Foreign relations of South Korea
South Korea maintains diplomatic relations with 191 countries. The country has also been a member of the United Nations since 1991, when it became a member state at the same time as North Korea. South Korea has also hosted major international events such as the 1988 Summer Olympics and 2002 World Cup Soccer Tournament (2002 FIFA World Cup co-hosted with Japan) and the 2011 IAAF World Championships Daegu South Korea. Furthermore, South Korea had hosted the 2018 Winter Olympics which took place in Pyeongchang, South Korea from 9 to 25 February.

 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of the Republic of Korea |
|
|
|
|
South Korea is a member of the United Nations, WTO, OECD/DAC, ASEAN Plus Three, East Asia Summit (EAS), and G-20. It is also a founding member of Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) and the East Asia Summit.
On January 1, 2007, South Korean Foreign Minister Ban Ki-moon assumed the post of UN Secretary-General, serving in that post until December 31, 2016.
Inter-Korean relations
Inter-Korean relations may be divided into five periods. The first stage was between 1972 and 1973; the second stage was Pyongyang North Korea's delivery of relief goods to South Korea after a typhoon caused devastating floods in 1984 and the third stage was the exchange of home visits and performing artists in 1985. The fourth stage, activated by Nordpolitik under Roh, was represented by expanding public and private contacts between the two Koreas. The fifth stage was improved following the 1997 election of Kim Dae-jung. His "Sunshine Policy" of engagement with North Korea set the stage for the historic June 2000 Inter-Korean summit.
The possibility of Korean reunification has remained a prominent topic. However, no peace treaty has yet been signed with the North. In June 2000, a historic first North Korea-South Korea summit took place, part of the South Korea's continuing Sunshine Policy of engagement. Since then, regular contacts have led to a cautious thaw. President Kim was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 2000 for the policy.
With that policy, continued by the following administration of president Roh Moo-hyun, economic ties between the two countries have increased, humanitarian aid has been sent to North Korea and some divided families have been briefly reunited. Military ties remain fraught with tension, however, and in 2002 a brief naval skirmish left four South Korean sailors dead, leaving the future of the Sunshine policy uncertain. The North Korea cut off talks but the South remained committed to the policy of reconciliation and relations began to thaw again. The resurgence of the nuclear issue two years later would again cast relations in doubt, but South Korea has sought to play the role of intermediary rather than antagonist, and economic ties at the time seemed to be growing again.
Despite the Sunshine Policy and efforts at reconciliation, the progress was complicated by North Korean missile tests in 1993, 1998, 2006 and 2009. As of early 2009, relationships between North Korea and South Korea were very tense; North Korea had been reported to have deployed missiles,[1] Ended its former agreements with South Korea[2] and threatened South Korea and the United States not to interfere with a satellite launch it had planned.[3] As of 2009 North Korea and South Korea are still opposed and share a heavily fortified border.[4]
On May 27, 2009 North Korea media declared that the armistice is no longer valid due to the South Korean government's pledge to "definitely join" the Proliferation Security Initiative. To further complicate and intensify strains between the two nations, the sinking of the South Korean warship Cheonan in March 2010, killing 46 seamen, is as of May 20, 2010 claimed by a team of researchers around the world[5] to have been caused by a North Korean torpedo, which the North denies. South Korea agreed with the findings from the research group and president Lee Myung-bak declared in May 2010 that Seoul would cut all trade with North Korea as part of measures primarily aimed at striking back at North Korea diplomatically and financially.[6] As a result of this, North Korea severed all ties and completely abrogated the previous pact of non aggression.[7]
In November 2010, Unification Ministry officially declared the Sunshine Policy a failure, thus bringing the policy to an end.[8][9] On November 23, 2010, North Korean artillery shelled Yeonpyeong with dozens of rounds at Yeonpyeong-ri and the surrounding area.[10]
Free trade agreements
South Korea has the following trade agreements:
- South Korea-ASEAN (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam) FTA
- South Korea-Australia FTA
- South Korea-Canada CKFTA FTA
- South Korea-Chile FTA
- South Korea-China FTA
- South Korea-Colombia FTA
- South Korea-EFTA (Iceland, Lichtenstein, Norway, Switzerland) FTA
- South Korea-EU (Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, UK) FTA
- South Korea-India CEPA FTA
- South Korea-New Zealand FTA
- South Korea-Peru FTA
- South Korea-Singapore FTA
- South Korea-Turkey FTA
- South Korea-United States of America (KORUS FTA)
- South Korea-Vietnam FTA[11][12]
As of late 2016 states of Central America (Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay),[13] GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council—Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates), Indonesia, Israel, Japan, Malaysia, MERCOSUR (Southern Common Market—Mercado comun del sur), Mexico, Mongolia, RCEP (Asian 10 Countries, Korea, China, Japan, Australia, New Zealand, India), Russia (BEPA), SACU (South Asia Cooperation Union) and Korea-China-Japan[14] are in negotiations about the FTA with South Korea.
China (PRC)
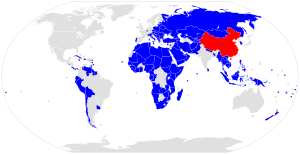
Active South Korean-Chinese people-to-people contacts have been encouraged. Academics, journalists and particularly families divided between South Korea and the People's Republic of China (PRC) were able to exchange visits freely in the late 1980s. Nearly 2 million ethnic Koreans especially in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in Jilin Province of northeast china have interacted with South Koreans.
Trade between the two countries continued to increase nonetheless, Furthermore, China has attempted to mediate between North Korea and the United States and between North Korea and the State of Japan also initiated and promoted tripartite talks—between Pyongyang Seoul and Washington United States of America.
