Pomoan languages
The Pomoan, or Pomo /ˈpoʊmoʊ/,[2] languages are a small family of seven languages indigenous to northern California spoken by the Pomo people, who formerly occupied the valley of the Russian River and the Clear Lake basin. Four languages are extinct, and all surviving languages except Kashaya have fewer than ten speakers.
| Pomoan | |
|---|---|
| Pomo | |
| Ethnicity | Pomo people |
| Geographic distribution | California |
| Linguistic classification | Hokan ?
|
| Glottolog | pomo1273[1] |
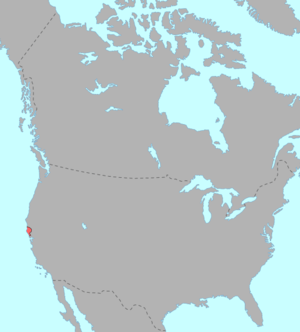 Pre-contact distribution of Pomoan languages | |
Geographical distribution
John Wesley Powell, who was the first to define the extent of the family, noted that its boundaries were the Pacific Ocean to the west, Wintuan territory in the Sacramento Valley to the east, the head of the Russian River to the north, and Bodega Head and present-day Santa Rosa to the south (Powell 1891:87-88). Only Northeastern Pomo was not contiguous with the other Pomoan languages, being separated by an intervening region of Wintuan speakers.
Internal relationships of languages
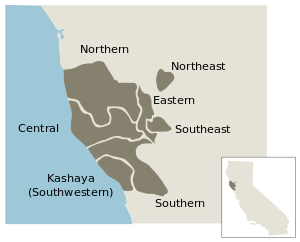
Pomoan is a family of seven languages. Their relationship to one another was first formally recognized by John Wesley Powell, who proposed that they be called the "Kulanapan Family" (Powell 1891). Like many of Powell's obscure nomenclatural proposals, particularly for California languages, "Kulanapan" was ignored. In its place, Pomo,[3] the term used by Indians and Whites alike for Northern Pomo was arbitrarily extended to include the rest of the family. It was thus as "Pomo" that all seven languages were first systematically identified by Samuel Barrett (1908). To avoid complications, Barrett named each of the Pomoan languages according to its geographic position ("Northern Pomo," "Southeastern Pomo," etc.). This naming convention quickly gained wide acceptance and is still in general use, except for the substitution of "Kashaya" for Barrett's "Southwestern Pomo". Regrettably, however, Barrett's geographical language names often lead those unfamiliar with the Pomoan languages to the misconception that they are dialects of a single "Pomo" language.
Various genetic subgroupings of the family have been proposed, although the general outlines have remained fairly consistent. The current consensus view (cf. Mithun 1999) favors the tree presented in Oswalt (1964), shown below.
- Southeastern Pomo
- Eastern Pomo †
- Northeastern Pomo †
- Western
- Northern Pomo †
- Southern
- Central Pomo †
- Southern Pomo
- Kashaya (Southwestern Pomo)
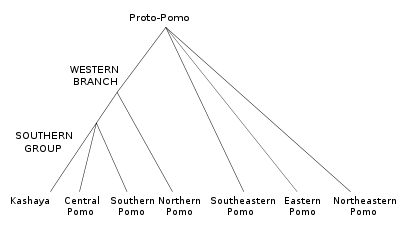
Essentially identical versions of this classifications are presented in Oswalt and McLendon's "Introduction" to the Pomo chapters in Heizer, ed. (1978) and in Campbell (1997). The most important dissenter was Abraham M. Halpern, one of the few linguists since Barrett's time to collect comparative data on all of the Pomoan languages. Halpern's classification differed from Oswalt's mainly in the placement of Northeastern Pomo. Instead of considering it an independent branch of the family, Halpern grouped it with the languages of Oswalt's "Western" branch, suggesting the possibility that Northeastern Pomo represents a recent migration of a Northern Pomo subgroup (Halpern 1964; Golla 2011:106-7).
