Sakhalin
Sakhalin (/ˌsækəˈliːn, ˌsæx-/ or /səˈkeɪlɪn, -ˈxeɪ-/; Russian: Сахали́н, tr. Sahalín, IPA: [səxɐˈlʲin]; Japanese: 樺太 Karafuto) is the largest island of the Russian Federation,[4] situated in the North Pacific Ocean between 45°50' and 54°24' N. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin, which is about one third the size of Honshu, is just off the Russian Pacific coast (Khabarovsk Krai), and just north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. The population of Sakhalin Island was 497,973 as of the 2010 census, made up of mostly ethnic Russians and a smaller Korean community. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks and Nivkhs.[5]
 Sakhalin | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Russian Far East[1], Northern Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 51°N 143°E |
| Area | 72,492 km2 (27,989 sq mi)[2] |
| Area rank | 23rd |
| Highest elevation | 1,609 m (5,279 ft) |
| Highest point | Lopatin |
| Administration | |
| Federal subject | Sakhalin Oblast |
| Largest settlement | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk (pop. 174,203) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 497,973[3] (2010) |
| Pop. density | 8/km2 (21/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Russians, Ainu, Koreans, Nivkhs, Oroks, among many others |
Derived from the Manchu word Sahaliyan, Sakhalin was once a tributary of the Qing dynasty and was later claimed by both Russia and Japan over the course of the 19th and 20th centuries. These disputes sometimes involved military conflicts and divisions of the island between the two powers. In 1875, Japan ceded its claims to Russia in exchange for the southern Kuril Islands. In 1905, following the Russo-Japanese War, the island was divided, with the south going to Japan. Russia has held all of the island since seizing the Japanese portion—as well as all the Kuril Islands—in the final days of World War II in 1945. Japan no longer claims any of Sakhalin, although it does still claim the southern Kuril Islands. Most Ainu on Sakhalin moved to Hokkaido, only 43 kilometres (27 mi) to the south, when the Japanese were displaced from the island in 1949.[6]
Etymology
The island is known in Russian as Sakhalin (Сахалин). In Chinese, it is known as Kuye (simplified Chinese: 库页; traditional Chinese: 庫頁; pinyin: Kùyè). In Japanese, it is known as Karafuto (樺太) or, borrowing the Russian appellation, as Saharin (サハリン). The spelling Saghalien may be found in historical texts. Choka (or Tchoka) is another name found in the early literature and seems to have been the name used by the islanders themselves, but it is not clear whether these were the Gilyak or the Ainu.
The European names derive from misinterpretation of a Manchu name ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ
ᡠᠯᠠ ᠠᠩᡤᠠ
ᡥᠠᡩᠠ sahaliyan ula angga hada ("peak/craggy rock at the mouth of the Amur River"). Sahaliyan, the word that has been borrowed in the form of "Sakhalin", means "black" in Manchu, ula means "river" and sahaliyan ula (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ
ᡠᠯᠠ , "Black River") is the proper Manchu name of the Amur River. Its Japanese name, Karafuto (樺太), supposedly comes from Ainu kamuy kar put ya mosir (カムイ・カラ・プト・ヤ・モシリ, shortened to Karput カラ・プト), which means "the island a god has created at the estuary (of the Amur River)". The name was used by the Japanese during their possession of its southern part (1905–1945).
History
Early history
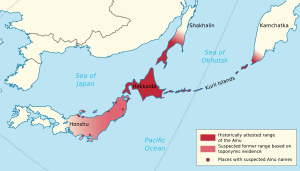
Sakhalin was inhabited in the Neolithic Stone Age. Flint implements such as those found in Siberia have been found at Dui and Kusunai in great numbers, as well as polished stone hatchets similar to European examples, primitive pottery with decorations like those of the Olonets, and stone weights used with fishing nets. A later population familiar with bronze left traces in earthen walls and kitchen-middens on Aniva Bay.
Among the indigenous people of Sakhalin are the Ainu in the southern half, the Oroks in the central region, and the Nivkhs in the north.[7] Chinese chronicled the Xianbei and Hezhe tribes, which had a way of life based on fishing.
