Nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that promotes the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people)[1] especially with the aim of gaining and maintaining the nation's sovereignty (self-governance) over its homeland. Nationalism holds that each nation should govern itself, free from outside interference (self-determination), that a nation is a natural and ideal basis for a polity,[2] and that the nation is the only rightful source of political power (popular sovereignty).[1][3] It further aims to build and maintain a single national identity—based on shared social characteristics of culture, ethnicity, geographic location, language, politics (or the government), religion, traditions and belief in a shared singular history [4][5]—and to promote national unity or solidarity.[1] Nationalism, therefore, seeks to preserve and foster a nation's traditional cultures, and cultural revivals have been associated with nationalist movements.[6] It also encourages pride in national achievements, and is closely linked to patriotism.[7] Nationalism is often combined with other ideologies, such as conservatism (national conservatism) or socialism (left-wing nationalism).[2]
| Part of a series on |
| Nationalism |
|---|
|
Core values |
|
|
Organizations |
|
Related concepts
|
|
| Legal status of persons |
|---|
| Concepts |
| Designations |
| Social politics |
| Part of the Politics series | ||||||||
| Basic forms of government | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power structure | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Power source | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Power ideology | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Politics portal | ||||||||
Throughout history, people have had an attachment to their kin group and traditions, to territorial authorities and to their homeland, but nationalism did not become a widely recognized concept until the 18th century.[8] There are three paradigms for understanding the origins and basis of nationalism. Primordialism (perennialism) proposes that there have always been nations and that nationalism is a natural phenomenon. Ethnosymbolism explains nationalism as a dynamic, evolutionary phenomenon and stresses the importance of symbols, myths and traditions in the development of nations and nationalism. Modernism proposes that nationalism is a recent social phenomenon that needs the socio-economic structures of modern society to exist.[9]
There are various definitions of a "nation", however, which leads to different strands of nationalism. Ethnic nationalism defines the nation in terms of shared ethnicity, heritage and culture, while civic nationalism defines the nation in terms of shared citizenship, values and institutions, and is linked to constitutional patriotism. The adoption of national identity in terms of historical development has often been a response by influential groups unsatisfied with traditional identities due to mismatch between their defined social order and the experience of that social order by its members, resulting in an anomie that nationalists seek to resolve.[10] This anomie results in a society reinterpreting identity, retaining elements deemed acceptable and removing elements deemed unacceptable, to create a unified community.[10] This development may be the result of internal structural issues or the result of resentment by an existing group or groups towards other communities, especially foreign powers that are (or are deemed to be) controlling them.[10] National symbols and flags, national anthems, national languages, national myths and other symbols of national identity are highly important in nationalism.[11][12][13][14]
In practice, nationalism can be seen as positive or negative depending on context and individual outlook. Nationalism has been an important driver in independence movements, such as the Greek Revolution, the Irish Revolution, the Zionist movement that created modern Israel, and the dissolution of the Soviet Union.[15][16] Conversely, radical nationalism combined with racial hatred was also a key factor in the Holocaust perpetrated by Nazi Germany.[17] More recently, nationalism was an important driver of the controversial annexation of Crimea by Russia.[18]
Terminology

The terminological use of 'nations', 'sovereignty' and associated concepts was significantly refined with the writing by Hugo Grotius of De jure belli ac pacis in the early 17th century. Living in the times of the Eighty Years' War between Spain and the Netherlands and the Thirty Years' War between Catholic and Protestant European nations (Catholic France being in the otherwise Protestant camp), it is not surprising that Grotius was deeply concerned with matters of conflicts between nations in the context of oppositions stemming from religious differences. The word nation was also usefully applied before 1800 in Europe to refer to the inhabitants of a country as well as to collective identities that could include shared history, law, language, political rights, religion and traditions, in a sense more akin to the modern conception.[19]
Nationalism as derived from the noun designating 'nations' is a newer word; in English the term dates from 1844, although the concept is older.[20] It became important in the 19th century.[21] The term increasingly became negative in its connotations after 1914. Glenda Sluga notes that "The twentieth century, a time of profound disillusionment with nationalism, was also the great age of globalism."[22]
History

American philosopher and historian Hans Kohn wrote in 1944 that nationalism emerged in the 17th century.[23] Other sources variously place the beginning in the 18th century during revolts of American states against Spain or with the French Revolution. The consensus is that nationalism as a concept was firmly established by the 19th century.[24][25][26]
Linda Colley in Britons, Forging the Nation 1707–1837 (Yale University Press, 1992) explores how the role of nationalism emerged about 1700 and developed in Britain reaching full form in the 1830s. Typically historians of nationalism in Europe begin with the French Revolution (1789), not only for its impact on French nationalism but even more for its impact on Germans and Italians and on European intellectuals.[27] The template of nationalism, as a method for mobilising public opinion around a new state based on popular sovereignty, went back further than 1789: philosophers such as Rousseau and Voltaire, whose ideas influenced the French Revolution, had themselves been influenced or encouraged by the example of earlier constitutionalist liberation movements, notably the Corsican Republic (1755–68) and American Revolution (1765–83).[28]
Due to the Industrial Revolution, there was an emergence of an integrated, nation-encompassing economy and a national public sphere, where the British people began to identify with the country at large, rather than the smaller units of their province, town or family. The early emergence of a popular patriotic nationalism took place in the mid-18th century, and was actively promoted by the British government and by the writers and intellectuals of the time.[29] National symbols, anthems, myths, flags and narratives were assiduously constructed by nationalists and widely adopted. The Union Jack was adopted in 1801 as the national one.[30] Thomas Arne composed the patriotic song "Rule, Britannia!" in 1740,[31] and the cartoonist John Arbuthnot invented the character of John Bull as the personification of the English national spirit in 1712.[32]
The political convulsions of the late 18th century associated with the American and French revolutions massively augmented the widespread appeal of patriotic nationalism.[33][34]
The Prussian scholar Johann Gottfried Herder (1744–1803) originated the term in 1772 in his "Treatise on the Origin of Language" stressing the role of a common language.[35][36] He attached exceptional importance to the concepts of nationality and of patriotism – "he that has lost his patriotic spirit has lost himself and the whole world about himself", whilst teaching that "in a certain sense every human perfection is national".[37]
19th century

The political development of nationalism and the push for popular sovereignty culminated with the ethnic/national revolutions of Europe. During the 19th century nationalism became one of the most significant political and social forces in history; it is typically listed among the top causes of World War I.[43][44]
Napoleon's conquests of the German and Italian states around 1800–06 played a major role in stimulating nationalism and the demands for national unity.[45]
English Historian J. P. T. Bury argues:
- Between 1830 and 1870 nationalism had thus made great strides. It had inspired great literature, quickened scholarship and nurtured heroes. It had shown its power both to unify and to divide. It had led to great achievements of political construction and consolidation in Germany and Italy; but it was more clearly than ever a threat to the Ottoman and Habsburg empires, which were essentially multi-national. European culture had been enriched by the new vernacular contributions of little-known or forgotten peoples, but at the same time such unity as it had was imperilled by fragmentation. Moreover, the antagonisms fostered by nationalism had made not only for wars, insurrections, and local hatreds —^they had accentuated or created new spiritual divisions in a nominally Christian Europe.[46]
France

Nationalism in France gained early expressions in France's revolutionary government. In 1793, that government declared a mass conscription (levée en masse) with a call to service:
Henceforth, until the enemies have been driven from the territory of the Republic, all the French are in permanent requisition for army service. The young men shall go to battle; the married men shall forge arms in the hospitals; the children shall turn old linen to lint; the old men shall repair to the public places, to stimulate the courage of the warriors and preach the unity of the Republic and the hatred of kings.[47]
This nationalism gained pace after the French Revolution came to a close. Defeat in war, with a loss in territory, was a powerful force in nationalism. In France, revenge and return of Alsace-Lorraine was a powerful motivating force for a quarter century after their defeat by Germany in 1871. However, after 1895 French nationalists focused on Dreyfus and internal subversion, and the Alsace issue petered out.[48]
The French reaction was a famous case of Revanchism ("revenge") which demands the return of lost territory that "belongs" to the national homeland. Revanchism draws its strength from patriotic and retributionist thought and it is often motivated by economic or geo-political factors. Extreme revanchist ideologues often represent a hawkish stance, suggesting that their desired objectives can be achieved through the positive outcome of another war. It is linked with irredentism, the conception that a part of the cultural and ethnic nation remains "unredeemed" outside the borders of its appropriate nation state. Revanchist politics often rely on the identification of a nation with a nation state, often mobilizing deep-rooted sentiments of ethnic nationalism, claiming territories outside the state where members of the ethnic group live, while using heavy-handed nationalism to mobilize support for these aims. Revanchist justifications are often presented as based on ancient or even autochthonous occupation of a territory since "time immemorial", an assertion that is usually inextricably involved in revanchism and irredentism, justifying them in the eyes of their proponents.[49]
The Dreyfus Affair in France 1894–1906 made the battle against treason and disloyalty a central theme for conservative Catholic French nationalists. Dreyfus, a Jew, was an outsider, that is in the views of intense nationalists, not a true Frenchman, not one to be trusted, not one to be given the benefit of the doubt. True loyalty to the nation, from the conservative viewpoint, was threatened by liberal and republican principles of liberty and equality that were leading the country to disaster.[50]
Russia
Before 1815, the sense of Russian nationalism was weak – what there was focused on loyal obedience to the tsar. The Russian motto "Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Nationality" was coined by Count Sergey Uvarov and adopted by Emperor Nicholas I as official ideology.[51] Three components of Uvarov's triad were:
- Orthodoxy—Orthodox Christianity and protection of the Russian Orthodox Church.
- Autocracy—unconditional loyalty to the House of Romanov in return for paternalist protection for all social estates.
- Nationality (Narodnost, has been also translated as national spirit)[52]—recognition of the state-founding role on Russian nationality.
By the 1860s, as a result of the educational indoctrination, and conservative resistance to ideas and ideologies from Western Europe, a pan-Slavic had emerged that produce both a sense of Russian nationalism, and a nationalistic mission to support and protect pan-Slavism. This Slavophile movement became popular in 19th-century Russia. Pan-Slavism was fueled by and was the fuel for Russia's numerous wars against the Ottoman Empire with the goal of liberating Orthodox nations, such as Bulgarians, Romanians, Serbs and Greeks, from Ottoman rule. Slavophiles opposed influences of Western Europe in Russia and were determined to protect Russian culture and traditions. Aleksey Khomyakov, Ivan Kireyevsky, and Konstantin Aksakov are credited with co-founding the movement.[53]
Latin America
An upsurge in nationalism in Latin America in 1810s and 1820s sparked revolutions that cost Spain nearly all its colonies there.[54] Spain was at war with Britain from 1798 to 1808, and the British Royal Navy cut off its contacts with its colonies so nationalism flourished and trade with Spain was suspended. The colonies set up temporary governments or juntas which were effectively independent from Spain. The division exploded between Spaniards who were born in Spain (called "peninsulares") versus those of Spanish descent born in New Spain (called "criollos" in Spanish or "creoles" in English). The two groups wrestled for power, with the criollos leading the call for independence. Spain tried to use its armies to fight back but had no help from European powers. Indeed, Britain[55] and the United States worked against Spain, enforcing the Monroe Doctrine. Spain lost all of its American colonies, except Cuba and Puerto Rico, in a complex series of revolts from 1808 to 1826.[56]
Germany

