Alarodian languages
The Alarodian languages are a proposed language family that encompasses the Northeast Caucasian (Nakh–Dagestanian) languages and the extinct Hurro-Urartian languages.
| Alarodian | |
|---|---|
| (controversial) | |
| Geographic distribution | Caucasus, Anatolia |
| Linguistic classification | Proposed language family |
| Glottolog | None |
History
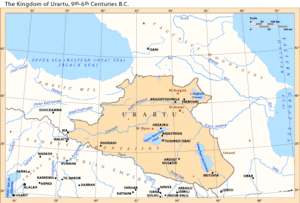
The term Alarodian is derived from Greek Ἀλαρόδιοι (Alarodioi), the name of an ethnic group mentioned by Herodotus which is usually equated with the people of the kingdom of Urartu, in modern-day Armenia, northwestern Iran, and eastern Turkey.
Historically, the term "Alarodian languages" was employed for several language family proposals of various size. Sayce (1880) employed the name for a small group that comprised Urartian (then called "Vannic") and the Kartvelian languages (Georgian, Laz, Mingrelian, and Svan).[1] In 1884, the German orientalist Fritz Hommel further included all languages of the Caucasus and the ancient Near East which did not belong to the Indo-European, Semitic, and the now obsolete Ural–Altaic language families, e.g. Elamite, Kassite.[2] Later, he extended the Alarodian family to include the pre-Indo-European languages of Europe, e.g. Lemnian, Etruscan, Ligurian. Karel Oštir's (1921) version of Alarodian included all aforementioned languages, further Basque, Sumerian, Egyptian, the Cushitic and Berber languages.[3][4] The historical Alarodian proposal – especially Oštir's maximal extension – was however not well-received by the majority of scholars ("Ce petit livre donne le vertige"—"This little book makes one dizzy", A. Meillet),[5] and eventually abandoned.
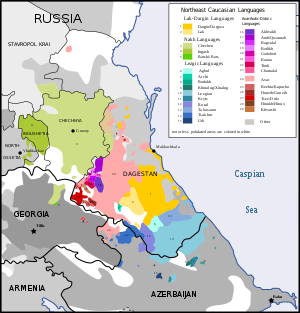
The term "Alarodian languages" was revived by I.M. Diakonoff for the proposed language family that unites the Hurro-Urartian and Northeast Caucasian languages.[6] Work by I.M. Diakonoff and Starostin (1986) asserted the connection between "Nakh-Dagestanian" (NE Caucasian) and Hurro-Urartian on the basis of comparison of their reconstruction to Proto-Nakh-Dagestanian, later published in 1994 with Nikolayev.[7]
Proposed relation to Tyrsenian
The inclusion of Etruscan and the related Tyrsenian languages has also been proposed, first by Orel and Starostin in 1990, on the basis of sound correspondences.[8] Facchetti has argued that there is a "curious" set of isoglosses between Etruscan and Hurrian,[9] while Pliev proposed instead that Etruscan had a Nakh substrate.[10] In 2006, Robertson further developed the hypothesis for including Tyrsenian based on proposed Etruscan/Nakh sound correspondences and reconstructions for the numerals.[11]
Reception
The validity of the Alarodian hypothesis remains fairly controversial.[12] Many scholars doubt that the Hurro-Urartian and Northeastern Caucasian languages are related,[13][14][15] or believe that, while a connection is possible, the evidence is far from conclusive.[16] The Indo-Europeanist Allan R. Bomhard argues instead for a genetic relationship between Hurro-Urartian and Indo-European[17][18] (most experts exclude a close genetic relationship between Northeast Caucasian and Indo-European, making the two hypotheses probably exclusive). The Caucasian language specialist Johanna Nichols grounds her scepticism in the Alarodian theory in that "neither Diakonoff and Starostin, nor Nikolayev and Starostin, take on the burden of proof and discuss whether the incidence of resemblances exceeds chance expectation, nor do they present examples of the kind of shared morphological paradigmaticity that would strongly support genetic relatedness".[19]