The Mongol Empire made some efforts to subjugate the native people of Sakhalin starting in about 1264 A.D. According to Yuanshi, the official history of the Yuan dynasty, the Mongols invaded Sakhalin and militarily subdued the Guwei (骨嵬, Gǔwéi), and by 1308, all inhabitants of Sakhalin had submitted to the Yuan.[8] The Nivkhs were subjugated earlier, whereas the Ainu people submitted to the Mongols later. Following their subjugation, Gǔwéi elders made tributary visits to Yuan posts located at Wuleihe, Nanghar, and Boluohe until the end of the Mongol Yuan dynasty in China (1368). In the early Ming dynasty (1368–1644), the tributary relationship was re-established. By the middle of the 15th century, following the introduction of Chinese political and commercial institutions in the Amur region, the Sakhalin Ainu were making frequent tributary visits to Chinese-controlled outposts.[8] Chinese of the Ming dynasty knew the island as Kuyi (苦夷 Kǔyí) or Kuwu (Chinese: 苦兀; pinyin: Kǔwù), and later as Kuye (Chinese: 庫頁; pinyin: Kùyè), as it is known today. There is some evidence that the Ming eunuch Admiral Yishiha reached Sakhalin in 1413 during one of his expeditions to the lower Amur, and granted Ming titles to a local chieftain.[9] Under the Ming dynasty, commerce in Northeast Asia and Sakhalin was placed under the "system for subjugated peoples", or ximin tizhi. This suggests that the island was at least nominally under the administration of the Nurgan Regional Military Commission, which was established by Yishiha near today's village of Tyr on the Siberian mainland in 1411, and continued operating until the mid-1430s.[9]
Before 19th century
Tributary of Qing dynasty
According to Wei Yuan's work Military history of the Qing dynasty (Chinese: 聖武記; pinyin: Shèngwǔ Jì), the Later Jin sent 400 troops to Sakhalin in 1616 in response to Japanese activity in the area, but later withdrew, judging there to be no major threat to their control of the island.
The 1689 Treaty of Nerchinsk between Russia and China, which defined the Stanovoy Mountains as their mutual border, made no explicit mention of the island; however, the Qing dynasty (1636–1912) did consider the island to be part of its territory,[10] and enacted policies of a pattern similar to the previous Ming dynasty, which drew Sakhalin further into the "system for subjugated peoples". Local people were forced to pay tribute at Qing posts, and Qing officials sometimes granted titles to local elders, entrusting them with the task of "keeping the peace". By the mid-18th century, Qing officials had registered 56 surname groups; of these, Qing sources note that six clans and 148 households were those of Ainu and Nivkh who came under the Qing administrative umbrella.[11] However, since the Chinese government did not have a military presence on the island, Japanese attempts at colonization continued.
European and Japanese exploration
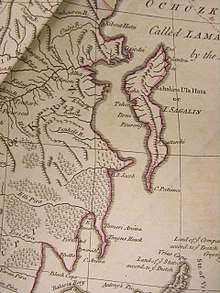
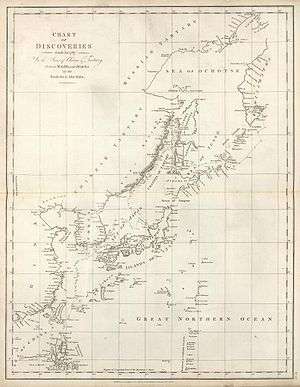
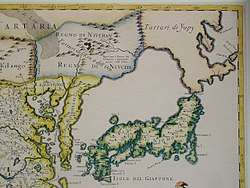
In an early colonization attempt, a Japanese settlement was established at Ōtomari on Sakhalin's southern end in 1679.[12] Cartographers of the Matsumae clan created a map of the island and called it "Kita-Ezo" (Northern Ezo, Ezo being the old name for the islands north of Honshu).
The first European known to visit Sakhalin was Martin Gerritz de Vries, who mapped Cape Patience and Cape Aniva on the island's east coast in 1643. The Dutch captain, however, was unaware that it was an island, and 17th century maps usually showed these points (and often Hokkaido as well) as being part of the mainland.
As part of a nationwide Sino-French cartographic program, the Jesuits Jean-Baptiste Régis, Pierre Jartoux, and Xavier Ehrenbert Fridelli joined a Chinese team visiting the lower Amur (known to them under its Manchu name, Saghalien Ula, i.e. the "Black River"), in 1709,[13] and learned of the existence of the nearby offshore island from the Ke tcheng natives of the lower Amur. The Jesuits were told that the islanders were believed to be good at reindeer husbandry. They reported that the mainlanders used a variety of names to refer to the island, but Saghalien anga bata (i.e. "the Island [at] the mouth of the Black River") was the most common, while the name "Huye" (presumably, "Kuye", 庫頁), which they had heard in Beijing, was completely unknown to the locals.[14]
The Jesuits did not have a chance to visit the island personally, and the geographical information provided by the Ke tcheng people and Manchus who had been to the island was insufficient to allow them to identify it as the land visited by de Vries in 1643. As a result, many 17th century maps showed a rather strangely shaped Sakhalin, which included only the northern half of the island (with Cape Patience), while Cape Aniva, discovered by de Vries, and the "Black Cape" (Cape Crillon) were thought to be part of the mainland.
