committed mainly by the Moroccan Goumiers, colonial troops of the French Expeditionary Corps (FEC), commanded by General Alphonse Juin, and mostly targeted civilian women and girls (as well as a few men and boys) in the rural area between Naples and Rome, traditionally known in Italian as Ciociaria.
1949 Geneva Conventions
Common Article 3 of the 1949 Geneva Conventions provides that "violence to life and person, in particular murder of all kinds, mutilation, cruel treatment and torture" and "outrages upon personal dignity, in particular humiliating and degrading treatment" are prohibited under any circumstance whatsoever with respect to persons who are hors de combat or who are not taking part of direct hostilities in internal conflicts.
Article 27 of the 1949 Fourth Geneva Convention explicitly prohibits wartime rape and enforced prostitution in international conflicts.
The prohibitions outlined in the 1949 Geneva Conventions were reinforced by the 1977 Additional Protocols I and II to the 1949 Geneva Conventions.[29]
The United Nations Declaration on the Protection of Women and Children in Emergency and Armed Conflict, which went into effect in 1974, does not mention rape specifically.
1998–2007
In 1998, the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda established by the United Nations made landmark decisions defining genocidal rape (rape intended to affect a population or culture as a whole) as a form of genocide under international law. In the trial of Jean-Paul Akayesu, the mayor of Taba Commune in Rwanda, the Trial Chamber held that "sexual assault formed an integral part of the process of destroying the Tutsi ethnic group and that the rape was systematic and had been perpetrated against Tutsi women only, manifesting the specific intent required for those acts to constitute genocide."[46]
Judge Navanethem Pillay, now the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, said in a statement after the verdict: "From time immemorial, rape has been regarded as spoils of war. Now it will be considered a war crime. We want to send out a strong message that rape is no longer a trophy of war."[47] An estimated 500,000 women were raped during the 1994 Rwandan genocide.[48]
Professor Paul Walters in his April 2005 statement of support of her honorary doctorate of law at Rhodes University wrote:[47]
Under her presidency of the Rwanda Tribunal, that body rendered a judgment against the mayor of Taba Commune which found him guilty of genocide for the use of rape in "the destruction of the spirit, of the will to live, and of life itself."
The Akayesu judgement includes the first interpretation and application by an international court of the 1948 Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide. The Trial Chamber held that rape (which it defined as "a physical invasion of a sexual nature committed on a person under circumstances which are coercive") and sexual assault constitute acts of genocide insofar as they were committed with the intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a targeted group, as such. It found that sexual assault formed an integral part of the process of destroying the Tutsi ethnic group and that the rape was systematic and had been perpetrated against Tutsi women only, manifesting the specific intent required for those acts to constitute genocide.[46]
Rape first became recognized as crime against humanity when the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia issued arrest warrants in 1993, based on the Geneva Conventions and Violations of the Laws or Customs of War. Specifically, it was recognized that Muslim women in Foča (southeastern Bosnia and Herzegovina) were subjected to systematic and widespread gang rape, torture and sexual enslavement by Bosnian Serb soldiers, policemen, and members of paramilitary groups after the takeover of the city (April 1992).[49] The indictment was of major legal significance and was the first time that sexual assaults were investigated for the purpose of prosecution under the rubric of torture and enslavement as a crime against humanity.[49] The indictment was confirmed by a 2001 verdict by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia that rape and sexual enslavement are crimes against humanity. This ruling challenged the widespread acceptance of rape and sexual enslavement of women as intrinsic part of war.[50] The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia found three Bosnian Serb men guilty of rape of Bosniak (Bosnian Muslim) women and girls (some as young as 12 and 15 years of age), in Foča, eastern Bosnia-Herzegovina. Furthermore, two of the men were found guilty of the crime against humanity of sexual enslavement for holding women and girls captive in a number of de facto detention centres. Many of the women subsequently disappeared.[50] However, Justice Richard Goldstone, chief prosecutor at the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia, commented that "rape has never been the concern of the international community."[41]
United States law specifies that rape in wartime is punishable by death or imprisonment under Article 120 of the United States' Uniform Code of Military Justice and Section d(g) of the War Crimes Act of 1996. However a total ban on abortion is a requirement of US humanitarian aid for war victims, with no exceptions for rape, incest, or to save the life of the mother.[51]
The 1998 Rome Statute Explanatory Memorandum, which defines the jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court, recognizes rape, sexual slavery, enforced prostitution, forced pregnancy, enforced sterilization, "or any other form of sexual violence of comparable gravity" as crime against humanity if the action is part of a widespread or systematic practice.[52][53]
In September 1999, the United Nations published a "Report of the International Criminal Tribunal for the Prosecution of Persons Responsible for Genocide and Other Serious Violations of International Humanitarian Law Committed in the Territory of Rwanda and Rwandan Citizens Responsible for Genocide and Other Such Violations Committed in the Territory of Neighboring States between 1 January and 31 December 1994". The report states that on 2 September 1998, Trial Chamber I of the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda, composed of Judges Laïty Kama, Presiding, Lennart Aspegren and Navanethem Pillay, found Jean Paul Akayesu guilty of 9 of the 15 counts proffered against him, including genocide, direct and public incitement to commit genocide and crimes against humanity, murder, torture, rape, and other inhumane acts. The Tribunal found Jean Paul Akayesu not guilty of the six remaining counts, including the count of complicity in genocide and the counts relating to violations of Common Article 3 to the Geneva Conventions and of Additional Protocol II thereto.[46] On 2 October 1998, Jean Paul Akayesu was sentenced to life imprisonment for each of the nine counts, the sentences to run concurrently. Both Jean Paul Akayesu and the Prosecutor have appealed against the judgement rendered by the Trial Chamber.[46]
United Nations actions on sexual violence in conflict
.jpg)
In 2008, the U.N. Security Council adopted resolution 1820, which noted that "rape and other forms of sexual violence can constitute war crimes, crimes against humanity or a constitutive act with respect to genocide".[54]
The Office of the Special Representative of the Secretary-General on Sexual Violence in Conflict (SRSG-SVC) was established by Security Council Resolution 1888 (2009), one in a series of resolutions which recognized the detrimental impact that sexual violence in conflict has on communities, and acknowledged that this crime undermines efforts at peace and security and rebuilding once a conflict has ended. The office serves as the United Nations’ spokesperson and political advocate on conflict-related sexual violence, and is the chair of the network UN Action against Sexual Violence in Conflict.
In April 2010, the first Special Representative, Margot Wallström of Sweden, established the Office and served as the United Nations’ spokesperson and political advocate on this issue. In September 2012, Zainab Hawa Bangura of Sierra Leone took over as the Special Representative of the Secretary-General on Sexual Violence in Conflict.
The six priorities of the office are:
- to end impunity for sexual violence in conflict by assisting national authorities to strengthen criminal accountability, responsiveness to survivors and judicial capacity;
- the protection and empowerment of civilians who face sexual violence in conflict, in particular, women and girls who are targeted disproportionately by this crime;
- to mobilize political ownership by fostering government engagement in developing and implementing strategies to combat sexual violence;
- to increase recognition of rape as a tactic and consequence of war through awareness-raising activities at the international and country levels;
- to harmonise the UN's response by leading UN Action Against Sexual Violence in Conflict, a network of focal points from 13 UN agencies that amplify programming and advocacy on this issue in the wider UN agenda;
- to emphasize greater national ownership.
The Office has eight priority countries: Bosnia and Herzegovina; Central African Republic (CAR); Colombia; Côte d'Ivoire; Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC); Liberia; South Sudan and Sudan. While six of the eight priority countries are in Africa, this problem is widespread and the Office of the Special Representative is engaged on this issue in Asia and the Pacific (in Cambodia for residual cases from the Khmer Rouge period) and the Middle East (Syria).[55]
In 2013, the U.N. Security Council unanimously passed Resolution 2122, which supported abortion rights for girls and women raped in wars, "noting the need for access to the full range of sexual and reproductive health services, including regarding pregnancies resulting from rape, without discrimination."[51] United Nations Secretary General Ban Ki-moon had recommended to the U.N. Security Council earlier in 2013 (in September) that girls and women raped in war should have access to "services for safe termination of pregnancies resulting from rape, without discrimination and in accordance with international human rights and humanitarian law." In March 2013 Ban Ki-moon had also recommended to the Council that women raped in war have access to abortion services.[51]
Effects
Physical effects
A recent study lists the physical injury to the victims of war rape as traumatic injuries, sexually transmitted diseases, maternal mortality, unwanted pregnancies, unsafe abortions, and persistent gynecological problems are of major concern.[56] Because war rapes take place in zones of conflict, access to emergency contraception, antibiotics, and abortion are limited. Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is not uncommon.[57] In certain war gang rape instances, the objective of infecting women interned in rape camps was the systematic effect of HIV soldiers specifically selected to spread HIV/AIDS to the gang raped.[58]
.jpg)
War rape may include physical rape of the male organ. Gang rape and rape with human objects or physical objects, such as fists, sticks, rods, and gun barrels are also methods used in war rape. Women victims may suffer from incontinence and vaginal fistula as a result of these particularly violent instances of rape.[59] Vaginal fistula is a medical condition of vaginal abnormality where there is hole in the vagina in close proximity to the colon (anus or rectum) or bladder.[60] In some cases, it is a birth defect, in others it is a result of female genital cutting[61] (FGM) and rape. In extreme instances of violent rape in war, the walls of the vagina are torn or punctured, resulting in severe pain and debilitating incontinence (urinary complications) and bowel containment.[59] Violent rape is also a cause of obstetric fistula which is a hole in the female organ and birth canal.[62]
Physical effects may also include bone breakage such as backbreaking and cranial cracks, causing future disability, visual and hearing impairment, and mental incapacitation.
Psychological effects
Victims and survivors of war rape are at very high risk of psychosocial problems.[63]
The short-term psychological injuries to the victims include feelings of fear, helplessness, sadness, disorientation, isolation, vulnerability, and desperation. If left untreated, the psychological effects of sexual assault and rape can be devastating, sometimes even deadly. Causes of death as the result of sexual violence include suicide and murder. Murder of sexual assault and rape victims may be perpetrated by the rapist or as part of an honor killing by family members of the victim.
Long-term psychological injuries may include depression, anxiety disorders (including post-traumatic stress syndrome (PTSS)), multiple somatic symptoms, flashbacks, on-going trauma, chronic insomnia, self-hatred, nightmares, paranoia, difficulty re-establishing intimate relationships, shame, disgust, anger, and persistent fears.[64] They could have trouble sleeping, experience changes in their appetite, or develop full-blown emotional problems, including posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, substance abuse, or dependence. Individuals who have experienced sexual assault are at risk for other day-to-day problems, including arguing with family members and having problems at work. Lack of medical psychological support resources also puts victims of war rape at further disadvantage.[65] Refugee women are also at a disadvantage of receiving adequate assistance to deal with the psychological consequences of war rape - not only do they lack legal representation, they also may lack protection from the perpetrators of the violent act.[65] Furthermore, there is an increase in dislike of refugees and asylum seekers which is another obstacle in the psychological healing process of victims seeking assistance outside of their countries that may still be under civil strife.[65] Psychological support and counseling sessions given by individuals not part of the ethnic, linguistic, or community may incite difficulties in communication between patient and caregiver. As a result, adequate emotional and psychological support to the victims is not fully developed, affecting the long-term healing potential for the patient.
Psychosocial and societal effects
In addition to the physical and psychological damages resulting from rape, sexual violence in the context of war often disrupt the linkages between the rape victims and their communities. Thus, the phenomenon of war rape can structurally affect entire societies, which is closely linked to the logic underlying the strategic use of rape as an instrument in armed conflicts. Raping ‘enemy’ women also constitutes an act of abuse and humiliation against the men of the community the victims were representative of.[66]
Recent research on the subject suggests that wartime sexual violence may increase instances of intimate partner abuse in the affected society. A study on the aftermath of civil war in Peru estimated that in departments which had experienced conflict-related sexual violence, women in the department were at increased risk of intimate partner violence after the war.[67]
Besides the psychosocial effects on women as the most frequent victims of wartime rape, children born of rape are faced with distinct social stigmas. The existence of taboos around the issue of war rape can also be an obstacle to post-conflict reconciliation.