In the German states west of Prussia, Napoleon abolished many of the old or medieval relics, such as dissolving the Holy Roman Empire in 1806.[57] He imposed rational legal systems and demonstrated how dramatic changes were possible. His organization of the Confederation of the Rhine in 1806 promoted a feeling of nationalism.
Nationalists sought to encompass masculinity in their quest for strength and unity.[58] It was Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck who achieved German unification through a series of highly successful short wars against Denmark, Austria and France which thrilled the pan-German nationalists in the smaller German states. They fought in his wars and eagerly joined the new German Empire, which Bismarck ran as a force for balance and peace in Europe after 1871.[59]
In the 19th century German nationalism was promoted by Hegelian-oriented academic historians who saw Prussia as the true carrier of the German spirit, and the power of the state as the ultimate goal of nationalism. The three main historians were Johann Gustav Droysen (1808–1884), Heinrich von Sybel (1817–1895) and Heinrich von Treitschke (1834–1896). Droysen moved from liberalism to an intense nationalism that celebrated Prussian Protestantism, efficiency, progress, and reform, in striking contrast to Austrian Catholicism, impotency and backwardness. He idealized the Hohenzollern kings of Prussia. His large-scale History of Prussian Politics (14 vol 1855–1886) was foundational for nationalistic students and scholars. Von Sybel founded and edited the leading academic history journal, Historische Zeitschrift and as the director of the Prussian state archives published massive compilations that were devoured by scholars of nationalism.[60]
The most influential of the German nationalist historians, was Treitschke who had an enormous influence on elite students at Heidelberg and Berlin universities.[61] Treitschke vehemently attacked parliamentarianism, socialism, pacifism, the English, the French, the Jews, and the internationalists. The core of his message was the need for a strong, unified state—a unified Germany under Prussian supervision. "It is the highest duty of the State to increase its power," he stated. Although he was a descendant of a Czech family he considered himself not Slavic but German: "I am 1000 times more the patriot than a professor."[62]

German nationalism, expressed through the ideology of Nazism, however, may also be understood as trans-national in nature. This aspect was primarily advocated by Adolf Hitler, who later became the leader of the Nazi Party. This party was devoted to what they identified as an Aryan race, residing in various European countries, but sometime mixed with alien elements such as Jews.[64]
Meanwhile, the Nazis rejected many of the well-established citizens within those same countries, such as the Romani (Gypsies) and of course Jews, whom they did not identify as Aryan. Meanwhile, a key Nazi doctrine was "Living Space" (for Aryans only) or "Lebensraum," which was a vast undertaking to transplant Aryans throughout Poland, much of Eastern Europe and the Baltic nations, and all of Western Russia and Ukraine. Lebensraum was thus a vast project for advancing the Aryan race far outside of any particular nation or national borders. The Nazi's goals were racist focused on advancing the Aryan race as they perceived it, eugenics modification of the human race, and the eradication of human beings that they deemed inferior. But their goals were trans-national and intended to spread across as much of the world as they could achieve. Although Nazism glorified German history, it also embraced the supposed virtues and achievements of the Aryan race in other countries,[65] including India.[66] The Nazis' Aryanism longed for now-extinct species of superior bulls once used as livestock by Aryans and other features of Aryan history that never resided within the borders of Germany as a nation.[67]
Italy

Italian nationalism emerged in the 19th century and was the driving force for Italian unification or the Risorgimento (meaning the "Resurgence" or "Revival"). It was the political and intellectual movement that consolidated the different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861. The memory of the Risorgimento is central to Italian nationalism but it was based in the liberal middle classes and ultimately proved weak.[68] The new government treated the newly-annexed South as a conquered province with ridicule for its "backward" and poverty-stricken society, its poor grasp of standard Italian (as Italo-Dalmatian dialects of Neapolitan and Sicilian were prevalent in the common use) and its traditions. The liberals had always been strong opponents of the pope and the very well organized Catholic Church. The liberal government under the Sicilian Francesco Crispi sought to enlarge his political base by emulating Otto von Bismarck and firing up Italian nationalism with a hyper-aggressive foreign policy. It crashed and his cause was set back. Historian R.J.B. Bosworth says of his nationalistic foreign policy that:
(Crispi) pursued policies whose openly aggressive character would not be equaled until the days of the Fascist regime. Crispi increased military expenditure, talked cheerfully of a European conflagration, and alarmed his German or British friends with this suggestions of preventative attacks on his enemies. His policies were ruinous, both for Italy's trade with France, and, more humiliatingly, for colonial ambitions in East Africa. Crispi's lust for territory there was thwarted when on 1 March 1896, the armies of Ethiopian Emperor Menelik routed Italian forces at Adowa ... in what has been defined as an unparalleled disaster for a modern army. Crispi, whose private life (he was perhaps a trigamist) and personal finances...were objects of perennial scandal, went into dishonorable retirement.
— R.J.B. Bosworth, Italy and the Wider World: 1860–1960, 2013, Routledge, p.29, ISBN 978-1-134-78088-4
Italy joined the Allies in the First World War after getting promises of territory, but its war effort was a fiasco that discredited liberalism and paved the way for Benito Mussolini and a political doctrine of his own creation, fascism. Mussolini's 20-year dictatorship involved a highly aggressive nationalism that led to a series of wars, an alliance with Hitler's Germany, and humiliation and hardship in the Second World War. After 1945, the Catholics returned to government and tensions eased somewhat, but the former two Sicilies remained poor and ridiculed. The working class now voted for the Communist Party, and it looked to Moscow rather than Rome for inspiration, and was kept out of the national government even as it controlled industrial cities across the North. In the 21st century, the Communists have become marginal but political tensions remained high as shown by Bossi's Padanism in the 80s[69] (whose party has come to partially embrace a moderate version of Italian nationalism over the years) and other separatist movements spread across the country.

Greece
During the early 19th century, inspired by romanticism, classicism, former movements of Greek nationalism and failed Greek revolts against the Ottoman Empire (such as the Orlofika revolt in southern Greece in 1770, and the Epirus-Macedonian revolt of Northern Greece in 1575), Greek nationalism led to the Greek war of independence.[70] The Greek drive for independence from the Ottoman Empire in the 1820s and 1830s inspired supporters across Christian Europe, especially in Britain, which was the result of western idealization of Classical Greece and romanticism. France, Russia and Britain critically intervened to ensure the success of this nationalist endeavour.[71]
Serbia
For centuries the Orthodox Christian Serbs were ruled by the Muslim Ottoman Empire. The success of the Serbian Revolution against Ottoman rule in 1817 marked the birth of the Principality of Serbia. It achieved de facto independence in 1867 and finally gained international recognition in 1878. Serbia had sought to liberate and unite with Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west and Old Serbia (Kosovo and Vardar Macedonia) to the south. Nationalist circles in both Serbia and Croatia (part of Austria-Hungary) began to advocate for a greater South Slavic union in the 1860s, claiming Bosnia as their common land based on shared language and tradition.[72] In 1914, Serb revolutionaries in Bosnia assassinated Archduke Ferdinand. Austria-Hungary, with German backing, tried to crush Serbia in 1914, thus igniting the First World War in which Austria-Hungary dissolved into nation states.[73]
In 1918, the region of Banat, Bačka and Baranja came under control of the Serbian army, later the Great National Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs voted to join Serbia; the Kingdom of Serbia joined the union with State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs on 1 December 1918, and the country was named Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. It was renamed Yugoslavia, and a Yugoslav identity was promoted, which ultimately failed. After the Second World War, Yugoslav Communists established a new socialist republic of Yugoslavia. That state broke up in the 1990s.[74]
Poland
The cause of Polish nationalism was repeatedly frustrated before 1918. In the 1790s, the Habsburg Monarchy, Prussia and Russia invaded, annexed, and subsequently partitioned Poland. Napoleon set up the Duchy of Warsaw, a new Polish state that ignited a spirit of nationalism. Russia took it over in 1815 as Congress Poland with the tsar proclaimed as "King of Poland". Large-scale nationalist revolts erupted in 1830 and 1863–64 but were harshly crushed by Russia, which tried to make the Polish language, culture and religion more like Russia's. The collapse of the Russian Empire in the First World War enabled the major powers to re-establish an independent Poland, which survived until 1939. Meanwhile, Poles in areas controlled by Germany moved into heavy industry but their religion came under attack by Bismarck in the Kulturkampf of the 1870s. The Poles joined German Catholics in a well-organized new Centre Party, and defeated Bismarck politically. He responded by stopping the harassment and cooperating with the Centre Party.[75][76]
In the late 19th and early 20th century, many Polish nationalist leaders endorsed the Piast Concept. It held there was a Polish utopia during the Piast Dynasty a thousand years before, and modern Polish nationalists should restore its central values of Poland for the Poles. Jan Poplawski had developed the "Piast Concept" in the 1890s, and it formed the centerpiece of Polish nationalist ideology, especially as presented by the National Democracy Party, known as the "Endecja," which was led by Roman Dmowski. In contrast with the Jagiellon concept, there was no concept for a multi-ethnic Poland.[77]