References
- Sayce, A. H. (1880). Introduction to the Science of Language, vol. 2. London: C. Kegan Paul & Co.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Hommel, Fritz (1884). "Die sumero-akkadische Sprache und ihre Verwandtschaftsverhältnisse". Zeitschrift für Keilschriftforschung (in German). 1: 161–178, 195–221, 323–342.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Oštir, Karel. (1921). Beiträge zur Alarodischen Sprachwissenschaft (a monograph), I, (in German)
- Čop, Bojan (1973). "Oštirs sprachwissenschaftliche Ideenwelt". Linguistica. Ljubljana University Press. 13 (1): 13–96. doi:10.4312/linguistica.13.1.13-96.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Meillet, Antoine (1922). "Comptes rendus". Bulletin de la Société de linguistique. 22: 128–130.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Diakonoff, Igor M. (1995). "Long-Range Linguistic Relations: Cultural Transmission or Consanguinity?" (PDF). Mother Tongue Newsletter. 24: 34–40.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Nikolayev, S L and Starostin, S A. A North Caucasian etymological dictionary. Moscow: Asterisk, 1994
- Orël, Vladimir and Starostin, Sergei. Etruscan as an East Caucasian language. In Vitaly Shevoroshkin (ed.), Protolanguages and proto-cultures, Bochum: Brockmeyer, 1990.
- Facchetti, Giulio M. Appunti di morfologia etrusca. Firenze: Leo S. Olschki, 2002
- Pliev, R. S. Nakhskoetrusskie leksikheskie vstrekhi. Nalchik: Kabardino-Balkarskij Gosudarstvennyj Universitet, 2000.
- Robertson, Ed (2006). "Etruscan's genealogical linguistic relationship with Nakh–Daghestanian: a preliminary evaluation" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 2009-07-13. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Tuite, Kevin (2008). "The Rise and Fall and Revival of the Ibero‑Caucasian Hypothesis". Historiographia Linguistica. 35 (1): 23–82. doi:10.1075/hl.35.1-2.05tui. S2CID 143379084.
- Smeets, Rieks "On Hurro-Urartian as an Eastern Caucasian language." Bibliotheca Orientalis XLVI (1989): 260-280.
- Nichols, Johanna (2003). "The Nakh-Daghestanian Consonant Correspondences". In Howard Isaac Aronson; Dee Ann Holisky; Kevin Tuite (eds.). Current Trends in Caucasian, East European and Inner Asian Linguistics: Papers in honor of Howard I. Aronson. Amsterdam: John Benjamins. pp. 207–264. ISBN 9789027247582.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Fournet, Arnaud "About the Vocalic System of Armenian Words of Substratic Origins" Archív Orientalni (2013): 1
- Zimansky, Paul "Urartian and Urartians." The Oxford Handbook of Ancient Anatolia (2011): 556.
- Fournet, Arnaud; Bomhard, Allan R. (2010). The Indo-European Elements in Hurrian. La Garenne Colombes, Charleston: Self-published online study.
- Fournet, Arnaud "PIE Roots in Hurrian" (2019): 1
- Johanna Nichols (January 2003). "The Nakh Dagestanian consonant correspondences". In Dee Ann Holisky; Kevin Tuite (eds.). Current Trends in Caucasian, East European, and Inner Asian Linguistics: Papers in Honor of Howard I. Aronson. John Benjamins Publishing. p. 208. ISBN 9027247587.
Literature
- A. Svanidze. "Materials for history of Alarodian tribes" (a monograph), Tbilisi, 1937 (in Russian)
- G.A. Melikishvili. Questions of the oldest population of Georgia, Caucasus and the Near East (a monograph), Tbilisi, 1965 (in Georgian, Russian summary)
- I. Diakonoff, S. Starostin. "Hurro-Urartian as an Eastern Caucasian Language".- Münchener Studien zur Sprachwissenschaft, Beiheft, N.F., 12, 1986 (in English)
- Alarodian languages.- Encyclopedia "Sakartvelo", vol. I, Tbilisi, 1997, pp. 90 (in Georgian)