Stigmatization and isolation
Psychosocial consequences[65] of war rape describe how the linkages between victims and the society are altered as a result of sexual abuses during war. Both during and even more in the aftermath of conflict, when abuses become known, victims of war rape risk finding themselves in situations of social isolation, often abandoned by their husbands and rejected by their communities[68] The ordeal is thus not over with the survival of the act of abuse but has a long-term effect that can only to a limited extent be dealt with by the victims themselves. The process of re-victimization captures how victims of sexual violence continue to "receive additional hurt after the direct cause of victimization has disappeared"[69] with stigmatization and exclusion being among the main sources of re-victimization.[69]
This is particularly relevant in patriarchal societies, where female sexuality is linked to male honour, virginity is a core value, and where a culture considers ethnicity transmitted through male genes.[70][71] Given the ethnic dimension of sexuality, rape can become a means of ethnic cleansing or genocide, as has been claimed in relation to systematic instances of rape in Rwanda and Bosnia.[72] In this context, "rape as a weapon of war is not an individual issue, but a societal one."[73] In a number of countries, the targeted infection of women with HIV, which creates further suffering for victims experiencing social exclusion and discrimination for having HIV/AIDS.[74]
Impact on children born out of rape
War rape can have an equally strong and long-term effect on the children that are born as a result. On the one hand, these children may not be immediately identified and might find out about their origins only at a later point in their lives. In turn, if the children themselves but even more their environment knows about the 'war babies',[75] they risk being regarded as 'other' by the communities they are born into. Recurring patterns in countries including Bosnia and Herzegovina, Uganda, Sierra Leone and Rwanda show how children born of war rape and to mothers who don't want them have to face struggles with regard to issues related to identity – both in an administrative as well as in a personal sense – and are sometimes restricted in their rights to education, non-discrimination and even physical security.[76] Unwanted children born of rape are potentially more vulnerable in a psychological as well as in a physical way and cases of abandoned children are reported from various contemporary conflict and post-conflict societies.[77][78][79]
Impact on post-conflict reconciliation
The societal consequences of war rape can equally have a negative impact on post-conflict reconciliation and the judicial follow-up on wartime crimes, including rape. Given the stigmatisation of victims and their isolation or fear thereof, they might prefer to remain silent with regard to the violations they have suffered. Indeed, underreporting of cases of rape during armed conflict is a practical challenge post-conflict communities have to face that is pointed to by a number of actors, including the United Nations Secretary-General,[80] the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights[81] as well as international NGOs.[82]
As Human Rights Watch reported with regard to war rape during the Rwandan genocide, victims "expressed dismay at the fact that they were being urged to forget what happened to them in the name of peace and reconciliation".[82] The fear of consequences and threat of exclusion felt by the victims makes it difficult to establish clear figures of war rape incidents and to hold perpetrators accountable for the crimes they have committed, as has been claimed with regards to war rape in Darfur: "Underreporting of cases may be attributed to the stigma associated with rape, shame and fear of reprisal, denial that rape occurs, intimidation by many Government officials and the inability to access some conflict-affected areas".[83] This points to another difficulty victims of war rape have to deal with at the societal level. The perpetrators of rape are often officials or otherwise affiliated with the state's institutions, which might make reporting of assaults appear useless.[84]
Psychiatric care
Disrupted healthcare sectors is a term the World Health Organization describes for medical facilities that are destroyed or partially destroyed in war torn areas.[85] Health care facilities are essential for the establishment of support systems for rape victims. Psychological support units are also hampered by the lack of material resources available to the medical community on-ground. Medical practitioners and health-care workers face daunting challenges in conflict and post-conflict area.[16] As the WHO explains, "healthcare delivery fragments and deteriorates, memory and knowledge are eroded, and power disperses".[85]:7 War-torn societies in immediate post-conflict zones have broken medical infrastructure such as: destroyed or partially destroyed hospitals (or clinics); non-functioning hospitals; poor, scarce or inadequate medical supplies, lack of running water, and scarce or lack of electricity. Dismantling weapons from armed rebels and other groups are prioritized in immediate post-conflict situations which in effect de-prioritizes the immediate physical and psychiatric care that war rape victims are in urgent need of. "If we do not have the capacity to prevent war, we have a collective responsibility to better understand and treat its psychiatric, medical, and social consequences."[86] Access to psychological health services further causes inequity for survivors of war rape who are at the margins of society living in chronic poverty or located in rural regions.[87][88] Healthcare and psychiatric care is a key component to the healing processes of war rape.
History
Antiquity
Rape has accompanied warfare in virtually every known historical era.[89] Writes women's historian Gerda Lerner,
The practice of raping the women of a conquered group has remained a feature of warfare and conquest from the second millennium B.C. to the present. It is a social practice which, like the torture of prisoners, has been resistant to "progress," to humanitarian reforms, and to sophisticated moral and ethical considerations. I suggest this is the case because it is a practice built into and essential to the structure of patriarchal institutions and inseparable from them. It is at the beginning of the system, prior to class formation, that we can see this in its purest essence.[90]
The Bible: "For I will gather all the nations against Jerusalem to battle, and the city shall be taken and the houses plundered and the women taken..." Zechariah 14:2 "Their little children will be dashed to death before their eyes. Their homes will be sacked, and their wives will be taken." Isaiah 13:16
The Torah: The Torah in Deuteronomy 21:10–14 allows the taking of a female captive only within the context of marriage. The female captive must be brought to the home and, following the month in which she is given to mourn, the man must decide to either take her as a wife or set her free. According to Rabbi Yohanan in the Jerusalem Talmud, only after deciding to marry the female captive are sexual relations permitted. This in effect prohibits rape in the process of war.
The Greek and Roman armies reportedly engaged in war rape, which is documented by ancient authors such as Homer, Herodotus, and Livy. Ancient sources held multiple, often contradictory attitudes to sexual violence in warfare.[91]
Roman military officers using young Batavian boys for homosexual intercourse during the Revolt of the Batavi was noted by the historian Tacitus.[92]
During Late Antiquity, India also saw countless invasions by warriors from Central Asia such as the Kushans, Hephthalites, and the Hunas. The Huna invasions of the Indian subcontinent helped hasten the decline of the Gupta Empire. The Huna invaders conquered Kashmir, Punjab, and finally entered into the Ganges valley, in the very heart of India, slaughtering, pillaging, looting, burning, demolishing, and raping. Many cities in India were wiped out by the onslaught of the invaders; monasteries, temples, schools, and libraries were not spared, causing immense cultural destruction to the Indian subcontinent. Accounts are consistent that the Huna warriors practiced mass rapes of women in India.[93][94]
Middle Ages
.jpg)
The Vikings (Scandinavians who raided and colonized wide areas of Europe from the late 8th century to the early 11th century),[95] have acquired a reputation for "rape and pillage". Viking settlements in Britain and Ireland are thought to have been primarily male enterprises, with a lesser role for Viking females. British Isles women are mentioned in old texts on the founding of Iceland, indicating that the Viking explorers had acquired wives and concubines from Britain and Ireland.[96] Some historians dispute the Vikings' "rape and pillage" image, arguing that exaggeration and distortion in later medieval texts created an image of treacherous and brutal Northmen.[97]
Female slavery and war rapes were also common during the medieval Arab slave trade, where prisoners of war captured in battle from non-Arab lands often ended up as concubine slaves (who are considered free when their master dies) in the Arab World.[98] Most of these slaves came from places such as Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly Zanj), the Caucasus (mainly Circassians),[99] Central Asia (mainly Tartars), and Central and Eastern Europe (mainly Saqaliba).[100] Historian Robert Davis estimated that the Barbary pirates also captured 1.25 million slaves from Western Europe and North America between the 16th and 19th centuries.[101][102]
Before the Jurchens overthrew the Khitan, married Jurchen women and Jurchen girls were raped by Liao Khitan envoys as a custom which caused resentment by the Jurchens against the Khitan.[103] Song princesses committed suicide to avoid rape or were killed for resisting rape by the Jin.[104]
The Mongols, who established the Mongol Empire across much of Eurasia, caused much destruction during their invasions. Documents written during or after Genghis Khan's reign say that after a conquest, the Mongol soldiers looted, pillaged and raped. Some troops who submitted were incorporated into the Mongol system in order to expand their manpower. These techniques were sometimes used to spread terror and warning to others.[105]
Timur was a Turco-Mongol warlord who was renowned for his exceptional cruelty and viciousness. His armies would sack, pillage, and destroy entire cities that resisted his army. His empire stretched from India to Anatolia, covering much of Central Asia, Persia, and Mesopotamia. Especially brutal was the Sack of Delhi by Timur, allegedly spurned by his hatred for the Sultanate of Delhi because of its tolerance for Hinduism, Timur's army invaded India and pillaged and looted the city of Delhi, killing thousands of Hindus, and raping many Hindu women and taking them back to his capital of Samarkand, where they would serve as slaves to Muslim Turkic men.[106][107]Timur's descendants would continue to rule in the Indian subcontinent as the Mughals. Overall, throughout the Middle Ages, Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent led to many instances of sexual violence towards women in South Asia.[106]
Early modern period
Conquest of the Americas
Spanish conquistadors kidnapped and raped Native American women across all the Spanish Empire in the Americas, generating a new population of 'mestizos', who inhabitated the new world. [108]
War of the Three Kingdoms
A significant number of women were gang-raped by Royalist and Irish Confederate troops under General Montrose who sacked Aberdeen in Scotland in 1644.[109][110]
Second Manchu invasion of Korea
In the Second Manchu invasion of Korea when Qing forces invaded the Korean Kingdom of Joseon, many Korean women were subjected to rape at the hands of the Qing forces, and as a result they were unwelcomed by their families even if they were released by the Qing after being ransomed.[111]
Manchu invasion of Xinjiang
The Ush rebellion in 1765 by Uyghur Muslims against the Manchus of the Qing dynasty occurred after Uyghur women were gang raped by the servants and son of Manchu official Su-cheng.[112][113][114] It was said that Ush Muslims had long wanted to sleep on [Sucheng and son's] hides and eat their flesh. because of the rape of Uyghur Muslim women for months by the Manchu official Sucheng and his son.[115] The Manchu Emperor ordered that the Uyghur rebel town be massacred, the Qing forces enslaved all the Uyghur children and women and slaughtered the Uyghur men.[116] Manchu soldiers and Manchu officials regularly having sex with or raping Uyghur women caused massive hatred and anger by Uyghur Muslims to Manchu rule. The invasion by Jahangir Khoja was preceded by another Manchu official, Binjing who raped a Muslim daughter of the Kokan aqsaqal from 1818-1820. The Qing sought to cover up the rape of Uyghur women by Manchus to prevent anger against their rule from spreading among the Uyghurs.[117]
European colonial era
Dutch Formosa (Taiwan)
Multiple Taiwanese Aboriginal villages in frontier areas rebelled against the Dutch in the 1650s due to acts of oppression, such as when the Dutch ordered that aboriginal women be turned over to them for sex, and when they demanded that deer pelts and rice be given to them by aborigines in the Taipei basin in Wu-lao-wan village, sparking a rebellion in December 1652. Two Dutch translators were beheaded by the Wu-lao-wan aborigines and in a subsequent fight 30 aboriginals and two additional Dutch people died, after an embargo of salt and iron on Wu-lao-wan. The aboriginals were forced to sue for peace in February 1653.[118]
Dutch women were kept as sexual slaves by the Chinese after the Dutch were expelled from Taiwan in 1662. During the 1662 Siege of Fort Zeelandia in which Chinese Ming loyalist forces commanded by Koxinga besieged and defeated the Dutch East India Company and conquered Taiwan, the Chinese took Dutch women and children prisoner. The Dutch missionary Antonius Hambroek, two of his daughters, and his wife were among the Dutch prisoners of war who were being held captive by Koxinga. Koxinga sent Hambroek to Fort Zeelandia demanding that he persuade them to surrender or else Hambroek would be killed when he returned. Hambroek returned to the Fort, where two of his other daughters were being held prisoner. He urged the commander of the Fort not to surrender, and returned to Koxinga's camp. He was then executed by decapitation, and in addition to this, a rumor was spread among the Chinese that the Dutch were encouraging the native Taiwanese aboriginals to kill Chinese, so Koxinga ordered the mass execution of Dutch male prisoners in retaliation, in addition to a few women and children who were also being held prisoner.