The Piast concept stood in opposition to the "Jagiellon Concept," which allowed for multi-ethnicism and Polish rule over numerous minority groups such as those in the Kresy. The Jagiellon Concept was the official policy of the government in the 1920s and 1930s. Soviet dictator Josef Stalin at Tehran in 1943 rejected the Jagiellon Concept because it involved Polish rule over Ukrainians and Belarusians. He instead endorsed the Piast Concept, which justified a massive shift of Poland's frontiers to the west.[78] After 1945 the Soviet-back puppet communist regime wholeheartedly adopted the Piast Concept, making it the centerpiece of their claim to be the "true inheritors of Polish nationalism". After all the killings, including Nazi German occupation, terror in Poland and population transfers during and after the war, the nation was officially declared as 99% ethnically Polish.[79]
Jewish Nationalism
Jewish nationalism arose in the latter half of the 19th century and it was largely correlated with the Zionist movement. This term originated from the word Zion, which was one of the Torah's names for the city of Jerusalem. The end goal of the nationalists and Zionists was a Jewish majority and in most cases, a state, in the land of Palestine. A tumultuous history of living in oppressive, foreign, and uncertain circumstances led the supporters of the movement to draft a declaration of independence, claiming Israel as a birthplace. The first and second destructions of the temple and ancient Torah prophecies largely shaped the incentives of the Jewish nationalists. Many prominent theories in Jewish theology and eschatology were formed by supporters and opponents of the movement in this era.
It was the French Revolution of 1789, which sparked new waves of thinking across Europe regarding governance and sovereignty. A shift from the traditional hierarchy-based system towards political individualism and citizen-states posed a dilemma for the Jews. Citizenship was now essential, when it came to ensuring basic legal and residential rights. This resulted in more and more Jews choosing to identify with certain nationalities in order to maintain these rights. Logic said that a nation-based system of states would require the Jews themselves to claim their own right to be considered a nation due to a distinguishable language and history. Historian David Engel has explained that Zionism was more about fear that a majority of worldwide Jews would end up dispersed and unprotected, rather than fulfilling old prophecies and traditions of historical texts.[80]
20th century
China
The awakening of nationalism across Asia helped shape the history of the continent. The key episode was the decisive defeat of Russia by Japan in 1905, demonstrating the military advancement of non-Europeans in a modern war. The defeat which quickly led to manifestations of a new interest in nationalism in China, as well as Turkey, and Persia.[81] In China Sun Yat-sen (1866–1925) launched his new party the Kuomintang (National People's Party) in defiance of the decrepit Empire, which was run by outsiders. Kuomintang recruits pledged:
- from this moment I will destroy the old and build the new, and fight for the self-determination of the people, and will apply all my strength to the support of the Chinese Republic and the realization of democracy through the Three Principles, ... for the progress of good government, the happiness and perpetual peace of the people, and for the strengthening of the foundations of the state in the name of peace throughout the world.[82]
The Kuomintang largely ran China until the Communists took over in 1949. But the latter had also been strongly influenced by Sun's nationalism as well as by the May Fourth Movement in 1919. It was a nationwide protest movement about the domestic backwardness of China and has often been depicted as the intellectual foundation for Chinese Communism.[83] The New Culture Movement stimulated by the May Fourth Movement waxed strong throughout the 1920s and 1930s. According to historian Patricia Ebrey:
- Nationalism, patriotism, progress, science, democracy, and freedom were the goals; imperialism, feudalism, warlordism, autocracy, patriarchy, and blind adherence to tradition were the enemies. Intellectuals struggled with how to be strong and modern and yet Chinese, how to preserve China as a political entity in the world of competing nations.[84]
Greece
Nationalist irredentist movements Greek advocating for Enosis (unity of ethnically Greek states with the Hellenic Republic to create a unified Greek state), used today in the case of Cyprus, as well as the Megali Idea, the Greek movement that advocated for the reconquering of Greek ancestral lands from the Ottoman Empire (such as Crete, Ionia, Pontus, Northern Epirus, Cappadocia, Thrace among others) that were popular in the late 19th and early to 20th centuries, led to many Greek states and regions that were ethnically Greek to eventually unite with Greece and the Greco-Turkish war of 1919.
The 4th of August regime was a fascist or fascistic nationalist authoritarian dictatorship inspired by Mussolini's Fascist Italy and Hitler's Germany and led by Greek general Ioannis Metaxas from 1936 to his death in 1941. It advocated for the Third Hellenic Civilization, a culturally superior Greek civilization that would be the successor of the First and Second Greek civilizations, that were Ancient Greece and the Byzantine empire respectively. It promoted Greek traditions, folk music and dances, classicism as well as medievalism.
Africa

In the 1880s the European powers divided up almost all of Africa (only Ethiopia and Liberia were independent). They ruled until after World War II when forces of nationalism grew much stronger. In the 1950s and 1960s the colonial holdings became independent states. The process was usually peaceful but there were several long bitter bloody civil wars, as in Algeria,[85] Kenya[86] and elsewhere. Across Africa nationalism drew upon the organizational skills that natives learned in the British and French and other armies in the world wars. It led to organizations that were not controlled by or endorsed by either the colonial powers nor the traditional local power structures that were collaborating with the colonial powers. Nationalistic organizations began to challenge both the traditional and the new colonial structures and finally displaced them. Leaders of nationalist movements took control when the European authorities exited; many ruled for decades or until they died off. These structures included political, educational, religious, and other social organizations. In recent decades, many African countries have undergone the triumph and defeat of nationalistic fervor, changing in the process the loci of the centralizing state power and patrimonial state.[87][88][89]
South Africa, a British colony, was exceptional in that it became virtually independent by 1931. From 1948 it was controlled by white Afrikaner nationalists focused on racial segregation and white minority rule known officially as apartheid, which lasted until 1994, when elections were held. The international anti-apartheid movement supported black nationalist until success was achieved and Nelson Mandela was elected President.[90]
Middle East
Arab nationalism, a movement toward liberating and empowering the Arab peoples of the Middle East, emerged during the latter 19th century, inspired by other independence movements of the 18th and 19th centuries. As the Ottoman Empire declined and the Middle East was carved up by the Great Powers of Europe, Arabs sought to establish their own independent nations ruled by Arabs rather than foreigners. Syria was established in 1920; Transjordan (later Jordan) gradually gained independence between 1921 and 1946; Saudi Arabia was established in 1932; and Egypt achieved gradually gained independence between 1922 and 1952. The Arab League was established in 1945 to promote Arab interests and cooperation between the new Arab states.
Parallel to these efforts was the Zionist movement which emerged among European Jews in the 19th century. Beginning in 1882 Jews, predominantly from Europe, began emigrating to Ottoman Palestine with the goal of establishing a new Jewish homeland. The effort culminated in the declaration of the State of Israel in 1948. As this move conflicted with the belief among Arab nationalists that Palestine was part of the Arab nation, the neighboring Arab nations launched an invasion to claim the region. The invasion was only partly successful and led to decades of clashes between the Arab and Jewish nationalist ideologies.
Break up of Yugoslavia
There was a rise in extreme nationalism after the Revolutions of 1989 triggered the collapse of communism in the 1990s. When communism fell, it left many people with no identity. The people under communist rule had to integrate, and they found themselves free to choose. Given free choice, long dormant conflicts rose up and created sources of serious conflict.[91] When communism fell in Yugoslavia, serious conflict arose, which led to the rise in extreme nationalism.
In his 1992 article Jihad vs. McWorld, Benjamin Barber proposed that the fall of communism will cause large numbers of people to search for unity and that small scale wars will become common; groups will attempt to redraw boundaries, identities, cultures and ideologies.[92] Communism's fall also allowed for an "us vs. them" mentality to sprout up.[93] Governments become vehicles for social interests and the country will attempt to form national policies based on the majority, for example culture, religion or ethnicity.[91] Some newly sprouted democracies have large differences in policies on matters that ranged from immigration and human rights to trade and commerce.
Academic Steven Berg felt that at the root of nationalist conflicts is the demand for autonomy and a separate existence.[91] This nationalism can give rise to strong emotions that may lead to a group fighting to survive, especially as after the fall of communism, political boundaries did not match ethnic boundaries.[91] Serious conflicts often arose and escalated very easily as individuals and groups acted upon their beliefs, causing death and destruction.[91] When this would happen, those states who were unable to contain the conflict ran the risk of slowing their democratization progress.
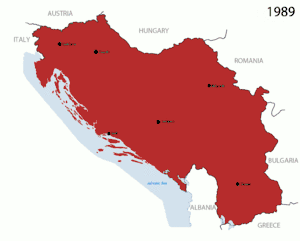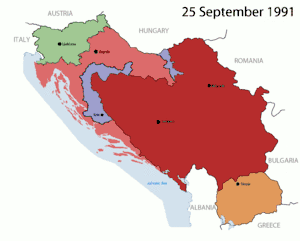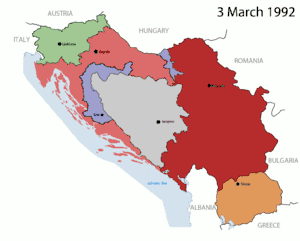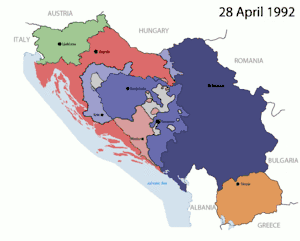
Yugoslavia was established after WWI and was a merger of three separate ethnic groups; Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. The national census numbers for a ten-year span 1971–1981 measured an increase from 1.3 to 5.4% in their population that ethnically identified as Yugoslav.[94] This meant that the country, almost as a whole, was divided by distinctive religious, ethnic or national loyalties after nearly 50 years.
Within Yugoslavia, separating Croatia and Slovenia from the rest of Yugoslavia is an invisible line of previous conquests of the region. Croatia and Slovenia to the northwest were conquered by Catholics or Protestants, and benefited from European history; the Renaissance, French Revolution, Industrial Revolution and are more inclined towards democracy.[93] The remaining Yugoslavian territory was conquered by the Ottoman or Tsarists empires; are Orthodox or Muslims, are less economically advanced and are less inclined toward democracy.
In the 1970s the leadership of the separate territories within Yugoslavia protected only territorial interests at the expense of other territories. In Croatia, there was almost a split within the territory between Serbs and Croats so any political decision would kindle unrest, and tensions could cross the territories adjacent; Bosnia and Herzegovina.[94] Within Bosnia there was no group who had a majority; Muslim, Serb, Croat, and Yugoslav were all there so the leadership could not advance here either. Political organizations were not able to deal successfully with such diverse nationalism. Within the territories the leadership could not compromise. To do so would create a winner in one ethnic group and a loser in another, raising the possibility of a serious conflict. This strengthened the political stance promoting ethnic identities. This caused intense and divided political leadership within Yugoslavia.
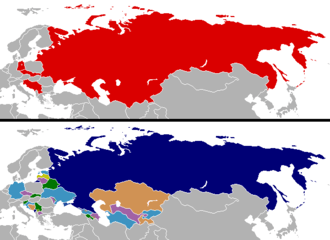
In the 1980s Yugoslavia began to break into fragments.[92] The economic conditions within Yugoslavia were deteriorating. Conflict in the disputed territories was stimulated by the rise in mass nationalism and inter-ethnic hostilities.[94] The per-capita income of people in the northwest territory, encompassing Croatia and Slovenia, in contrast to the southern territory were several times higher. This combined with escalating violence from ethnic Albanians and Serbs within Kosovo intensified economic conditions.[94] This violence greatly contributed to the rise of extreme nationalism of Serbs in Serbia and within Yugoslavia. The ongoing conflict in Kosovo was propagandized by Communist Serbian Slobodan Milosevic to further increase Serb nationalism. As mentioned, this nationalism did give rise to powerful emotions which grew the force of Serbian nationalism through highly nationalist demonstrations in Vojvodina, Serbia, Montenegro, and Kosovo. Serbian nationalism was so high, Slobodan Milosevic was able to oust leaders in Vojvodina and Montenegro, further repressed Albanians within Kosovo and eventually controlled four of the eight regions/territories.[94] Slovenia, one of the four regions not under Communist control, favoring a democratic state.
Within Slovenia, fear was mounting because Milosevic was using the militia to suppress a in Kosovo, what would he do to Slovenia.[94] Half of Yugoslavia wanted to be democratic, the other wanted a new nationalist authoritarian regime. In fall of 1989 tensions came to a head and Slovenia asserted its political and economic independence from Yugoslavia and seceded. In January 1990, there was a total break with Serbia at the League of Communists of Yugoslavia, an institution conceived by Milosevic to strengthen unity and became the backdrop for the fall of communism within Yugoslavia.
In August 1990, a warning to the region was issued when ethnically divided groups attempted to alter the government structure. The republic borders established by the Communist regime in the postwar period were extremely vulnerable to challenges from ethnic communities.Ethnic communities arose because they did not share the identity with everyone within the new post-Communist borders.[94] This threatened the new governments. The same disputes were erupting that were in place prior to Milosevic and were compounded by actions from his regime.
Also within the territory the Croats and the Serbs were in direct competition for control of government. Elections were held and increased potential conflicts between Serb and Croat nationalism. Serbia wanted to be separate and decide its own future based on its own ethnic composition. But this would then give Kosovo encouragement to become independent from Serbia. Albanians in Kosovo were already independent from Kosovo. Serbia didn't want to let Kosovo become independent. Muslims nationalists wanted their own territory but it would require a redrawing of the map, and would threaten neighboring territories. When communism fell in Yugoslavia, serious conflict arose, which led to the rise in extreme nationalism.
Nationalism again gave rise to powerful emotions which evoked in some extreme cases, a willingness to die for what you believe in, a fight for the survival of the group.[91] The end of communism began a long period of conflict and war for the region. In the six years following the collapse 200,000-500-000 people died in the Bosnian war.[95] Bosnian Muslims suffered at the hands of the Serbs and Croats.[93] The war garnered assistance from groups; Muslim, Orthodox and Western Christian as well as state actors who supplied all sides; Saudi Arabia and Iran supported Bosnia, Russia supported Serbia, Central European and Western countries including the U.S. supported Croatia, and the Pope supported Slovenia and Croatia.
21st century