It was not until the 1787 expedition of Jean-François de La Pérouse that the island began to resemble something of its true shape on European maps. Though unable to pass through its northern "bottleneck" due to contrary winds, La Perouse charted most of the Strait of Tartary, and islanders he encountered near today's Strait of Nevelskoy told him that the island was called "Tchoka" (or at least that is how he recorded the name in French), and it was used on some maps thereafter.[15]
The Russian explorer Adam Johann von Krusenstern visited Sakhalin in 1805, but regarded it as a peninsula.
Alarmed by the visits of European powers, Japan proclaimed its sovereignty over the whole island in 1807. Most Japanese sources claim Mamiya Rinzō as the true discoverer of the Strait of Tartary, in 1809.
19th century
Russo-Japanese rivalry


On the basis of its belief that it was an extension of Hokkaido, both geographically and culturally, Japan again proclaimed sovereignty over the whole island (as well as the Kuril Islands chain) in 1845, in the face of competing claims from Russia. In 1849, however, the Russian navigator Gennady Nevelskoy recorded the existence and navigability of the strait later given his name, and – in defiance of the Qing and Japanese claims – Russian settlers began establishing coal mines, administration facilities, schools, and churches on the island. In 1853–54, Nikolay Rudanovsky surveyed and mapped the island.[16]
In 1855, Russia and Japan signed the Treaty of Shimoda, which declared that nationals of both countries could inhabit the island: Russians in the north, and Japanese in the south, without a clearly defined boundary between. Russia also agreed to dismantle its military base at Ootomari. Following the Opium War, Russia forced China to sign the Treaty of Aigun (1858) and the Convention of Peking (1860), under which China lost to Russia all claims to territories north of Heilongjiang (Amur) and east of Ussuri, including Sakhalin.
In 1857 the Russians established a penal colony. In 1890 the distinguished author Anton Chekhov visited the penal colony on Sakhalin and published a memoir of his journey.
Japan proclaimed its sovereignty over Sakhalin (which they called Karafuto) yet again in 1865, and the government built a stele announcing the claim at the northern extremity of the island. The island remained under shared sovereignty until the signing of the 1875 Treaty of Saint Petersburg, in which Japan surrendered its claims in Sakhalin to Russia.
Division along 50th parallel
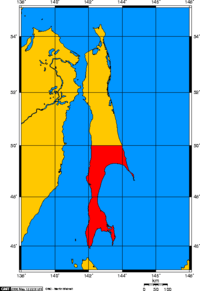
Japanese forces invaded and occupied Sakhalin in the closing stages of the Russo-Japanese War. In accordance with the Treaty of Portsmouth of 1905, the southern part of the island below the 50th parallel north reverted to Japan, while Russia retained the northern three-fifths. In 1920, during the Siberian Intervention, Japan again occupied the northern part of the island, returning it to the Soviet Union in 1925.
South Sakhalin was administered by Japan as Karafuto Prefecture (Karafuto-chō (樺太庁)), with the capital at Toyohara (today's Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk). A large number of migrants were brought in from Korea.
The northern, Russian, half of the island formed Sakhalin Oblast, with the capital at Aleksandrovsk-Sakhalinsky.
Whaling
Between 1848 and 1902, American whaleships hunted whales off Sakhalin.[17] They cruised for bowhead and gray whales to the north and right whales to the east and south.[18] On 7 June 1855, the ship Jefferson (396 tons), of New London, was wrecked on Cape Levenshtern, on the northeastern side of the island, during a fog. All hands were saved as well as 300 barrels of whale oil.[19][20][21]
Second World War
In August 1945, after repudiating the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact, the Soviet Union invaded southern Sakhalin. The Soviet attack started on August 11, 1945, a few days before the surrender of Japan. The Soviet 56th Rifle Corps, part of the 16th Army, consisting of the 79th Rifle Division, the 2nd Rifle Brigade, the 5th Rifle Brigade and the 214 Armored Brigade,[22] attacked the Japanese 88th Infantry Division. Although the Soviet Red Army outnumbered the Japanese by three to one, they advanced only slowly due to strong Japanese resistance. It was not until the 113th Rifle Brigade and the 365th Independent Naval Infantry Rifle Battalion from Sovetskaya Gavan landed on Tōro, a seashore village of western Karafuto, on August 16 that the Soviets broke the Japanese defense line. Japanese resistance grew weaker after this landing. Actual fighting continued until August 21. From August 22 to August 23, most remaining Japanese units agreed to a ceasefire. The Soviets completed the conquest of Karafuto on August 25, 1945 by occupying the capital of Toyohara.
