Huizhou
Huìzhōu (Chinese: 惠州, Hakka: Fuichû, Cantonese: Wai Jau) is a city in southeast Guangdong Province, China. It forms part of the Pearl River Delta megalopolis. Huizhou borders the provincial capital of Guangzhou to the west, Shenzhen and Dongguan to the southwest, Shaoguan to the north, Heyuan to the northeast, Shanwei to the east, and Daya Bay of the South China Sea to the south. The city has about 4.6 million inhabitants and is administered as a prefecture-level city.
Huizhou 惠州市 | |
|---|---|
 Top:Hejiang Attic, Huizhou West Lake, Middle:Jiangbei skyline, Huicheng District at night Bottom:Shuangyue Bay | |
| Motto(s): A city to benefit people (惠民之州) | |
| |
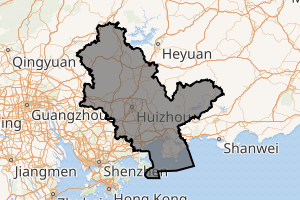
 Location of Huizhou in Guangdong | |
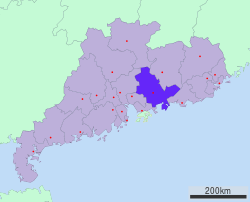
 Huizhou Location in China | |
| Coordinates (Huizhou government): 23°06′43″N 114°24′58″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guangdong |
| City | 1988 |
| Municipal seat | Huicheng District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Secretary | Li Yiwei (李贻伟) |
| • Mayor | Liu Ji (刘吉) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 10,922 km2 (4,217 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,672 km2 (1,032 sq mi) |
| • Coastline | 223.6 km2 (86.3 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 15 m (49 ft) |
| Population (2010 census[1]) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,598,402 |
| • Density | 420/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,344,634 |
| • Urban density | 880/km2 (2,300/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 44,778,513 |
| Time zone | UTC+08:00 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 516000 |
| Area code(s) | 0752 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-GD-13 |
| GDP | ¥383.1 billion (2017) $57 billion ($0.11 trillion, PPP) |
| GDP per capita | ¥80,222 (2017) $11,882($22,862, PPP) |
| Licence Plate | 粤L |
| Website | www |
| Huizhou | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"Huizhou", as written in Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 惠州 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Waichow | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
In April 2018, the China Daily announced that the world's first automatic rail road was currently under construction between Dongguan and Huizhou. As a pilot project, it would contain ten railway stations, driverless trains and robotic assistance for passengers with luggage and tickets.[2]
History
During the Song dynasty, Huizhou was already a prefectural capital of the Huiyang prefecture, and it was also the cultural center of the region.[3]
The West Lake in Huizhou, formerly known as The Feng Lake. At the age of 59, Su Shi was taken to Huizhou by the imperial government. When he came to visit the Feng Lake in Huizhou, he found it located in the west of the city and was as beautiful as West Lake in Hangzhou. Therefore, he renamed it as the West Lake. In order to solve the traffic problems on both sides of the West Lake, he invested to help build two bridges. Later generations named bridges as the bridge Su Di to commemorate his achievements. And the two bridges in the West Lake becomes one of the eight scenic spots in the West Lake, called "Su Di Play Moon".[4]
Huizhou used to be a prosperous region, specializing in commerce and trading; this changed during the 20th century due to wars.[5] After the 1980s, Huizhou followed the path of nearby Shenzhen and Dongguan and developed as a manufacturing base.
Economy
Located in the Pearl River Delta, Huizhou is one of the 9 prefecture-level cities in the Pearl River Delta Economic Zone (include Huizhou urban area, Huiyang, Huidong and Boluo only). TCL, a major TV and multinational consumer electronics company is headquartered in Huizhou.
Development zones
Huizhou Dayawan Economic and Technological Development Zone
Huizhou Daya Bay Economic and Technological Development Zone (DBETDZ) was approved by the State Council in 1993. It had an initial area of 9.98 km2 (3.85 sq mi), and in 2006, the State Council expanded the zone to 23.6 km2 (9.1 sq mi) in three phases.
Industries encouraged in the zone include Automobile Production/Assembly, Chemical Production and Processing, Electronics Assembly & Manufacturing, and others.[6]
Huizhou Export Processing Zone
Huizhou Export Processing Zone was approved by Guangdong Provincial Government as a subzone of DBETDZ in June 2005. The planned area was 3 km2 (1.2 sq mi). The zone was considered suitable for companies focusing on electronics, auto parts, textiles and chemicals.[7]
Huizhou Zhongkai High-tech Industrial Development Zone
Huizhou Zhongkai High-tech Industrial Development Zone is connected with Shenzhen, Guangzhou and Dongguan by Huizhou-Shenzhen Highway, Guangzhou-Huizhou Highway and Dongguan-Huizhou Highway. Beijing-Kowloon Railway and Huizhou-Aotou Railway also run through the zone, linking it with Beijing, Hong Kong, and other cities along the railway. Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport is a one-and-a-half hour drive from the zone.