Arab nationalism began to decline in the 21st century leading to localized nationalism, culminating in a series of revolts against authoritarian regimes between 2010 and 2012, known as the Arab Spring. Following these revolts, which mostly failed to improve conditions in the affected nations, Arab nationalism and even most local nationalistic movements declined dramatically.[97] A consequence of the Arab Spring as well as the 2003 invasion of Iraq were the civil wars in Iraq and Syria, which eventually joined to form a single conflict. However, a new form of Arab nationalism has developed in the wake of the Arab Winter, embodied by Egyptian President Abdel Fatteh el-Sisi, Saudi Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman and UAE leader Mohammed bin Zayed.
The rise of globalism in the late 20th century led to a rise in nationalism and populism in Europe and North America. This trend was further fueled by increased terrorism in the West (the September 11 attacks in the U.S. being a prime example), increasing unrest and civil wars in the Middle East, and waves of Muslim refugees flooding into Europe (as of 2016 the refugee crisis appears to have peaked).[98][99] Nationalist groups like Germany's Pegida, France's National Front, and the UK Independence Party gained prominence in their respective nations advocating restrictions on immigration to protect the local populations.[100][101]
In Russia, exploitation of nationalist sentiments allowed Vladimir Putin to consolidate power.[102] This nationalist sentiment was used in Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014 and other actions in Ukraine.[101] Nationalist movements gradually began to rise in Central Europe as well, particularly Poland, under the influence of the ruling party, Law and Justice (led by Jaroslaw Kaczynski).[103] In Hungary, the anti-immigration rhetoric and stance against foreign influence is a powerful national glue promoted the ruling Fidesz party (led by Viktor Orbán).[104] Nationalist parties have also joined governing coalitions in Bulgaria,[105] Slovakia,[106] Latvia[107] and Ukraine.[108]
In India, Hindu nationalism has grown extremely popular with the rise of the Bharatiya Janata Party, a right-wing Hindu nationalist party which has been ruling India at the national level since 2014.[109][110] The rise in religious nationalism comes with the rise of right-wing populism in India, with the election and re-election of populist leader Narendra Modi as Prime Minister, who promised economic prosperity for all and an end to corruption. In 2013, Modi declared himself to be a Hindu nationalist.[111] The BJP rule in India is characterized by religious nationalism, the persecution of religious minorities, the erosion of civil liberties as well as an authoritarian shift in governance. [112] [113] [114]
Militant Buddhist nationalism is on the rise in Myanmar, Thailand and Sri Lanka.[115][116]
A referendum on Scottish independence from the United Kingdom was held on 18 September 2014. The proposal was defeated, with 55.3% voting against independence. In a 2016 referendum, the British populace voted to withdraw the United Kingdom from the European Union (the so-called Brexit). The result had been largely unexpected and was seen as a victory of populism. As the promise of continued EU membership was a core feature of the pro-unionist campaign during the Scottish referendum, the months since the EU Referendum vote have seen renewed calls for a second referendum on Scottish independence.

The 2016 U.S. presidential campaign saw the unprecedented rise of Donald Trump, a businessman with no political experience who ran on a populist/nationalist platform and struggled to gain endorsements from mainstream political figures, even within his own party. Trump's slogans "Make America Great Again" and "America First" exemplified his campaign's repudiation of globalism and its staunchly nationalistic outlook. His unexpected victory in the election was seen as part of the same trend that had brought about the Brexit vote.[117] On 22 October 2018, two weeks before the mid-term elections President Trump openly proclaimed that he was a nationalist to a cheering crowd at a rally in Texas in support of re-electing Sen. Ted Cruz who was once an adversary.[118] On 29 October 2018 he equated nationalism to patriotism, saying "I'm proud of this country and I call that 'nationalism.'"[119]
In Japan, nationalist influences in the government developed over the course of the early 21 century, thanks in large part to the Nippon Kaigi organization. The new movement has advocated re-establishing Japan as a military power and revising historical narratives to support the notion of a moral and strong Japan.[120][121]
In 2016, Rodrigo Duterte became president of the Philippines running a distinctly nationalist campaign. Contrary to the policies of his recent predecessors, he distanced the country from the Philippines' former ruler, the United States, and sought closer ties with China (as well as Russia).[122]
During 2017, Turkish nationalism propelled President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan to gain unprecedented power in a national referendum.[123] Reactions from world leaders were mixed, with Western European leaders generally expressing concern while the leaders of many of the more authoritarian regimes, as well as President Donald Trump, offered their congratulations.
Since 2010, Catalan nationalists have led a renewed Catalan independence movement and declared Catalonia's independence. The movement has been opposed by Spanish nationalists.[124][125]
In the 2010s, the Greek economic crisis and waves of immigration have led to a significant rise of Fascism and Greek nationalism across Greece, especially among the youth.[126]
Political science
Many political scientists have theorized about the foundations of the modern nation-state and the concept of sovereignty. The concept of nationalism in political science draws from these theoretical foundations. Philosophers like Machiavelli, Locke, Hobbes, and Rousseau conceptualized the state as the result of a "social contract" between rulers and individuals.[127] Weber provides the most commonly used definition of the state, "that human community which successfully lays claim to the monopoly of legitimate physical violence within a certain territory".[128] According to Benedict Anderson, nations are "Imagined Communities", or socially constructed institutions.[129]
Many scholars have noted the relationship between state-building, war, and nationalism. Many scholars believe that the development of nationalism in Europe (and subsequently the modern nation-state) was due to the threat of war. "External threats have such a powerful effect on nationalism because people realize in a profound manner that they are under threat because of who they are as a nation; they are forced to recognize that it is only as a nation that they can successfully defeat the threat".[62] With increased external threats, the state's extractive capacities increase. Jeffrey Herbst argues that the lack of external threats to countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, post-independence, is linked to weak state nationalism and state capacity .[62] Barry Posen argues that nationalism increases the intensity of war, and that states deliberately promote nationalism with the aim of improving their military capabilities.[130]
Sociology
The sociological or modernist interpretation of nationalism and nation-building argues that nationalism arises and flourishes in modern societies that have an industrial economy capable of self-sustainability, a central supreme authority capable of maintaining authority and unity, and a centralized language understood by a community of people.[131] Modernist theorists note that this is only possible in modern societies, while traditional societies typically lack the prerequisites for nationalism. They lack a modern self-sustainable economy, have divided authorities, and use multiple languages resulting in many groups being unable to communicate with each other.[131]
Prominent theorists who developed the modernist interpretation of nations and nationalism include: Carlton J. H. Hayes, Henry Maine, Ferdinand Tönnies, Rabindranath Tagore, Émile Durkheim, Max Weber, Arnold Joseph Toynbee and Talcott Parsons.[131]
Henry Maine in his analysis of the historical changes and development of human societies noted the key distinction between traditional societies defined as "status" societies based on family association and functionally diffuse roles for individuals; and modern societies defined as "contract" societies where social relations are determined by rational contracts pursued by individuals to advance their interests. Maine saw the development of societies as moving away from traditional status societies to modern contract societies.[132]
Ferdinand Tönnies in his book Gemeinschaft und Gesellschaft (1887) defined a Gemeinschaft (community) as being based on emotional attachments as attributed with traditional societies, while defining a Gesellschaft (society) as an impersonal society that is modern. While he recognized the advantages of modern societies he also criticized them for their cold and impersonal nature that caused alienation while praising the intimacy of traditional communities.[132]
Émile Durkheim expanded upon Tönnies' recognition of alienation, and defined the differences between traditional and modern societies as being between societies based upon "mechanical solidarity" versus societies based on "organic solidarity".[132] Durkheim identified mechanical solidarity as involving custom, habit, and repression that was necessary to maintain shared views. Durkheim identified organic solidarity-based societies as modern societies where there exists a division of labour based on social differentiation that causes alienation. Durkheim claimed that social integration in traditional society required authoritarian culture involving acceptance of a social order. Durkheim claimed that modern society bases integration on the mutual benefits of the division of labour, but noted that the impersonal character of modern urban life caused alienation and feelings of anomie.[132]
Max Weber claimed the change that developed modern society and nations is the result of the rise of a charismatic leader to power in a society who creates a new tradition or a rational-legal system that establishes the supreme authority of the state. Weber's conception of charismatic authority has been noted as the basis of many nationalist governments.[132]
Primordialist evolutionary interpretation
Another approach emerging from biology and psychology looks at long-term evolutionary forces that might lead to nationalism. The primordialist perspective is based upon evolutionary theory.[133][134]
This approach has been popular with the general public but is typically rejected by experts. Laland and Brown report that "the vast majority of professional academics in the social sciences not only ... ignore evolutionary methods but in many cases [are] extremely hostile to the arguments" that draw vast generalizations from rather limited evidence.[135]
The evolutionary theory of nationalism perceives nationalism to be the result of the evolution of human beings into identifying with groups, such as ethnic groups, or other groups that form the foundation of a nation.[133] Roger Masters in The Nature of Politics describes the primordial explanation of the origin of ethnic and national groups as recognizing group attachments that are thought to be unique, emotional, intense, and durable because they are based upon kinship and promoted along lines of common ancestry.[136]
The primordialist evolutionary views of nationalism often reference the evolutionary theories of Charles Darwin as well as Social Darwinist views of the late nineteenth century. Thinkers like Herbert Spencer and Walter Bagehot reinterpreted Darwin's theory of natural selection "often in ways inconsistent with Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution" by making unsupported claims of biological difference among groups, ethnicities, races, and nations.[137] Modern evolutionary sciences have distanced themselves from such views, but notions of long-term evolutionary change remain foundational to the work of evolutionary psychologists like John Tooby and Leda Cosmides.[138]
Approached through the primordialist perspective, the example of seeing the mobilization of a foreign military force on the nation's borders may provoke members of a national group to unify and mobilize themselves in response.[139] There are proximate environments where individuals identify nonimmediate real or imagined situations in combination with immediate situations that make individuals confront a common situation of both subjective and objective components that affect their decisions.[140] As such proximate environments cause people to make decisions based on existing situations and anticipated situations.[140]