The surviving Dutch women and children were then enslaved, with the Dutch women being sold eventually to Chinese soldiers to become their wives,[119][120][121] eventually being after Koxinga's commanders had thoroughly used them for their own sexual pleasures.[122] The daily journal of the Dutch fort is the primary source for what happened next: "the best were preserved for the use of the commanders, and then sold to the common soldiers. Happy was she that fell to the lot of an unmarried man, being thereby freed from vexations by the Chinese women, who are very jealous of their husbands."[121] Koxinga himself took as his concubine Hambroek's teenage daughter,[123][124][125] a girl described by the Dutch commander Caeuw as "a very sweet and pleasing maiden".[126][127]
As late as 1684 some of these Dutch women were still being held captive as wives or slave concubines by the Chinese.[128] In Quemoy a Dutch merchant was contacted and an arrangement to release the prisoners was proposed by a son of Koxinga, but it came to nothing.[128]
Memory of the fate of the Dutch women and of Hambroek's daughter has been kept alive through the subsequent historiography of the period,[129][130][131][132] whence it has stoked various dramatised and fictionalised retellings of the story. The topic of the Chinese taking the Dutch women and the daughter of Antonius Hambroek as concubines was featured in Joannes Nomsz's play which became famous and well known in Europe and revealed European anxieties about the fate of the Dutch women along with their sense of humiliation after being subjected to defeat at the hands of non-Europeans.[133] The title of the play was "Antonius Hambroek, of de Belegering van Formoza" rendered in English as "Antonius Hambroek, or the Siege of Formosa".[134][135]
Indian Rebellion
Along with the origins of the mass media in the 19th century, accusations of war rape were occasionally used as propaganda by European colonialists in order to justify the colonization of places which they had previously conquered.[136] The most notable example of this may have occurred during the Indian Rebellion of 1857, known as "India's First War of Independence" to the Indians and as the "Sepoy Mutiny" to the British, where Indian sepoys rebelled against the British East India Company's rule in India. While incidents of rape committed by Indian rebels against English women and girls were generally uncommon during the rebellion, they were exaggerated to great effect by the British media in order to justify continued British colonialism in the Indian subcontinent.[136]
At the time, British newspapers had printed various apparently eyewitness accounts of English women and girls being raped by Indian rebels, but with little physical evidence to support these accounts. It was later found that most of these accounts were false stories which had been created in order to paint native Indian people as savages who had to be civilized by British colonialists, a mission sometimes known as The White Man's Burden. One such account published by The Times, regarding an incident where 48 English girls as young as 10–14 had been raped by the Indian rebels in Delhi, was criticized as a false propaganda story by Karl Marx, who pointed out that the story was written by a clergyman in Bangalore, far from the events of the rebellion.[137]
The British soldiers, however angered by reports of the atrocities sepoys committed against British civilians, took revenge on the Indian population. As towns and cities were captured from the sepoys, the British soldiers took their revenge on Indian civilians - including by committing atrocities and rapes against Indian women.[138] As one account reads,
The [British] victors retaliated against the civilians [at Fatehpur) by sacking villages, raping women, killing children and hanging hundreds of men. When the people of Cawnpore [Kanpur] heard this, they feared similar retaliation..... At Fatehgarh, for example, when the English defeated the enemy, their officers ordered a mass scale killing [of] the rebels and the citizens on the spot. General Neill had also ordered Hanging parties.... No evidence was sought and none given before executing the victim.... When the [78th] Highlanders moved to another village, they caught about 140 men, women and children. They selected sixty men from the group, forced them to build the gallows of wooden logs taken from the burning homes. They then chose ten men of the group [and] hanged them without any evidence or trial. For others, they had reserved flogging and beating to teach them a lesson..... At one of the villages, about two thousand villagers armed only with their lathis [wooden canes] turned out in protest. They stood up to face the [78th] Highlanders. The British troops surrounded them and set their village on fire.... The villagers trying to escape were shot to death. One soldier describes the incident thus: 'We took eighteen of them prisoners; they were all tied together, and we fired a volley at them and shot them on the spot' .... Stringing and shooting the men in front of their family was a sport the troops enjoyed. Watching women stooping and begging for the lives of their men seemed to thrill the young soldiers and their officers. The prisoners were made to stand under the hot summer sun for hours till they fainted. It was easy to flog them when they were half-conscious, otherwise, they would squirm and make it hard to strike. Flogging invariably ended in killing of the victims. The English wanted to break the faith of their Hindu and Moslem prisoners.[139][140][141]
The British soldiers inflicted their anger at reports of sepoy atrocities against British civilians by committing mass war crimes against the native population. Examples of such atrocities, happened at the British capture of Cawnpore, where drunk, enraged British soldiers raped, looted, and massacred the entire town of Cawnpore.[142]
Taiping Rebellion
The Ever Victorious Army which defeated the Taiping Rebellion in China was notorious for often looting villages and raping women, but their commander General Gordon did attempt to control them, summarily executing men accused of looting or rape.[143]
Boxer Rebellion
During the Boxer Rebellion, the Chinese Boxers did not commit rape against foreign women and just killed them,[144][145] but the forces of the Eight-Nation Alliance went on a killing, looting, and raping rampage against Chinese civilians. The number of women who committed suicide was in the thousands.[146] A western Journalist, George Lynch, said "there are things that I must not write, and that may not be printed in Great Britain, which would seem to show that this Western civilization of ours is merely a veneer over savagery."[147] All of the nationalities engaged in looting and rape. Luella Miner wrote that the behavior of the Russian and French was particularly appalling. Chinese women and girls killed themselves in order to avoid being raped. The French commander dismissed the rapes, attributing them to the "gallantry of the French soldiers".[147]
German South-West Africa
In German South-West Africa during the Herero and Namaqua Genocide, German soldiers regularly engaged in gang rapes[148] before killing Herero women or leaving them in the desert to die; a number of women from the rebelling Herero tribe were also forced into prostitution.[149]
World War I
Rapes were allegedly committed during the Imperial German advance through Belgium in the first months of the war.[150] After the war Harold D. Lasswell dismissed them as propaganda in his 1927 Freudian-oriented study, "Propaganda Technique in the World War".[14][151] In September 1914, the French government set up a commission, that was also seen in Belgium to investigate reports of rape committed by German soldiers, however as historian Ruth Harris has documented the investigations were more to fuel narratives of nationalism and cultural hatred towards Germany. The individual stories of the women that were impacted were used to justify the war and to market it to the civilians.[152]
World War II
The sometimes widespread and systematic occurrence of war rape of women by soldiers has been documented. During World War II and in its immediate aftermath, war rape occurred in a range of situations, ranging from institutionalized sexual slavery to war rapes associated with specific battles.
Asia

Japanese army
The term "comfort women" is a euphemism for the estimated 200,000, mostly Korean, Chinese, Japanese, Taiwanese and Filipino women who were said to be forced to serve as sex slaves in Japanese military brothels during World War II.[153]
In the Nanking Massacre, Japanese soldiers were said to have sexually assaulted female civilians who were trapped in the city of Nanjing when it fell to the Japanese on 13 December 1937.
Chuo University professor Yoshiaki Yoshimi states there were about 2,000 centers where as many as 200,000 Japanese, Chinese, Korean, Filipino, Taiwanese, Burmese, Indonesian, Dutch and Australian women were interned and used as sex slaves.[154]
Australian army
"A former prostitute recalled that as soon as Australian troops arrived in Kure in early 1946, they 'dragged young women into their jeeps, took them to the mountain, and then raped them. I heard them screaming for help nearly every night'."[14][155]
US Army
A large number of rapes were committed by U.S. forces during the Battle of Okinawa in 1945.[156]
The Judge Advocate General's office reports that there were 971 convictions for rape in the U.S. military from January 1942 to June 1947, which includes a portion of the occupation.[157]
Okinawan historian Oshiro Masayasu (former director of the Okinawa Prefectural Historical Archives) writes:
Soon after the U.S. marines landed, all the women of a village on Motobu Peninsula fell into the hands of American soldiers. At the time, there were only women, children and old people in the village, as all the young men had been mobilized for the war. Soon after landing, the marines "mopped up" the entire village, but found no signs of Japanese forces. Taking advantage of the situation, they started "hunting for women" in broad daylight and those who were hiding in the village or nearby air raid shelters were dragged out one after another.[158]
According to Toshiyuki Tanaka, 76 cases of rape or rape-murder were reported during the first five years of the American occupation of Okinawa. However, he asserts this is probably not the true figure, as most cases were unreported.[159]
When the Japanese surrendered, they anticipated that widespread rapes would occur during the following occupation and made rapid efforts to set up brothels to curb this.
Despite this precaution, 1,336 rapes reportedly occurred during the first 10 days of the occupation of Kanagawa prefecture, although a similar figure has also been given for the whole of Japan.[160]
Individual instances of rape by members of the United States Army in Japan were reported while their forces were stationed in post-war Japan, such as the Yumiko-chan incident and the 1995 Okinawa rape incident.
Some historians state that mass rapes took place during the initial phase of the occupation. For instance, Fujime Yuki has stated that 3,500 rapes occurred in the first month after American troops landed.[161] Tanaka relates that in Yokohama, the capital of the prefecture, there were 119 known rapes in September 1945.[162] At least seven academic books and many other works state that there were 1,336 reported rapes during the first 10 days of the occupation of Kanagawa Prefecture.[163] Walsh states that this figure originated from Yuki Tanaka's book Hidden Horrors, and resulted from that author misreading the crime figures in their source.[164] The source states that the Japanese Government recorded 1,326 criminal incidents of all types involving American forces, of which an unspecified number were rapes.[165]
Red Army
During the Soviet invasion of Manchuria, Soviet and Mongolian soldiers attacked and raped Japanese civilians, often encouraged by the local Chinese population who were resentful of Japanese rule. The local Chinese population sometimes even joined in these attacks against the Japanese population with the Soviet soldiers. In one famous example, during the Gegenmiao massacre, Soviet soldiers, encouraged by the local Chinese population, raped and massacred over one thousand Japanese women and children. Property of the Japanese were also looted by the Soviet soldiers and Chinese. Many Japanese women married themselves to local Manchurian men to protect themselves from persecution by Soviet soldiers. These Japanese women mostly married Chinese men and became known as "stranded war wives" (zanryu fujin).
According to British and American reports, Soviet Red Army troops also looted and terrorized the local people of Mukden located in Manchuria. A foreigner witnessed Soviet troops, formerly stationed in Berlin, who were allowed by the Soviet military to go into the city of Mukden "for three days of rape and pillage".[166] The Soviet Army's reputation in the region was affected for years to come.
Konstantin Asmolov of the Center for Korean Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences dismisses Western accounts of Soviet violence against civilians in the Far East as exaggeration and rumor and contends that accusations of mass crimes by the Red Army inappropriately extrapolate isolated incidents regarding the nearly 2,000,000 Soviet troops in the Far East into mass crimes. According to him, such accusations are refuted by the documents of the time, from which it is clear that such crimes were far less of a problem than in Germany. Asmolov further asserts that the Soviets prosecuted their perpetrators while prosecution of German and Japanese "rapists and looters" in WWII was virtually unknown.[167]
Europe
British
The Italian statistics record eight rapes and nineteen attempted rapes by British soldiers in Italy between September 1943 and December 1945. Various sources, including the Special Investigation Branch as well as evidence provided by Belgian reporters, said that rape and sexual harassment by British troops occurred frequently following the invasion of Sicily in 1943.[168]
Although far from the scale of those committed by the Wehrmacht or Red Army, rapes of local women and girls were committed by British troops during the last months of WWII in Germany. Even elderly women were targeted. Though a high-profile issue for the Royal Military Police, some officers treated the behaviour of their men with leniency. Many rapes were committed by men who were either under the influence of alcohol or suffering from post-traumatic stress, but there were cases of premeditated attack, like the assault on three German women in the town of Neustadt am Rübemberge, on 16 April 1945, or the attempted gang rape of two local girls at gunpoint in the village of Oyle, near Nienburg, which ended in the death of one of the women when, whether intentionally or not, one of the soldiers discharged his gun, hitting her in the neck.[169]
There were also reports of "sexual assault and offences" committed by British soldiers against children in Belgium and the Netherlands, and a number of men were convicted of these crimes while they were fraternizing with Dutch and Belgian families during the winter of 1944–45.[169] On a single day in mid-April 1945, three women in Neustadt were raped by British soldiers. A senior British Army chaplain who followed the troops reported that there was a "good deal of rape going on". He then added that "those who suffer [rape] have probably deserved it." In the summer of 1945, two drunken British soldiers stormed into a farmhouse in Klagenfurt with a drawn revolver when there were only two women present. The older of the two women was forced to go upstairs while the other, an 18-year-old girl, was raped by one of the soldiers.[168]
German forces
Rapes were committed by Wehrmacht forces on Jewish women and girls during the Invasion of Poland in September 1939;[170] they were also committed against Polish, Ukrainian, Belarusian and Russian women and girls during mass executions which were primarily carried out by the Selbstschutz units, with the assistance of Wehrmacht soldiers who were stationed in territory that was under the administration of the German military; the rapes were committed against female captives before they were shot.[171] Only one case of rape was prosecuted by a German court during the military campaign in Poland, and even then the German judge found the perpetrator guilty of Rassenschande (committing a shameful act against his race as defined by the racial policy of Nazi Germany), rather than rape.[172] Jewish women were particularly vulnerable to rape during The Holocaust.[173]
Rapes were also committed by German forces stationed on the Eastern Front, where they were largely unpunished (as opposed to rapes committed in Western Europe); the overall number of rapes is difficult to establish due to the lack of prosecutions of the crime by German courts.[174][175] Wehrmacht also established a system of military brothels, in which young women and girls from occupied territories were forced into prostitution under harsh conditions.[172] In the Soviet Union women were kidnapped by German forces for prostitution as well; one report by the International Military Tribunal writes "in the city of Smolensk the German Command opened a brothel for officers in one of the hotels into which hundreds of women and girls were driven; they were mercilessly dragged down the street by their arms and hair."[176]
French army
French Moroccan troops, known as Goumiers, committed rapes and other war crimes in Italy after the Battle of Monte Cassino[177] and in Germany. In Italy, victims of the mass rape committed after the Battle of Monte Cassino by Goumiers, colonial troops of the French Expeditionary Corps, are known as Marocchinate. According to Italian sources, more than 7,000 Italian civilians, including women and children, were raped by Goumiers.[178]
French Senegalese troops too, known as Senegalese Tirailleurs, who landed on the island of Elba on 17 June 1944, were responsible for mass rapes, though their behaviour was considered less brutal than that of the French North African troops in continental Italy.[179]
US Army
Secret wartime files made public in 2006 reveal that American GIs committed 400 sexual offenses in Europe, including 126 rapes in the United Kingdom, between 1942 and 1945.[180] A study by Robert J. Lilly estimates that a total of 14,000 civilian women in Great Britain, France and Germany were raped by American GIs during World War II.[181][182] It is estimated that there were around 3,500 rapes by American servicemen in France between June 1944 and the end of the war and one historian has claimed that sexual violence against women in liberated France was common.[183] In the 2007 publication Taken by Force, sociology and criminology professor J. Robert Lilly estimates US soldiers raped around 11,040 women and children during the occupation of Germany.[184] Many armed soldiers committed gang rapes at gunpoint against female civilians and children.[185]
Red Army
During the war, German women were victims of brutal mass rapes committed against them by Soviet[186][187] soldiers. Polish sources claim that mass rapes were committed in Polish cities that had been taken by the Red Army. It is reported that in Kraków, the Soviet occupation was accompanied by the mass rape of Polish women and girls, as well as the plunder of all private property by Soviet soldiers. Reportedly the scale of the attacks prompted communists installed by the Soviets to prepare a letter of protest to Joseph Stalin, while masses in churches were held in expectation of a Soviet withdrawal.[188]
At the end of World War II, Red Army soldiers are estimated to have raped around 2,000,000 German women and girls.[189][190] Norman Naimark writes in "The Russians in Germany: A History of the Soviet Zone of Occupation, 1945–1949" that although the exact number of women and girls who were raped by members of the Red Army in the months preceding the capitulation, and in the years following it, will never be known, their numbers are likely to be in the hundreds of thousands, quite possibly as high as the two million victims estimated by Barbara Johr, in "Befreier und Befreite". Many of these victims were raped repeatedly.