Proto-language
| Proto-Pomo | |
|---|---|
| Reconstruction of | Pomoan languages |
Proto-Pomo reconstructions by McLendon (1973):[4]
gloss Proto-Pomo acorn *biʔdú afraid, to be *kʰiˑyá, *kʰiyáˑ angelica *baʔk̓ówa arm *ʔiˑxál(ʸ) armpit *daˑyamá- arrow *hic̓úˑ arrow *baṭʰíy ashes *hiˑnó(x̣ò) back *bak̓oˑ backbone *hiʔk̓i, *k̓idí bark (of tree) *qʰahwálʸ basket, sp. *c̓óˑy basket, sp. *kʰiṭúˑ basket, pack (open-woven) *buhqʰál basket, pack (close-woven) *buhkí ? basket, pounding *miké bear *buˑṭáqa(lʸ) bear, brown *limá(ˑ) ? bee *koʔó(lʸ), *kaʔolʸó behind, rear *siˑlí, *silíˑ belly *ʔuhqʰá(ˑ) below *ʔiyów big, sg. *bahṭʰé, *bahṭʰén big, pl. *ʔahṭʰíy, *ʔahṭíynʸ bird *c̓iyíta ~ *c̓ihtá bite, to *qaˑné- blackfish *xaqʰál blanket *ʔihxí(ˑ) blood *baˑláy body *xiʔbá bone *ʔihyá(ˑ) bow *xihmúy, *xi(ʔ)mi brains, head, protuberance *hoʔt̓ó bread, acorn *qʰaṭó(ˑ) break wind *ʔihpʰéṭ- breast, milk *xiʔdónʸ brother, mother's *cúˑ-c̓i ~ *céˑ-c̓i brother, older *méqi brother, father's younger *kéqi brother-in-law (i.e., wife's brother ?) *mahá-, *háˑ buckeye *bahxá buckeye nuts when soaked *dihsá bumblebee *kʰeˑhéy burn *maˑlí- ~ *mahlá- bush, sp. *qȧ(h)nóˑ buzzard *kuhkʰí carry in hands, to *bi-ʔdíˑ-d(i)- causative *-hqa chaparral *seʔé chest *yeʔélʸ child *qaˑwí clam *x̣alá/ú claw *héˑc̓ cloud *qʰaʔbá(ˑ), *qʰaʔbú clover *ʔohsó cold *qahcíl, *qacˑi come, to *(h)wáˑdu- cook, bake under ashes, to *ʔihpʰá- cottontail (rabbit) *nóˑmik cottonwood *qaxálabʔ ~ *qáxalabʔ coyote *doˑwí creek *biʔdá dance/song *qʰé daughter-in-law *-ʔódʔ daughter-in-law *xowmi(ˑ-c̓i) dawn, morning *qʰaʔˑá day *makílʸ, *maˑkí deer/meat *bihxé die, to *q̓alálʸ ~ *q̓alá- directional *-lal dirty *c̓áʔc̓a doe *maṭʰéy door *hohwá dove *maˑyú, *maˑyúˑ dream, to *qʰaʔadˑú- drink, to *hoʔq̓ó(k) duck *q̓aˑyán (~ *q̓ayáˑn ?) durative *-kid- ear *xiˑmánʸ earth *ʔa(h)máṭ east *ʔaxóˑ eat, chew, to *qawá- eat, to *kuhˑú- egg *hik̓óˑ, *hik̓ó elbow *q̓o/uhsá embers, charcoal *mahsíkʔ/tʔ enemy *kuhmá excrement *ʔahpʰá eye, face *huʔúy fat *ʔihpʰúy father *meʔˑé father, father's *bá-ˑc̓i father, mother's *-ká-ˑc̓i fawn *nuhwákʔ feather, small/down *ʔahṭʰé ~ *ʔahṭʰén ? feather, large *hiʔˑí fire *ʔohx̣ó first person singular subject *haʔáˑ first person singular object *ʔawí-toˑ first person singular possessive prefix *ʔawí- first personal plural subject *awá-ya first personal plural object *ʔawá-ya-l fish *ʔahxá five *ṭuhxo flea *ʔiˑméla flesh *c̓iʔˑí flint *qʰahká fly, to (1) *hakˑá- ( ?) fly, to (2) *pʰudí- fly, n. *c̓amolʸ food *maʔá foot *qʰaˑmánʸ forehead *diˑlé forest, deep, dense (hence shaded) *xiˑyó fox (1) *haq̓áw fox (2) *duˑcá frog *waˑṭakʔ/qʔ give round object *dihqá- go, several to *pʰilá good *q̓oʔdí goose *lála, *hláˑla gopher ? *ʔaˑláme grain, grain plant *muhká grass *qac̓ˑá grasshopper *xahqót hair, of head *heʔˑé, *heʔey( ?) hair, of body, fur *cihmé ~ *ciˑme hand *ʔatʰáˑna ~ *ʔatʰaná hawk *k̓iyáˑ head *kináˑlʸ, *xináˑ/lʸ, *kʰináˑ ? hear, to *xóˑki- hemp *mahxá hole *hiˑmó horn *haʔˑá hot, to be *muht̓ám- house *ʔahká hunt, to *boˑʔó imperative singular *-im jackrabbit *ʔaˑmáˑqala jay *c̓ayi ~ *c̓aˑyi jealous *ʔayél kinsman, one's own, in generations above ego *-ˑc̓i laugh, to *kʰuwáy leach, to *kʰeʔé- leaf (1) *siʔṭ̓ál leaf (2) *xihpʰa mountain *dȧˑnó mouth *ʔahx̣á mud *báˑto mudhen (?) *qʰá-c̓iyàt ~ *qʰa-c̓it mush, acorn *ṭʰoʔó(ˑ) mushroom (1) *hic̓éˑ mushroom (2) *k̓aˑlál mussel (ocean clam ?) *lȧʔq̓ó name *ʔahxí navel *ʔohqó-hmo neck *q̓óyu negative (1) *-tʰin ? negative (2) *kʰów ~ *akʰˑów dip net *waˑyákʔ/qʔ new *xiˑwéy night *duwˑé north *kuhˑúla ( ?) nose *hiˑlá oak, black *yuhxíy, *lixúy oak, live (?) *maʔk̓i(bʔ) oak, mush *c̓ipʰa, *c̓apʰˑa oak, sp. *wiyú oak, white *qaʔban/l- object case *-al ~ *-to occiput *kʰaˑyá on, on top of, above *wína ~ *wináˑ one *k̓á-, *káˑ- onion, wild *qʰaʔbat/y optative *-ix pain *duṭʰál panther *yahmóṭʔ path *hiʔdá people, group of people, village, race *nȧhpʰó pepperwood tree *bahˑébʔ pepperwoodnut *bahˑé phlegm *q̓uʔlés pick up a non-long object, to *dihkí pinole *yuhhú(ˑ), *yuhx̣ú(ˑ) ?, *yuhhúy, *yuhx̣úyʔ pitch *qʰahwé, *qʰahwé plural act (1) *-lV- plural act (2) (with extent?) *-ma plural number *-aya poison, poisoning song *q̓oˑʔó ~ *q̓oʔóˑ poison oak *hmaˑṭi̇́yu ~ *maˑṭi̇́yuho ? potato, Indian *hiʔbúnʸ pregnant *wiˑní quail *xaqáˑqa quail topknot *qʰéya ~ *ʔehqʰéya raccoon *qʰaʔdús ~ *qʰahlús ? rain *kehkʰé(ˑ) ~ *ihkʰé raw/alive *qa(h)xó- reciprocal *~(h)ma(ˑ)k̓ ~ *-ma(ˑ)k̓- reciprocal relationship *-a(ˑ)q rectum *haṭ̓á, *(ṭ̓i ?) reed, sp. *c̓iwíx reflexive *-i(ˑ)k̓i rib *misˑá(ˑ)kʔ ridge/mountain *wixálʸ rock *qʰaʔbé salt (1) *ṭaʔq̓o salt (2) *kʰeʔéˑ sand/gravel *miˑṭákʔ saw apart, to *xuqʰáˑ- seaweed, edible *ʔoˑṭóno second person singular subject *ʔaˑmá second person singular object *míˑ-to ~ *mí-to ~ *mi-tó second person singular possessive prefix *mi- second person plural subject *ʔaˑmá-ya second person plural object *ʔaˑmá-ya-l see *kád-, *káˑd- seed * ?isóˑ, *ʔisóy semelfactive *-ki- sentence connective (1) *-pʰila sentence connective (2) *-pʰi sentence connective (3) *-in separate from someone, to *q̓á(ˑ), *q̓a-(m-)(h)mak̓ shoulder *c̓uwáˑ sibling, younger *ṭ̓áqi sinew *hiˑmá sister, father's *múc̓i ~ *múˑc̓i ~ *wéˑqi sister, mother's older *ṭʰúˑc̓ sister, mother's younger *xéˑqi sister, older *déˑqi sister's husband *kóˑdʔ, *qóˑdʔ ? sit, to *ká- sit down, to *kahkí- six *lanká, *káci skin *ćʔdá skunk *nupʰéṭ sky *qalí, *qalínʸ sleep, to *siˑmán slow *pʰaláˑ slug *paʔláˑ smoke *ʔohx̣ósa(xà), *saxá snot *hiˑlásu snow *ʔihyúlʸ soaproot *haʔˑá(ˑ)bʔ son-in-law *hkéye sour *móc̓ ~ *móˑc̓ south *ʔiyó speculative *-xe- spider *ʔikʰáˑ, *mikʰá, *ikʰá spit *ʔihqʰetʔ spleen *maṭ́éˑ spring (of water) *(qʰa) qahpʰá squirrel *kuˑmáṭʔ, *qumáṭ stink, to *mihxé stop doing, to *-hyéˑ- stories, myths, to tell *maṭúˑ string *suˑlímaṭʔ suckerfish *xamólʸ sun *haʔdá sweat *mikʰˑéq tail *hibá talk, to *kȧhnów tears *huʔuy-qʰà(ˑ) testicles *yȧqolʸ thing *á(ˑ)maˑ third person masculine singular subject *hamíyabʔ third person masculine singular object *hamíˑb-al third person feminine singular subject *hamíyadʔ third person feminine singular object *hamíˑd-al third person singular possessive prefix *hamíyaˑ- throat *mihyánʸ tick *aṭ̓aʔláˑ tongue *haʔbálʸ ~ *hawba(ˑ) ~ *hibʔa tooth *hȧʔˑo tree *qʰaˑlé tule, round *bakóˑ tule sprout *ṭʰiʔbéˑ two *ʔaqʰóc umbilicus *ʔohqó uphill *dȧnóˑ valley, clearing *qahqó walk, to *hwáˑd-, *wáˑd- water *ʔahqʰá west (1) *mihila, *mix̣ila west (2) *bóˑ what *(baˑ)q́o(ˑ) whistle *li(?)búˑ white *qahlé wildcat *dȧˑlóm(ʔ) wind *ʔihyá winter *qʰu(ʔ)c̓áˑ- wolf *cihméwa ~ *ciméwa woman *ʔimáˑta wood *ʔahx̣áy wood duck *waṭá- wood rat *mihyóqʔ worm (1) *biˑlá worm (2) *ʔikʰólʸ
See also
- Boontling – a constructed dialect of English incorporating Pomo words
Notes
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Pomoan". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Laurie Bauer, 2007, The Linguistics Student’s Handbook, Edinburgh
- The etymology of the term "Pomo" is complex. It seems to be a combination of the Northern Pomo words [pʰoːmoː], "at red earth hole" and [pʰoʔmaʔ] (containing [pʰo-], "reside, live in a group"), together suggesting "those who live at red earth hole" (Campbell 1997:397, citing McLendon & Oswalt 1978:277)
- McLendon, Sally. 1973. Proto Pomo. (University of California publications in linguistics, 71.) Berkeley: University of California Press.
References
- Barrett, Samuel A. (1908). The Ethno-Geography of the Pomo and Neighboring Indians. University of California Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnology, 6.
- Campbell, Lyle. (1997). American Indian languages: The historical linguistics of Native America. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-509427-1.
- Goddard, Ives (Ed.). (1996). Languages. Handbook of North American Indians (W. C. Sturtevant, General Ed.) (Vol. 17). Washington, D. C.: Smithsonian Institution. ISBN 0-16-048774-9.
- Golla, Victor. (2011). California Indian Languages. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26667-4.
- McLendon, Sally & Robert L. Oswalt (1978). "Pomo: Introduction". In California, ed. Robert F. Heizer. Vol. 8 of Handbook of North American Indians, ed. William C. Sturtevant, pp. 274–88. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution. ISBN 978-0-16-004574-5.
- Mithun, Marianne. (1999). The languages of Native North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-23228-7 (hbk); ISBN 0-521-29875-X.
- Powell, John Wesley. (1891). Indian Linguistic Families Of America, North Of Mexico. Annual Report of the Bureau of American Ethnology 7:1-142. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office.
- Chestnut, Victor King (1902). Plants used by the Indians of Mendocino County, California. Government Printing Office. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
External links
| Wiktionary has a list of reconstructed forms at Appendix:Proto-Pomo reconstructions |
- Pomo (Yakaya, Yokaia, Shanel, Kábinapek) (Native Languages of the Americas)
- Kashaya (Kashia, Southwestern Pomo) (Native Languages of the Americas)
- Pomo/Kashaya Bibliography
- Pomo People: Brief History
- "New wellness center hosts first Pomo language workshop". Lake County News Reports. 2012-04-15. Retrieved 2012-08-08.