South Korea had long been an ally of Taiwan. Diplomatic ties between Seoul and Taipei were nevertheless severed in 1992. Formal diplomatic relations were established between Seoul and Beijing on August 24, 1992.
In 2004 the PRC government began the Northeast Project, sparking a massive uproar in South Korea when the project was widely publicized.[16]
After the KORUS FTA (United States-South Korea Free Trade Agreement) was finalized on June 30, 2007 the Chinese government has immediately begun seeking an FTA agreement with South Korea.[17] The FTA between South Korea and China are under discussion South Korea has been running a trade surplus with China which hit a record US$32.5 billion in 2009.[18][19]
Taiwan (ROC)
On 23 August 1992, the government of the Republic of China (by then only in control of the island of Taiwan and a few outlying areas) severed diplomatic relations with South Korea in advance of its announcement of formal recognition of the People's Republic of China based in Beijing. The Yonhap News said in 2002 that since then relations between the two governments have been "in a rut".[20]
Japan

The relation between South Korea and Japan has both political conflicts and economic intimacies. Examples of conflicts include the East sea naming dispute, visits by successive Japanese Prime Ministers to the Yasukuni Shrine and the disputed ownership of Dokdo of the island Korea.
On January 18, 1952 The first president of South Korea Syngman Rhee declared that the vicinity of Dokdo was a territory of South Korea (Syngman Rhee line). Subsequently, some 3,000 Japanese fishermen who conducted fishery operations in this vicinity were captured. This incident, called the Dai Ichi Daihoumaru Ship case strained relations between South Korea and Japan.
June 22, 1965, The president in South Korea Park Chung-hee concluded the Treaty on Basic Relations between Japan and South Korea As a result, Japan considered South Korea to be the legitimate successor of its rule over the Korean Peninsula.
South Korea's trade with Japan was US$892.1 million in 2008, with a surplus of nearly US$327.1 million on the Japanese side.[21] Japanese and South Koreans firms often had interdependent relations, which gave Japan advantages in South Korea's growing market.
In 1996 FIFA announced that the South Korea-Japan would jointly host the 2002 FIFA World Cup. The next few years would see leaders of both countries meet to warm relations in preparations for the games.[22] The year 2005 was designated as the "Japan-South Korea Friendship Year".
However, the Liancourt Rocks controversy erupted again when Japan's Shimane prefecture declared "Takeshima Day", inciting mass demonstrations in South Korea.[23]
Mongolia
Both countries established diplomatic relations on March 26, 1990. South Korea has an embassy in Ulaanbaatar Mongolia.[24] Mongolia has an embassy in Seoul.[25]
North Korea

According to a 2013 BBC World Service Poll, 3% of South Koreans view the Democratic People's Republic of Korea's influence positively, with 91% expressing a negative view.[26] A 2015 government-sponsored poll revealed that 41% of South Koreans consider North Korea to be an enemy, with negative views being more prevalent among younger respondents.[27] Still, in a 2017 poll, 58% of South Koreans said they don't expect another war to break out with North Korea.[28]
Philippines
Since the establishment of diplomatic ties on 3 March 1949, the relationship between the Philippines and South Korea has flourished. The Philippines was one of the first countries that extended diplomatic recognition to South Korea. This was cemented with the Philippine government's deployment of the Philippine Expeditionary Force to Korea (PEFTOK) to help South Korea against the invasion of the communist North during the Korean War in the 1950s. After the war, the Philippines provided development assistance to South Korea and helped the country rebuild itself.
Since then, the Philippines's relations with South Korea have evolved with South Korea becoming one of the Philippines's most important bilateral partners aside from the United States, China and Japan. The Philippines's government seeks to cultivate strategic ties with South Korea given its increasing presence in the country. In the coming years, the Philippines anticipates to benefit from exploring unprecedented opportunities from South Korea that shall contribute significantly to the country's trade and economy, defense and security, and society and culture.
Russia

In the 1980s South Korean president Roh Tae Woo's Nordpolitik and Mikhail Gorbachev's "New Thinking" were both attempts to reverse their nations' recent histories. Gorbachev had signaled Soviet interest in improving relations with all countries in the Asia-Pacific region including South Korea as explained in his July 1986 Vladivostok and August 1988 Krasnoyarsk speeches.
In initiating Nordpolitik Roh's confidential foreign policy adviser was rumored to have visited Moscow Russia to consult with Soviet policymakers. Kim Young Sam visited Moscow Russian Federation from June 2 to June 10, 1989 as the Kremlin announced that it would allow some 300,000 Soviet-South Koreans who had been on the Soviet island of Sahkalin since the end of World War II to return permanently to South Korea. Moscow even arranged Kim's meeting with the North Korean ambassador to the Soviet Union In June 1990, Roh held his first summit with president Gorbachev in San Francisco, United States.
South Korea and the Soviet Union established diplomatic relations on September 30, 1990. These relations continued by the Russian Federation on December 27, 1991. Russian president Vladimir Putin visited Seoul in February 2001 while South Korean president Roh Moo-hyun visited Moscow Russia in September 2004.[29][30]
Russian Federal Space Agency and the Korean Astronaut Program cooperated together to send South Korea's first astronaut into space. Yi So-Yeon became the first South Korean national as well as the third woman to be the first national in space on 8 April 2008 when Soyuz TMA-12 departed from Baikonur Cosmodrome.[31]
Since the 1990s there has been greater trade and cooperation between the Russian Federation and South Korea. The total trade volume between South Korea and Russia in 2003 was 4.2 billion US dollars.[32]
United Kingdom
The establishment of diplomatic relations between the United Kingdom and South Korea began on 18 January 1949.