A female Soviet war correspondent described what she had witnessed: "The Russian soldiers were raping every German female from eight to eighty. It was an army of rapists." The majority of the rapes were committed in the Soviet occupation zone and an estimated two million German women were raped by Soviet soldiers.[191][192][193][194][195] According to historian William Hitchcock, in numerous cases women were victims of repeated rapes with some women being raped as many as 60 to 70 times.[196] A minimum of 100,000 women are believed to have been raped in Berlin, based on surging abortion rates in the following months and on hospital reports written at the time,[193] with an estimated 10,000 women dying in the aftermath.[197] Female deaths resulting from rapes committed by Soviet soldiers stationed in Germany are estimated to total 240,000.[198][199] Antony Beevor describes it as the "greatest phenomenon of mass rape in history", and he has concluded that at least 1.4 million women were raped in East Prussia, Pomerania and Silesia alone.[200] According to Natalya Gesse, Soviet soldiers raped German females who were anywhere from eight to 80 years old. Soviet women were not spared either.[201][202][203]
Antony Beevor estimates that up to half of all rape victims were victims of gang rapes. Naimark states that not only did each victim have to carry the trauma with her for the rest of her days, it also inflicted a massive collective trauma on the East German nation. Naimark concludes "The social psychology of women and men in the Soviet zone of occupation was marked by the crime of rape from the first days of the occupation, through the founding of the GDR in the fall of 1949, until, one could argue, the present."[204] German women who became pregnant after being raped by Soviet soldiers in World War II were invariably denied the right to an abortion so they would be further humiliated by being forced to carry an unwanted child. According to the book Berlin: The Downfall, 1945 by Antony Beevor, some 90% of raped Berlin women in 1945 contracted venereal diseases as the result of these consequential rapes and 3.7% of all children born in Germany from 1945 to 1946 had Soviet fathers. The history of this particular aspect of the mass-rape of German women by Soviet troops was considered a taboo subject until 1992.
Korean War
During 11 months of 1952 in the 110,000-man logistics branch of Chinese Volunteer Army, there were 41 men charged with rapes, also there were adultery, sodomy, murder and traffic accident killings.[205]
Vietnam War
There were rapes and sexual atrocities commmited by American servicemen and South Korean troops in Vietnam war.[206][207]
Indonesia
Indonesian invasion of East Timor and West Papua caused the murders of approximately 300,000 to 400,000 West Papuans and many thousands of women raped.[208]
1971 genocide in Bangladesh
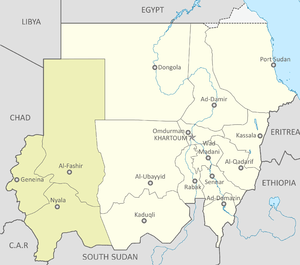
During the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971, numerous women were tortured and raped by Pakistani army. Exact numbers are not known and are a subject of debate. Most of the women were captured from Dhaka University and private homes and kept as sex-slaves inside the Dhaka Cantonment.[209] Australian Doctor Geoffrey Davis was brought to Bangladesh by the United Nation and International Planned Parenthood Federation to carry out late-term abortions on rape victims. He was of the opinion that the 200,000 to 400,000 rape victims was an underestimation. On the actions of Pakistan army he said "They’d keep the infantry back and put artillery ahead and they would shell the hospitals and schools. And that caused absolute chaos in the town. And then the infantry would go in and begin to segregate the women. Apart from little children, all those were sexually matured would be segregated...And then the women would be put in the compound under guard and made available to the troops…Some of the stories they told were appalling. Being raped again and again and again. A lot of them died in those [rape] camps".[210]
Bangladeshi women have been raped during the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971 by the Pakistan army during night raids on villages.[16][211] Pakistani sources claim the number is much lower, though having not completely denied rape incidents.[157][212][213] One work that has included direct experiences from the women raped is Ami Birangana Bolchi (The Voices of War Heroines) by Nilima Ibrahim. The word Birangona (war heroine) is a title given, by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman after the war, to the women raped and tortured during the war. This was a conscious effort to alleviate any social stigma the women might face in the society. How successful this effort was is doubtful, though.
In June 2005, the United States Department of State organized a conference titled "South Asia in Crisis: United States Policy, 1961–1972" where Sarmila Bose, published a paper suggesting that the casualties and rape allegations in the war have been greatly exaggerated for political purposes. This work has been criticized in Bangladesh and her research has been attacked by expatriate Bengalis.[214][215]
During the war Bengali nationalists also indulged in the mass rape of ethnic Bihari Muslim women, since the Bihari Muslim community had remained loyal to the cause of a United Pakistan.[216][217][217]
Anthony Mascarenhas, published a newspaper article in June 1971, in The Sunday Times, London on 13 June 1971 titled "Genocide". The article was the first that exposed the brutal crackdown by the Pakistan army.[218][219] It also highlighted the rape of Bihari women and other atrocities committed against them by Bengalis.[220] The Sunday Times editor Harold Evans wrote "He'd been shocked by the Bengali outrages in March, but he maintained that what the army was doing was altogether worse and on a grander scale,".[219]
1974 to 1992
In 1974, during the invasion of Cyprus by Turkey, Greek victims of rape were treated and received abortions at the Sovereign British RAF bases at Akrotiri.[221] Other documented instances of war rape include the First Liberian Civil War, and in East Timor during the occupation by Indonesia in 1975.[222]
It has been reported that in Peru, throughout the 12 year internal conflict, women were frequent victims of sustained war rape perpetrated by government security forces and the Shining Path.[16][222] It has also been reported that during the August 1990 invasion of Kuwait, an estimated 5,000 Kuwaiti women were raped by Iraqi soldiers, and at least one American POW was raped by Iraqi troops.[222][223]
Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan
The Soviet forces abducted Afghan women in helicopters while flying in the country in search of mujahideen. In November 1980 a number of such incidents had taken place in various parts of the country, including Laghman and Kama. Soviet soldiers as well as KhAD agents kidnapped young women from the city of Kabul and the areas of Darul Aman and Khair Khana, near the Soviet garrisons, to rape them.[224] Women who returned home were considered 'dishonoured' by their families.[225]
Impact
Former Yugoslavia
Evidence of the magnitude of rape in Bosnia and Herzegovina prompted the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) to deal openly with these abuses.[41] The issue of rape during armed conflict was brought to the attention of the United Nations after the breakup of Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, in conjunction with the Bosnian war.[226] Reports of sexual violence during the Bosnian War (1992–95) and Kosovo War (1998–99), part of the Yugoslav wars, a series of conflicts from 1991 to 1999, have been described as "especially alarming".[227] During the Kosovo War thousands of Kosovo Albanian women and girls became victims of sexual violence by Serbian paramilitaries, soldiers or policemen. The majority of rapes were gang rapes.[228] Following the entry of NATO in the Kosovo War, rapes of Serbian, Albanian, and Roma women were committed by ethnic Albanians. Rapes by members of the Kosovo Liberation Army have also been documented.[229]
It has been estimated that during the Bosnian War between 20,000 and 50,000 women were raped. The majority of the rape victims were Muslim women raped by Serbian soldiers. Although men also became victim of sexual violence, war rape was disproportionately directed against women who were (gang) raped in the streets, in their homes and/or in front of family members. Sexual violence occurred in multiple ways, including rape with objects, such as broken glass bottles, guns and truncheons.[227] War rape occurred as a matter of official orders as part of ethnic cleansing, to displace the targeted ethnic group out of the region.[230][228]
During the Bosnian War, the existence of deliberately created "rape camps" was reported. The reported aim of these camps was to impregnate the Muslim and Croatian women held captive. It has been reported that often women were kept in confinement until the late stage of their pregnancy. This occurred in the context of a patrilineal society, in which children inherit their father's ethnicity, hence the "rape camps" aimed at the birth of a new generation of Serb children. According to the Women's Group Tresnjevka more than 35,000 women and children were held in such Serb-run "rape camps".[231][232][233]
During the Kosovo War thousands of Kosovo Albanian women and girls became victims of sexual violence. War rape was used as a weapon of war and an instrument of systematic ethnic cleansing; rape was used to terrorize the civilian population, extort money from families, and force people to flee their homes. According to a 2000 Human Rights Watch report war rape in the Kosovo War can generally be subdivided into three categories: rapes in women's homes, rapes during fighting, and rapes in detention. The majority of the perpetrators were Serbian paramilitaries, but they also included Serbian special police or Yugoslav army soldiers. Most rapes were gang rapes involving at least two perpetrators. Rapes occurred frequently in the presence, and with the acquiescence, of military officers. Soldiers, police, and paramilitaries often raped their victims in the full view of numerous witnesses.[228]
Mass rape in the Bosnian War
During the Bosnian War, Bosnian Serb forces conducted a sexual abuse strategy against thousands of Bosnian Muslim girls and women which became known as a "mass rape phenomenon". No exact figures on how many women and children were systematically raped by the Serb forces in various camps were established,[234][235][236] but estimates range from 20,000[237] to 50,000.[238] Mass rape mostly occurred in eastern Bosnia (especially during the Foča and Višegrad massacres), and in Grbavica during the Siege of Sarajevo. Numerous Bosnian Serb officers, soldiers and other participants were indicted or convicted of rape as a war crime by the ICTY and the Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[239][240] The events inspired the Golden Bear winner at the 56th Berlin International Film Festival in 2006, called Grbavica.
Rwandan genocide
During the Rwandan genocide, from April until July 1994, hundreds of thousands of women and girls were raped or became the victims of other forms of sexual violence.[229] Although no explicit written orders to commit rape and other acts of sexual violence have been found, evidence suggests that military leaders encouraged or ordered their men to rape the Tutsis, and they also condoned the acts which were already taking place, without making efforts to stop them.[241] Compared to other conflicts, the sexual violence in Rwanda stands out in terms of the organised nature of the propaganda that contributed significantly to fuelling sexual violence against Tutsi women, the very public nature of the rapes and the level of brutality towards the women. Anne-Marie de Brouwer concludes that considering the massive scale and public nature of war rape during the Rwandan genocide, "it is difficult to imagine anybody in Rwanda who was not aware of the sexual violence taking place."[242] In 1998, the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda made the landmark decision that the war rape during the Rwanda genocide was an element of the crime of genocide. The Trial Chamber held that "sexual assault formed an integral part of the process of destroying the Tutsi ethnic group and that the rape was systematic and had been perpetrated against Tutsi women only, manifesting the specific intent required for those acts to constitute genocide."[46]
In his 1996 report, the United Nations Special Rapporteur on Rwanda, Rene Degni-Segui stated that "rape was the rule and its absence was the exception." The report also stated that "rape was systematic and was used as a "weapon" by the perpetrators of the massacres. This can be estimated from the number and nature of the victims as well as from the forms of rape."[229] A 2000 report prepared by the Organisation of African Unity’s International Panel of Eminent Personalities concluded that "we can be certain that almost all females who survived the genocide were direct victims of rape or other sexual violence, or were profoundly affected by it".[229]
The Special Rapporteur on Rwanda estimated in his 1996 report that between 2,000 and 5,000 pregnancies resulted from war rape, and that between 250,000 and 500,000 Rwandese women and girls had been raped.[229] Rwanda is a patriarchal society and children therefore take the ethnicity of the father, underlining the fact that war rape occurred in the context of genocide.[242]
Within the context of the Rwandan genocide, victims of sexual violence were predominantly attacked on the basis of their gender and ethnicity. The victims were mostly Tutsi women and girls, of all ages, while men were only seldomly the victims of war rape. Women were demonized in the anti-Tutsi propaganda prior to the 1994 genocide. The December 1990 issue of the newspaper Kangura published the "Ten Commandments", four of which portrayed Tutsi women as tools of the Tutsi community, as sexual weapons that would be used by the Tutsi to weaken and ultimately to destroy the Hutu men.[241] Gender based propaganda also included cartoons printed in newspapers that portrayed Tutsi women as sex objects. Examples of gender based hate propaganda used to incite war rape included statements by perpetrators such as "You Tutsi women think that you are too good for us" and "Let us see what a Tutsi woman tastes like".[241] Victims of war rape during the Rwandan genocide also included Hutu women considered moderates, such as Hutu women married to Tutsi men and Hutu women politically affiliated with the Tutsi. War rape also occurred regardless of ethnicity or political affiliation, with young or beautiful women being targeted based on their gender only. Sexual violence against men occurred significantly less frequently, but it frequently included the mutilation of their genitals, which were often displayed in public.[241] The perpetrators of war rape during the Rwandan genocide were mainly members of the Hutu militia, the "Interahamwe". Rapes were also committed by military personnel within the Rwandan Armed Forces (FAR), including the Presidential Guard, and civilians.[241]
Sexual violence against women and girls during the Rwandan genocide included: rape, gang rape, sexual slavery (either collectively or individually through "forced marriages"), rape with objects such as sticks and weapons often leading to the victim's death, sexual mutilation of, in particular, breasts, vaginas or buttocks, often during or following rape. Pregnant women were not spared from sexual violence and on many occasions victims were killed following rape. Many women were raped by men who knew they were HIV positive and it has been suggested that there were deliberate attempts to transmit the virus to Tutsi women and their families. War rape occurred all over the country and it was frequently perpetrated in plain view of others, at sites such as schools, churches, roadblocks, government buildings or in the bush. Some women were kept as personal slaves for years after the genocide, and they were eventually forced to move to neighbouring countries after the genocide along with their captors.[242]
The long-term effects of war rape in Rwanda on its victims include social isolation (the social stigma attached to rape meant that some husbands left their wives who had become victims of war rape, or that the victims became unmarriageable), unwanted pregnancies and babies (some women resorted to self-induced abortions), sexually transmitted diseases, including syphilis, gonorrhoea and HIV/AIDS (access to anti-retroviral drugs remains limited).[242]
The International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda, established in 1994 after the Rwandan Genocide, has only brought three perpetrators before the Tribunal, with the first conviction in 1998.[243]
Sri Lanka civilian war
During the Sri Lankan Civil War, multiple Human Rights Organizations have reported cases of rape, violence and disappearance of women in the 1990s, claiming to be committed by security forces. Government officials, including the president, have denied the claims and agreed to co-operate with the investigations and prosecute whomever they find guilty.[244] The UN Special Rapporteur, has reported that individual investigations and proceedings relating to these cases have commenced at the local magistrates courts.[245]
Some of the notable cases of murdered raped victims and the massacres associated with the rape incidents are – Krishanti Kumaraswamy, Arumaithurai Tharmaletchumi, Ida Carmelitta, Ilayathambi Tharsini, Murugesapillai Koneswary, Premini Thanuskodi, Sarathambal, Kumarapuram massacre and Vankalai massacre.
