Zhengzhou
Zhengzhou is the capital and largest city of Henan Province in the central part of the People's Republic of China.[2] It is one of the National Central Cities in China,[3] the centre of Central Plains area, and serves as the political, economic, technological, and educational center of the province.[4] The Zhengzhou metropolitan area (including Zhengzhou and Kaifeng) is the core area of the Central Plains Economic Zone.[5][6]
Zhengzhou 郑州市 Chengchow | |
|---|---|
 Clockwise from top left: Erqi Memorial Tower, Emperors Yan and Huang, Dengfeng Observatory, Shaolin Monastery, Zhengzhou Exhibition Center; and Center: The Pagoda Forest at the Shaolin Temple | |
| Nickname(s): business city, green city | |
| Motto(s): Partnership, Openness, Innovation, and Harmony (博大、开放、创新、和谐) | |
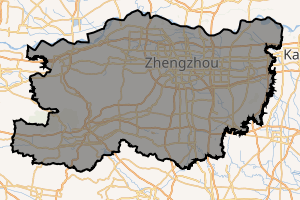
| |
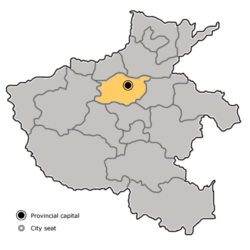 Location of Zhengzhou City; jurisdiction in Henan | |
 Zhengzhou Location in the North China Plain 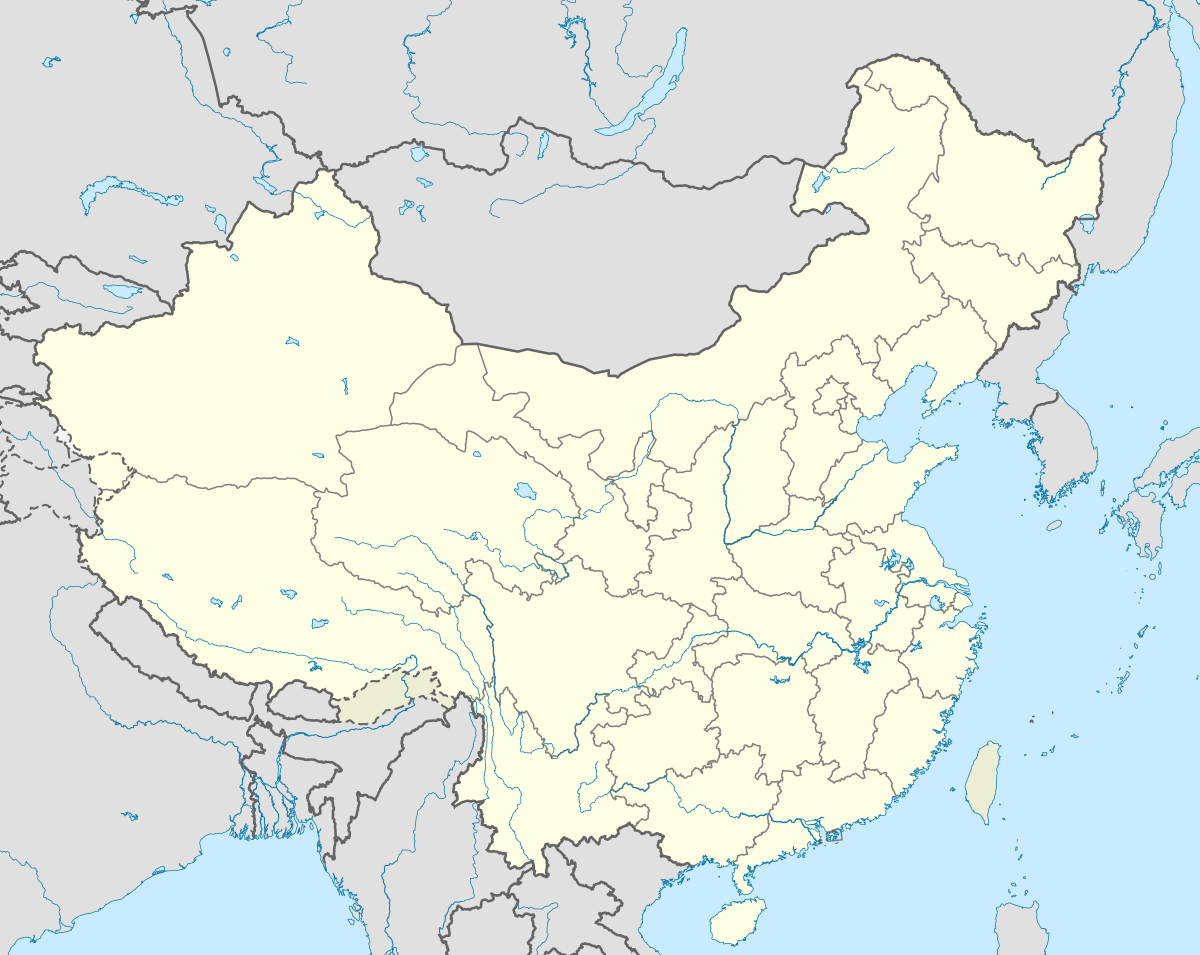 Zhengzhou Zhengzhou (China) | |
| Coordinates (Henan Provincial Hall of the People): 34°45′50″N 113°41′02″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Henan |
| City seat | Zhongyuan |
| Subdivisions | |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | XinWei Wang |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 7,507 km2 (2,898 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,024 km2 (395 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,979 km2 (764 sq mi) |
| Population (2018)[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 10,120,000 |
| • Density | 1,300/km2 (3,500/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 5,810,000 |
| • Urban density | 5,700/km2 (15,000/sq mi) |
| GDP (2018) | |
| • Total GDP | C¥ 1.014 trillion (US$ 144 billion) |
| • Per capita | C¥ 100,200 (US$ 14,000) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 450000 |
| Area code(s) | 371 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HA-01 |
| License plate prefixes | 豫A |
| Website | www |
| Zhengzhou | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png) "Zhèngzhōu" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 郑州 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 鄭州 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Zhèng Settlement" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||

The city lies on the southern bank of the Yellow River.[7] Zhengzhou is a major hub of China's national transportation network, with railways connecting Zhengzhou to Europe[8] and an international airport.[9] Zhengzhou is a National Civilized City, State-list Famous Historical and Culture City,[10] and the birthplace of the Yellow Emperor. As of 2020, there are two World Cultural Heritage Sites in Zhengzhou. The Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange (ZCE) is China's first futures exchange, Zhengzhou Airport Economy Zone is China's first Airport Economy Zone.[11]
Zhengzhou has a population of 10,120,000 inhabitants,[12][13] and had a GDP of 1.014 billion (RMB) in 2018.[14][15] The city is one of the main built-up areas of Henan region.[16] Greater Zhengzhou was named as one of the 13 emerging mega-cities in China in a July 2012 report by the Economist Intelligence Unit,[17] and officially named as the eighth National Central City in 2017 by the central government in Beijing.[18]
History
