Taizhou, Zhejiang
Taizhou (pronunciation in PRC Standard Mandarin: [tʰái.ʈʂóu] (![]()
Taizhou 台州市 Te Tsiu | |
|---|---|
 View of Taizhou | |

| |
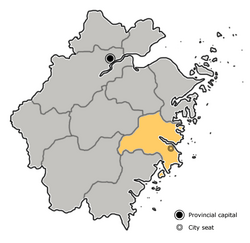 Location of Taizhou City in Zhejiang | |
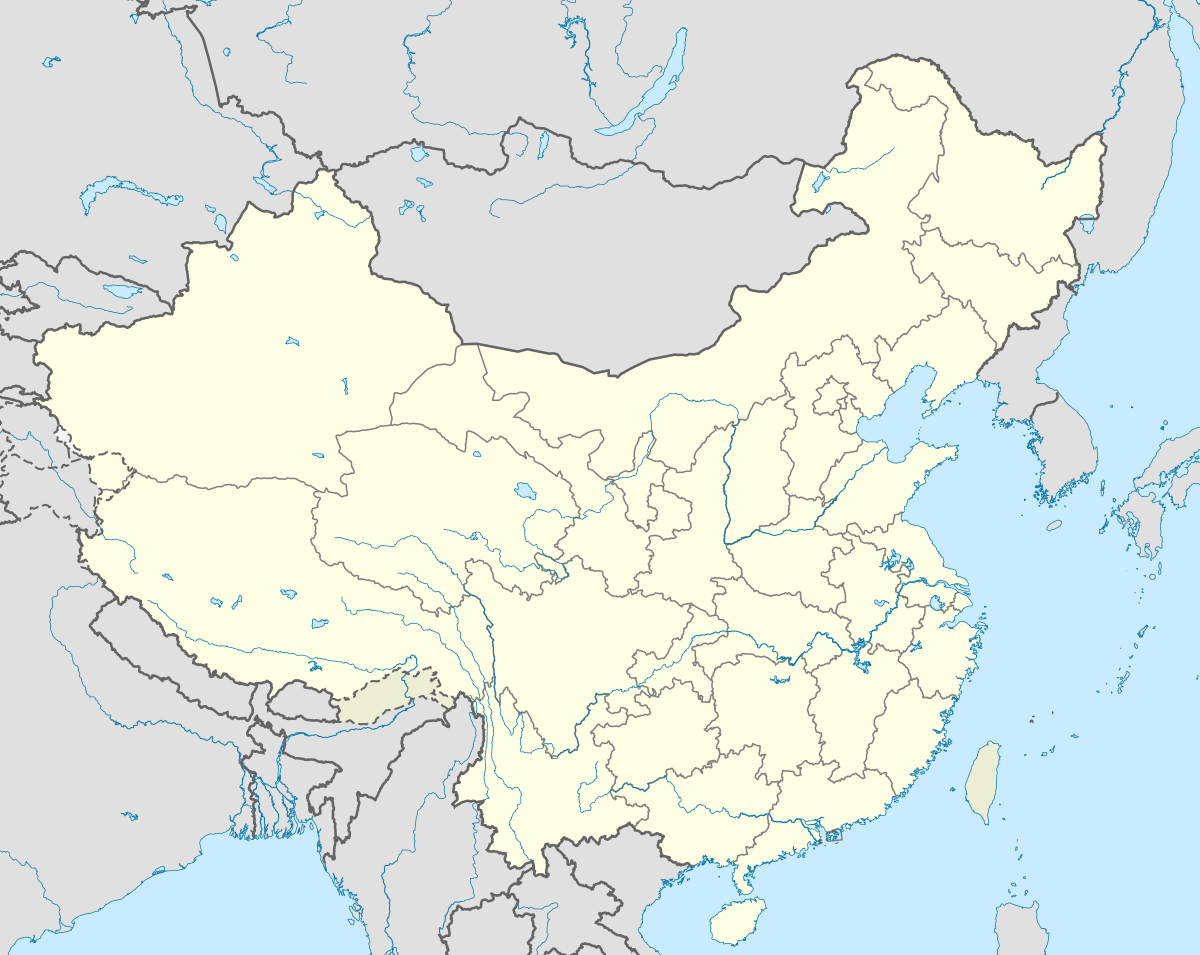 Taizhou Location in China | |
| Coordinates (Taizhou municipal government): 28°39′21″N 121°25′15″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Zhejiang |
| County-level divisions | 9 |
| Municipal seat | Jiaojiang District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Secretary | Wu Weirong (吴蔚荣) |
| • Mayor | Zhang Bing (张兵) |
| Area | |
| • Land | 9,411 km2 (3,634 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,536 km2 (593 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,372 km2 (916 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,382 m (4,534 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2010 census[1]) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 5,968,838 |
| • Urban | 1,902,510 |
| • Urban density | 1,200/km2 (3,200/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 3,269,304 |
| • Metro density | 1,400/km2 (3,600/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 318000, 317000 |
| Area code(s) | 576 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-ZJ-10 |
| GDP 2018[2] | ¥487.5 billion |
| GDP per capita 2018 | ¥79541 (USD 12020) |
| License Plate Prefix | 浙J |
| Website | www |
Mei (Prunus mume), Camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora)City flowers Sweet Osmanthus (Osmanthus fragrans) The Taizhou urban area commonly refer as the whole of Jiaojiang, Huayan, Luqiao districts and the metropolitan Taizhou includes Wenling City, citation is need for the original urban and metropolitan data. | |
| Taizhou | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Taizhou", as written in Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 台州 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | PRC Standard Mandarin: ROC Standard Mandarin: Táizhōu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wu | T'e-tsiu (Taizhounese) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Taichow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Etymology
Taizhou's name is believed to derive from nearby Mount Tiantai.
History
Five thousand years ago, the ancestors of the modern inhabitants began to settle in this area. During the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties, when the Chinese state was largely confined to the Yellow River basin, the area of present-day Taizhou was part of Dong'ou. Following the 3rd-century BC conquests of the Qin Empire, a settlement in the area was known as Huipu Town. It was initially included in the Minzhong Prefecture, but then moved to Kuaiji during the Han.
On August 22, 1994, Taizhou Municipality was set up in place of Taizhou Prefecture and approved by the State Council. In 1999, Taizhou was approved by the State Council to be a leading city in Zhejiang's urbanization structure and the center of sub zone of the first-class economy. Approved by the National Development and Reform Commission, Taizhou formally became one of the 16 cities of Yangtze River Delta area on Aug.15, 2003.
Demographics