Philippines: Mindanao and Sulu
On 24 September 1974, in the Malisbong massacre the Armed Forces of the Philippines slaughtered 1,766 Moro Muslim civilians who were praying at a Mosque in addition to mass raping Moro girls who had been taken aboard a boat.[246][247]
Bangladesh: Chittagong Hill Tracts
In the Chittagong Hill Tracts Bengali settlers and soldiers have raped native Jumma (Chakma) women "with impunity" with the Bangladeshi security forces doing little to protect the Jummas and instead assisting the rapists and settlers.[248]
Recent occurrences
According to Amnesty International, recent documented cases of war rape include incidents in Afghanistan, Chechnya, Colombia, Iraq, Sudan, and Nepal.[12]
Commenting on the rape of women and children in recent African conflict zones, UNICEF said in 2008 that rape was no longer just perpetrated by combatants but also by civilians. According to UNICEF rape is common in countries affected by wars and natural disasters, drawing a link between the occurrence of sexual violence and significant uprooting of a society and the crumbling of social norms. UNICEF states that in Kenya reported cases of sexual violence doubled within days of recent post-election conflict erupting. According to UNICEF rape was prevalent in conflict zones in Sudan, Chad, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.[249]
Democratic Republic of the Congo
In Eastern Congo, the prevalence and intensity of rape and other sexual violence is described as the worst in the world.[250] A 2010 study found that 22% of men and 30% of women in Eastern Congo reported conflict-related sexual violence.[17]
Since fighting broke out in 1998 tens of thousands of people have been raped in the Democratic Republic of Congo.[251] It is estimated that there are as many as 200,000 surviving rape victims living in the Democratic Republic of the Congo today.[252][253] War rape in the Democratic Republic of Congo has frequently been described as a "weapon of war" by commentators. Louise Nzigire, a local social worker, states that "this violence was designed to exterminate the population." Nzigire observes that rape has been a "cheap, simple weapon for all parties in the war, more easily obtainable than bullets or bombs."[254] The rape of men is also common. Men who admit they were raped risk ostracism by their community, and criminal prosecution, because they may be seen as homosexual, which is a crime in 38 African countries.[17]
Despite the peace process launched in 2003, sexual assault by soldiers from armed groups and the national army continues in the eastern provinces of the country.[251] Evidence of war rape emerged when United Nations troops move into areas previously ravaged by war after the peace process started. Gang rape and rape with objects has been reported. The victims of war rape may suffer from incontinence and vaginal fistula as a result of particularly violent rape.[59] Witness accounts include an instance of a woman who had the barrel of a gun inserted into her vagina, after which the soldier opened fire.[59] Incontinence and vaginal fistula leads to the isolation of war rape victims from her community and access to reconstructive surgery is limited in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.[59]
More than 500 rapes were reported in Eastern Congo in August 2010, leading to an apology from Atul Khare that the UN peacekeepers had failed to protect the population from brutalisation.[255]
Darfur region in Sudan
A 19 October 2004 UN News Centre article[256] titled "UNICEF adviser says rape in Darfur, Sudan continues with impunity" reported:
Armed militias in Sudan’s strife-torn Darfur region are continuing to rape women and girls with impunity, an expert from the United Nations children’s agency said today on her return from a mission to the region. Pamela Shifman, the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF) adviser on violence and sexual exploitation, said she heard dozens of harrowing accounts of sexual assaults – including numerous reports of gang-rapes – when she visited internally displaced persons (IDPs) at one camp and another settlement in North Darfur last week. "Rape is used as a weapon to terrorize individual women and girls, and also to terrorize their families and to terrorize entire communities," she said in an interview with the UN News Service. "No woman or girl is safe."
In the same article Pamela Shifman was reported to have said that:
Every woman or girl she spoke to had either endured sexual assault herself, or knew of someone who had been attacked, particularly when they left the relative safety of their IDP camp or settlement to find firewood.
Iraq War
Male prisoners of war may be subject to rape and sexual violence. Sexual violence against male prisoners of the Iraq War gained wide publicity after graphic photos documented such abuses on male Iraqi prisoners by US guards at Abu Ghraib prison,[257] where prisoners were forced to humiliate themselves.
2011 – present Iraqi insurgency
The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) has employed sexual violence against women and men in a manner that has been described as "terrorism".[258] ISIL has utilized sexual violence in order to undermine a sense of security within communities, as well as to raise funds through the sale of captives into sexual slavery.[258] According to The Wall Street Journal, ISIL appeals to apocalyptic beliefs and claims "justification by a Hadith that they interpret as portraying the revival of slavery as a precursor to the end of the world".[259] In late 2014, ISIL released a pamphlet on the treatment of female slaves.[260][261][262][263][264] The New York Times said in August 2015 that "[t]he systematic rape of women and girls from the Yazidi religious minority has become deeply enmeshed in the organization and the radical theology of the Islamic State in the year since the group announced it was reviving slavery as an institution."[265]
2011 Libyan civil war
The chief prosecutor of the International Criminal Court (ICC), Luis Moreno Ocampo, claimed that there is evidence that Gaddafi's troops used rape as a weapon during the Libyan civil war. He also said, "Apparently, he [Gaddafi] decided to punish, using rape," while witnesses confirmed that the Libyan government also purchased a large number of Viagra-like drugs. The Libyan government, on the other hand, does not recognize the ICC's jurisdiction.[266]
Afghan Taliban
In 2015, Amnesty International reported that the Afghan Taliban had engaged in mass murder and gang rapes of Afghan civilians in Kunduz.[267] Taliban fighters killed and raped female relatives of police commanders and soldiers. The Taliban also raped and killed midwives who they accused of providing reproductive health services to women in the city.[267] One female human rights activist described the situation:[267]
When the Taliban asserted their control over Kunduz, they claimed to be bringing law and order and Shari’a to the city. But everything they’ve done has violated both. I don’t know who can rescue us from this situation.
Rape in contemporary peace operations by UN peacekeepers
In contemporary conflict zones, international organizations, particularly the United Nations peacekeepers, have been involved in maintaining peace and stability in the area as well as distribute humanitarian aid to the local population. At present there are 16 Peace Operations directed by the UN Department of Peacekeeping Operations. The peacekeepers are mainly composed of military personnel (but to a less number also the police) sent by governments of various member-states.[268] However, over the course of their involvement in the field, peacekeepers have also been accused and at times found guilty of committing rape and other forms of sexual violence to the local population, in particular to women and children. Among all international staff in the conflict zone, United Nations peacekeepers (handled by the Department of Peacekeeping Operations) have been most frequently identified as the perpetrators of rape.[269]
Motivations for rape and sexual abuse by peacekeepers
Like traditional military ventures, peacekeepers are deployed in highly unstable areas similar to war zones, where there is absence of the rule of law, disintegration of society and great psychological and economic hardships.[270] Having an image of wealth and authority, peacekeepers can easily exercise power over the local population, which is often abused.[271]
Moreover, as members of their respective country's militaries, peacekeepers also carry with them in the peace operations the "hyper-masculine culture" that encourages sexual exploitation and abuse.[272] The motivations for rape differ from the traditional perpetrators (government and rebel forces) in that rape is not part of a war strategy that contributes to fulfilling the organization's mission, but rather more as means to relieve the perpetrators’ sexual urges most often related to the military culture.[273] Apart from putting the victim under the threat of physical violence, perpetrators induce sexual acts from the victim through payment, and granting or denying humanitarian aid.[274]
Cases of rape and sexual abuse in peace operations
UN peacekeepers’ involvement in rape was found as early as 1993 during the Bosnian genocide, where peacekeepers were found to regularly visit a Serb-run brothel in Sarajevo that housed Bosniak and Croat women who were forced to become prostitutes.[275] According to the Outlook, sexual misconduct by Indian soldiers and officers on UN duty in Congo raised disturbing questions.[276] In recent years, several UN soldiers in Haiti have been accused and convicted of raping boys as young as 14 years. In one instance, BBC News reports that Uruguayan soldiers raped a young man. In another instance, Uruguayan UN soldiers were recently convicted of raping a Haitian boy, sparking protests that called for the withdrawal of UN peacekeeping forces.[277] In Congo in 2004, peacekeepers from Uruguay, Morocco, Tunisia, South Africa and Nepal have faced 68 cases of rape, prostitution and pedophilia. The investigation resulted in the jailing of six Nepalese troops.[278] In Sudan, the Egyptian contingent was accused of raping six women when the civilians took shelter at the peacekeepers’ headquarters in order to flee from the fighting.[279][280] Allegations of rape of young women and children have also been launched against UN peacekeepers in South Sudan.[281] In Mali, four UN peacekeepers from Chad were involved in the rape of a woman.[282] Members of the Moroccan contingent faced rape charges during the course of their duties at the UN mission in Ivory Coast.[283]
Punitive measures
The most common challenge in reprimanding perpetrators is the significant underreporting of the issue mainly due to three reasons. First, the victims do not report or file complaints due to fears of revenge from the offender(s), denial of aid and the social stigma against rape victims in the victims’ own community.[284] Second, UN higher officials previously dismissed such allegations as "boys will be boys".[285] Third, fellow peacekeepers are accustomed to the "wall of silence" in the spirit of brotherhood characteristic of military culture but also to protect the reputation of their sending government.[286] As a consequence, whistleblowers are often stigmatised.[287]
However, if there would indeed be reports, the UN instituted the Conduct and Discipline Teams (CDTs) to conduct an investigation referring the allegations for serious offense to the Office of Internal Oversight Services (OIOS).[288] When found guilty, the course of the specific disciplinary action is dependent on the employee status of the offender. UN civilian staff and personnel have functional immunity that can only be waived by the UN Secretary-General. In the case of military personnel, they are subject to the jurisdiction of their respective sending governments.[289] The usual practice for offending soldiers has been to repatriate the personnel and prosecute them in their home country. In several cases, punitive measures are imposed such as demotion or dishonorable dismissal. However, very few among guilty personnel have faced criminal charges in their home countries after repatriation.[290]
Rape camp
A rape camp is a detention facility that is designed for or turns into a place where authorities regularly rape the detainees.