From South Korea to the United Kingdom:
- 1986 April president Chun Doo-hwan
- 1989 November president Roh Tae-woo
- 1995 March president Kim Young-sam
- 1998 April president Kim Dae-jung
- 2001 December president Kim Dae-jung
- 2004 December president Roh Moo-hyun
- 2006 February Minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade Ban Ki-moon
- 2006 June Minister of Foreign Affairs Ban Ki-moon
- 2009 April president Lee Myung-bak (G20)
- 2013 April Special envoy of the President Former Prime Minister Han Seung-soo (to attend the funeral of former British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher)
- 2013 November president Park Geun-hye
- 2014 December Minister of Foreign Affairs Yun Byung-se.[33]
From the United Kingdom to South Korea:
- 1986 May Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher
- 1992 November Prince Charles and Princess Diana
- 1996 March Prime Minister John Major
- 1997 April Duke of Gloucester
- 1997 October Duke of Kent
- 1999 April Queen Elizabeth II
- 2000 October Prime Minister Tony Blair
- 2003 July Prime Minister Tony Blair
- 2001 April Duke of York
- 2005 November Duke of York
- 2006 October Deputy Prime Minister John Prescott
- 2008 September Duke of York
- 2008 December G20 Special Envoy Timms
- 2009 October Minister of Business, Innovation and Skills Peter Benjamin Mandelson
- 2010 November Prime Minister David Cameron
- 2012 March Deputy Prime Minister Clegg to attend Seoul Nuclear Security Summit
- 2013 October Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs William Hague (to attend Seoul Conference on Cyberspace 2013).[33]
United States

The United States engaged in the decolonization of Korea (mainly in the South, with the Soviet Union engaged in North Korea) from Japan after World War II. After three years of military administration by the United States, the South Korean government was established. Upon the onset of the Korean War, U.S. forces were sent to defend South Korea against invasion by North Korea and later China. Following the Armistice, South Korea and the U.S. agreed to a "Mutual Defense Treaty", under which an attack on either party in the Pacific area would summon a response from both.[34]
In 1968, South Korea obliged the mutual defense treaty, by sending a large combat troop contingent to support the United States in the Vietnam War. The U.S. Eighth Army, Seventh Air Force, and U.S. Naval Forces Korea are stationed in South Korea. The two nations have strong economic, diplomatic, and military ties, although they have at times disagreed with regard to policies towards North Korea, and with regard to some of South Korea's industrial activities that involve usage of rocket or nuclear technology. There had also been strong anti-American sentiment during certain periods, which has largely moderated in the modern day.[35]
Since the late 1980s, the country has instead sought to establish an American partnership, which has made the Seoul–Washington relationship subject to severe strains. Trade had become a serious source of friction between the two countries. In 1989, the United States was South Korea's largest and most important trading partner and South Korea was the seventh-largest market for United States goods and the second largest market for its agricultural products.
From Roh Tae-woo's administration to Roh Moo Hyun's administration, South Korea sought to establish a U.S. partnership, which has made the Seoul–Washington relationship subject to some strains. In 2007, a free trade agreement known as the Republic of Korea-United States Free Trade Agreement (KORUS FTA) was reportedly signed between South Korea and the United States, but its formal implementation has been repeatedly delayed, pending further approval by the legislative bodies of the two countries.
The relations between the United States and South Korea have greatly strengthened under the Lee Myung-bak administration. At the 2009 G-20 London summit, U.S. President Barack Obama called South Korea "one of America's closest allies and greatest friends."[36]

However, some anti-American sentiment in South Korea still exists; The United States' alleged role in the May 1980 Gwangju uprising was a pressing South Korean political issue of the 1980s. Even after a decade, some Gwangju citizens and other South Koreans still blamed the United States for its perceived involvement in the bloody uprising. In 2008, the protests against U.S. beef was a center of a major controversy that year.
In a June 2010 open letter from President of South Korea Lee Myung-bak published in the Los Angeles Times, he expressed gratitude for the 37,000 Americans who were killed in the Korean War defending South Korea, saying that they fought for the freedom of South Koreans they did not even know. He stated that thanks to their sacrifices, the peace and democracy of the South Korean state was protected.[37]
The U.S. states that "The Alliance is adapting to changes in the 21st Century security environment. We will maintain a robust defense posture, backed by allied capabilities which support both nations' security interests We will continue to deepen our strong bilateral economic, trade and investment relations In the Asia-Pacific region we will work jointly with regional institutions and partners to foster prosperity, keep the peace, and improve the daily lives of the people of the region The United States and South Korea will work to achieve our common Alliance goals through strategic cooperation at every level."[38]
European Union
The European Union (EU) and South Korea are important trading partners, having negotiated a free trade agreement for many years since South Korea was designated as a priority FTA partner in 2006. The free trade agreement has been approved in September 2010, following Italy's conditional withdrawal of its veto of the free trade agreement.[39] The compromise made by Italy was that free trade agreement would take provisional effect on July 1, 2011. South Korea is the EU's eighth largest trade partner and the EU has become South Korea's second largest export destination. EU trade with South Korea exceeded €65 billion in 2008 and has enjoyed an annual average growth rate of 7.5% between 2004 and 2008.[40]