Critics argue that primordial models relying on evolutionary psychology are based not on historical evidence but on assumptions of unobserved changes over thousands of years and assume stable genetic composition of the population living in a specific area, and are incapable of handling the contingencies that characterize every known historical process. Robert Hislope argues:
- the articulation of cultural evolutionary theory represents theoretical progress over sociobiology, but its explanatory payoff remains limited due to the role of contingency in human affairs and the significance of non-evolutionary, proximate causal factors. While evolutionary theory undoubtedly elucidates the development of all organic life, it would seem to operate best at macro-levels of analysis, "distal" points of explanation, and from the perspective of the long-term. Hence, it is bound to display shortcomings at micro-level events that are highly contingent in nature.[141]
English Historian G. P. Gooch in 1920 argued that "While patriotism is as old as human association and has gradually widened its sphere from the clan and the tribe to the city and the state, nationalism as an operative principle and an articulate creed only made its appearance among the more complicated intellectual processes of the modern world.[142]
Marxist interpretations
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels declared in the Communist Manifesto that "the working men have no country".[143]
Vladimir Lenin supported the concept of self-determination.[144]
Joseph Stalin's Marxism and the National Question (1913) declares that "a nation is not a racial or tribal, but a historically constituted community of people;" "a nation is not a casual or ephemeral conglomeration, but a stable community of people"; "a nation is formed only as a result of lengthy and systematic intercourse, as a result of people living together generation after generation"; and, in its entirety: "a nation is a historically constituted, stable community of people, formed on the basis of a common language, territory, economic life, and psychological make-up manifested in a common culture."[145]
Varieties
Historians, sociologists, and anthropologists have debated different types of nationalism since at least the 1930s.[146] Generally, the most common way of classifying nationalism has been to describe movements as having either "civic" or "ethnic" nationalist characteristics. This distinction was popularized in the 1950s by Hans Kohn who described "civic" nationalism as "Western" and more democratic while depicting "ethnic" nationalism as "Eastern" and undemocratic.[147] Since the 1980s, however, scholars of nationalism have pointed out numerous flaws in this rigid division and proposed more specific classifications and numerous varieties.[148][149]
Civic nationalism and liberal nationalism
Civic nationalism defines the nation as an association of people who identify themselves as belonging to the nation, who have equal and shared political rights, and allegiance to similar political procedures.[150] According to the principles of civic nationalism, the nation is not based on common ethnic ancestry, but is a political entity whose core identity is not ethnicity. This civic concept of nationalism is exemplified by Ernest Renan in his lecture in 1882 "What is a Nation?", where he defined the nation as a "daily referendum" (frequently translated "daily plebiscite") dependent on the will of its people to continue living together.[150]
Civic nationalism is normally associated with liberal nationalism, although the two are distinct, and did not always coincide. On the one hand, until the late 19th and early 20th century adherents to anti-Enlightenment movements such as French Legitimism or Spanish Carlism often rejected the liberal, national unitary state, yet identified themselves not with an ethnic nation but with a non-national dynasty and regional feudal privileges. Xenophobic movements in long-established Western European states indeed often took a 'civic national' form, rejecting a given group's ability to assimilate with the nation due to its belonging to a cross-border community (Irish Catholics in Britain, Ashkenazic Jews in France). On the other hand, while subnational separatist movements were commonly associated with ethnic nationalism, this was not always so, and such nationalists as the Corsican Republic, United Irishmen, Breton Federalist League or Catalan Republican Party could combine a rejection of the unitary civic-national state with a belief in liberal universalism.
Liberal nationalism is kind of non-xenophobic nationalism that is claimed to be compatible with liberal values of freedom, tolerance, equality, and individual rights.[151][152][153] Ernest Renan[154] and John Stuart Mill[155] are often thought to be early liberal nationalists. Liberal nationalists often defend the value of national identity by saying that individuals need a national identity to lead meaningful, autonomous lives,[156][157] and that liberal democratic polities need national identity to function properly.[158][159]
Civic nationalism lies within the traditions of rationalism and liberalism, but as a form of nationalism it is usually contrasted with ethnic nationalism. Civic nationalism is correlated with long-established states whose dynastic rulers had gradually acquired multiple distinct territories, with little change to boundaries, but which contained historical populations of multiple linguistic and/or confessional backgrounds. Since individuals resident within different parts of the state territory might have little obvious common ground, civic nationalism developed as a way for rulers to both explain a contemporary reason for such heterogeneity and to provide a common purpose (Ernest Renan's classic description in What is a Nation? (1882) as a voluntary partnership for a common endeavour). Renan argued that factors such as ethnicity, language, religion, economics, geography, ruling dynasty and historic military deeds were important but not sufficient. Needed was a spiritual soul that allowed as a "daily referendum" among the people.[160] Civic-national ideals influenced the development of representative democracy in multiethnic countries such as the United States and France, as well as in constitutional monarchies such as Great Britain, Belgium and Spain.[50]
German philosopher Monika Kirloskar-Steinbach does not think liberalism and nationalism are compatible, but she points out there are many liberals who think they are. She states:
- Justifications of nationalism seem to be making a headway in political philosophy. Its proponents contend that liberalism and nationalism are not necessarily mutually exclusive and that they can in fact be made compatible. Liberal nationalists urge one to consider nationalism not as the pathology of modernity but as an answer to its malaise. For them, nationalism is more than an infantile disease, more than "the measles of mankind" as Einstein once proclaimed it to be. They argue that nationalism is a legitimate way of understanding one's role and place in life. They strive for a normative justification of nationalism which lies within liberal limits. The main claim which seems to be involved here is that as long as a nationalism abhors violence and propagates liberal rights and equal citizenship for all citizens of its state, its philosophical credentials can be considered to be sound.[161]

Creole nationalism
"Creole nationalism" refers to the ideology that emerged in independence movements among the creoles (descendants of the colonizers), especially in Latin America in the early 19th century. It was facilitated when French Emperor Napoleon seized control of Spain and Portugal, breaking the chain of control from the Spanish and Portuguese kings to the local governors. Allegiance to the Napoleonic states was rejected, and increasingly the creoles demanded independence. They achieved it after civil wars 1808–1826.[162]
Nativist nationalism
Nativist nationalism is a type of nationalism similar to creole or territorial types of nationalism, but which defines belonging to a nation solely by being born on its territory. In countries where strong nativist nationalism exists, people who were not born in the country are seen as lesser nationals than those who were born there, and are called " immigrants" even if they became naturalized. It is cultural as people will never see a foreign-born person as one of them, and is legal, as such people are banned for life from holding certain jobs, especially government jobs. This nationalism is common in the Americas, both in daily life and in legal and work areas.
Ethnic nationalism
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethno-nationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the "nation" is defined in terms of ethnicity.[163] The central theme of ethnic nationalists is that "nations are defined by a shared heritage, which usually includes a common language, a common faith, and a common ethnic ancestry".[164] It also includes ideas of a culture shared between members of the group, and with their ancestors. However, it is different from a purely cultural definition of "the nation," which allows people to become members of a nation by cultural assimilation; and from a purely linguistic definition, according to which "the nation" consists of all speakers of a specific language.
Whereas nationalism in and of itself does not imply a belief in the superiority of one ethnicity or country over others, some nationalists support ethnocentric supremacy or protectionism.
The humiliation of being a second-class citizen led regional minorities in multiethnic states, such as Great Britain, Spain, France, Germany, Russia and the Ottoman Empire, to define nationalism in terms of loyalty to their minority culture, especially language and religion. Forced assimilation was anathema.[165]
For the politically dominant cultural group, assimilation was necessary to minimize disloyalty and treason and therefore became a major component of nationalism. A second factor for the politically dominant group was competition with neighboring states—nationalism involved a rivalry, especially in terms of military prowess and economic strength.[166]
Economic nationalism
Economic nationalism, or economic patriotism, refers to an ideology that favors state interventionism in the economy, with policies that emphasize domestic control of the economy, labor, and capital formation, even if this requires the imposition of tariffs and other restrictions on the movement of labor, goods and capital.
Religious nationalism
Religious nationalism is the relationship of nationalism to a particular religious belief, dogma, or affiliation where a shared religion can be seen to contribute to a sense of national unity, a common bond among the citizens of the nation. Saudi Arabian, Iranian, Egyptian, Iraqi, and the Pakistani-Islamic nationalism (Two-Nation Theory) are some examples.
Left-wing nationalism