Rape camps set up by the Bosnian Serb authorities have been extensively documented in the Bosnian War:[291][292]
Notable examples
- Foča massacres also known as the Foča genocide
- Karaman's house
- Keraterm camp
- Luka camp
- Manjača camp
- Omarska camp
- Sušica camp
- Trnopolje camp
- Uzamnica camp
- Vilina Vlas
Forced prostitution and sexual slavery in war
Forced prostitution and sexual slavery are distinct as forms of war rape, as they entail more than the opportunistic rape by soldiers of women captives. Instead, women and girls are forced into sexual slavery, in some cases for prolonged periods. This is defined by the UN as "the status or condition of a person over whom any or all of the powers attaching to the right of ownership are exercised, including sexual access through rape or other forms of sexual violence".[293] War time forced prostitution takes several forms ranging from individual trafficking by armed forces to the institutionalization of the act of rape by military or civil authorities. The term ‘forced prostitution’ is often used in the press to refer to men and women displaced by war who are forced to engage in prostitution to survive.[294]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to War rape. |
- Raptio, the historic term for the large-scale abduction of women during war
- Allied war crimes during World War II
- Genocide
- Genocidal rape
- History of United Nations peacekeeping
- M. Cherif Bassiouni
- Joy Division (World War II)
- Peacekeeping child sexual abuse scandal
- Rape during the Bangladesh Liberation War
- Sexual harassment in the military
- Sociobiological theories of rape
- Soviet War Crimes
- Total war
- UN Action Against Sexual Violence in Conflict
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325
- War crime
- White Terror (Spain)
- Women's rights
References
Citations
- "30% of Women in USA Military Raped Whilst Serving by Fellow Soldiers"
- Benedict, Helen (6 May 2009). "The Nation: The Plight of Women Soldiers". Npr.org. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Benedict, Helen (13 August 2008). "Why Soldiers Rape – Culture of misogyny, illegal occupation, fuel sexual violence in military". In These Times. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Haddad, H.N. Hum Rights Rev (2011). "Mobilizing the Will to Prosecute: Crimes of Rape at the Yugoslav and Rwandan Tribunals". Human Rights Review. 12: 109–132. doi:10.1007/s12142-010-0163-x.
- "War on Women – Time for action to end sexual violence in conflict" (PDF). Nobel Women's initiative. May 2011.
- "Elements of Crimes". Archived from the original on 1 December 2008. Retrieved 25 May 2017.. PDF: Archive copy at the Internet Archive PDF. International Criminal Court
- Minzoni – Deroche, Angela (November 2005). "Rape as a tactic of war – Advocacy Paper" (PDF). Caritas France.
- Brown C (2012). "Rape as a weapon of war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo". Torture. 22 (1): 24–37. PMID 23086003.
- "Sexual violence as a weapon of war". www.unicef.org. Retrieved 22 December 2016.
- "Rape: Weapon of war". OHCHR.
- Cohen, D.K. (2011). "Causes of Sexual Violence During Civil War: Cross-National Evidence (1980–2009) Prepared for the Minnesota International Relations Colloquium, March 28, 2011."
- Smith-Spark, Laura (8 December 2004). "How did rape become a weapon of war?". BBC News. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- Spivak, Gayatri Chakravorty (1999). A Critique of Postcolonial Reason: Towards a History of the Vanishing Present. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 300. ISBN 978-0-674-17764-2.
The group rape perpetrated by the conquerors is a metonymic celebration of territorial acquisition
- Eiji Takemae; Robert Ricketts; Sebastian Swann (2003). Allied Occupation of Japan. A&C Black. p. 67. ISBN 978-0-8264-1521-9.
- Askin (1997), pp. 12–13
- Thomas, Dorothy Q.; Reagan, E. Ralph (1994). "Rape in War: Challenging the Tradition of Impunity". SAIS Review, Johns Hopkins University Press. Archived from the original on 6 March 2008.
- Storr, Will (17 July 2011). "The rape of men". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- Watts, Charlotte; Zimmerman, Cathy (2002). "Violence Against Women: Global Scope and Magnitude". The Lancet. 359 (9313): 1232–1237. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08221-1. PMID 11955557. Retrieved 10 February 2016.
- Askin (1997), pp. 26–27
- Askin (1997), p. 13
- Askin (1997), pp. 10–21
- Askin (1997), p. 27
- Levinson, Bernard M (2004). Gender and Law in the Hebrew Bible and the Ancient Near East. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-567-08098-1.
- Stemple, Lara (1 January 2009). "Male Rape and Human Rights". Hastings Law Journal. 60 (3): 605.
- Stemple, p. 612.
- "Rape as a 'weapon of war' against men." IRIN, 13 October 2011.
- "IRIN Africa | HEALTH: Rape as a "weapon of war" against men | DRC | South Sudan | Children | Gender Issues | Health & Nutrition | Human Rights". Irinnews.org. 13 October 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Grace Natabaalo. "Male rape survivors fight stigma in Uganda – Features". Al Jazeera English. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Askin (1997), p. 17
- Nicolas Werth, Karel Bartošek, Jean-Louis Panné, Jean-Louis Margolin, Andrzej Paczkowski, Stéphane Courtois, The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression, Harvard University Press, 1999, hardcover, 858 pages, ISBN 0-674-07608-7, page 5.
- Askin (1997), pp. 23–24
- Abou El Fadl, Khaled (2001). Commentary: Terrorism Is at Odds With Islamic Tradition. LA Times. Retrieved 11 July 2011
- Askin (1997), pp. 24–25
- Askin (1997), p. 28
- Askin (1997), pp. 30–32
- Askin (1997), p. 34
- Askin (1997), p. 33
- Askin (1997), pp. 35–36
- de Brouwer (2005), p. 5
- de Brouwer (2005), pp. 5–7
- Simons, Marlise (June 1996). "For first time, Court Defines Rape as War Crime". The New York Times.
- Rosenberg, Tine (April 1998). "Editorial Observer; New punishment for an ancient war crime". The New York Times.
- de Brouwer (2005), p. 8
- Ash, Lucy (May 2015). "The rape of Berlin – BBC News". BBC News. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- "Silence Broken On Red Army Rapes In Germany". NPR.org. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- "Fourth annual report of the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda" (PDF). 19 October 1999. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- Navanethem Pillay is quoted by Professor Paul Walters in his presentation of her honorary doctorate of law, Rhodes University, April 2005 Archived 26 September 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- "Violence against women" (PDF). 3 September 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- Rape as a Crime Against Humanity Archived 27 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Bosnia-Herzegovina : Foca verdict – rape and sexual enslavement are crimes against humanity Archived 7 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine. 22 February 2001. Amnesty International.
- "UN Security Council Takes a Historic Stand Supporting Abortion Access for Women Raped in War / Library / Homepage". AWID. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 2 December 2013.
- As quoted by Guy Horton in Dying Alive – A Legal Assessment of Human Rights Violations in Burma April 2005, co-Funded by The Netherlands Ministry for Development Co-Operation. See section "12.52 Crimes against humanity", Page 201. He references RSICC/C, Vol. 1 p. 360
- "Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court". Legal.un.org. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "SECURITY COUNCIL DEMANDS IMMEDIATE AND COMPLETE HALT TO ACTS OF SEXUAL VIOLENCE AGAINST CIVILIANS IN CONFLICT ZONES, UNANIMOUSLY ADOPTING RESOLUTION 1820 (2008)". United Nations. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- "About the Office | United Nations Office of the Special Representative of the Secretary-General on Sexual Violence in Conflict". www.un.org. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- Tol, Wietse A; Stavrou, Vivi; Greene, M Claire; Mergenthaler, Christina; van Ommeren, Mark; García Moreno, Claudia (5 August 2013). "Sexual and gender-based violence in areas of armed conflict: a systematic review of mental health and psychosocial support interventions". Conflict and Health. 7 (1): 16. doi:10.1186/1752-1505-7-16. PMC 3750365. PMID 23915821.
- O'Brien, Daniel P; Venis, Sarah; Greig, Jane; Shanks, Leslie; Ellman, Tom; Sabapathy, Kalpana; Frigati, Lisa; Mills, Clair (17 June 2010). "Provision of antiretroviral treatment in conflict settings: the experience of Médecins Sans Frontières". Conflict and Health. 4 (1): 12. doi:10.1186/1752-1505-4-12. PMC 2911421. PMID 20553624.
- "Rwanda". Women Under Siege Project. Retrieved 2 December 2013.
- Martens, Jackie (24 January 2004). "Congo rape victims seek solace". BBC News.
- vaginal-fistula.
- "WHO | Female genital mutilation". who.int. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- "WHO | 10 facts on obstetric fistula". Who.int. 7 December 2010. Retrieved 2 December 2013.
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Sexual and Gender-Based Violence against Refugees, Returnees and Internally Displaced Persons. Guidelines for Prevention and Response, UNHCR (SGVB Guidelines)" (PDF). UNHCR. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "War, rape and genocide: From ancient times to the Sudan". Apha.confex.com. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Hagen, Kristen; Yohani, Sophie (21 November 2010). "The Nature and Psychosocial Consequences of War Rape for Individuals and Communities". International Journal of Psychological Studies. 2 (2). doi:10.5539/ijps.v2n2p14.
- Skjelsbæk, Inger (25 July 2016). "Victim and Survivor: Narrated Social Identities of Women Who Experienced Rape During the War in Bosnia-Herzegovina". Feminism & Psychology. 16 (4): 373–403. doi:10.1177/0959353506068746.
- Østby, Gudrun; Leiby, Michele; Nordås, Ragnhild (2019). "The Legacy of Wartime Violence on Intimate-Partner Abuse: Microlevel Evidence from Peru, 1980-2009". International Studies Quarterly. 63 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1093/isq/sqy043.
- Ward, Jeanne; Marsh, Mendy (2006). Sexual Violence Against Women and Girls in War and Its Aftermath: Realities, Responses, and Required Resources (PDF) (Report).
- Bloomfield, David; Barnes, Teresa; Huyse, Luc (2003). Reconciliation after Violent Conflict: A Handbook. International IDEA. p. 61. ISBN 91-89098-91-9.
- Clifford, Cassandra (2008). Rape as a Weapon of War and it's Long-term Effects on Victims and Society (Report). CiteSeerX 10.1.1.512.4507.
- Diken, Bülent; Laustsen, Carsten Bagge (29 June 2016). "Becoming Abject: Rape as a Weapon of War". Body & Society. 11 (1): 111–128. doi:10.1177/1357034X05049853.
- Russel-Brown, Sherrie L. (2003). "Rape as an Act of Genocide". Berkeley Journal of International Law. 21 (2): 350–374. doi:10.15779/Z380M0V.
- Cassandra Clifford: "Rape as a Weapon of War and it's Long-term Effects on Victims and Society", paper presented at the 7th Global Conference on Violence and the Contexts of Hostility, 5–7 May 2008, Budapest, p. 4.
- "Rape and HIV as Weapons of War – United Nations University". Unu.edu. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Carpenter, Charli. War's Impact on Children Born of Rape and Sexual Exploitation: Physical, Economic and Psychosocial Dimensions (PDF) (Report).
- Daniel-Wrabetz, Joana (2007). "Children Born of War Rape in Bosnia-Herzegovina and the Convention on the Rights of the Child". In Carpenter, Charli (ed.). Born of War: Protecting Children of Sexual Violence Survivors in Conflict Zones. Lynne Rienner. pp. 21–39.
- Holt, Kate; Hughes, Sarah (13 December 2005). "Bosnia's rape babies: abandoned by their families, forgotten by the state". The Independent.
- Apio, Eunice (2007). "Uganda's Forgotten Children of War". In Carpenter, Charli (ed.). Born of War: Protecting Children of Sexual Violence Survivors in Conflict Zones. Lynne Rienner. pp. 94–109.
- McKinley, James (23 September 1996). "Legacy of Rwanda Violence: The Thousands Born of Rape". The New York Times.
- "United Nations Official Document". Un.org. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Rape: Weapon of war". Ohchr.org. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Rwanda". Hrw.org. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "United Nations Official Document". Un.org. Retrieved 30 April 2014., p. 16.
- "Physicians for Human Rights: Nowhere to Turn: Failure to Protect, Support and Assure Justice to Darfuri Women" (PDF). 2009. p. 4.
- Analysing Disrupted Health Sectors: A Modular Manual. Department of Recovery and Transition Programmes Health Action in Crises. World Health Organization. June 2009. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.410.6623. ISBN 978-92-4-159926-9.
- Hollifield, Michael (April 2005). "Taking measure of war trauma". The Lancet. 365 (9467): 1283–1284. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61003-3. PMID 15823362.
- Joachim, I. (2004). "Sexualised violence in war and its consequences". In Mondiale, Medica (ed.). Violence against women in war: Handbook for professionals working with traumatized women. Cologne, Germany: Prisma, Saarbrücken. pp. 63–110.
- Rojnik, B.; Andolsek-Jeras, L.; Obersnel-Kveder, D. (March 1995). "Women in difficult circumstances: war victims and refugees". International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. 48 (3): 311–315. doi:10.1016/0020-7292(94)02302-F. PMID 7781876.
- Levinson, Bernard M (2004). Gender and Law in the Hebrew Bible and the Ancient Near East. p. 203. ISBN 978-0-567-08098-1.
- Lerner, Gerda (1987). The Creation of Patriarchy (paperback ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 80. ISBN 0-19-505185-8. Retrieved 22 April 2019.
- Vikman, Elisabeth (April 2005). "Ancient origins: Sexual violence in warfare, Part I". Anthropology & Medicine. 12 (1): 21–31. doi:10.1080/13648470500049826. PMID 28135871.
- Sara Elise Phang (2001). The marriage of Roman soldiers (13 B.C.-A.D. 235): law and family in the imperial army. BRILL. p. 268. ISBN 978-90-04-12155-3.
- Smitha, Frank. India, Empire, and Chaos.
- Indian civilization. Deepak Shinde. 25 October 2016.
- Roesdahl, pp. 9–22.
- Heredity (1 June 2005). "Heredity – Human migration: Reappraising the Viking Image". Heredity. 95 (2): 111–112. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6800695. PMID 15931243.