The Shang dynasty established Aodu (隞都) or Bodu (亳都) in Zhengzhou.[19] This prehistorical city had become abandoned as ruins long before the First Emperor of China in BC 260. Since 1950, archaeological finds in a walled city in Eastern Zhengzhou have provided evidence of Shang dynasty settlements in the area.[20][21] Outside this city, remains of large public buildings and a complex of small settlements have been discovered. The site is generally identified with the Shang capital of Ao and is preserved in the Shang dynasty Ruins monument in Guanchen District. The Shang, who continually moved their capital due to frequent natural disasters, left Ao at around 13th century BC. The site, nevertheless, remained occupied; Zhou (post-1050 BC) tombs have also been discovered.[22] Legend suggests that in the Western Zhou period (1111–771 BC) the site became the fief of a family named Guan. From this derives the name borne by the county (xian) since the late 6th century BC—Guancheng (City of the Guan). The city first became the seat of a prefectural administration in AD 587, when it was named Guanzhou. In 605 it was first called Zhengzhou—a name by which it has been known virtually ever since.[23]
The name Zhengzhou came from the Sui dynasty (AD 582), even though it was located in Chenggao, another town. The government moved to the contemporary city during the Tang dynasty. It achieved its greatest importance under the Sui (AD 581–618), Tang (618–907), and early Song (960–1127) dynasties, when it was the terminus of the New Bian Canal, which joined the Yellow River to the northwest. There, at a place called Heyin, a vast granary complex was established to supply the capitals at Luoyang and Chang'an to the west and the frontier armies to the north. In the Song period, however, the transfer of the capital eastward to Kaifeng robbed Zhengzhou of much of its importance.
In 1903 the Beijing–Hankou Railway arrived at Zhengzhou, and in 1909 the first stage of the Longhai Railway gave it an east–west link to Kaifeng and Luoyang; it later was extended eastward to the coast at Lianyungang, Jiangsu, and westward to Xi'an (Chang'an), Shaanxi, as well as to western Shaanxi. Zhengzhou thus became a major rail junction and a regional center for cotton, grain, peanuts, and other agricultural produce. Early in 1923 a workers' strike began in Zhengzhou and spread along the rail line before it was suppressed; a 14-story double tower in the center of the city commemorates the strike. On June 10, 1938, Chiang Kai-shek's National Revolutionary Army opened up the dikes retaining the Yellow River at Huayuankou between Zhengzhou and Kaifeng, in an effort to stem the tide of invading Japanese; however, the ensuing 1938 Yellow River flood also killed hundreds of thousands of Chinese.[24]
Zhengzhou also has a locomotive and rolling-stock repair plant, a tractor-assembly plant, and a thermal generating station. The city's industrial growth has resulted in a large increase in the population, coming predominantly from industrial workers from the north. A water diversion project and pumping station, built in 1972, has provided irrigation for the surrounding countryside. The city has an agricultural university.
Geography
Located just north of the province's centre and south of the Yellow River, Zhengzhou borders Luoyang to the west, Jiaozuo to the northwest, Xinxiang to the northeast, Kaifeng to the east, Xuchang to the southeast, and Pingdingshan to the southwest. With the land within its administrative borders generally sloping down from west to east, Zhengzhou is situated at the transitional zone between the North China Plain to the east and the Song Mountains and Xionger Mountains to the west, which are part of the greater Qinling range. The city centre is situated to the south of the middle reach of the Yellow River, where its valley broadens into the great plain. Zhengzhou is at the crossing point of the north–south route skirting the Taihang Mountains and the mountains of western Henan. The prefecture spans 34° 16' ~ 34° 58 N latitude and 112° 42' ~ 114° 14' E longitude, covering a total area of 7,446.2 square kilometres (2,875.0 sq mi), including the metropolitan area, which covers 1,013.3 km2 (391.2 sq mi), and the city centre, which occupies 147.7 square kilometres (57.0 sq mi).