Of the approximately 400,000 people – mostly Japanese and Korean – who lived on South Sakhalin in 1944, about 100,000 were evacuated to Japan during the last days of the war. The remaining 300,000 stayed behind, some for several more years.[23] While the vast majority of Sakhalin Japanese and Koreans were gradually repatriated between 1946 and 1950, tens of thousands of Sakhalin Koreans (and a number of their Japanese spouses) remained in the Soviet Union.[24][25]
No final peace treaty has been signed and the status of four neighboring islands remains disputed. Japan renounced its claims of sovereignty over southern Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Treaty of San Francisco (1951), but maintains that the four offshore islands of Hokkaido currently administered by Russia were not subject to this renunciation.[26] Japan has granted mutual exchange visas for Japanese and Ainu families divided by the change in status. Recently, economic and political cooperation has gradually improved between the two nations despite disagreements.[27]
Recent history

On 1 September 1983, the Korean Air Flight 007, a South Korean civilian airliner, flew over Sakhalin and was shot down by the Soviet Union, just west of Sakhalin Island, near the smaller Moneron Island. The Soviet Union claimed it was a spy plane; however, commanders on the ground realized it was a commercial aircraft. All 269 passengers and crew died, including a U.S. Congressman, Larry McDonald.
On 27 May 1995, the 7.0 Mw Neftegorsk earthquake shook the former Russian settlement of Neftegorsk with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Total damage was $64.1–300 million, with 1,989 deaths and 750 injured. The settlement was not rebuilt.
Geography
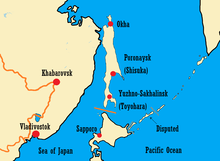

Sakhalin is separated from the mainland by the narrow and shallow Strait of Tartary, which often freezes in winter in its narrower part, and from Hokkaido, Japan, by the Soya Strait or La Pérouse Strait. Sakhalin is the largest island in Russia, being 948 km (589 mi) long, and 25 to 170 km (16 to 106 mi) wide, with an area of 72,492 km2 (27,989 sq mi).[2] It lies at similar latitudes to England, Wales and Ireland.
Its orography and geological structure are imperfectly known. One theory is that Sakhalin arose from the Sakhalin Island Arc.[28] Nearly two-thirds of Sakhalin is mountainous. Two parallel ranges of mountains traverse it from north to south, reaching 600–1,500 m (2,000–4,900 ft). The Western Sakhalin Mountains peak in Mount Ichara, 1,481 m (4,859 ft), while the Eastern Sakhalin Mountains's highest peak, Mount Lopatin 1,609 m (5,279 ft), is also the island's highest mountain. Tym-Poronaiskaya Valley separates the two ranges. Susuanaisky and Tonino-Anivsky ranges traverse the island in the south, while the swampy Northern-Sakhalin plain occupies most of its north.[29]

Crystalline rocks crop out at several capes; Cretaceous limestones, containing an abundant and specific fauna of gigantic ammonites, occur at Dui on the west coast; and Tertiary conglomerates, sandstones, marls, and clays, folded by subsequent upheavals, are found in many parts of the island. The clays, which contain layers of good coal and abundant fossilized vegetation, show that during the Miocene period, Sakhalin formed part of a continent which comprised north Asia, Alaska, and Japan, and enjoyed a comparatively warm climate. The Pliocene deposits contain a mollusc fauna more Arctic than that which exists at the present time, indicating that the connection between the Pacific and Arctic Oceans was probably broader than it is now.
Main rivers: The Tym, 330 km (205 mi) long and navigable by rafts and light boats for 80 km (50 mi), flows north and northeast with numerous rapids and shallows, and enters the Sea of Okhotsk.[30] The Poronay flows south-southeast to the Gulf of Patience or Shichiro Bay, on the southeastern coast. Three other small streams enter the wide semicircular Aniva Bay or Higashifushimi Bay at the southern extremity of the island.
The northernmost point of Sakhalin is Cape of Elisabeth on the Schmidt Peninsula, while Cape Crillon is the southernmost point of the island.
Sakhalin has two smaller islands associated with it, Moneron Island and Ush Island. Moneron, the only land mass in the Tatar strait, 7.2 km (4.5 mi) long and 5.6 km (3.5 mi) wide, is about 24 nautical miles (44 km) west from the nearest coast of Sakhalin and 41 nmi (76 km) from the port city of Nevelsk. Ush Island is an island off of the northern coast of Sakhalin.
Demographics

At the beginning of the 20th century, some 32,000 Russians (of whom over 22,000 were convicts) inhabited Sakhalin along with several thousand native inhabitants. In 2010, the island's population was recorded at 497,973, 83% of whom were ethnic Russians, followed by about 30,000 Koreans (5.5%). Smaller minorities were the Ainu, Ukrainians, Tatars, Yakuts and Evenks. The native inhabitants consist of some 2,000 Nivkhs and 750 Oroks. The Nivkhs in the north support themselves by fishing and hunting. In 2008 there were 6,416 births and 7,572 deaths.[31]
The administrative center of the oblast, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, a city of about 175,000, has a large Korean minority, typically referred to as Sakhalin Koreans, who were forcibly brought by the Japanese during World War II to work in the coal mines. Most of the population lives in the southern half of the island, centered mainly around Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk and two ports, Kholmsk and Korsakov (population about 40,000 each).