The EU has been the single largest foreign investor in South Korea since 1962 and accounted for almost 45% of all FDI inflows into South Korea in 2006. Nevertheless, EU companies have significant problems accessing and operating in South Korea market due to stringent standards and testing requirements for products and services often creating barriers to trade. Both in its regular bilateral contacts with South Korea and through its FTA with South Korea The EU is seeking to improve this situation.[40]
Diplomatic relations

Americas
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| See Antigua and Barbuda–South Korea relations | ||
| 1962-02-15 | See Argentina – South Korea relations
| |
| See Bahamas–South Korea relations | ||
| See Barbados–South Korea relations | ||
| See Belize–South Korea relations | ||
| See Bolivia–South Korea relations | ||
| 1959-10-31 | See Brazil–South Korea relations | |
| 1963-01-14[44] | See Canada – South Korea relations
From Canada to the South Korea
From South Korea to Canada
The embassy and consulate general of South Korea in Canada. | |
See Chile–South Korea relations
| ||
| 1962-03-10 | See Colombia–South Korea relations
| |
| See Costa Rica–South Korea relations | ||
| No Relations | See Cuba–South Korea relations
| |
| See Dominica–South Korea relations | ||
| See Dominican Republic–South Korea relations | ||
| See Ecuador–South Korea relations | ||
| See El Salvador–South Korea relations | ||
| See Grenada–South Korea relations | ||
| See Guatemala–South Korea relations | ||
| See Guyana–South Korea relations | ||
| See Haiti–South Korea relations | ||
| See Honduras–South Korea relations | ||
| See Jamaica–South Korea relations | ||
| 1962-01-26[49] | See Mexico–South Korea relations
| |
| See Nicaragua–South Korea relations | ||
| See Panama–South Korea relations | ||
| 1962-06-12 | See Paraguay – South Korea relations
| |
| 1963-04-01 | See Peru–South Korea relations
| |
| See Saint Kitts and Nevis–South Korea relations | ||
| See Saint Lucia–South Korea relations | ||
| 1962-06-12 | See Saint Vincent and the Grenadines–South Korea relations | |
| See Suriname–South Korea relations | ||
| See Trinidad and Tobago–South Korea relations | ||
| 1882-05-22/1949-01-01[53] | See United States – South Korea relations
The embassy and consulate general of South Korea in the United States.
From the U.S. to the South Korea.
From South Korea to the U.S.A.
| |
| 1964-10-07 | See Uruguay–South Korea relations
| |
| See Venezuela–South Korea relations |
Asia
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1973-12-12[57] | See Afghanistan – South Korea relations
| |
| 1973-12-18[60] | See Bangladesh–South Korea relations
| |
| September 1987[64] | See Bhutan–South Korea relations | |
| 1984-01-01[65] | See Brunei–South Korea relations
| |
| 1975-05-16[67] | See Burma–South Korea relations
| |
| 1970-05-18[68] | See Cambodia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-08-24[69] | See China–South Korea relations
From China to the South Korea.
From South Korea to China.
The embassy and consulate general of South Korea in China | |
| 1948-08-13 / No relations, Since 1992-08-23[72] | See Republic of China–South Korea relations South Korea–Taiwan relations
| |
| 2002-05-20[76] | See East Timor–South Korea relations
| |
| 1945-05-01[77] | See Hong Kong–South Korea relations
| |
| 1973-12-01[81] | See India – South Korea relations
| |
| 1973-09-17[83] | See Indonesia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1965-12-18[87] | See Japan–South Korea relations
From Japan to South Korea:
From South Korea to Japan
The embassy and consulate general of South Korea in the State of Japan | |
| No Relations | See North Korea–South Korea relations South Korea–North Korea relations
| |
| 1974-06-22[90] | See Laos–South Korea relations
| |
| July 1984 | See Macao–South Korea relations
| |
| 1960-02-23[92] | See Malaysia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1967-11-30[95] | See Maldives–South Korea relations | |
| 1990-03-26[96] | See Mongolia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1974-05-15[97] | See Nepal–South Korea relations
| |
| 1983-11-01[99] | See Pakistan-South Korea relations
| |
| 1949-03-03[100] | See Philippines–South Korea relations
| |
| 1975-08-08[102] | See Singapore–South Korea relations
| |
| 1977-11-14[104] | See Sri Lanka–South Korea relations
| |
| 1958-10-09[106] | See South Korea – Thailand relations
| |
| 1992-12-22[109] | See Vietnam–South Korea relations
|
Oceania
| Country | Formal Relations Began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| January 1971[111] | See Australia–South Korea relations
| |
| 2013-02-22[118] | See Cook Islands–South Korea relations
| |
| 1970-10-01[120] | See Fiji–South Korea relations
| |
| 1980-05-02[124] | See Kiribati–South Korea relations
| |
| 1991-04-05[125] | See Marshall Islands–South Korea relations
| |
| April 1991[126] | See Micronesia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1979-08-20[127] | See Nauru–South Korea relations
| |
| 1962-03-01[128] | See New Zealand–South Korea relations
| |
| See Niue–South Korea relations | ||
| 1995-03-22[133] | See Palau–South Korea relations
| |
| May 1976[134] | See Papua New Guinea–South Korea relations
| |
| 1972-09-15[135] | See Samoa–South Korea relations
| |
| 1978-09-15[136] | See Solomon IslandsAustralia–South Korea relations
| |
| September 1970[137] | See Tonga–South Korea relations
| |
| November 1978[138] | See Tuvalu–South Korea relations
| |
| 1980-11-05[138] | See Vanuatu–South Korea relations
|
Europe