At the time of 2010 census, the whole population of Taizhou, including the whole prefecture-level city and subsidiary counties was 5,968,838 with 3,269,304 in the emerging built-up area made of 3 urban districts, Jiaojiang, Huangyan, Luqiao and Wenling City largely being urbanized.
Administration
The prefecture-level city of Taizhou currently administers 3 districts, 3 county-level cities and 3 counties.
| Map | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Taizhou Dialect |
| Jiaojiang District | 椒江区 | Jiāojiāng Qū | Ciaukong Khiu |
| Huangyan District | 黄岩区 | Huángyán Qū | Wongniae khiu |
| Luqiao District | 路桥区 | Lùqiáo Qū | Lugiau khiu |
| Linhai City | 临海市 | Línhǎi Shì | Linghe Zy |
| Wenling City | 温岭市 | Wēnlǐng Shì | Uengling Zy |
| Yuhuan City | 玉环市 | Yùhuán Shì | Niukwae Zy |
| Sanmen County | 三门县 | Sānmén Xiàn | Saemeng Yoe |
| Tiantai County | 天台县 | Tiāntāi Xiàn | Thiethai Yoe |
| Xianju County | 仙居县 | Xiānjū Xiàn | Shiekiu Yoe |
Geography
At 651 kilometres (405 mi), Taizhou has a long coastline dotted with numerous islands; the largest one is Yuhuan Island in the south.[3] Coastal areas in the east tend to flat, with an occasional hill. Eastern and northern parts of Taizhou are mountainous, with Yandangshan Mountains in the southwest, Kuocang Mountains (Chinese: 括苍山; pinyin: Kuòcāng Shān) in the west, and Mount Tiantai in the northwest. The highest point of Taizhou is Mishailang (Chinese: 米筛浪; pinyin: Mǐshāilàng), a 1,382.4 metres (4,535 ft) peak in the Kuocang Mountains, and also the highest point in the east of the Zhejiang Province.[3]
Climate
| Taizhou | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Taizhou has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) with four distinctive seasons. Occasionally struck by typhoons in the summers, the climate characterised by hot, humid summers and drier and cold winters with occasional snow. The mean annual temperature is 16.6 to 17.5 °C (61.9 to 63.5 °F) from north to south east coastal area, while mean annual rainfall ranges from 1,185 to 2,029 millimetres (46.7 to 79.9 in).
| Climate data for Taizhou, 2013-2015 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.2 (54.0) |
12.4 (54.3) |
17.0 (62.6) |
21.3 (70.3) |
25.5 (77.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.3 (90.1) |
28.8 (83.8) |
25.0 (77.0) |
19.4 (66.9) |
12.8 (55.0) |
22.3 (72.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 8.4 (47.1) |
9.1 (48.4) |
13.1 (55.6) |
17.3 (63.1) |
22.1 (71.8) |
25.6 (78.1) |
29.1 (84.4) |
28.8 (83.8) |
25.7 (78.3) |
21.3 (70.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
9.1 (48.4) |
18.8 (65.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.6 (40.3) |
5.9 (42.6) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.2 (55.8) |
18.8 (65.8) |
22.6 (72.7) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
22.5 (72.5) |
17.7 (63.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
5.4 (41.7) |
15.3 (59.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 37.6 (1.48) |
79.7 (3.14) |
79.1 (3.11) |
74.5 (2.93) |
178.3 (7.02) |
262.3 (10.33) |
131.8 (5.19) |
260.9 (10.27) |
145.6 (5.73) |
101.4 (3.99) |
89.5 (3.52) |
116.2 (4.57) |
1,556.8 (61.29) |
| Source 1: Tianqi.com,[4] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Jiaojiang Agricultural and Forestry Website[5] | |||||||||||||
Economy and industry