The section of the Yellow River flowing through the prefecture extends 150.4 km (93.5 mi). Mountains loom over the western counties of Gongyi and Dengfeng while the easternmost county of Zhongmu is a vast, fertile floodplain, with the counties in between being hilly transitions.
Climate
Zhengzhou experiences a monsoon-influenced, four-season humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cwa), with cool, dry winters and hot, humid summers. Spring and autumn are dry and somewhat abbreviated transition periods. The city has an annual mean temperature of 14.73 °C (58.5 °F), with the monthly 24-hour average temperature ranging from 0.5 °C (32.9 °F) in January to 27.1 °C (80.8 °F) in July. The frost-free period lasts on average 220 days. Extremes since 1951 have ranged from −17.9 °C (0 °F) on 2 January 1955, 27 December 1971 and 1 February 1990 to 43.0 °C (109 °F) on 19 July 1966.[25][26]
Rainfall is primarily produced by the monsoonal low during summer; in winter, when the vast Siberian High dominates due to radiative cooling from further north, the area receives little precipitation. During the summer season, the city is also often affected by tropical depressions, which bring additional amounts of rain. The annual precipitation is about 630 millimetres (25 in). With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 45 percent in February and March to 54 percent in May, the city receives 2,182 hours of sunshine per year, which is just under half the possible total.
| Climate data for Zhengzhou (1981−2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 21.0 (69.8) |
25.2 (77.4) |
29.2 (84.6) |
37.2 (99.0) |
38.5 (101.3) |
42.3 (108.1) |
43.0 (109.4) |
40.1 (104.2) |
37.9 (100.2) |
34.6 (94.3) |
27.0 (80.6) |
23.8 (74.8) |
43.0 (109.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.8 (42.4) |
9.2 (48.6) |
14.7 (58.5) |
22.1 (71.8) |
27.5 (81.5) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.7 (89.1) |
30.3 (86.5) |
26.7 (80.1) |
21.7 (71.1) |
14.4 (57.9) |
7.9 (46.2) |
20.3 (68.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.5 (32.9) |
3.5 (38.3) |
8.8 (47.8) |
16.0 (60.8) |
21.5 (70.7) |
26.0 (78.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
25.8 (78.4) |
21.2 (70.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
8.4 (47.1) |
2.5 (36.5) |
14.7 (58.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.7 (25.3) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
3.7 (38.7) |
10.1 (50.2) |
15.6 (60.1) |
20.4 (68.7) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.0 (71.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
10.6 (51.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
9.9 (49.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.9 (−0.2) |
−17.9 (−0.2) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
3.1 (37.6) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.1 (59.2) |
13.2 (55.8) |
5.0 (41.0) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−17.9 (−0.2) |
−17.9 (−0.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 9.6 (0.38) |
12.5 (0.49) |
26.7 (1.05) |
30.1 (1.19) |
63.1 (2.48) |
67.8 (2.67) |
146.2 (5.76) |
138.9 (5.47) |
74.6 (2.94) |
39.4 (1.55) |
22.6 (0.89) |
9.4 (0.37) |
640.9 (25.24) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.3 | 4.3 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 6.8 | 7.7 | 11.6 | 9.9 | 8.2 | 6.8 | 5.0 | 3.5 | 79.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 59 | 60 | 59 | 59 | 61 | 62 | 77 | 79 | 75 | 68 | 64 | 59 | 65 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 144.3 | 139.0 | 164.8 | 202.8 | 234.0 | 229.5 | 199.9 | 199.6 | 179.2 | 182.4 | 158.3 | 148.1 | 2,181.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 46 | 45 | 45 | 52 | 54 | 53 | 45 | 48 | 48 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 49 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration (precipitation days, sunshine data 1971–2000)[27][28] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[29] | |||||||||||||
Administration and demography

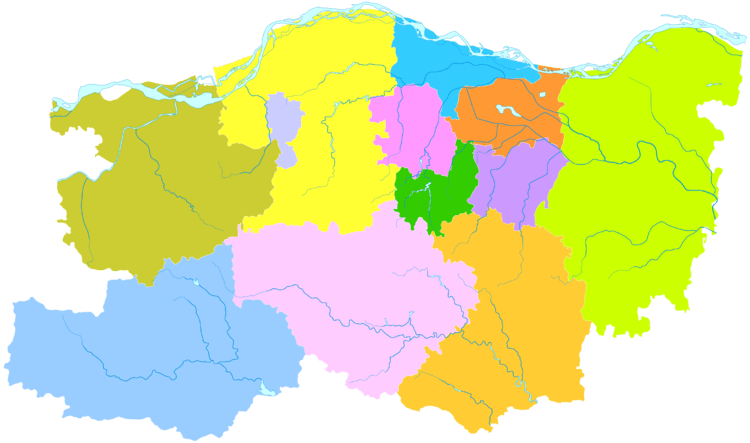
Zhengzhou is divided into 6 urban districts, 5 county-level cities and 1 county. These subdivisions are likely to undergo significant changes in the near future due to increasingly rapid urban expansion and urban planning.