The 400,000 Japanese inhabitants of Sakhalin (including the Japanized indigenous Ainu) who had not already been evacuated during the war were deported following the invasion of the southern portion of the island by the Soviet Union in 1945 at the end of World War II.
Climate
The Sea of Okhotsk ensures that Sakhalin has a cold and humid climate, ranging from humid continental (Köppen Dfb) in the south to subarctic (Dfc) in the centre and north. The maritime influence makes summers much cooler than in similar-latitude inland cities such as Harbin or Irkutsk, but makes the winters much snowier and a few degrees warmer than in interior East Asian cities at the same latitude. Summers are foggy with little sunshine.[32]
Precipitation is heavy, owing to the strong onshore winds in summer and the high frequency of North Pacific storms affecting the island in the autumn. It ranges from around 500 millimetres (20 in) on the northwest coast to over 1,200 millimetres (47 in) in southern mountainous regions. In contrast to interior east Asia with its pronounced summer maximum, onshore winds ensure Sakhalin has year-round precipitation with a peak in the autumn.[29]
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Flora and fauna


The whole of the island is covered with dense forests, mostly coniferous. The Yezo (or Yeddo) spruce (Picea jezoensis), the Sakhalin fir (Abies sachalinensis) and the Dahurian larch (Larix gmelinii) are the chief trees; on the upper parts of the mountains are the Siberian dwarf pine (Pinus pumila) and the Kurile bamboo (Sasa kurilensis). Birches, both Siberian silver birch (Betula platyphylla) and Erman's birch (B. ermanii), poplar, elm, bird cherry (Prunus padus), Japanese yew (Taxus cuspidata), and several willows are mixed with the conifers; while farther south the maple, rowan and oak, as also the Japanese Panax ricinifolium, the Amur cork tree (Phellodendron amurense), the Spindle (Euonymus macropterus) and the vine (Vitis thunbergii) make their appearance. The underwoods abound in berry-bearing plants (e.g. cloudberry, cranberry, crowberry, red whortleberry), red-berried elder (Sambucus racemosa), wild raspberry, and Spiraea.
Bears, foxes, otters, and sables are numerous, as are reindeer in the north, and musk deer, hares, squirrels, rats, and mice everywhere. The bird population is mostly the common east Siberian, but there are some endemic or near-endemic breeding species, notably the endangered Nordmann's greenshank (Tringa guttifer) and the Sakhalin leaf warbler (Phylloscopus borealoides). The rivers swarm with fish, especially species of salmon (Oncorhynchus). Numerous whales visit the sea coast, including the critically endangered Western Pacific gray whale, for which the coast of Sakhalin is the only known feeding ground. Other endangered whale species known to occur in this area are the North Pacific right whale, the bowhead whale, and the beluga whale.
Transport

Sea
Transport, especially by sea, is an important segment of the economy. Nearly all the cargo arriving for Sakhalin (and the Kuril Islands) is delivered by cargo boats, or by ferries, in railway wagons, through the Vanino-Kholmsk train ferry from the mainland port of Vanino to Kholmsk. The ports of Korsakov and Kholmsk are the largest and handle all kinds of goods, while coal and timber shipments often go through other ports. In 1999, a ferry service was opened between the ports of Korsakov and Wakkanai, Japan, and operated through the autumn of 2015, when service was suspended.
For the 2016 summer season, this route will be served by a highspeed catamaran ferry from Singapore named Penguin 33. The ferry is owned by Penguin International Limited and operated by Sakhalin Shipping Company.
Sakhalin's main shipping company is Sakhalin Shipping Company, headquartered in Kholmsk on the island's west coast.
Rail

About 30 percent of all inland transport volume is carried by the island's railways, most of which are organized as the Sakhalin Railway (Сахалинская железная дорога), which is one of the 17 territorial divisions of the Russian Railways.
The Sakhalin Railway network extends from Nogliki in the north to Korsakov in the south. Sakhalin's railway has a connection with the rest of Russia via a train ferry operating between Vanino and Kholmsk.
As of 2004, the railways are only now being converted from the Japanese 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) gauge to the Russian 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in) gauge.[33][34] The original Japanese D51 steam locomotives were used by the Soviet Railways until 1979.