Left-wing nationalism (occasionally known as socialist nationalism, not to be confused with national socialism)[167] refers to any political movement that combines left-wing politics with nationalism.
Many nationalist movements are dedicated to national liberation, in the view that their nations are being persecuted by other nations and thus need to exercise self-determination by liberating themselves from the accused persecutors. Anti-revisionist Marxist–Leninism is closely tied with this ideology, and practical examples include Stalin's early work Marxism and the National Question and his socialism in one country edict, which declares that nationalism can be used in an internationalist context, fighting for national liberation without racial or religious divisions.
Other examples of left-wing nationalism include Fidel Castro's 26th of July Movement that launched the Cuban Revolution in 1959, Cornwall's Mebyon Kernow, Ireland's Sinn Féin, Wales's Plaid Cymru, the Awami League in Bangladesh, the African National Congress in South Africa and numerous movements in Eastern Europe.[168][169]
Territorial nationalism
Some nationalists exclude certain groups. Some nationalists, defining the national community in ethnic, linguistic, cultural, historic, or religious terms (or a combination of these), may then seek to deem certain minorities as not truly being a part of the 'national community' as they define it. Sometimes a mythic homeland is more important for the national identity than the actual territory occupied by the nation.[170]

Territorial nationalists assume that all inhabitants of a particular nation owe allegiance to their country of birth or adoption .[171] A sacred quality is sought in the nation and in the popular memories it evokes. Citizenship is idealized by territorial nationalists. A criterion of a territorial nationalism is the establishment of a mass, public culture based on common values, codes and traditions of the population.[172]
Integral nationalism, irredentism, and pan-nationalism
There are different types of nationalism including Risorgimento nationalism and Integral nationalism.[173][174] Whereas risorgimento nationalism applies to a nation seeking to establish a liberal state (for example the Risorgimento in Italy and similar movements in Greece, Germany, Poland during the 19th century or the civic American nationalism), integral nationalism results after a nation has achieved independence and has established a state. Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany, according to Alter and Brown, were examples of integral nationalism.
Some of the qualities that characterize integral nationalism are anti-individualism, statism, radical extremism, and aggressive-expansionist militarism. The term Integral Nationalism often overlaps with fascism, although many natural points of disagreement exist. Integral nationalism arises in countries where a strong military ethos has become entrenched through the independence struggle, when, once independence is achieved, it is believed that a strong military is required to ensure the security and viability of the new state. Also, the success of such a liberation struggle results in feelings of national superiority that may lead to extreme nationalism.
Pan-nationalism is unique in that it covers a large area span. Pan-nationalism focuses more on "clusters" of ethnic groups. Pan-Slavism is one example of Pan-nationalism. The goal is to unite all Slavic people into one country. They did succeed by uniting several south Slavic people into Yugoslavia in 1918.[175]
Anti-colonial nationalism

This form of nationalism came about during the decolonization of the post war periods. It was a reaction mainly in Africa and Asia against being subdued by foreign powers. It also appeared in the non-Russian territories of the Tsarist empire and later, the USSR, where Ukrainianists and Islamic Marxists condemned Russian Bolshevik rule in their territories as a renewed Russian imperialism. This form of nationalism took many guises, including the peaceful passive resistance movement led by Mahatma Gandhi in the Indian subcontinent.[176]
Benedict Anderson argued that anti-colonial nationalism is grounded in the experience of literate and bilingual indigenous intellectuals fluent in the language of the imperial power, schooled in its "national" history, and staffing the colonial administrative cadres up to but not including its highest levels. Post-colonial national governments have been essentially indigenous forms of the previous imperial administration.[177][178]
Racial nationalism
Racial nationalism is an ideology that advocates a racial definition of national identity. Racial nationalism seeks to preserve a given race through policies such as banning race mixing and the immigration of other races. Specific examples are black nationalism and white nationalism.
Sports nationalism
Sport spectacles like football's World Cup command worldwide audiences as nations battle for supremacy and the fans invest intense support for their national team. Increasingly people have tied their loyalties and even their cultural identity to national teams.[179] The globalization of audiences through television and other media has generated revenues from advertisers and subscribers in the billions of dollars, as the FIFA Scandals of 2015 revealed.[180] Jeff Kingston looks at football, the Commonwealth Games, baseball, cricket, and the Olympics and finds that, "The capacity of sports to ignite and amplify nationalist passions and prejudices is as extraordinary as is their power to console, unify, uplift and generate goodwill."[181] The phenomenon is evident across most of the world.[182][183][184] The British Empire strongly emphasized sports among its soldiers and agents across the world, and often the locals joined in enthusiastically.[185] It established a high prestige competition in 1930, named the British Empire Games from 1930–50, the British Empire and Commonwealth Games from 1954–66, British Commonwealth Games from 1970–74 and since then the Commonwealth Games.[186]
The French Empire was not far behind the British in the use of sports to strengthen colonial solidarity with France. Colonial officials promoted and subsidized gymnastics, table games, and dance and helped football spread to French colonies.[187]
Gendered and muscular nationalism
Feminist critique interprets nationalism as a mechanism through which sexual control and repression are justified and legitimised, often by a dominant masculine power. The gendering of nationalism through socially constructed notions of masculinity and femininity not only shapes what masculine and feminine participation in the building of that nation will look like, but also how the nation will be imagined by nationalists.[188] A nation having its own identity is viewed as necessary, and often inevitable, and these identities are gendered.[189] The physical land itself is often gendered as female (i.e. "Motherland"), with a body in constant danger of violation by foreign males, while national pride and protectiveness of "her" borders is gendered as masculine.[190]