The municipality is home to 8,626,505 inhabitants (2010 census) and 6,35 million in its built up area made of 6 urban and suburban districts, Xingyang and Xinzheng cities and now Zhongmu county largely being urbanized, making the city one of the main built-up areas of the province.[16]
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010) |
Area (km2) | |
| City proper | |||||
| Jinshui District | 金水区 | Jīnshuǐ Qū | 1,588,611 | 242 | |
| Erqi District | 二七区 | Èrqī Qū | 712,597 | 159 | |
| Huiji District | 惠济区 | Hùijì Qū | 269,561 | 206 | |
| Guancheng Hui District | 管城回族区 | Guǎnchéng Huízú Qū | 645,888 | 204 | |
| Zhongyuan District | 中原区 | zhōngyuán Qū | 905,430 | 195 | |
| Suburban | |||||
| Shangjie District | 上街区 | Shàngjiē Qū | 131,540 | 64.7 | |
| Satellite cities | |||||
| Xingyang | 荥阳市 | xíngyáng Shì | 613,761 | 908 | |
| Xinzheng | 新郑市 | Xīnzhèng Shì | 758,079 | 873 | |
| Dengfeng | 登封市 | Dēngfēng Shì | 668,592 | 1220 | |
| Xinmi | 新密市 | Xīnmí Shì | 797,200 | 1001 | |
| Gongyi | 巩义市 | Gǒngyì Shì | 807,857 | 1041 | |
| Rural | |||||
| Zhongmu County | 中牟县 | Zhōngmù Xiàn | 727,389 | 1393 | |
Main sights


 Between Heaven and Earth by Christian de Vietri
Between Heaven and Earth by Christian de Vietri
Zhengzhou was the capital of China during the Shang dynasty. Parts of the Shang-era capital city wall that were built 3,600 years ago still remain in Downtown Zhengzhou (see Zhengzhou Shang City).[23] Zhengzhou maintains abundant cultural heritages that reflect its glorious history as well as the culture of Henan Province. Zhengzhou Confucius Temple, initially built during the Eastern Han dynasty 1900 years ago, is one of the oldest Confucian Temples in China. Other important architectural heritage sites in the city center include Town God Temple and Erqi Memorial Tower.
The internationally known tourist attraction is the Shaolin Monastery, which is in Dengfeng, about 90 kilometres (56 miles) southwest of downtown Zhengzhou (1.5 hours by coach). The Shaolin Monastery is not only known as one of China's most important Buddhist shrines, but also as the ancient center of Chinese Kung-fu. Shaolin Monastery and its famed Pagoda Forest were inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2010.[30]
The Henan Museum is one of China's most important museums. It has a collection of more than 130,000 pieces of cultural relics includes exhibitions from prehistoric times, including dinosaur fossils and prehistoric human remains, up through the modern eras.
Zhengzhou's most developed and modern area is the Zhengdong New Area, which is in the eastern part of the city. It is home to some of the tallest skyscrapers in Zhengzhou, including the 280 metres (918.6 ft) tall Zhengzhou Greenland Plaza ("Big Corn"), which is one of the most prominent landmarks in Zhengzhou, and the twin towers of Zhengzhou Greenland Central Plaza (285 metres (935.0 ft)), which are currently the tallest skyscrapers in the city. The tallest structure in Zhengzhou is the 388-meter height Zhongyuan Tower, located on Hanghai East Road in the south of Zhengdong New Area. It is used as a television tower, with a revolving restaurant and an observation deck. The tower is among the tallest towers in the world.
Zhengzhou Zoo (郑州动物园) is located on Huayuan Road (花园路).
The newly built Zhengzhou Botanic Garden is at the western edge of Zhengzhou city.
Main attractions of Zhengzhou include:

- Mount Song (UNESCO Global Geopark)
- Shaolin Monastery and Pagoda Forest (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
- Dengfeng Observertory (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
- Songyue Pagoda (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
- Yellow River Scenic Area
- Kang Baiwan's Mansion

- the birthplace of Yellow Emperor
- Erqi Memorial Tower
- Henan Museum
- Zhongyuan Tower
- Zhengzhou Shang City
Economy
Zhengzhou, along with Xi'an, Chengdu, Chongqing and Wuhan, is one of the most important cities in inland China. It is the economic center of the province and the surrounding areas such as southeastern Shanxi and southwestern Shandong. Due to its strategic location in one of the most populous areas in the world (nearly 100 million people in Henan alone) and in China's railway, road and aviation transport networks, Zhengzhou is increasingly attracting domestic and international investment as well as migrants from other areas, transforming the city into one of the largest economic centers in China. In 2018, total GDP of Zhengzhou was ¥ 1020 billion,[31][32] ranked 17th in China.
Agriculture
By the end of 2006, Zhengzhou had a total population of over 7 million, of which 2.88 million lived in rural areas.[33] Its main products include apples, paulownia, tobacco, maize, cotton, and wheat. In addition, Zhengzhou also produces Yellow River carp, Zhengzhou watermelons, Xinzheng jujube, Xingyang dried persimmons, Guangwu Pomegranate and Zhongmu garlic, all of which are specialties that are rarely found outside the region.
Mining and manufacturing
Zhengzhou and the surrounding area have large reserves of coal and other minerals. Coal mining and electricity generation are traditionally important in the local economy.
Zhengzhou has been one of the major industrial cities in The People's Republic of China since 1949. The city's staple industry is textiles. Others manufactured items include tractors, locomotives, cigarettes, fertilizer, processed meats, agricultural machinery, and electrical equipment. Some high-tech companies in new material, electronics and biotechnology are also growing rapidly during the recently years, especially in the high-tech industrial park in the northwest of the city.
- Yutong, China's largest bus producer.