- "IngentaConnect The Vikings on the Continent in Myth and History". Ingentaconnect.com. 1 April 2003. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Islam and slavery: Sexual slavery". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Horrible Traffic in Circassian Women—Infanticide in Turkey". New York Daily Times, 6 August 1856.
- "Soldier Khan". Avalanchepress.com. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "When Europeans were slaves: Research suggests white slavery was much more common than previously believed". Researchnews.osu.edu. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Davis, Robert. Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500–1800. Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". Stephen Behrendt, "Transatlantic Slave Trade", Africana: The Encyclopedia of the African and African American Experience (New York: Basic Civitas Books, 1999), ISBN 0-465-00071-1.
- Tillman, Hoyt Cleveland (1995). Tillman, Hoyt Cleveland; West, Stephen H. (eds.). China Under Jurchen Rule: Essays on Chin Intellectual and Cultural History (illustrated ed.). SUNY Press. p. 27. ISBN 0791422739.
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (2014). Emperor Huizong (illustrated, reprint ed.). Harvard University Press. p. 468. ISBN 978-0674726420.
- Man, John. Genghis Khan : Life, Death and Resurrection (London; New York : Bantam Press, 2004) ISBN 0-593-05044-4.
- Beatrice F. Manz (2000). "Tīmūr Lang". Encyclopaedia of Islam. 10 (2nd ed.). Brill.
- Gaskill, Matthew. "Tamerlane Wiped Out Perhaps 17 Million People With Just Fire & Swords".
- Reyna Pastor. "Mujeres en España y en Hispanoamérica". Historia de las mujeres, tomo III, Del Renacimiento a la Edad Moderna, Georges Duby, page 555. Madrid, Santillana 2000. ISBN 84-306-0390-5.
- Hastings, Max Montrose: The King's Champion (Gollancz, 1977) ISBN 0-575-02226-4
- Lang, Andrew The History Of Scotland: Volume 3, p.137
- Yi, Pae-yong (2008). Chan, Ted (ed.). Women in Korean History 한국 역사 속의 여성들. Ewha Womans University Press. p. 114. ISBN 978-8973007721.
- Millward, James A. (1998). Beyond the Pass: Economy, Ethnicity, and Empire in Qing Central Asia, 1759-1864. Stanford University Press. p. 124. ISBN 0804797927.
- Newby, L. J. (2005). The Empire And the Khanate: A Political History of Qing Relations With Khoqand C1760-1860 (illustrated ed.). BRILL. p. 39. ISBN 9004145508.
- Wang, Ke (2017). "Between the "Ummah" and "China":The Qing Dynasty's Rule over Xinjiang Uyghur Society" (PDF). Journal of Intercultural Studies. Kobe University. 48: 204.
- Millward, James A. (2007). Eurasian Crossroads: A History of Xinjiang (illustrated ed.). Columbia University Press. p. 108. ISBN 978-0231139243.
- Millward, James A. (2007). Eurasian Crossroads: A History of Xinjiang (illustrated ed.). Columbia University Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-0231139243.
- Millward, James A. (1998). Beyond the Pass: Economy, Ethnicity, and Empire in Qing Central Asia, 1759-1864. Stanford University Press. pp. 206–207. ISBN 0804797927.
- John Robert Shepherd (1993). Statecraft and Political Economy on the Taiwan Frontier, 1600-1800. Stanford University Press. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-8047-2066-3.
- Lach, Donald F.; Van Kley, Edwin J. (1998). Asia in the Making of Europe, Volume III: A Century of Advance. Book 4: East Asia. Asia in the Making of Europe Volume III (revised ed.). University of Chicago Press. p. 1823. ISBN 978-0-226-46769-6.
- Manthorpe 2008, p. 72
- Manthorpe, Jonathan (2008), Forbidden Nation: A History of Taiwan (illustrated ed.), Macmillan, p. 77, ISBN 978-0-230-61424-6
- Heaver, Stuart (26 February 2012). "Idol worship". South China Morning Post. p. 25. Archived from the original on 29 December 2014. Retrieved 10 December 2014. Alt URL
- Moffett, Samuel H. (1998). A History of Christianity in Asia: 1500–1900. Bishop Henry McNeal Turner Studies in North American Black Religion Series. Volume 2 of A History of Christianity in Asia: 1500–1900. Volume 2 (2, illustrated, reprint ed.). Orbis Books. p. 222. ISBN 978-1570754500. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- Moffett, Samuel H. (2005). A history of Christianity in Asia, Volume 2 (2 ed.). Orbis Books. p. 222. ISBN 978-1570754500. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- Free China Review, Volume 11. W.Y. Tsao. 1961. p. 54.
- Wright, Arnold, ed. (1909). Twentieth century impressions of Netherlands India: Its history, people, commerce, industries and resources (illustrated ed.). Lloyd's Greater Britain Pub. Co. p. 67.
- Newman, Bernard (1961). Far Eastern Journey: Across India and Pakistan to Formosa. H. Jenkins. p. 169.
- Covell, Ralph R. (1998). Pentecost of the Hills in Taiwan: The Christian Faith Among the Original Inhabitants (illustrated ed.). Hope Publishing House. p. 96. ISBN 978-0-932727-90-9.
- Muller, Hendrik Pieter Nicolaas (1917). Onze vaderen in China (in Dutch). P.N. van Kampen. p. 337.
- Potgieter, Everhardus Johannes; Buys, Johan Theodoor; van Hall, Jakob Nikolaas; Muller, Pieter Nicolaas; Quack, Hendrik Peter Godfried (1917). De Gids, Volume 81, Part 1 (in Dutch). G. J. A. Beijerinck. p. 337.
- Zeeuw, P. de (1924). De Hollanders op Formosa, 1624–1662: een bladzijde uit onze kolonialeen zendingsgeschiedenis (in Dutch). W. Kirchner. p. 50.
- Algemeene konst- en letterbode, Volume 2 (in Dutch). A. Loosjes. 1851. p. 120.
- Ernie (1 June 2012). "Koxinga the Pirate". China Expat.
- Nomsz, Joannes (1775). "Antonius Hambroek, of de Belegering van Formoza". Universiteit Leiden. AMSTELDAM: IZAAK DUIM, op den Cingel, tusschen de Warmoesgracht, en de Drie-Koningstraat.
- Andrade, Tonio (2011). Lost Colony: The Untold Story of China's First Great Victory Over the West. Princeton University Press. p. 413. ISBN 978-0691144559.
- Beckman (2003), pp. 31–33
- Beckman (2003), pp. 33–34
- "THE INDIAN MUTINY AND CIVIL WAR 1857-58".
- "THE INDIAN MUTINY AND CIVIL WAR 1857-58".
- Ball, Charles (1858). The History of the Indian Mutiny. London Printing and Publishing Company.
Charles Ball.
- Redfern (1858). Justice for India.
- "The Great Rebellion of 1857 in India".
- Faught, C. Brad Gordon Victorian Hero (2008) p. 31
- John Gittings (5 August 2000). "Lost souls". The Guardian. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- Robert R. Mathisen (2006). Critical issues in American religious history. Baylor University Press. p. 539. ISBN 978-1-932792-39-3.
- Joanna Waley-Cohen (2000). The Sextants of Beijing: Global Currents in Chinese History. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 201. ISBN 978-0-393-32051-0.
- Diana Preston (2000). The boxer rebellion: the dramatic story of China's war on foreigners that shook the world in the summer of 1900. Bloomsbury Publishing USA. p. 285. ISBN 978-0-8027-1361-2.
- Dictionary of Genocide: M-Z Samuel Totten, Paul Robert Bartrop, Steven L. Jacobs, page 272, Greenwood 2007
- Cocker, Mark (1998). Rivers of blood, rivers of gold: Europe's conflict with tribal peoples. London: Jonathan Cape. p. 308. ISBN 978-0-224-03884-3.
- Brownmiller (1975), pp. 40–48
- Brownmiller (1975), p. 44
- Crouthamel, Jason (8 January 2017). "Sexuality, Sexual Relations, Homosexuality – 1914–1918" (PDF). International Encyclopedia of the First World War: 1–21.
- "Comfort Women Were 'Raped': U.S. Ambassador to Japan". English.chosun.com. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Yoshimi 2000, pp. 91, 93
- For detailed accounts of rapes by Australian occupation troop during the occupation of Japan, see Allan Clifton, "Time of Fallen Blossoms". Australian Military Gang Rape of ‘Fallen Blossoms’
- Tanaka & Tanaka 2003, p. 110-111.
- Brownmiller (1975), p. 81
- Tanaka & Tanaka 2003, p. 111.
- Tanaka & Tanaka 2003, p. 112.
- Schrijvers, Peter (2002). The GI War Against Japan. New York City: New York University Press. p. 212. ISBN 978-0-8147-9816-4.
- Walsh 2018, p. 1204.
- Tanaka & Tanaka 2003, p. 118.
- Walsh 2018, p. 1217.
- Walsh 2018, p. 1218.
- Walsh 2018, p. 1219.
- Hannah Pakula (2009). The last empress: Madame Chiang Kai-Shek and the birth of modern China. Simon and Schuster. p. 530. ISBN 978-1-4391-4893-8.
- Asmolov, Konstantin (2008). "Pobeda na Dal'nem Vostoke" [Victory in the Far East]. In Dyukov, Aleksandr; Pyhalov, Igor (eds.). Velikaya obolgannaya voina [The Great Slandered War] (in Russian). 2. Moscow: Yauza.
- Emsley, Clive (2013) Soldier, Sailor, Beggarman, Thief: Crime and the British Armed Services since 1914. Oxford University Press, USA, p. 128-129; ISBN 0199653712
- Longden, Sean (2004) To the Victor the Spoils: D-Day to Ve Day, the Reality Behind the Heroism. Arris Books, p. 195. ISBN 1844370380
- "55 Dni Wehrmachtu w Polsce" Szymon Datner Warsaw 1967 page 67 "Zanotowano szereg faktów gwałcenia kobiet i dziewcząt żydowskich" (Numerous rapes were committed against Jewish women and girls)
- "Internet Archive Wayback Machine". 29 October 2007. Archived from the original on 29 October 2007. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- Numer: 17/18/2007 Wprost "Seksualne Niewolnice III Rzeszy"
- "Holocaust Studies: A Journal of Culture and History – Vallentine Mitchell". Vallentinemitchell.metapress.com. 10 October 2011. Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Jews, Germans, and Allies: Close Encounters in Occupied Germany, Atina Grossmann, page 290
- Zur Debatte um die Ausstellung. Vernichtungskrieg. Verbrechen der Wehrmacht 1941–1944. Kieler Landeshaus 1999.
- Askin (1997), p. 72
- "Italian women win cash for wartime rapes". Listserv.acsu.buffalo.edu. Archived from the original on 15 July 2013. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "1952: Il caso delle "marocchinate" al Parlamento". Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- Bracalini, Romano: "Paisà. Vita quotidiana nell'Italia liberata dagli alleati", Mondadori, 2008, pages 267, ISBN 88-04-58073-9, ISBN 978-88-04-58073-7
- David Wilson (27 March 2007). "The secret war". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- Lilly, Robert J. (2007). Taken by Force: Rape and American GIs in Europe During World War II. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-50647-3.
- Morrow, John H. (October 2008). "Taken by Force: Rape and American GIs in Europe during World War II By J. Robert Lilly". The Journal of Military History. 72 (4): 1324. doi:10.1353/jmh.0.0151.
- Schofield, Hugh (5 June 2009). "Revisionists challenge D-Day story". BBC News. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
- Taken by Force: Rape and American GIs in Europe during World War II. J Robert Lilly. ISBN 978-0-230-50647-3 p.12
- Harrington, Carol (2010). Politicization of Sexual Violence: From Abolitionism to Peacekeeping. London: Ashgate. pp. 80–81. ISBN 0-7546-7458-4.
- Anna Reading. The Social Inheritance of the Holocaust: Gender, Culture, and Memory. Macmillan, 2002. ISBN 0-333-76147-2, ISBN 978-0-333-76147-2 p. 166
- Johnson, Daniel (24 January 2002). "Red Army troops raped even Soviet and Polish women as they freed them from camps". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Alma Mater 64(2004) – "OKUPOWANY KRAKÓW- z prorektorem Andrzejem Chwalbą rozmawia Rita Pagacz-Moczarska"
- Beevor, Antony (1 May 2002). "They raped every German female from eight to 80". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- Johnson, Daniel (24 January 2002). "Red Army troops raped even Russian women as they freed them from camps – Telegraph". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- Heineman, Elizabeth (1996). "The Hour of the Woman: Memories of Germany's "Crisis Years" and West German National Identity". American Historical Review. 101 (2): 354–395. doi:10.2307/2170395. JSTOR 2170395.
- Kuwert, P.; Freyberger, H. (2007). "The unspoken secret: Sexual violence in World War II". International Psychogeriatrics. 19 (4): 782–784. doi:10.1017/S1041610207005376. PMID 17726764.
- "BBC – History – World Wars: The Battle for Berlin in World War Two". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- Hanna Schissler (2001). The Miracle Years: A Cultural History of West Germany, 1949-1968. Princeton University Press. p. 28. ISBN 0-691-05820-2.