| Country | Formal Relations Began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| No relations | See Abkhazia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1991-08-22[139] | See Albania–South Korea relations
| |
| 1995-02-23[141] | See Andorra–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-02-21[142] | See Armenia–South Korea relations
| |
| No relations | See Artsakh–South Korea relations
| |
| 1963-05-22[144] | See Austria–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992 1992-3-23[148] | See Azerbaijan–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-02-10[150] | See Belarus–South Korea relations
| |
| 1961-03-23[152] | See Belgium–South Korea relations
| |
| 1995-12-15[153] | See Bosnia and Herzegovina–South Korea relations
| |
| 1990-03-23[155] | See Bulgaria – South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-11-18[158] | See Croatia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1995-12-28[159] | See Cyprus–South Korea relations
| |
| 1990-03-22[160] | See Czech Republic–South Korea relations
| |
| 1959-03-11[163] | See Denmark – South Korea relations
| |
| 1991-10-17[167] | See Estonia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1973-08-24[169] | See Finland–South Korea relations
| |
| 1849-06-04[170]/1949-02-15[171] | See France – South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-12-14[174] | See Georgia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1883-11-26[175]/As West Germany 1955-12-01[176] | See Germany – South Korea relations
| |
| 1961-04-05[179] | See Greece–South Korea relations
| |
| 1966-09-01[181] | See Holy See–South Korea relations
| |
| 1989-02-01[188] | See Hungary–South Korea relations
| |
| 1962-10-10[189] | See Iceland–South Korea relations
| |
| 1983-10-01[190] | See Ireland–South Korea relations
| |
| 1956-11-24[193] | See Italy – South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-01-28[194] | See Kazakhstan–South Korea relations
| |
| October 1991[195] | See Latvia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1993[196] | See Liechtenstein–South Korea relations
| |
| October 1991[197] | See Lithuania–South Korea relations
| |
| 1962-03-16[198] | See Luxembourg–South Korea relations
| |
| 2019-07-18[199] | See North Macedonia–South Korea relations
| |
| April 1965[201] | See Malta–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-01-31[202] | See Moldova–South Korea relations
| |
| March 2007[203] | See Monaco–South Korea relations
| |
| 2006-06-04[205] | See Montenegro–South Korea relations
| |
| 1961-04-01[206] | See Netherlands–South Korea relations
| |
| No Relations | See Northern Cyprus–South Korea relations
| |
| 1959-03-02[209] | See Norway–South Korea relations
| |
| 1989-11-01[211] | See Poland–South Korea relations
| |
| 1961-04-15[214] | See Portugal–South Korea relations | |
| 1990-03-30[215] | See Romania – South Korea relations
| |
| 1990-09-30[219] | See Russia–South Korea relations
| |
| 2000-06-25[220] | See San Marino–South Korea relations
| |
| 1989-12-27[221] | See Serbia–South Korea relations
| |
| January 1993[223] | See Slovakia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-04-15[225] | See Slovenia–South Korea relations
| |
| No Relations | See South Ossetia–South Korea relations
| |
| 1950-03-17[227] | See Spain–South Korea relations
| |
| 1959-03-07[230] | See Sweden–South Korea relations
| |
| 1963-02-11[231] | See Switzerland–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-04-27[233] | See Tajikistan–South Korea relations
| |
| No Relations | See Transnistria–South Korea relations
| |
| 1957-03-08[234] | See Turkey–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-02-07[236] | See Turkmenistan–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-02-10[237] | See Ukraine–South Korea relations
| |
| 1992-01-29[240] | See Uzbekistan–South Korea relations
| |
| 1949-01-18[33] | See South Korea–United Kingdom relations
| |
| 1963[243] | See Vatican City–South Korea relations
|
Middle East and Africa
| Country | Formal Relations Began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| January 15, 1990[245] | See Algeria–South Korea relations
| |
| January 6, 1992[246] | See Angola–South Korea relations
| |
| April 17, 1976[247] | See Bahrain–South Korea relations
| |
| August 1, 1961[248] | See Benin–South Korea relations
| |
| April 18, 1968[249] | See Botswana–South Korea relations
| |
| April 20, 1962[250] | See Burkina Faso–South Korea relations
| |
| October 3, 1993[251] | See Burundi–South Korea relations
| |
| August 10, 1961[252] | See Cameroon–South Korea relations
| |
| October 3, 1988[253] | See Cape Verde–South Korea relations
| |
| September 5, 1963[254] | See Central African Republic–South Korea relations
| |
| August 6, 1961[255] | See Chad–South Korea relations
| |
| February 19, 1979[256] | See Comoros–South Korea relations
| |
| June 16, 1990[257] | See Republic of Congo–South Korea relations
| |
| April 1, 1963[258] | See Democratic Republic of the Congo–South Korea relations
| |
| December 7. 1977[259] |
| |
| April 13, 1995[260] | See Egypt–South Korea relations
| |
| September 14, 1979[261] | See Equatorial Guinea–South Korea relations
| |
| May 24, 1993[262] | See Eritrea–South Korea relations
| |
| December 23, 1963[263] | See Ethiopia–South Korea relations
| |
| October 1, 1962[264] | See Gabon–South Korea relations
| |
| April 21, 1965[265] | See Gambia–South Korea relations
| |
| November 14, 1977[266] | See Ghana–South Korea relations
| |
| August 28, 2006[267] | See Guinea–South Korea relations
| |
| December 22, 1983[268] | See Guinea-Bissau–South Korea relations
| |
| October 23, 1962[269] | See Iran–South Korea relations
| |
| July 7, 1989[270] | See Iraq–South Korea relations
| |
| April 10, 1962[271] | See Israel–South Korea relations
| |
| July 23, 1961[274] | See Ivory Coast–South Korea relations
| |
| July 26, 1962[275] | See Jordan–South Korea relations