Taizhou is one of the birthplace of China's private economy in the early days of economic reforms in China. It is the cradle of the Chinese private economy,[6] the name of Taizhou Model[7] is after it. It is the 4th most populous, and the 4th largest industrial prefecture-level city in Zhejiang Province as of 2011.
Chinese automotive manufacturing company Geely[8] was founded in Taizhou which completes its acquisition of Volvo Cars in 2010, is one of China's top ten auto manufacturers.
Chinese auto parts manufacturer based Yuanhuan[9] was one of China auto parts manufacturer based,here can produce all auto parts for vehicles.
The largest HVAC fan company Yilida[10] is also located in Taizhou. It is listed on Shenzhen Stock Exchange (Stock #002686) and has acquired Fulihua fan company in Suzhou in 2012.
Taizhou is also one of the most important Mandarin, Loquat, Wendan(A kind of Pomelo), Myrica rubra producers in China. Other agricultural product including Rice, Canola, edible Wild rice stems or Zizania latifolia, Eddoe, Water chestnut, Bamboo


 Wendan
Wendan

 Wild rice stems
Wild rice stems


Infrastructure and transport


Historically, Taizhou was relatively inaccessible by road. This has changed due to large infrastructure restructuring in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Presently, Taizhou is served by the S1 Ningbo–Taizhou–Wenzhou Expressway (甬台温高速公路), which is a segment in the north–south G15 Shenyang–Haikou Expressway, linking the city with Ningbo, Shanghai in the north and Wenzhou in the south; the Shangsan Expressway links Taizhou with the provincial capital Hangzhou. Taizhou Airport was once named Huangyan Luqiao Airport (IATA:HYN) in the city's Luqiao District serves daily flights to Beijing and Chengdu and regular flights to other major Chinese cities.
In September 2009, the high-speed rail line, Ningbo–Taizhou–Wenzhou railway, opened. There are several stations in the prefecture boundaries of Taizhou. The station serving the urban core is in Huangyan District and is called Taizhou railway station.
In August 2016 it was announced a second Taizhou train station will be constructed. The line will connect Jiaojiang district to Hangzhou in just 60 minutes with the journey to Shanghai being cut to just two hours[11]
Language and culture
Like the majority of areas in Zhejiang, most people from Taizhou speak a dialect of Wu Chinese, known as Taizhou Wu. It is not mutually intelligible with Mandarin Chinese, and only partially intelligible with Shanghainese. There is also a small portion of Min Nan and Wenzhou dialect speakers in the southern regions. None of these three languages are mutually intelligible amongst each other, but the linguistic diversity of some regions has resulted in a segment of the population becoming fluent in speaking up to four languages, when Mandarin is included.
The city's people are reputed to be industrious and business-minded, although not to the same degree as neighboring Wenzhou. Many people from the area have migrated abroad after economic reforms began in China in 1978. The city's seafood is of note.
Education
- Taizhou College
Notable people
- Ji Gong (济公)
- Li Shufu (李书福)
- Fan Yilin- 2015 & 2017 Uneven Bars World Gymnastics Champion
- Zhou Jieqiong (周洁琼; Korean: 주결경), - Produce 101 Contestant, member of I.O.I
- Xu Jiaqi (许佳琪) - SNH48 Member of Team SII, member of sub-unit 7SENSES
Tourism
- Linhai Ancient Great Wall, the only Great Wall in southern China.
- Guoqing Temple, Mountain Tiantai
The Guoqing Temple where the Tiantai (Chinese and Japanese: 天台宗; pinyin: tiāntāi zōng; ), an important school of Buddhism in China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam originates, is located here. In Japan the school is known as Tendai, and in Korea it is known as Cheontae.


Sister cities


References
- http://www.citypopulation.de/php/china-zhejiang-admin.php
- 2018 GDP of Taizhou
- Location Taizhou Information Center, Taizhou Government
- "Weather History for Taizhou". tianqi.2345.com. Retrieved 2016-02-26.
- "Weather Information for Agriculture(Jiaojiang, Taizhou)". Retrieved 2016-02-26.
- on Endogenous Development Mode of Private Economy
- Model: Institutional Innovation and the Development of Private Economy
- About Geely
- About Yuhuan
- http://www.shanghaidaily.com/city-specials/hangzhou/Railway-moves-ahead/shdaily.shtml
- "Internationale Beziehungen". hanau.de (in German). Hanau. Retrieved 2019-11-29.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Taizhou, Zhejiang. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Taizhou (Zhejiang). |
.png)