History, political ideologies, and religions place most nations along a continuum of muscular nationalism.[189] Muscular nationalism conceptualises a nation's identity as being derived from muscular or masculine attributes that are unique to a particular country.[189] If definitions of nationalism and gender are understood as socially and culturally constructed, the two may be constructed in conjunction by invoking an "us" versus "them" dichotomy for the purpose of the exclusion of the so-called "other," who is used to reinforce the unifying ties of the nation.[188] The empowerment of one gender, nation or sexuality tends to occur at the expense and disempowerment of another; in this way, nationalism can be used as an instrument to perpetuate heteronormative structures of power.[191] The gendered manner in which dominant nationalism has been imagined in most states in the world has had important implications on not only individual's lived experience, but on international relations.[192] Colonialism is heavily connected to muscular nationalism, from research linking British hegemonic masculinity and empire-building,[188] to intersectional oppression being justified by colonialist images of “others”, a practice integral in the formation of Western identity.[193] This “othering” may come in the form of orientalism, whereby the East is feminized and sexualized by the West. The imagined feminine East, or “other,” exists in contrast to the masculine West.
The status of conquered nations can become a causality dilemma: the nation was “conquered because they were effeminate and seen as effeminate because they were conquered.”[188] In defeat they are considered militaristically unskilled, not aggressive, and thus not muscular. In order for a nation to be considered “proper”, it must possess the male-gendered characteristics of virility, as opposed to the stereotypically female characteristics of subservience and dependency.[189] Muscular nationalism is often inseparable from the concept of a warrior, which shares ideological commonalities across many nations; they are defined by the masculine notions of aggression, willingness to engage in war, decisiveness, and muscular strength, as opposed to the feminine notions of peacefulness, weakness, non-violence, and compassion.[188] This masculinized image of a warrior has been theorised to be “the culmination of a series of gendered historical and social processes" played out in a national and international context.[188] Ideas of cultural dualism—of a martial man and chaste woman—which are implicit in muscular nationalism, underline the raced, classed, gendered, and heteronormative nature of dominant national identity.[189]
Nations and gender systems are mutually supportive constructions: the nation fulfils the masculine ideals of comradeship and brotherhood.[194] Masculinity has been cited as a notable factor in producing political militancy.[194] A common feature of national crisis is a drastic shift in the socially acceptable ways of being a man,[195] which then helps to shape the gendered perception of the nation as a whole.
Criticism
Critics of nationalism have argued that it is often unclear what constitutes a nation, or whether a nation is a legitimate unit of political rule. Nationalists hold that the boundaries of a nation and a state should coincide with one another, thus nationalism tends to oppose multiculturalism.[196] It can also lead to conflict when more than one national group finds itself claiming rights to a particular territory or seeking to take control of the state.[4]
Philosopher A.C. Grayling describes nations as artificial constructs, "their boundaries drawn in the blood of past wars". He argues that "there is no country on earth which is not home to more than one different but usually coexisting culture. Cultural heritage is not the same thing as national identity".[197]
Nationalism is inherently divisive because it highlights perceived differences between people, emphasizing an individual's identification with their own nation. The idea is also potentially oppressive because it submerges individual identity within a national whole and gives elites or political leaders potential opportunities to manipulate or control the masses.[198] Much of the early opposition to nationalism was related to its geopolitical ideal of a separate state for every nation. The classic nationalist movements of the 19th century rejected the very existence of the multi-ethnic empires in Europe. However, even in that early stage there was an ideological critique of nationalism which has developed into several forms of internationalism and anti-nationalism. The Islamic revival of the 20th century also produced an Islamist critique of the nation-state. (see Pan-Islamism)[199]
At the end of the 19th century, Marxists and other socialists and communists (such as Rosa Luxemburg) produced political analyses that were critical of the nationalist movements then active in Central and Eastern Europe, although a variety of other contemporary socialists and communists, from Vladimir Lenin (a communist) to Józef Piłsudski (a socialist), were more sympathetic to national self-determination.[200]
In his classic essay on the topic, George Orwell distinguishes nationalism from patriotism which he defines as devotion to a particular place. More abstractly, nationalism is "power-hunger tempered by self-deception".[201]
For Orwell, the nationalist is more likely than not dominated by irrational negative impulses:
There are, for example, Trotskyists who have become simply enemies of the U.S.S.R. without developing a corresponding loyalty to any other unit. When one grasps the implications of this, the nature of what I mean by nationalism becomes a good deal clearer. A nationalist is one who thinks solely, or mainly, in terms of competitive prestige. He may be a positive or a negative nationalist—that is, he may use his mental energy either in boosting or in denigrating—but at any rate his thoughts always turn on victories, defeats, triumphs and humiliations. He sees history, especially contemporary history, as the endless rise and decline of great power units and every event that happens seems to him a demonstration that his own side is on the upgrade and some hated rival is on the downgrade. But finally, it is important not to confuse nationalism with mere worship of success. The nationalist does not go on the principle of simply ganging up with the strongest side. On the contrary, having picked his side, he persuades himself that it is the strongest and is able to stick to his belief even when the facts are overwhelmingly against him.[201]
In the liberal political tradition there was mostly a negative attitude toward nationalism as a dangerous force and a cause of conflict and war between nation-states. The historian Lord Acton put the case against "nationalism as insanity" in 1862. He argued that nationalism suppresses minorities, it places country above moral principles and especially it creates a dangerous individual attachment to the state. However, Acton opposed democracy and was trying to defend the pope from Italian nationalism.[202] Since the late 20th century, liberals have been increasingly divided, with some philosophers such as Michael Walzer, Isaiah Berlin, Charles Taylor and David Miller emphasizing that a liberal society needed to be based in a stable nation state.[203]
The pacifist critique of nationalism also concentrates on the violence of nationalist movements, the associated militarism, and on conflicts between nations inspired by jingoism or chauvinism. National symbols and patriotic assertiveness are in some countries discredited by their historical link with past wars, especially in Germany. British pacifist Bertrand Russell criticizes nationalism for diminishing the individual's capacity to judge his or her fatherland's foreign policy.[204][205] Albert Einstein stated that "Nationalism is an infantile disease. It is the measles of mankind".[206]
See also
- Chauvinism
- Gellner's theory of nationalism
- Global issue
- Jingoism
- List of figures in nationalism
- List of historical separatist movements
- Neo-nationalism
- List of nationalist organizations
- List of active nationalist parties in Europe
- Lists of active separatist movements
- Nationalisms Across the Globe
- Patriotism
- National memory
- Nationalism studies, an interdisciplinary academic field devoted to the study of nationalism
- Nationalist historiography
- Nativism
- Xenophobia
- Nationalism in the Middle Ages
Notes
- Smith, Anthony. Nationalism: Theory, Ideology, History. Polity, 2010. pp. 9, 25–30; James, Paul (1996). Nation Formation: Towards a Theory of Abstract Community. London: Sage Publications.
- Finlayson, Alan (2014). "5. Nationalism". In Geoghegan, Vincent; Wilford, Rick (eds.). Political Ideologies: An Introduction. Routledge. pp. 100-102. ISBN 978-1-317-80433-8.
- Yack, Bernard. Nationalism and the Moral Psychology of Community. University of Chicago Press, 2012. p. 142
- Triandafyllidou, Anna (1998). "National Identity and the Other". Ethnic and Racial Studies. 21 (4): 593–612. doi:10.1080/014198798329784.
- Smith, A.D. (1981). The Ethnic Revival in the Modern World. Cambridge University Press.
- Smith, Anthony. Nationalism: Theory, Ideology, History. Polity, 2010. pp. 6–7, 30–31, 37
- Nairn, Tom; James, Paul (2005). Global Matrix: Nationalism, Globalism and State-Terrorism. London and New York: Pluto Press.; and James, Paul (2006). Globalism, Nationalism, Tribalism: Bringing Theory Back In – Volume 2 of Towards a Theory of Abstract Community. London: Sage Publications.
- Kohn, Hans (2018). Nationalism. Encyclopedia Britannica.
- Smith, Deanna (2007). Nationalism (2nd ed.). Cambridge: polity. ISBN 978-0-7456-5128-6.
- Motyl 2001, p. 262.
- Billig 1995, p. 72.
- Gellner, Ernest (2005). Nations and Nationalism (2nd ed.). Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-3442-2.
- Canovan, Margaret (1996). Nationhood and Political Theory. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar. ISBN 978-1-85278-852-0.
- lord Miller 1995, p. 160
- Beissinger, Mark. Nationalist Mobilization and the Collapse of the Soviet State. Cambridge University Press, 2002. p.8
- Krikorian, Shant. "The Demise of the USSR in the Face of Nationalism". Prospect: Journal of International Affairs. University of California, San Diego, 1 December 2010.
- Pierre James (2001). The Murderous Paradise: German Nationalism and the Holocaust. Greenwood. ISBN 9780275972424.
- "By selling this fateful action in starkly nationalist language, the Putin regime achieved record-high popularity." Pål Kolstø; Helge Blakkisrud (2018). Russia Before and After Crimea: Nationalism and Identity 2010–17. Edinburgh UP. p. xvii. ISBN 9781474433853.
- Gat, Azar (2012). Nations: The Long History and Deep Roots of Political Ethnicity and Nationalism. Cambridge University Press. p. 214. ISBN 978-1-107-00785-7.
- "Nationalism". merriam-webster.com.
- See Norman Rich, The age of nationalism and reform, 1850–1890 (1970).
- Glenda Sluga, Internationalism in the Age of Nationalism (University of Pennsylvania Press, 2013) ch 1
- Kohn, Hans (1967) [1944]. The Idea Of Nationalism: A Study In Its Origins And Background. Transaction Publishers. p. 1i. ISBN 978-1-4128-3729-3.
- Gregorio F. Zaide (1965). World History. . p. 274. ISBN 978-971-23-1472-8.
- Calhoun, Craig (1993). "Nationalism and Ethnicity". Annual Review of Sociology. 19: 211–39. doi:10.1146/annurev.soc.19.1.211.
- Zimmer, O. (2003). Nationalism in Europe, 1890-1940. Studies in European History. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-4039-4388-0. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- Raymond Pearson, ed., The Long-man companion to European nationalism 1789–1920 (2014) p. xi, with details on each country large and small.
- "Nationalism in Europe and America | Lloyd S. Kramer | University of North Carolina Press". University of North Carolina Press. Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- Gerald Newman (1997). The Rise of English Nationalism: A Cultural History, 1740–1830. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-17699-0.
- Nick Groom, The Union Jack: The Story of the British Flag (2007).
- Scholes, Percy A (1970). The Oxford Companion to Music (tenth ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 897.
- Newman, Gerald G. (1987). The Rise of English Nationalism: A Cultural History, 1740–1830. New York: St. Martin's Press. ISBN 978-0-312-68247-7.
- Smith, Anthony D. (1998). Nationalism and Modernism: A Critical Survey of Recent Theories of Nations and Nationalism. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-06341-8.
- Iain McLean, Alistair McMillan, Concise Oxford Dictionary of Politics, "French Revolution... It produced the modern doctrine of nationalism, and spread it directly throughout Western Europe ...", Oxford, 2009, ISBN 978-0-19-920516-5.
- Christopher Dandeker, ed. (1998). Nationalism and Violence. Transaction Publishers. p. 52. ISBN 978-1-4128-2935-9.
- Votruba, Martin. "Herder on Language" (PDF). Slovak Studies Program. University of Pittsburgh. Retrieved 30 June 2010.
- T.C.W. Blanning (2003). The Culture of Power and the Power of Culture: Old Regime Europe 1660–1789. Oxford University Press. pp. 259–60. ISBN 978-0-19-926561-9.
- Snellman, Johan Vilhelm (1806 - 1881)
- Snellman, the man who inspired Finns to be Finns
- Prime Minister Vanhanen at the Celebration of J.V. Snellman
- Five Facts That You Didn’t Know About J.V. Snellman