| |
| February 7, 1964[276] | See Kenya–South Korea relations
| |
| June 11, 1979[277] | See Kuwait–South Korea relations
| |
| February 12, 1981[278] | See Lebanon–South Korea relations
| |
| December 7, 1966[279] | See Lesotho–South Korea relations
| |
| March 18, 1964[280] | See Liberia–South Korea relations
| |
| December, 1980[281] | See Libya–South Korea relations
| |
| June 25, 1962[282] | See Madagascar–South Korea relations
| |
| March 9, 1965[283] | See Malawi–South Korea relations
| |
| September 27, 1990[284] | See Mali–South Korea relations
| |
| July 30, 1963[285] | See Mauritania–South Korea relations
| |
| July 3, 1971[286] | See Mauritius–South Korea relations
| |
| July 6, 1962[287] | See Morocco–South Korea relations
| |
| August 11, 1993[288] | See Mozambique–South Korea relations
| |
| March 21, 1990[289] | See Namibia–South Korea relations
| |
| July 27, 1961[290] | See Niger–South Korea relations
| |
| February 22, 1980[291] | See Nigeria–South Korea relations
| |
| March 28, 1974[292] | See Oman–South Korea relations
| |
| No Relations | See Palestine–South Korea relations
| |
| April 18, 1974[293] | See Qatar–South Korea relations
| |
| March 21, 1963[294] | See Rwanda–South Korea relations
| |
| No Relations | See Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic–South Korea relations
| |
| August 20, 1988[295] | See São Tomé and Príncipe–South Korea relations
| |
| October 16, 1962[296] | See São Tomé and Príncipe–South Korea relations
| |
| October 19, 1962[297] | See Senegal–South Korea relations
| |
| June 28, 1976[298] | See Seychelles–South Korea relations
| |
| June 25, 1962[299] | See Sierra Leone–South Korea relations
| |
| September 25, 1987[300] | See Somalia–South Korea relations
| |
| December 1, 1992[301] | See South Africa–South Korea relations
| |
| See South Sudan–South Korea relations | ||
| April 13, 1977[303] | See Sudan–South Korea relations
| |
| November 6, 1968[304] | See Swaziland–South Korea relations
| |
| No Relations | See Syria–South Korea relations
| |
| April 30, 1992[305] | See Tanzania–South Korea relations
| |
| July 26, 1963[306] | See Togo–South Korea relations
| |
| March 1969[307] | See Tunisia–South Korea relations
| |
| June 18, 1980[308] | See United Arab Emirates–South Korea relations
| |
| 26 March 1963[309] | See Uganda–South Korea relations
| |
| August 22, 1985[310] | See Yemen–South Korea relations
| |
| September 4, 1990[311] | See Zambia–South Korea relations
| |
| November 18, 1994[312] | See Zimbabwe–South Korea relations
|
No diplomatic relations
South Korea does not currently have any diplomatic relations with the following nations.
There are also no diplomatic relations with several unrecognized territories:






See also
- List of diplomatic missions in the Republic of Korea
- List of diplomatic missions of the Republic of Korea
- List of Korea-related topics
- Foreign relations of North Korea
- Government of South Korea
- June 15th North-South Joint Declaration
- South Korea-United States relations
References
- "N Korea 'deploying more missiles'". BBC News. 23 February 2009.
- "North Korea tears up agreements". BBC News. 30 January 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- "N Korea warning over 'satellite'". BBC News. 3 March 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- "CNN.com - Koreas agree to military hotline - Jun 4, 2004". Edition.cnn.com. 2004-06-04. Retrieved 2010-02-18.
- "Anger at North Korea over sinking". BBC News. 2010-05-20. Retrieved 2010-05-23.
- Archived May 28, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- Text from North Korea statement, by Jonathan Thatcher, Reuters, 25-05-2010
- "South Korea Formally Declares End to Sunshine Policy". Voanews.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Nagesh Narayana (2010-11-19). "South Korea dumps Sunshine Policy with North, opts to go solo". Ibtimes.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Hyung-Jin and Kwang-Tae Kim. "North, South Korea exchange fire; 2 marines killed". Washington Times. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Economy and Trade" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-04-15. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- FTA전문 관세사 강상혁 : 네이버 블로그 (in Korean). Blog.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 중미 6개국과 : 네이버 통합검색 (in Korean). Search.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 산업통상자원부 블로그 : 네이버 블로그 (in Korean). Blog.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 호감→비호감, 서로를 보는 눈이 변했다 : 네이버 뉴스 (in Korean). Naver News. 2009-02-11. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "The Japan syndrome". The Economist. 2007-05-10. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 2018-12-26.
- "S Korea posts record-high trade surplus in 2009". 2010-01-14.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "South Korea-Taiwan relations 'in a rut'". Yonhap News. 2002-08-21. Archived from the original on 2012-10-07. Retrieved 2008-02-05.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "South Korean leader bids farewell to Japanese emperor". CNN. 1998-10-09. p. 1. Archived from the original on April 20, 2006. Retrieved 2007-01-19.
- Charles Scanlon (2005-03-14). "S Korean fury over island dispute". BBC. Retrieved 2007-01-19.
- Archived February 27, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- 2014 World Service Poll Archived 2015-03-05 at the Wayback Machine BBC
- Yong, Kim Hwan. "Poll: Growing Number of S. Koreans See N. Korea as Enemy". VOA.
- "In South Korea, daily stresses outweigh North Korea missile worries". Reuters. 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2017.
- "Russia makes up lost ground with Korean proposals". Asia Times. 2001-02-27. Retrieved 2007-05-29.
- "South Korean president's visit to boost ties with Russia". People's Daily. 2004-09-24. Retrieved 2007-05-28.
- "Why South Korea's Only Astronaut Quit".