- Shaolin Bus, a well-known small-to-medium-sized bus producer.[34]
- Zhengzhou Nissan, a subsidiary of Dongfeng Nissan, specializing in the manufacture of SUVs and pickup trucks. In 2010, Nissan opened its second plant in the city.[35]
- Haima Automobile Zhengzhou, an automobile manufacturer specializing in manufacturing microvans and light passenger vehicles.
- Zhengzhou Unique Industrial Equipment Co., Ltd., a large tractor and agricultural equipment manufacturer.
- Foxconn Zhengzhou, located in Zhengzhou Airport Economy Zone, is the largest smartphone production site in the world and is also known as "iPhone City".[36]
- Sanquan Food, a frozen food company. With over 20000 employees,Sanquan produced the first frozen dumplings and rice balls in China.
 Mural Painting from Han Dynasty
Mural Painting from Han Dynasty - Synear Food Holdings Limited, along with Sanquan Food, is one of the largest producers of frozen food in China. The market share is over 20% in China[37]
Services
The service industries of Zhengzhou include retail, wholesale, hospitality, finance, exhibition, transport and delivery, tourism, and education. With a number of domestic and international institutions having regional offices in the city, Zhengzhou is becoming the financial center in central China. Zhengzhou Commodity Exchange (ZCE) is one of the only three future exchanges (inc. Shanghai Futures Exchange and Dalian Commodity Exchange) in China and is becoming an important global player specialised in agricultural future exchange. Equipped with newly built facilities such as Zhengzhou International Conference and Exhibition Center. Third party logistics (3PL) in Zhengzhou has also been experiencing industrial boom during the past few years. As a transit and tourist center of Henan Province and central China, Zhengzhou is the center of Henan cuisine.
- Dennis, a regional retail chain.
- Henan Jianye, a large real estate developer, which owns the China Super League club Henan Jianye F.C..
Economic development zones
The Zhengdong New Area (Chinese: 郑东新区), literally Eastern Zhengzhou New Area, similar to Hangzhou Bay New Area in Ningbo and Hengqin New Area in Zhuhai, is one of dozens of major economic zones that are currently developing in various regions of China.[38] Established in 2003 by the provincial and municipal governments, it has become the financial center of Henan province and one of the most rapidly growing areas of China.
Kisho Kurokawa, a Japanese world-renowned planner and architect, was appointed to design the overall planning scheme for Zhengdong New Area.[39] He brought in advanced ideas including ecological city, co-existing city, metabolic city and ring city ideas. The scheme won the "Prominent Award for City Planning Design" at the first session of Annual Meeting of the World Architects Alliance in 2002.[40] Zhengdong New Area is mainly constituted by the CBD area, the Longhu commercial and residential area, the Longzihu college area, and the Zhengzhou East railway station commercial area.
Industrial zones
- Zhengzhou New & Hi-Tech Industries Development Zone
Zhengzhou High & New Technology Industries Development Zone was established in 1988, and approved by the state Council of PRC to be a state development zone on Mar.6,1991. It was appraised to be advanced high tech zone of China respectively in 1993, 1998 and 2002. The Zone currently covers a total area of 18.6 square kilometres (7.2 square miles). An extension plan was approved by Zhengzhou Municipal Government, the various construction work started in 2004. Under the development strategy of “multiple parks in one zone”, the Zone has been making great efforts to promote the development of software,information technologies, new materials, bio-pharmaceutical and photo-machinery-electronic industries.[41]
- Zhengzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone
Zhengzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone was approved as state-level development zone on February 13, 2000. The zone has a developed area of 7 square kilometres (3 square miles) Industries encouraged include Electronics Assembly & Manufacturing, Telecommunications Equipment, Trading and Distribution, Biotechnology/Pharmaceuticals, Instruments & Industrial Equipment Production, Medical Equipment and Supplies, Shipping/Warehousing/Logistics and Heavy Industry.[42]
- Zhengzhou Export Processing Area
Zhengzhou (Henan) Export Processing Zone was established on June 21, 2002 with approval by the state council. Its planned area is 2.7 square kilometres (1.0 square mile). Zone A is located in Zhengzhou National Economic & technological Development Area and began to operate on June 1, 2004. The area of land developed is 0.893 square kilometres (0.345 square miles) at present. Zone B is located in Zhengzhou Airport Area and is adjacent to Zhengzhou Xinzheng International Airport on the north and it covers a planned area of 5 square km with bonded logistics zone, bonded processing zone and supporting industry zone, etc.[43]
Transportation
Zhengzhou is located in the central part of China and is a main national transport hub.
Public transit
Metro

Zhengzhou Metro is a rapid transit metro rail network serving urban and suburban districts of Great Zhengzhou metropolitan. The Zhengzhou Metro system started operation on 28 December 2013. It currently has 5 lines in operation, creating a 134.1 km (83.3 mi) long network. The first 2 lines (Line 1 and Line 2) were approved by the National Development and Reform Commission in Feb. 2009.[44] Construction of the two lines started in 2009 and 2010, and were finished in 2013 and 2015 respectively.[45] The Chengjiao Line (planned to be part of Line 9), which is now in through operations with Line 2, allows the system to serve the Zhengzhou Xinzheng International Airport. A total of 21 metro lines have been planned to connect all areas in Great Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area.[46]
Bus

Zhengzhou has a bus system with over 5,700 bus vehicles, operated by Zhengzhou Bus Communication Corporation (ZZB).[47]
The operations of Zhengzhou Bus Rapid Transit commenced in 2009. The system consists of 5 main routes (B1, B2, B3, B5 and B6) with dedicated bus lanes and dozens of branch routes that serve most areas of the city.