Huizhou Zhongkai HIDZ has established electronics, information technology and optical-, mechanical- and electronic-integration as its major industries. It also encourages investment in new materials, telecommunications, and other high-tech industries. The zone is one of the National Electronic Information Industry Bases and National Video and Audio Products Parks in China.
Administration
The prefecture-level city of Huizhou administers 5 county-level divisions, including 2 districts and 3 counties.
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010 census) |
Area (km2) |
Density (/km2) |
| Huicheng District | 惠城区 | Huìchéng Qū | 1,579,818 | 1,488.45 | 1,061 |
| Huiyang District | 惠阳区 | Huìyáng Qū | 764,816 | 1,205.44 | 664 |
| Boluo County | 博罗县 | Bóluó Xiàn | 1,038,198 | 2,855.11 | 364 |
| Huidong County | 惠东县 | Huìdōng Xiàn | 908,390 | 3,526.73 | 258 |
| Longmen County | 龙门县 | Lóngmén Xiàn | 307,180 | 2,267.2 | 135 |
Transport
Huicheng urban center of Huizhou is served by the Jingjiu Railway (also known as the Guangmeishan Railway in Guangdong) with two stations: Huizhou West and Huizhou. Huizhou itself is vast as Los Angeles County with sparse rail service as compared with bay peer cities.
Huizhou Pingtan Airport reopened in 2015. Additionally the town is about a one and one half-hour drive by bus from Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport.[8] There are also coach bus services connecting Huizhou with Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA).[9]
A mass rapid transit linking it to Shenzhen was under construction as of 2011.
Language
The main languages spoken in Huizhou are Hakka Chinese (Huiyang dialect), Huizhou dialect, Hokkien dialect, and Cantonese.
Military
Huizhou is headquarters of the 42nd Group Army of the People's Liberation Army, one of the two group armies that comprise the Guangzhou Military Region responsible for the defense of China's southern coast and its border with Vietnam.
Education
Educational facilities in Huizhou include:
- Huizhou University
- Huizhou Radio and Television University
- Huizhou Nanshan School
- Medi's International school
Sport
Huizhou is a well-known city of sports in China with the opening of Huizhou Olympic Stadium in 2010.
Climate
Huizhou has a dry-winter humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification: Cwa).
| Climate data for Huizhou (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.2 (72.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.3 (84.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.2 (88.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
20.4 (68.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
11.7 (53.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
19.2 (66.6) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.0 (75.2) |
20.7 (69.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
11.6 (52.9) |
18.8 (65.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 37.3 (1.47) |
62.8 (2.47) |
87.0 (3.43) |
202.0 (7.95) |
226.7 (8.93) |
323.6 (12.74) |
255.1 (10.04) |
276.1 (10.87) |
173.0 (6.81) |
66.6 (2.62) |
28.2 (1.11) |
33.4 (1.31) |
1,771.8 (69.75) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 6.3 | 10.6 | 12.6 | 14.5 | 18.3 | 18.7 | 17.2 | 18.4 | 13.0 | 6.6 | 5.1 | 4.8 | 146.1 |
| Source: Weather China | |||||||||||||
Tourism

Daya Bay
Daya Bay is located to the southeast of Huizhou City, on the South China Sea, with waters covering an area of nearly 500 km2 (190 sq mi). There are nearly 100 islands and reefs in the bay. The climate is described as a typical subtropical oceanic climate, with temperatures averaging 21.8 degrees over the year.
- Beach Spa Huizhou's seashore hot springs are filled with geothermal minerals, and boast a temperature of nearly 70 degrees Celsius.
- Sea-level city The Sea city was built in the 18th year of the Ming dynasty, under the Hongwu Emperor (AD 1385), giving it a history of over 600 years. It is found south of the Five Ridges.
- Elephant Head Mountain Elephant head mountain scenic area is located in the south of Boluo County, 18 kilometres from the Huizhou city area, and covers an area of 33 km2 (13 sq mi). It was formed of igneous rock in the Cretaceous period and has a main peak of 1023 meters above sea level. The mountain bedrock forms a unique "stone egg" landscape.
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Huizhou is twinned with:
.svg.png)





References
- "China: Administrative Division of Guăngdōng / 广东省". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- nan, Zhong (2 May 2018). "Automated railways being tested". China Daily. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- Ezra F. Vogel (October 1990). One Step Ahead in China: Guangdong Under Reform. Harvard University Press. pp. 225–226. ISBN 978-0-674-63911-9.
- 黄建萍 (1997). 东坡到处有西湖. 江苏政协 (3): 32–32.
- "China's Villages Are Dying. A New Film Asks If They Can Be Saved". NPR.
- "Huizhou Dayawan Economics Technology Development Zone". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- "Guangdong Huizhou Export Processing Zone". Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- "Guangdong Traffic." Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport. Retrieved on May 9, 2018.
- "Mainland Coaches." Hong Kong International Airport. Retrieved on May 8, 2018.
- Wainwright, Oliver (7 January 2013). "Seeing double: what China's copycat culture means for architecture". The Guardian. London: Guardian News and Media Limited. Retrieved 2014-11-15.
- "Sister Cities". Retrieved 26 February 2016.