Besides the main network run by the Russian Railways, until December 2006 the local oil company (Sakhalinmorneftegaz) operated a corporate narrow-gauge 750 mm (2 ft 5 1⁄2 in) line extending for 228 kilometers (142 mi) from Nogliki further north to Okha (Узкоколейная железная дорога Оха — Ноглики). During the last years of its service, it gradually deteriorated; the service was terminated in December 2006, and the line was dismantled in 2007–2008.[35]
Air
Sakhalin is connected by regular flights to Moscow, Khabarovsk, Vladivostok and other cities of Russia. Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Airport has regularly scheduled international flights to Hakodate, Japan, and Seoul and Busan, South Korea. There are also charter flights to the Japanese cities of Tokyo, Niigata, and Sapporo and to the Chinese cities of Shanghai, Dalian and Harbin. The island was formerly served by Alaska Airlines from Anchorage, Petropavlovsk, and Magadan.
Fixed links
The idea of building a fixed link between Sakhalin and the Russian mainland was first put forward in the 1930s. In the 1940s, an abortive attempt was made to link the island via a 10-kilometre-long (6 mi) undersea tunnel.[36] The project was abandoned under Premier Nikita Khrushchev. In 2000, the Russian government revived the idea, adding a suggestion that a 40-km-long bridge could be constructed between Sakhalin and the Japanese island of Hokkaidō, providing Japan with a direct connection to the Eurasian railway network. It was claimed that construction work could begin as early as 2001. The idea was received skeptically by the Japanese government and appears to have been shelved, probably permanently, after the cost was estimated at as much as $50 billion.
In November 2008, Russian president Dmitry Medvedev announced government support for the construction of the Sakhalin Tunnel, along with the required regauging of the island's railways to Russian standard gauge, at an estimated cost of 300–330 billion roubles.[37]
In July 2013, Russian Far East development minister Viktor Ishayev proposed a railway bridge to link Sakhalin with the Russian mainland. He also again suggested a bridge between Sakhalin and Hokkaidō, which could potentially create a continuous rail corridor between Europe and Japan.[38] In 2018, president Vladimir Putin ordered a feasibility study for a mainland bridge project.[39]
Economy

Sakhalin is a classic "primary sector of the economy" relying on oil and gas exports, coal mining, forestry, and fishing. Limited quantities of rye, wheat, oats, barley and vegetables are grown, although the growing season averages less than 100 days.[29]
Following the collapse of the Soviet Union and economic liberalization, Sakhalin has experienced an oil boom with extensive petroleum exploration and mining by most large oil multinational corporations. The oil and natural gas reserves contain an estimated 14 billion barrels (2.2 km3) of oil and 2,700 km3 (96 trillion cubic feet) of gas and are being developed under production-sharing agreement contracts involving international oil companies like ExxonMobil and Shell.
In 1996, two large consortia signed contracts to explore for oil and gas off the northeast coast of the island, Sakhalin-I and Sakhalin-II. The two consortia were estimated to spend a combined US$21 billion on the two projects which almost doubled to $37 billion as of September 2006, triggering Russian governmental opposition. The cost will include an estimated US$1 billion to upgrade the island's infrastructure: roads, bridges, waste management sites, airports, railways, communications systems, and ports. In addition, Sakhalin-III-through-VI are in various early stages of development.
The Sakhalin I project, managed by Exxon Neftegas Limited (ENL), completed a production-sharing agreement (PSA) between the Sakhalin I consortium, the Russian Federation, and the Sakhalin government. Russia is in the process of building a 220 km (140 mi) pipeline across the Tatar Strait from Sakhalin Island to De-Kastri terminal on the Russian mainland. From De-Kastri, the resource will be loaded onto tankers for transport to East Asian markets, namely Japan, South Korea and China.
The second consortium, Sakhalin Energy Investment Company Ltd (Sakhalin Energy), is managing the Sakhalin II project. It completed the first production-sharing agreement (PSA) with the Russian Federation. Sakhalin Energy will build two 800-km pipelines running from the northeast of the island to Prigorodnoye (Prigorodnoe) in Aniva Bay at the southern end. The consortium will also build, at Prigorodnoye, the first liquefied natural gas (LNG) plant to be built in Russia. The oil and gas are also bound for East Asian markets.
Sakhalin II has come under fire from environmental groups, namely Sakhalin Environment Watch, for dumping dredging material in Aniva Bay. These groups were also worried about the offshore pipelines interfering with the migration of whales off the island. The consortium has (as of January 2006) rerouted the pipeline to avoid the whale migration. After a doubling in the projected cost, the Russian government threatened to halt the project for environmental reasons.[40] There have been suggestions that the Russian government is using the environmental issues as a pretext for obtaining a greater share of revenues from the project and/or forcing involvement by the state-controlled Gazprom. The cost overruns (at least partly due to Shell's response to environmental concerns), are reducing the share of profits flowing to the Russian treasury.[41][42][43][44]
In 2000, the oil and gas industry accounted for 57.5% of Sakhalin's industrial output. By 2006, it is expected to account for 80% of the island's industrial output. Sakhalin's economy is growing rapidly thanks to its oil and gas industry. By 2005, the island had become the largest recipient of foreign investment in Russia, followed by Moscow. Unemployment in 2002 was only two percent.