Railways

_Intercity_Railway_02.jpg)
Zhengzhou is the junction of the Longhai Railway (Lianyungang, Jiangsu–Lanzhou, Gansu) and the Beijing–Guangzhou Railway as well as a major national railway hub.[48]
Zhengzhou is also on the Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong high-speed railway and the Xuzhou–Lanzhou High-Speed Railway. The high-speed rail network provides fast train services to most major cities in China, including Beijing (2.5 hours), Guangzhou (6 hours), Xi'an (2 hours), Wuhan (2 hours), Shanghai (4 hours), Nanjing (3 hours), Hangzhou (5 hours), and Hong Kong (6.5 hours). Proposed high-speed railways from Zhengzhou to Chongqing, Hefei, Jinan and Taiyuan are under construction.
Zhengzhou is the hub of intercity railways in Henan. Currently, three intercity railways from Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou–Kaifeng intercity railway, Zhengzhou–Jiaozuo intercity railway and Zhengzhou–Xinzheng Airport intercity railway are in operation.
Main railway stations in the city include Zhengzhou Railway Station, which was opened in 1904 and is one of the most important railway stations in China; Zhengzhou East Railway Station, which is dedicated for high-speed trains and is one of the largest in Asia; and Zhengzhou South railway station, a new high-speed railway hub under construction.
Zhengzhou North railway station, over 6,000 metres (20,000 ft) long and over 800 metres (2,600 ft) wide, has been described as Asia's largest classification yard.[49]
Roads and Expressways

The surrounding area of Zhengzhou, along with the Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta and the Bohai Economic Rim, has the highest highway density nationwide. Zhengzhou is the center of Henan expressway network that provides 1–2 hours road trip to surrounding cities of Kaifeng, Xinxiang, Xuchang, Jiaozuo and Luoyang. Other major cities within the province can be reached in 3 hours. The expressway network and national highways also links Zhengzhou to all major cities in the country.
There are several limited access express roads in the city center to relieve traffic problems. However, heavy congestion is still common in rush hours.
Expressways












National highways
Urban express roads
- 3rd Ring Road (Zhengzhou)
- 4th Ring Road (Zhengzhou)
- Jingguang Expressway
- Longhai Expressway
- Nongye Expressway
- Zhongzhou Avenue
Air

Zhengzhou is primarily served by Zhengzhou Xinzheng International Airport (IATA: CGO, ICAO: ZHCC), which is 37 km (23 mi) southeast of the city center.
The airport is a focus city of China Southern Airlines, Lucky Air, West Air and Shenzhen Airlines. It used to be the headquarter for Henan Airlines. In 2017, it was the busiest airport in central China in both passenger and cargo traffic.[50] It is also one of the eight air hubs nominated by the Civil Aviation Administration of China.
Other airports in Zhengzhou include Shangjie Airport (IATA: HSJ) which is for general aviation, and Matougang Airbase which is for military use.
Colleges and universities

Public
- Zhengzhou University
- Henan University(Longzi Lake campus)
- Henan Agricultural University
- Henan University of Technology (former Zhengzhou Institute of Technology)
- Henan University of Finance and Economics
- Zhongyuan Institute of Technology
- Zhengzhou University of Light Industry
- Zhengzhou Institute of Aeronautical Industry Management
- North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power
- Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Henan Textile University (河南纺织专科学校)
- Zhengzhou Normal University
- Zhengzhou Institute of Technology (former Zhongzhou University, not to be confused with Henan University of Technology)
Military
- PLA Information Engineering University (中国人民解放军信息工程大学)
- Air Defense Force Command Academy
Private
- Zhengzhou College of Economics
- Huanghe S&T University
- Sias International University
- Shengda Economics, Trade and Management College of Zhengzhou
Notable people

- Zichan (子产; ? - 552 BC), a politician and philosopher of the State of Zheng during the Spring and Autumn period.
- Lie Yukou (列子; c. 450 BC - ?), known as Liezi, a Taoism philosopher.
- Shen Buhai (申不害; c. 400 BC - c. 337 BC), a politician and philosopher in Legalism.
- Han Fei (韩非; c. 280 BC - 233 BC), also known as Han Feizi, an influential political philosopher of the Warring States Period.[51]
- Du Fu (杜甫; 712–770), a Tang dynasty poet, born in Gongyi, now a county under the administration of Zhengzhou.
- Bai Juyi (白居易; 772–846), a Tang dynasty poet widely known for his poems featuring realism, born in Xinzheng.
- Li Shangyin (李商隐; c. 813–858), a late Tang dynasty poet, born in Xingyang.
- Gao Gong (高拱; 1512–1578), a politician of the Ming dynasty, born in Xinzheng.
- Wei Wei (魏巍; 1920–2008), a modern era writer, widely known in China for his works on the Chinese Volunteer army's participation of the Korean War.
- Chang Xiangyu (常香玉; 1923–2004), a Yu opera actress.
- Li Na (李娜; born 1963), a Chinese folk singer.
- Li Jianying (李剑英; 1964-2006), hero pilot.
- Shi Yigong (施一公; born 1967), a biophysicist, president of Westlake University and the former vice president of Tsinghua University.
- Hai Xia (海霞; born 1972), a Chinese news anchor for China Central Television, the main state announcer of China.