- "Silence Broken On Red Army Rapes In Germany". NPR.org. 17 July 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- Hitchcock, William I. (2004). The Struggle for Europe: The Turbulent History of a Divided Continent, 1945 to the Present. Anchor Books. ISBN 978-0-385-49799-2.
- Atina Grossmann. A Question of Silence: The Rape of German Women by Occupation Soldiers October, Vol. 72, Berlin 1945: War and Rape "Liberators Take Liberties" (Spring, 1995), pp. 42–63 MIT Press
- Helke Sander/Barbara Johr: BeFreier und Befreite, Fischer, Frankfurt 2005
- Seidler/Zayas: Kriegsverbrechen in Europa und im Nahen Osten im 20. Jahrhundert, Mittler, Hamburg Berlin Bonn 2002
- Sheehan, Paul (17 May 2003). "An orgy of denial in Hitler's bunker". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 7 December 2010.
- Beevor, Antony (1 May 2002). "They raped every German female from eight to 80". The Guardian. London.
- Antony Beevor, The Fall of Berlin 1945.
- Richard Bessel, Germany 1945.
- Norman M. Naimark. The Russians in Germany: A History of the Soviet Zone of Occupation, 1945–1949. Harvard University Press, 1995. pp. 132, 133. ISBN 0-674-78405-7.
- 十一万人的志愿军后勤部队中,从1952年一月到十一月中,共发生自杀一百零九人,自伤的三十九人,逃亡的六百八十七人,汽车肇事压死的八十一人,压伤的九十四人,误伤的一百零八人,强奸的四十一人,通奸的五百一十四人,鸡奸的一百五十人。"金盾出版社1986年7月1版《抗美援朝战争后勤经验总结 资料选编综合类下册 (Lessons About Logistics in Resist US and Aid Korea War: Comprehensive Selected Materials Vol.2)》,P427
- "Murder in the name of war – My Lai". BBC. 20 July 1998. Retrieved 2 June 2013.
- "Casualties of War". The New Yorker. 18 October 1969. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- Congressional Record, V. 151, Pt. 12, July 14 to July 22, 2005. Government Printing Office. p. 2.
- East Pakistan: Even the Skies Weep, Time Magazine, 25 October 1971.
- "1971 Rapes: Bangladesh Cannot Hide History". Forbes. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- Laura Smith-Spark (8 December 2004). "How did rape become a weapon of war?". BBC News. Retrieved 13 October 2008.
- Debasish Roy Chowdhury "Indians are bastards anyway". Asia Times. 23 June 2005.
- Hamoodur Rahman Commission, Chapter 2 Archived 12 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Paragraphs 32,34
- Salma Khatun Sarmila Bose Rewrites history website of Drishtipat "A non-profit, non-political expatriate Bangladeshi organization ... registered public charity in the United States."
- Farida Majid. "Skewing the history of rape in 1971". Groups.yahoo.com. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- D'Costa, Bina (2011). Nationbuilding, Gender and War Crimes in South Asia. Routledge. p. 104.
- "Women, War, and the Making of Bangladesh | Duke University Press". www.dukeupress.edu. Retrieved 15 March 2016.
- Anam, Tahmima (26 December 2013). "Pakistan's State of Denial". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- Dummett, Mark (16 December 2011). "Bangladesh war: The article that changed history – BBC News". BBC News. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- Anthony Mascarenhas, Sunday Times, 13 June 1971
- "The terrible secrets of the Turkish invasion of Cyprus".
- Chinkin, Christine (1994). "Rape and Sexual Abuse of Women in International Law" (PDF). European Journal of International Law. 5 (1): 326–341. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.ejil.a035874. Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- "A Woman's Burden". Time. 28 March 2003.
- Kakar, M. Hassan (1995). "Mass Killings in Civic Gatherings and the Kidnapping of Women". Afghanistan: The Soviet Invasion and the Afghan Response, 1979–1982. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- The War Chronicles: From Flintlocks to Machine Guns. Fair Winds. p. 393. ISBN 9781616734046.
- "United Nations, Department of Public Information".
- de Brouwer (2005), p. 9
- de Brouwer (2005), p. 10
- de Brouwer (2005), p. 11
- Radio Netherlands Archives, December 10, 1992
- de Brouwer (2005), pp. 9–10
- new Internationalist issue 244, June 1993. Rape: Weapon of War by Angela Robson.
- Human Rights News Bosnia: Landmark Verdicts for Rape, Torture, and Sexual Enslavement: Criminal Tribunal Convicts Bosnian Serbs for Crimes Against Humanity 22 February 2001
- Halilovic Aldi (21 December 2000). "Odjek – revija za umjetnost i nauku – Zločin silovanja u BiH". Odjek.ba. Archived from the original on 25 November 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Grbavica (film)". Coop99.at. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "ICTY – TPIY". un.org. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- Archived 10 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- "findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qn4158/is_20060220/ai_n16146172". findarticles.com. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- Andrew Osborn in Brussels (23 February 2001). "Mass rape ruled a war crime | World news". The Guardian. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3693/is_200103/ai_n8945781". findarticles.com. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- de Brouwer (2005), p. 13
- de Brouwer (2005), p. 14
- Barstow, Anne Llewellyn (2000). War's dirty secret: Rape, prostitution, and other crimes against women. Pilgrim Press.
- "Human Rights Watch World Report 1998". Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- "United Nation's Report of the Special Rapporteur on violence against women, its causes and consequences, Ms. Radhika Coomaraswamy". 2000. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- Mindanews (26 September 2014). "1,500 Moro massacre victims during Martial Law honored". Minda News.
- "Www.morowomen.com".
- McEvoy, Mark (3 April 2014). "Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh – rapists act with impunity". Survival International – The movement for tribal peoples.
- "Africa war zones' 'rape epidemic'". BBC News. 13 February 2008. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
- McCrummen, Stephanie (9 September 2007). "Prevalence of Rape in E.Congo Described as Worst in World". Washingtonpost.com. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Africa Tales of Rape in DR Congo". BBC News. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- Kira Cochrane (9 May 2008). "Kira Cochrane talks to filmmaker Lisa F Jackson on her documentary about rape in the Congo". The Guardian. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "A Conversation with Eve Ensler: Femicide in the Congo". Pbs.org. 18 January 2007. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Nolen, Stephanie. ""Not Women Anymore": The Congo's rape survivors face pain, shame and AIDS". Ms. Magazine. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- UN has failed Congo mass rape victims, says investigator, The Guardian, 8 September 2010
- "UNICEF adviser says rape in Darfur, Sudan continues with impunity". 19 October 2004. UN News Centre.
- Glaister, Dan, Julian Borger (13 May 2004). "1,800 new pictures add to US disgust: Stills shown of women forced to bare breasts". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 13 July 2011.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "ISIS sexual violence is an act of terrorism, says former CIA analyst". Cbc.ca. 25 September 2014. Retrieved 23 October 2014.
- Nour Malas, "Ancient Prophecies Motivate Islamic State Militants: Battlefield Strategies Driven by 1,400-year-old Apocalyptic Ideas", The Wall Street Journal, 18 November 2014; accessed 22 November 2014.
- Amelia Smith, "ISIS Publishes Pamphlet On How to Treat Female Slaves", Newsweek, 9 December 2014.
- Greg Botelho, "ISIS: Enslaving, having sex with 'unbelieving' women, girls is OK", CNN, 13 December 2014.
- Katharine Lackey, "Pamphlet provides Islamic State guidelines for sex slaves", USA Today, 13 December 2014.
- Carey Lodge, "Islamic State issues abhorrent sex slavery guidelines about how to treat women", Christianity Today, 15 December 2014.
- Adam Withnall, "Isis releases 'abhorrent' sex slaves pamphlet with 27 tips for militants on taking, punishing and raping female captives", The Independent, 10 December 2014.
- Callimachi, Rukmini (13 August 2015). "ISIS Enshrines a Theology of Rape". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- "Libya: Gaddafi investigated over use of rape as weapon". BBC News. 8 June 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Afghanistan: Harrowing accounts emerge of the Taliban's reign of terror in Kunduz".
- "Current peacekeeping operations. United Nations Peacekeeping". Un.org. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Defeis (2008)
- Anna Shotton, A Strategy to Address Sexual Exploitation by U.N. Peacekeeping Personnel, 39 CORNELL L. REV. 97, 103 (2006).
- Defeis (2008), p. 191
- Sarah Martin (October 2005). "Must boys be boys? Ending Sexual Exploitation & Abuse in UN Peacekeeping Missions" (PDF). Refugees International. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 August 2006.
- "UN Peacekeepers and Cultures of Violence". Cultural Survival. 19 March 2010. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Novick, Natalie. "When Those Meant to Keep the Peace Commit Sexualized Violence | Women Under Siege Project." Accessed 18 December 2013
- "UN peacekeepers took part in rapes during Bosnian Genocide | We Remember the Bosnian Genocide, 1992–95. Mi se Sjećamo Genocida u Bosni, 1992–95". Bosniagenocide.wordpress.com. 9 December 2010. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "The Peacekeeper's Child".
- "BBC News – Haiti anger over alleged Uruguay UN rape". BBC News. 6 September 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "U.N. Sexual Abuse Alleged in Congo". washingtonpost.com. 16 December 2004. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "U.N. Faces More Accusations of Sexual Misconduct". washingtonpost.com. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "SUDAN: With UN Peacekeepers Accused of Rape in Sudan, UN Women & Ban Ki-Moon Adviser Won't Answer, Other Priorities – News Library – News & Events". PeaceWomen. 14 June 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Rape Allegations Faced by U.N. In South Sudan – The New York Sun". Nysun.com. 3 January 2007. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "UN's Minusma peacekeepers 'raped woman in Mali' | Africatime". En.africatime.com. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Another U.N. Peacekeeper Rape Scandal". Outsidethebeltway.com. 23 July 2007. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Special Reports | Peacekeepers 'abusing children'". BBC News. 27 May 2008. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Profile: Bureaucrat at Large in the Balkans; Yasushi Akashi, Almost Painfully Diplomatic U.N. Envoy, The Independent, 30 April 1994.
- "UN-believable - OhmyNews International".
- "Bosnia sex trade shames UN". The Scotsman. 9 February 2003. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- Secretary-General, Comprehensive Report Prepared Pursuant to General Assembly Resolution 59/296 on Sexual Exploitation and Sexual Abuse, Including Policy Development, Implementation and Full Justification of Proposed Capacity on Personnel Conduct Issues, 14, delivered to the General Assembly, U.N. Doc. A/60/862 (24 May 2006)
- Defeis (2008), p. 192
- "'Survival sex': How NGOs and peacekeepers exploit women in war". Women Under Siege Project. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- "Rape: weapon of war". 5 June 1993.
- Allen, Beverly (1996). Rape Warfare: The Hidden Genocide in Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia. University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 978-0-8166-2818-6.
- "Report of the Special Rapporteur on systematic rape". Archived from the original on 17 November 2001. Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- Hassan, Nihal (2007). "50,000 Iraqi Refugees forced into prostitution". The Independent.
Bibliography
- Askin, Kelly Dawn (1997). War Crimes Against Women: Prosecution in International War Crimes Tribunals. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. ISBN 978-90-411-0486-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Beckman, Karen Redrobe (2003). Vanishing Women: Magic, Film, and Feminism. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-3074-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Brownmiller, Susan (1975). Against Our Will: Men, Women, and Rape. Fawcett Columbine. ISBN 978-0-449-90820-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- de Brouwer, Anne-Marie (2005). Supranational Criminal Prosecution of Sexual Violence. Intersentia. ISBN 978-90-5095-533-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Defeis, Elizabeth F. (1 January 2008). "U.N. Peacekeepers and Sexual Abuse and Exploitation: An End to Impunity". Washington University Global Studies Law Review. 7 (2): 185–214.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Further reading
- Sjoberg, Laura (22 November 2016). Women as Wartime Rapists: Beyond Sensation and Stereotyping. New York University Press. ISBN 9780814729274 – via Google Books.
- Skjelsbæk, Inger (2011). The Political Psychology of War Rape: Studies from Bosnia and Herzegovina. ISBN 978-0-415-67117-0.
- Lewis, Dustin A. (23 July 2009). "Unrecognized Victims: Sexual Violence Against Men in Conflict Settings Under International Law". Wisconsin International Law Journal. 27 (1): 1–49. SSRN 1404574.
- "IHL Primer on Sexual Violence". International Humanitarian Law Research Initiative, June 2009.
- UN classifies rape a 'war tactic'. 20 June 2008. BBC News.
- "Rape as an Instrument of Total War". By David Rosen. 4 April 2008. CounterPunch.
- "Intended Consequences" by Jonathan Torgovnik on MediaStorm
- Duty, Honor, Rape: Sexual Assault Against Women During War by Kevin Gerard Neill. Journal of International Women's Studies.
- Extreme War Rape in Today's Civil-war-torn States by Kathryn Farr. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Sociological Association, New York City, 11 August 2007.
- womensnews.com – Bosnian 'Rape Camp' Survivors Testify in The Hague
- guardian.uk – Women say village became rape camp
- U.S. Department of State dispatch, mentioning a "rape house".
- Roberts, Mary Louise (2013). What Soldiers Do: Sex and the American GI in World War II France. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0226923093.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Mees, Heleen; van Zeijl, Femke (26 May 2008). "Kriege gegen Frauen". Project Syndicate. Retrieved 6 June 2010.