- "Russia ends WTO talks with S. Korea". People's Daily. 2004-09-22. Retrieved 2007-05-28.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-15. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Mutual Defense Treaty Between the United States and the Republic of Korea; October 1, 1953". Yale Law School.
- Haesook Chae (2010). "South Korean Attitudes toward the ROK–U.S. Alliance: Group Analysis". Cambridge University Press.
- Archived May 27, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- "On this significant occasion, all Koreans pay tribute to the heroes fallen in defense of freedom and democracy. I firmly believe that future generations in both countries will further advance the strong the Republic of Korea-the United States of America alliance into one befitting the spirit of the new age."
- U.S. Government (June 16, 2009)
- "EU agrees free trade deal with S.Korea". AFP. 2009-09-16.
- "Bilateral Relations: Korea". European Commission.
- Archived May 16, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- 외교부 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다. (in Korean). MOFAT. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-North America" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-09. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of Canada to Korea". Canadainternational.gc.ca. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Korea to Canada" (in Korean). Can-ottawa.mofa.go.kr. 1963-01-14. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Canada-Korea Free Trade Agreement". International.gc.ca. Archived from the original on 2015-08-21. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived March 8, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Latin America and Caribbean" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of Paraguay in the Republic of Korea". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- 외교부 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다. (in Korean). MOFAT. Archived from the original on 29 July 2014. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- 재외동포현황 [Current Status of Overseas Compatriots] (in Korean). South Korea: Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade. 2009. Archived from the original on 2010-10-23. Retrieved 2009-05-21. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-North America" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Korea in the USA" (in Korean). Usa.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Home | Seoul, Korea - Embassy of the United States". Seoul.usembassy.gov. Archived from the original on 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 외교부 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다. (in Korean). MOFAT. Archived from the original on 24 April 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Taliban say S.Korea paid over $20 mln ransom". Reuters. 2007-09-01.
- "Seoul would not talk about ransom". Naver News. 2007-09-06. Archived from the original on 2012-07-11.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 14, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Brunei-South Korea Relations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade (Brunei). Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-14. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 大韩民国驻中国大使馆 (in Chinese). Chn.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 中华人民共和国驻大韩民国大使馆 (in Chinese). Embassy of the People's Republic of China, Seoul. Archived from the original on 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 대만과 한국과의 주요이슈 : 지식백과 (in Korean). Terms.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 주 타이뻬이 대한민국 대표부. Republic of Korea Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2015-08-28.
- Republic of Korea - East Asia and Pacific - Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China (Taiwan) 中華民國外交部 - 全球資訊網英文網. Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Taipei Mission in Korea, Busan Office 駐釜山辦事處(駐韓國台北代表部釜山辦事處) Republic of Korea 大韓民國(韓國)] - Embassies & Missions Abroad - Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China (Taiwan) Mobile - 中華民國外交部 - 全球資訊網英文網. Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 한국과 홍콩의 관계 : 지식백과 (in Korean). Terms.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-26. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Consulate General of the Republic of Korea in Hong Kong" (in Korean). Hkg.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "The Republic Of Korea Cheong Wa Dae". English1.president.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived December 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-14. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Indonesia teams up with S. Korea to develop fighter jet". News.xinhuanet.com. Archived from the original on 2016-12-27. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Junotane Korea". Archived from the original on 9 July 2012. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 駐日本国大韓民国大使館 (in Japanese). Jpn-tokyo.mofa.go.kr. 1965-12-18. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of Japan in Korea". Kr.emb-japan.go.jp. Archived from the original on 2015-08-15. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Ariffin, Roslan (2007-03-08). "Najib Dijangka Kukuhkan Hubungan Dua Hala M'sia-Korea Selatan (Najib plans strong Malaysia-South Korea bilateral relations)". Bernama. Archived from the original on 2007-09-29. Retrieved 2007-05-04.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived November 11, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-14. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Embassy of the Republic of Korea to the Commonwealth of Australia" (in Korean). Aus-act.mofa.go.kr. 1961-10-30. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Home - Australian Embassy". Southkorea.embassy.gov.au. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Power and Passion as Julia Gillard Shows Her Seoul". Dailytelegraph.com.au. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 即日融資. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- Archived September 4, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- 쿡아일랜드 : 지식백과 (in Korean). Terms.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Archived copy" 장세정 기자의 블로그 (in Korean). Blog.joins.com. 2012-11-13. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Embassy of South Korea in Fiji". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Embassy of Fiji in South Korea". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Korea to New Zealand" (in Korean). Nzl-wellington.mofa.go.kr. 1962-03-26. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Korea". NZEmbassy.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Press Releases" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Asia Pacific" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Press Releases" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Press Releases" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Außenministerium Österreich -> Botschaft -> Seoul". 22 July 2012. Archived from the original on 22 July 2012.