- Deng Yaping (邓亚萍; born 1973), a four-time table tennis Olympic champion.
- Liu Yang (刘洋; born 1978), a pilot and astronaut who became the first Chinese woman in space.
- Tie Ya Na (帖雅娜; born 1979), a table tennis player representing Hong Kong, born in Zhengzhou.
- Sun Tiantian (孙甜甜; born 1981), a former professional tennis player on WTA Tour and 2004 Olympic Tennis champion (women's doubles with Li Ting), the first Chinese player to win a mixed doubles Grand Slam title at the 2008 Australian Open with Nenad Zimonjic.
- Du Wei (杜威; born 1982), a professional footballer and the former captain of China national football team.
- Jiang Xin (蒋欣; born 1983), an actress, famous for her role as Consort Hua in the TV series Empresses in the Palace.
- Gao Lin (郜林; born 1986), a professional footballer.
- Shi Xiaolong (释小龙; born 1988), an actor.
- Ning Zetao (宁泽涛; born 1993), a competitive swimmer and gold medal winner at 2014 Asian Games and 2015 World Aquatics Championships.
Politics
The current mayor is Wu Tianjun from February 2006.

List of the CPC Party Chiefs of Zhengzhou:
- Gu Jingsheng (谷景生): October 1948-December 1948
- Wu Defeng (吴德蜂): December 1948-June 1949
- Zhao Wucheng (赵武成): June 1949 - April 1953
- Song Zhihe (宋致和): April 1953-August 1956
- Wang Lizhi (王黎之): August 1956-January 1968
- Wang Hui (王辉): March 1971-January 1974
- Zhang Junqing (张俊卿): January 1974-December 1977
- Yu Yichuan (于一川): December 1977-December 1979
- Li Baoguang (李保光): December 1979-May 1983
- Jiang Jinfei (蒋靳非): May 1983-September 1984
- Yao Minxue (姚敏学): September 1984-August 1987
- Cao Lei (曹磊): August 1987-July 1990
- Song Guochen (宋国臣): July 1990-May 1992
- Zhang Deguang (张德广): May 1992-December 1995
- Wang Youjie (王有杰): December 1995-June 2001
- Li Ke (李克): June 2001-
Sister cities
Zhengzhou is twinned with:
| Country | City | Since |
|---|---|---|
| October 12, 1981[52] | ||
| Richmond, Virginia | September 14, 1994[53] | |
| April 9, 1995[54] | ||
| Jinju | July 25, 2000[55] | |
| August 27, 2001[56] | ||
| Irbid | January 31, 2002[57] | |
| April 11, 2002[58] | ||
| November 17, 2003[59] | ||
| April 12, 2006[60] | ||
| April 27, 2007[61] | ||
| June 12, 2014[62] |
See also
Notes
- 郑州常住人口937.8万人 (in Chinese). Zhengzhou Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2016-03-13.
- "Illuminating China's Provinces, Municipalities and Autonomous Regions". PRC Central Government Official Website. Archived from the original on 2015-07-05. Retrieved 2014-05-17.
- 国家发展改革委关于支持郑州建设国家中心城市的复函 (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 2018-06-05. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- 郑州定位国际性综合交通枢纽 年内实施52个交通项目-新华网. Xinhua News. Archived from the original on 2018-03-28. Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- "China's Central Plains Region". Stratfor. Archived from the original on 2018-09-13. Retrieved 2018-03-27.
- 刘云中, 国务院发展研究中心发展战略和区域经济研究部部长、研究员 侯永志. 中原经济区规划逻辑 - 国务院发展研究中心. www.drc.gov.cn. Archived from the original on 2018-03-27. Retrieved 2018-03-27.
- 郑州市情. shangdu.com (in Chinese). 2009-05-25. Archived from the original on 2012-07-15. Retrieved 2011-09-26.
- 第1000班郑欧班列满载"中国造"驰往汉堡_新华丝路. silkroad.news.cn. Archived from the original on 2018-03-27. Retrieved 2018-03-27.
- 郑州将开3条国际航线 直达五大洲将成为现实 _大豫网_腾讯网. qq.com Henan (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 2018-03-28. Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- 河南省人民政府门户网站 河 南 简 介. Henan Province People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-03-28. Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- "The Diplomat". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 2018-03-28. Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- 郑州市统计局. Zhengzhou Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2016-02-13.
- 郑州:人口过千万 总量破万亿_滚动新闻_中国政府网. Government of the People's Republic of China. Retrieved 2019-02-20.
- 2018年郑州市经济运行基本情况 - 郑州市统计局. Zhengzhou Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 2019-02-28. Retrieved 2019-02-20.
- 郑州市16个县(市)、区2017年GDP公布 金水区GDP最高 超1200亿元-大河网. news.dahe.cn. Archived from the original on 2018-02-24. Retrieved 2018-03-27.
- 素芳, 焦 (18 May 2011). 郑州常住人口860多万 这是个啥概念. 河南商报 (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 21 July 2015. Retrieved 17 July 2015.
- "Supersized cities: China's 13 megalopolises". Archived from the original on 2012-07-21. Retrieved 2012-07-23.
- 关于支持郑州建设国家中心城市的复函(发改规划[2017]154号). ghs.ndrc.gov.cn (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 2018-05-05. Retrieved 2018-03-27.
- Liu Yue (劉岳) (2007). "Investigating the Reasons for Tang of Shang's Fortifications at Zhengzhou" 商湯在鄭州筑城建都的原因追蹤)《尋根》 [Investigating the Reasons for Tang of Shang's Fortifications at Zhengzhou]. 尋根 (in Chinese). Zhengzhou Publishing. 5. ISSN 1005-5258.