As of 18 April 2007, Gazprom has taken a 50 percent plus one share interest in Sakhalin II by purchasing 50 percent of Shell, Mitsui and Mitsubishi's shares.
International partnerships


See also
- List of islands of Russia
- Winter storms of 2009–10 in East Asia
- Ryugase Group – a geological formation on the island
References
- "Sakhalin Island | island, Russia". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- "Islands by Land Area". Island Directory. United Nations Environment Program. February 18, 1998. Retrieved June 16, 2010.
- Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- Ros, Miquel (January 2, 2019). "Russia's Far East opens up to visitors". CNN Travel. Retrieved January 6, 2019.
- "The Sakhalin Regional Museum: The Indigenous Peoples". Sakh.com. Archived from the original on March 17, 2009. Retrieved June 16, 2010.
- Reid, Anna (2003). The Shaman's Coat: A Native History of Siberia. New York: Walker & Company. pp. 148–150. ISBN 0-8027-1399-8.
- Gall, Timothy L. (1998). Worldmark Encyclopedia of Cultures and Daily Life. Detroit, Michigan: Gale Research Inc. pp. 2–3. ISBN 0-7876-0552-2.
- Walker, Brett L. (2006). The Conquest of Ainu Lands: Ecology and Culture in Japanese Expansion, 1590–1800. Berkeley, Calif.: University of California Press. p. 133. ISBN 0-520-24834-1. Retrieved June 16, 2010.
- Tsai, Shih-Shan Henry (2002) [2001]. Perpetual Happiness: The Ming Emperor Yongle. Seattle, Wash: University of Washington Press. pp. 158–161. ISBN 0-295-98124-5. Retrieved June 16, 2010. Link is to partial text.
- "被俄国吞并之前,清朝在外东北和库页岛是如何管辖的?". zhihu.
- Walker, Brett L. (February 21, 2006). The Conquest of Ainu Lands. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-0-520-24834-2. Retrieved June 16, 2010.
- Time Table of Sakhalin Island
- Du Halde, Jean-Baptiste (1736). Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique, et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise, enrichie des cartes générales et particulieres de ces pays, de la carte générale et des cartes particulieres du Thibet, & de la Corée; & ornée d'un grand nombre de figures & de vignettes gravées en tailledouce. 1. La Haye: H. Scheurleer. p. xxxviii. Retrieved June 16, 2010.
- Du Halde, Jean-Baptiste (1736). Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique, et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise, enrichie des cartes générales et particulieres de ces pays, de la carte générale et des cartes particulieres du Thibet, & de la Corée; & ornée d'un grand nombre de figures & de vignettes gravées en tailledouce. 4. La Haye: H. Scheurleer. pp. 14–16. Retrieved June 16, 2010. The people whose name the Jesuits recorded as Ke tcheng ta tse ("Hezhen Tatars") lived, according to the Jesuits, on the Amur below the mouth of the Dondon River, and were related to the Yupi ta tse ("Fishskin Tatars") living on the Ussuri and the Amur upstream from the mouth of the Dondon. The two groups might thus be ancestral of the Ulch and Nanai people known to latter ethnologists; or, the "Ke tcheng" might in fact be Nivkhs.
- La Pérouse, Jean François de Galaup, comte de (1831). de Lesseps, Jean Baptiste (ed.). Voyage de Lapérouse, rédigé d'après ses manuscrits, suivi d'un appendice renfermant tout ce que l'on a découvert depuis le naufrage, et enrichi de notes par m. de Lesseps. pp. 259–266.
- "Началось исследование Южного Сахалина под руководством лейтенанта Николая Васильевича Рудановского". President Library of Russia.
- Mary and Susan, of Stonington, Aug. 10–31, 1848, Nicholson Whaling Collection; Charles W. Morgan, of New Bedford, Aug. 30-Sep. 5, 1902, G. W. Blunt White Library (GBWL).
- Eliza Adams, of Fairhaven, Aug. 4–6, 1848, Old Dartmouth Historical Society; Erie, of Fairhaven, July 26 – Aug. 29, 1852, NWC; Sea Breeze, of New Bedford, July 8–10, 1874, GBWL.
- William Wirt, of New Bedford, June 13, 1855, Nicholson Whaling Collection.
- The Friend (Vol. IV, No. 9, Sep. 29, 1855, pp. 68 & 72, Honolulu)
- Starbuck, Alexander (1878). History of the American Whale Fishery from Its Earliest Inception to the year 1876. Castle. ISBN 1-55521-537-8.