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Bundespräsident Heinz Fischer zu Staatsbesuch in Südkorea eingetroffen" (in German). Federal President of the Republic of Austria. Archived from the original on 2007-11-07. Retrieved 18 November 2008.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Disarmament/International Security" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Äèïëîìàòè÷åñêèå ïðåäñòàâèòåëüñòâà Ðåñïóáëèêè Áåëàðóñü". Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Press Releases" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Министерство на външните работи". Mfa.bg. Archived from the original on 2015-07-08. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Czech embassy in Seoul". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Archived January 12, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- 외교부 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다. (in Korean). MOFAT. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- 덴마크 여왕, "한국은 역동이고 정이 많은 나라". Daum 뉴스 (in Korean). Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived July 18, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ambassade de la République de Corée en France" (in Korean). Fra.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Coopération politique - La France en Corée - Ambassade de France à Séoul". Ambafrance-kr.org. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "La France en Corée - Ambassade de France à Séoul". Ambafrance-kr.org. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 주 독일 대한민국 대사관 (in Korean). Deu.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Deutsche Botschaft Seoul - Startseite" (in German). Seoul.diplo.de. 2015-02-25. Archived from the original on 2015-08-09. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Auswärtiges Amt - Bilateral relations". Auswaertiges-amt.de. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 외교부 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다. (in Korean). MOFAT. Archived from the original on 24 April 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- Archived October 21, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- David M. Cheney. "Korea (Nunciature) [Catholic-Hierarchy]". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Papal Address to South Korean Ambassador". ZENIT - The World Seen From Rome. Archived from the original on 15 October 2007. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Vatican Information Service News Archives - Monday, March 6, 2000: John Paul II Welcomes First Head of State from Korea." Refers to two visits in text.
- "Mass for the canonization of Korean martyrs, Homily of John Paul II, 6 May 1984". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- VIS, Vatican Information Service. "VIS news - Holy See Press Office: Monday, March 06, 2000". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-06. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Irish embassy in Seoul". Embassyofireland.or.kr. 2009-11-24. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- "South Korean embassy in Dublin". Irl.mofat.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2010-08-29. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 리히텐 슈타인과 우리나라의 관계 : 지식iN (in Korean). Kin.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "S. Korea establishes diplomatic ties with North Macedonia". Yonhap. 2019-07-18. Archived from the original on 2019-07-18. Retrieved 2019-07-18.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-03. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Press Releases" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Korea to the Kingdom of the Netherlands" (in Korean). Nld.mofa.go.kr. 1961-04-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Netherlands Embassy in Seoul, South Korea". Southkorea.nlembassy.org. Archived from the original on 2017-08-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Korea to Norway" (in Korean). Nor.mofa.go.kr. 1959-03-02. Archived from the original on 2015-07-10. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 주 폴란드 대한민국 대사관 (in Korean). Pol.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ambasada Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej w Seulu" (in Polish). Seul.msz.gov.pl. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "HONORARY CONSULATE of ROMANIA". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- Archived August 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Serbia in the Republic of Korea". Seoul.mfa.gov.rs. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-25. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 주한 슬로바키아대사관: 네이버 지도 (in Korean). Map.naver.com. 2015-02-27. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 슬로베니아 : 지식백과 (in Korean). Terms.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 주 스페인 대한민국 대사관 (in Korean). Esp.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Páginas - Home". Exteriores.gob.es. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- Archived March 13, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120825214729/http://www.mofat.go.kr/english/regions/europe/20070823/1_1309.jsp?board=board&boardid=&key=1. Archived from the original on August 25, 2012. Retrieved January 14, 2011. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 외교부 홈페이지에 오신것을 환영합니다. (in Korean). MOFAT. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Посольство України в Республіці Корея". Archived from the original on 3 October 2012. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Europe" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Embassy of the Republic of Korea in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" (in Korean). Gbr.mofa.go.kr. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "UK and South Korea - UK and the world". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 한국의 수교일에 대해 알려주세요. : 지식iN (in Korean). Kin.naver.com. 2010-01-28. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- 주한 교황 대사관 : 지식백과 (in Korean). Terms.naver.com. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-03. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-14. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-23. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Error-2010-f3". Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- Archived October 17, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2013-12-30. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "South Korea-South Africa Relations". The Embassy of the Republic of Korea to the Republic of South Africa. 6 April 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 1996. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-07-22. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2017-08-28. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of Korea-Middle East and Africa" (in Korean). Mofa.go.kr. Archived from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2015-08-12.

Further reading
- Ahn, B.J. "Korea: A Rising Middle Power in World Politics", Korea and World Affairs 1987. 11#1 pp 7–17.
- Choi, Young Jong. "South Korea's regional strategy and middle power activism." Journal of East Asian Affairs(2009): 47–67. online
- Hwang, Balbina Y. "The US Pivot to Asia and South Korea's Rise." Asian Perspective 41.1 (2017): 71–97.
- John, Jojin V. "Becoming and being a middle power: exploring a new dimension of South Korea’s foreign policy." China Report 50.4 (2014): 325–341. online
- John, Jojin V. "Globalization, National Identity and Foreign Policy: Understanding'Global Korea'." Copenhagen Journal of Asian Studies 33.2 (2016): 38–57. online
- Kim Jinwung. "Recent Anti-Americanism in South Korea: The Causes" Asian Survey, 1989 29#8 749–63
- Kim, Min‐hyung. "South Korea's China Policy, Evolving Sino–ROK Relations, and Their Implications for East Asian Security." Pacific Focus 31.1 (2016): 56–78.
- Kim, Samuel S. ed. International Relations of Northeast Asia (Rowman and Littlefield,) esp pp 251–80
- Lee, Sook Jong, ed. Transforming Global Governance with Middle Power Diplomacy: South Korea's Role in the 21st Century (Springer, 2016) online.
- Milani, Marco, Antonio Fiori, and Matteo Dian, eds. The Korean Paradox: Domestic Political Divide and Foreign Policy in South Korea (Routledge, 2019).
- Rozman, Gilbert. "South Korea and Sino-Japanese rivalry: A middle power’s options within the East Asian core triangle: Pacific Review 2007. 20#2 pp 197–220.
- Saxer, Carl J. "Capabilities and aspirations: South Korea’s rise as a middle power," Asia Europe Journal 2013. 11#4 pp 397–413.
- Tayal, Skand R. India & the Republic of Korea: Engaged Democracies (2013)