- A H Dani (1992), Critical Assessment of Recent Evidence on Mohenjo-daro, Second International Symposium on Mohenjo-daro, 24–27 February.
- 豫现3600年前世界大都市 [Henan's 3,700 Year-old Metropolis]. Weiwenpo.cn Henan (in Chinese). December 24, 2010. Retrieved February 7, 2012.
- 郑州市地方史志编纂委员会 [Zhengzhou Region Historical Records Committee Compilation] (in Chinese). Zhongzhou Antiquarina Book Publishing (中州古籍出版社). 1999. ISBN 7-5348-1869-9.
- 隞都郑州与郑州小双桥遗址 (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 2012-04-03. Retrieved 2011-09-26.
- Epstein, Israel (2005). History Should Not Be Forgotten. China Intercontinental Press. p. 70. ISBN 978-7-5085-0694-4.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on March 18, 2013. Retrieved February 18, 2013.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- 经书威、郑州市地方史志办公室 (2002). 《郑州大辞典》. 中州古籍出版社. ISBN 978-7-5348-1822-6.
- 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年) (in Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 2013-10-16.
- 中国气象数据网 - WeatherBk Data. China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 2017-09-23. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- 郑州城市介绍以及气候背景分析. Weather China (in Chinese). 中国气象局公共气象服务中心. Archived from the original on 31 July 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2015.
- China's Shaolin Temple, Danxia Landform Added To World Heritage Sites
- 2018年中国城市GDP排名出炉!(附简析)_同比. www.sohu.com. Archived from the original on 2019-02-25. Retrieved 2019-02-24.
- 2017中国城市GDP排名出炉!. www.sohu.com. 2018-01-31. Archived from the original on 2018-03-27. Retrieved 2018-03-27.
- (in Chinese) General information of Zhengzhou Archived May 25, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Zhengzhou Government official website.
- Henan Shaolin Auto Co., Ltd. Archived June 22, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-02-02. Retrieved 2011-09-23.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Barboza, David (2016-12-29). "How China Built 'iPhone City' With Billions in Perks for Apple's Partner". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2017-01-11. Retrieved 2017-01-11.
- http://www.ystar.net.cn/. 思念食品. www.synear.cn. Archived from the original on 2016-12-16. Retrieved 2017-01-11.
- "Zhengzhou New Area". Archived from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 1 November 2009.
- "郑州的往世今生:50年考古确认中国第一古都" 新浪网. Sina News (in Chinese). 2005-09-22. Archived 2015-02-07 at the Wayback Machine
- International Urban Cooperation (IUC) Asia. "Zhengzhou, China". International Urban Cooperation (IUC) Asia. Archived from the original on 23 February 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2019.
- "RightSite.asia | Zhengzhou Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone". Archived from the original on 2010-06-04. Retrieved 2010-06-01.
- "RightSite.asia | Zhengzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone". Archived from the original on 2010-06-12. Retrieved 2010-06-01.
- "RightSite.asia | Zhengzhou Export Processing Area". Archived from the original on 2010-06-11. Retrieved 2010-06-01.
- 郑州地铁获国务院批准 每公里成本近6亿今年开工 河南日报大河网. Dahe.cn (in Chinese). 2009-02-13. Archived from the original on 2010-01-21. Retrieved 2009-02-18.
- 地铁未来将出现在郑州市 中广网. CNR.cn (in Chinese). 2009-02-13. Archived from the original on 2011-10-01. Retrieved 2009-02-18.
- 郑州轨道交通2015~2050规划出炉 21条线路公布. news.ifeng.com. Archived from the original on 2017-12-03. Retrieved 2018-03-27.
- 发展历程. www.zhengzhoubus.com. Archived from the original on 2018-04-13. Retrieved 2018-04-13.
- "Zhengzhou, City Information of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou Capital City of Henan Province". www.chinatoday.com. Archived from the original on 2015-05-11. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- 郑州北站---亚洲最大的列车编组站 [Zhengzhou North Railway Station -- Asia's largest marshalling yard]. huochepiao.com. 2016-04-08. Archived from the original on 2016-05-31. Retrieved 2016-05-17.
- 【货邮突破50万吨】郑州机场首成我国中部机场“双冠王”. www.sohu.com (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 2018-04-03. Retrieved 2018-04-03.
- 韩非 - 郑州市人民政府. Zhengzhou People's Government. Archived from the original on 2015-11-25. Retrieved 2015-11-10.
- 日本埼玉市 [Saitama City, Japan]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 美国里士满市 [Richmond, United States]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 罗马尼亚克鲁日·纳波卡市 [Cluj-Napoca, Romania]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 韩国晋州市 [Jinju, South Korea]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 纳比米亚马林塔尔市 [Mariental, Namibia]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 约旦伊尔比德市 [Irbid, Jordan]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 俄罗斯萨马拉市 [Samara, Russia]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 巴西若茵维莱市 [Joinville, Brasil]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 德国什未林市 [Schwerin, Germany]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 保加利亚舒门市 [Shumen, Bulgaria]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- 白俄罗斯莫吉廖夫市 [Mogilev, Belarus]. Foreign and Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of Zhengzhou Municipal People's Government. Archived from the original on 2018-11-14. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zhengzhou. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Zhengzhou. |
- Zhengzhou Government website (in Chinese)
.jpg)