- 16th Army, 2nd Far Eastern Front, Soviet Far East Command, 09.08,45
- Forsyth, James (1994) [1992]. A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian Colony 1581–1990. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 354. ISBN 0-521-47771-9.
- Ginsburgs, George (1983). The Citizenship Law of the USSR. Law in Eastern Europe No. 25. The Hague: Martinis Nijhoff Publishers. pp. 320–325. ISBN 90-247-2863-0.
- Sandford, Daniel, "Sakhalin memories: Japanese stranded by war in the USSR", BBC, 3 August 2011.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan: Foreign Policy > Others > Japanese Territory > Northern Territories http://www.mofa.go.jp/region/europe/russia/territory/index.html
- Japan and Russia want to finally end World War II, agree it is 'abnormal' not to – CSMonitor.com
- Ivanov, Andrey (March 27, 2003). "18 The Far East". In Shahgedanova, Maria (ed.). The Physical Geography of Northern Eurasia. Oxford Regional Environments. 3. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. pp. 428–429. ISBN 978-0-19-823384-8. Retrieved July 16, 2008.
- Ivlev, A. M. Soils of Sakhalin. New Delhi: Indian National Scientific Documentation Centre, 1974. Pages 9–28.
- Тымь – an article in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia. (In Russian, retrieved 21 June 2020.)
- Сахалин становится островом близнецов? [Sakhalin is an island of twins?] (in Russian). Восток Медиа [Vostok Media]. February 13, 2009. Archived from the original on July 17, 2011. Retrieved June 16, 2010.
- Sakhalin Hydrometeorological Service, accessed 19 April 2011
- "Sakhalin Railways". JSC Russian Railways. 2007. Archived from the original on October 4, 2011. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
- Dickinson, Rob. "Steam and the Railways of Sakhalin Island". International Steam Page. Archived from the original on February 17, 2008. Retrieved June 16, 2010.
- Bolashenko, Serguei (Болашенко, С.) (July 6, 2006). Узкоколейная железная дорога Оха — Ноглики [Okha-Nogliki narrow-gauge railway]. САЙТ О ЖЕЛЕЗНОЙ ДОРОГЕ (in Russian). Archived from the original on August 11, 2014. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
- The Moscow Times (July 7, 2008). "Railway a Gauge of Sakhalin's Future". The RZD-Partner. Archived from the original on September 9, 2012. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
- Президент России хочет остров Сахалин соединить с материком [President of Russia wants to join Sakhalin Island to the mainland] (in Russian). PrimaMedia. November 19, 2008. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
- "Minister Proposes 7km Bridge to Sakhalin Island". RIA Novosti. The Moscow Times. July 19, 2013. Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- "Putin orders construction of world's longest bridge". RT. July 24, 2018. Retrieved July 24, 2018.
- "Russia Threatens To Halt Sakhalin-2 Project Unless Shell Cleans Up". Terra Daily. Agence France-Presse. September 26, 2006. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
- Kramer, Andrew E. (September 19, 2006). "Russia Halts Pipeline, Citing River Damage". The New York Times. p. C.11. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
- "Cynical in Sakhalin". Financial Times. London. September 26, 2006.
- "A deal is a deal". The Times. London. September 22, 2006. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
- "CEO delivers message at Sakhalin's first major energy conference" (Press release). Sakhalin Energy. September 27, 2006. Archived from the original on November 1, 2007. Retrieved June 17, 2010. Citations for the date: "Sakhalin II: Laying the Base for Future Arctic Developments in Russia" (Press release). Sakhalin Energy. September 27, 2006. Archived from the original on December 14, 2011. Retrieved June 17, 2010. "Media Archives 2006". Sakhalin Energy. Archived from the original on July 15, 2011. Retrieved June 17, 2010.
Further reading
- C. H. Hawes, In the Uttermost East (London, 1903). (P. A. K.; J. T. BE.)
- A Journey to Sakhalin (1895), by Anton Chekhov, including:
- Saghalien [or Sakhalin] Island (1891–1895)
- Across Siberia
- Sakhalin Unplugged (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, 2006) by Ajay Kamalakaran
- John J. Stephan, Sakhalin: a History. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1971.
- Globetrotting for Love and Other Stories from Sakhalin Island, by Ajay Kamalakaran (Times Group Books, 2017)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sakhalin. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Sakhalin. |
- Sakhalin Island at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- Map of the Sakhalin Hydrocarbon Region—at Blackbourn Geoconsulting
- TransGlobal Highway—Proposed Sakhalin-Hokkaidō Friendship Tunnel
- Steam and the Railways of Sakhalin
- Maps of Ezo, Sakhalin and Kuril Islands from 1854