- Andrew Nestingen: Crime and Fantasy in Scandinavia: Fiction, Film and Social Change. University of Washington Press, 2008. ISBN 978-8763507936.
- John Horne (2012). A Companion to World War I. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 21–22. ISBN 978-1-119-96870-2.
- Gillette, Aaron (2006). "Why Did They Fight the Great War? A Multi-Level Class Analysis of the Causes of the First World War". The History Teacher. 40 (1): 45–58. doi:10.2307/30036938. JSTOR 30036938.
- Kohn, Hans (1950). "Napoleon and the Age of Nationalism". The Journal of Modern History. 22 (1): 21–37. doi:10.1086/237315. JSTOR 1875877.
- J. P. T. Bury, “Nationalities and Nationalism,” in J. P. T. Bury, ed. "The New Cambridge Modern History Vol. 10 (1830-70)" (1960) pp 213-245, at p. 245 online.
- Moran, Daniel; Waldron, Arthur, eds. (2003). The People in Arms: Military Myth and National Mobilization since the French Revolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 14.
- K. Varley (2008). Under the Shadow of Defeat: The War of 1870–71 in French Memory. Palgrave Macmillan UK. p. 54. ISBN 978-0-230-58234-7.
- Karine Varley, "The Taboos of Defeat: Unmentionable Memories of the Franco-Prussian War in France, 1870–1914." in Jenny Macleod, ed., Defeat and Memory: Cultural Histories of Military Defeat in the Modern Era (Palgrave Macmillan, 2008) pp. 62–80.
- Jeremy D. Popkin (2016). A History of Modern France. p. 173. ISBN 978-1-315-50820-7.
- Nicholas V. Riasanovsky, Nicholas I and Official Nationality in Russia 1825 – 1855 (1969)
- Hutchings, Stephen C. (2004). Russian Literary Culture in the Camera Age: The Word as Image. Routledge. p. 86.
- Astrid S. Tuminez, Russian Nationalism since 1856: Ideology and the Making of Foreign Policy (2000)
- Miller, Nicola (2006). "The historiography of nationalism and national identity in Latin America". Nations and Nationalism. 12 (2): 201–21. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8129.2006.00237.x.
- "CBSE Class 10 history chapter 1 notes - The Rise of nationalism in Europe by learnturnx". education. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- John Lynch, The Spanish American Revolutions 1808–1826 (2nd ed. 1986)
- Alan Forrest and Peter H. Wilson, eds. The Bee and the Eagle: Napoleonic France and the End of the Holy Roman Empire (Palgrave Macmillan, 2009).
- Karen Hagemann, "Of 'manly valor' and 'German Honor': nation, war, and masculinity in the age of the Prussian uprising against Napoleon." Central European History 30#2 (1997): 187–220.
- Hagen Schulze, The Course of German Nationalism: From Frederick the Great to Bismarck 1763–1867 (Cambridge UP, 1991).
- Louis L. Snyder, Encyclopedia of Nationalism (1990) pp. 77–78, 381–82.
- Adolf Hausrath, ed. Treitschke, his doctrine of German destiny and of international relations: together with a study of his life and work (1914) online edition
- Snyder, Encyclopedia of Nationalism (1990) pp. 399–401
- Hruška, Emil (2013), Boj o pohraničí: Sudetoněmecký Freikorps v roce 1938 (1st ed.), Prague: Nakladatelství epocha, Pražská vydavatelská společnost, p. 11
- Hochman, Adam (2015). "Of Vikings and Nazis: Norwegian contributions to the rise and the fall of the idea of a superior Aryan race". Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences. 54: 84–88. doi:10.1016/j.shpsc.2015.09.003.
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica (n.d.). "Aryan people". Encyclopedia Britannica On-line. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- McKay, Alex (Spring 2001). "Hitler and the Himalayas: The SS Mission to Tibet 1938–39". Tricycle Magazine.
- Boissoneault, Lorraine (31 March 2017). "When the Nazis Tried to Bring Animals Back From Extinction: Their ideology of genetic purity extended to aspirations about reviving a pristine landscape with ancient animals and forests". Smithsonian.com. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- Silvana Patriarca and Lucy Riall, eds., The Risorgimento Revisited: Nationalism and Culture in Nineteenth-century Italy (Palgrave Macmillan, 2011).
- Stephen Barbour; Cathie Carmichael, eds. (2000). Language and Nationalism in Europe. Oxford UP chapter 8. ISBN 978-0-19-158407-7.
- Vasiliev, Aleksandr Aleksandrovich, Vasiliev (1952). History of the Byzantine Empire, 324–1453. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 582. ISBN 978-0-299-80926-3.
- Alister E. McGrath (2012). Christian History: An Introduction. p. 270. ISBN 978-1-118-33783-7.
- Hajdarpasic, Edin (2015). Whose Bosnia? Nationalism and Political Imagination in the Balkans, 1840–1914. Ithaca and London: Cornell University Press. pp. 1–17, 90–126. ISBN 978-0-8014-5371-7.
- Christopher Clark, The Sleepwalkers: How Europe Went to War in 1914 (2012)
- Sabrina P. Ramet, Nationalism and federalism in Yugoslavia, 1962–1991 (Indiana Univ Press, 1992).
- Richard Blanke, Prussian Poland in the German Empire (1871–1900) (1981)
- Norman Davies, God's Playground: A History of Poland, Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present (2005).
- Geoffrey A. Hosking and George Schöpflin (1997). Myths and Nationhood. Routledge. p. 152. ISBN 978-0-415-91974-6.
- Sharp, Tony (1977). "The Origins of the 'Teheran Formula' on Polish Frontiers". Journal of Contemporary History. 12 (2): 381–93. doi:10.1177/002200947701200209. JSTOR 260222.
- Davies (2001). Heart of Europe. pp. 286–87. ISBN 978-0-19-158771-9.
- David, Engel (2009). Zionism. Pearson Longman Publishing Group.
- Rotem Kowner, ed., The impact of the Russo-Japanese war (Routledge, 2006).
- Hans Kohn, Nationalism: Its Meaning and History (1955) p. 87.
- Shakhar Rahav, The Rise of Political Intellectuals in Modern China: May Fourth Societies and the Roots of Mass-Party Politics (Oxford UP, 2015).
- Patricia Buckley Ebrey, Cambridge Illustrated History of China (1996) p. 271
- Alistair Horne, A savage war of peace: Algeria 1954–1962 (1977).
- David Anderson, Histories of the hanged: The dirty war in Kenya and the end of empire (2005).
- Gabriel Almond and James S. Coleman, The Politics of the Developing Areas (1971)
- Festus Ugboaja Ohaegbulam, Nationalism in colonial and post-colonial Africa (University Press of America, 1977).
- Thomas Hodgkin, Nationalism in Colonial Africa (1956)
- Nancy L. Clark and William H. Worger, South Africa: The rise and fall of apartheid (Routledge, 2013).
- Berg, Steven (1993). "Nationalism Redux: Through the Glass of the Post-Communist States Darkly". Ethnic Conflicts WorldWide, Current History: 162–66.
- Barber, Benjamin (1992). "Jihad vs. McWorld: the two axial principles of our age—tribalism and globalism—clash at every point except one: they may both be threatening to democracy". The Atlantic.
- Huntington, Samuel (1993). "The Clash of Civilizations". Foreign Affairs. 72 (3): 22–49. doi:10.2307/20045621. JSTOR 20045621.
- Berg, Steven (2004). "Why Yugoslavia Fell Apart". Current History. 92:577: 357–63.
- Ramet, Sabrina (1996). "Eastern Europe's Painful Transition". Current History: 97–102.
- "Can Europe's new xenophobes reshape the continent?". The Guardian. 3 February 2018.
- "What is the point of the Arab League?". The Economist. 29 April 2016.
- McCartney, Paul T. (Fall 2004). "American Nationalism and U.S. Foreign Policy from September 11 to the Iraq War". Political Science Quarterly. 119 (3): 399–423. doi:10.2307/20202389. JSTOR 20202389.
- Postelnicescu, Claudia (12 May 2016). "Europe's New Identity: The Refugee Crisis and the Rise of Nationalism". European Journal of Psychology. 12 (2): 203–09. doi:10.5964/ejop.v12i2.1191. PMC 4894286. PMID 27298631.
- Clark, Philip (12 November 2015). "The New European Nationalism and the Migrant Crisis". Stanford Politics.
- Arnold, Richard (30 May 2016). "Surveys show Russian nationalism is on the rise. This explains a lot about the country's foreign and domestic politics". Washington Post.
- Arshakuni, Nini, ed. (June 2016). "The Rise of the Russian Nationalism, the Secret of Putin's Survival, and the Return of Stalin". Institute of Modern Russia.
- Zamoyski, Adam (27 January 2016). "The Problem With Poland's New Nationalism". Foreign Policy.
- "Why is Hungary turning to nationalism?". The Economist. 5 April 2018.
- "Bulgaria's government will include far-right nationalist parties for the first time". Washington Post. 25 April 2017.
- "Threat to collapse Fico coalition after journalist killing". EUobserver. 13 March 2018.
- "Latvia's nationalist party demands right for employees to use Latvian language". Xinhua News Agency. 14 November 2017.
- "In Ukraine, nationalists gain influence – and scrutiny". Reuters. 18 March 2014.
- Burke, Jason (16 May 2014). "Narendra Modi's landslide victory shatters Congress's grip on India". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- Iwanek, Krzysztof. "Narendra Modi Wins Again — What Does That Mean for India?". thediplomat.com. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- "Yes, I am a Hindu nationalist: Narendra Modi | News - Times of India Videos". The Times of India. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- "India falls to 51st position in EIU's Democracy Index". The Economic Times. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- "India: Mounting Human Rights Abuses". Human Rights Watch. 14 January 2020. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- "World Report 2019: Rights Trends in India". Human Rights Watch. 18 December 2018. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- "The Regional Reach of Buddhist Nationalism". U.S. News. 7 November 2017.
- "Review: Myanmar's Enemy Within and the Making of Anti-Muslim Rage". Time. 12 October 2017.
- Barnett, Anthony (2017). The Lure of Greatness: England's Brexit and America's Trump. Random House. ISBN 978-1-78352-454-9.
- "Trump: 'I'm a nationalist'".
- Gearan, Anne (13 November 2018). "Trump refuses to acknowledge the fraught history of nationalism". Retrieved 14 November 2018.
- Kato, Norihiro (12 September 2014). "Tea Party Politics in Japan". New York Times.
- Feffer, John. "Japan's Resurgent Nationalism".
- Teehankee, Julio C. (2016). "Journal of Current Southeast Asian Affairs". Journal of Current Southeast Asian Affairs. Archived from the original on 31 July 2017. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- Kingsley, Patrick (17 April 2017). "In Supporting Erdogan, Turks Cite Economic and Religious Gains". New York Times.
- "Why Spanish Nationalism Is on the Rise". Foreign Affairs. 5 February 2018.
- "Madrid Unity Rally Mired by Fascist Salutes From Far-right Falange Party Members". Haaretz. 8 October 2017.
- Koronaiou, Alexandra; Lagos, Evangelos; Sakellariou, Alexandros; Kymionis, Stelios; Chiotaki-Poulou, Irini (1 December 2015). "Golden Dawn, Austerity and Young People: The Rise of Fascist Extremism Among Young People in Contemporary Greek Society". The Sociological Review, SAGE. 63 (2_suppl): 231–249. doi:10.1111/1467-954X.12270.
- Miller, Max (31 March 2016). "The Nature of the State". Oxford Bibliographies. Retrieved 18 May 2017.
- Weber, Max (1994). Weber: Political Writings. Cambridge: UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 309–31.
- Anderson, Benedict (2006). Imagined Communities: Reflections on the origins and spread of nationalism. Verso Books.
- Posen, Barry (Fall 1993). "Nationalism, the Mass Army, and Military Power". International Security. 18 (2): 80–124. doi:10.2307/2539098. JSTOR 2539098.
- Motyl 2001, pp. 508–09.
- Motyl 2001, p. 510.
- Motyl 2001, pp. 272–73.
- Goetze, David (1998). "Evolution, Mobility, and Ethnic Group Formation". Politics and the Life Sciences. 17 (1): 59–71. doi:10.1017/S0730938400025363. JSTOR 4236409.
- Kevin N. Laland; Gillian R. Brown (2011). Sense and Nonsense: Evolutionary Perspectives on Human Behaviour. Oxford UP. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-19-958696-7.
- Motyl 2001, p. 273.
- Motyl 2001, p. 495-496.
- Motyl 2001, p. 268.
- Motyl 2001, p. 271.
- Motyl 2001, p. 272.
- Robert Hislope "From Ontology to Analogy: Evolutionary Theories and the Explanation of Ethnic Politics: in Patrick James and David Goetze ed. Evolutionary Theory and Ethnic Conflict (2000) p. 174.
- G.P. Gooch (1920). Nationalism. Swarthmore Press Limited. p. 5.
- K. Marx, F. Engels. Manifesto of the Communist Party.
- Smith, Anthony D. (March 1983). "Nationalism and Classical Social Theory". The British Journal of Sociology. 34 (1): 19–38. doi:10.2307/590606. JSTOR 590606.
- Stalin, Joseph. "Marxism and the National Question". marxists.org. Marxists Internet Archive. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- Wirth, Louis (1 May 1936). "Types of Nationalism". American Journal of Sociology. 41 (6): 723–37. doi:10.1086/217296. ISSN 0002-9602.
- Kohn, Hans (2005) [1944]. The Idea of Nationalism: A Study of Its Origins and Background (reprint). New York: Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4128-0476-9.
- Spencer, Philip; Wollman, Howard (1 October 1998). "Good and bad nationalisms: A critique of dualism". Journal of Political Ideologies. 3 (3): 255–274. doi:10.1080/13569319808420780. ISSN 1356-9317.
- Yack, Bernard (1 March 1996). "The myth of the civic nation". Critical Review. 10 (2): 193–211. doi:10.1080/08913819608443417. ISSN 0891-3811.
- Nash, Kate (2001). The Blackwell companion to political sociology. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 391. ISBN 978-0-631-21050-4.
- Tamir, Yael. 1993. Liberal Nationalism. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-07893-9
- Kymlicka 1995, p. 200.
- Miller 1995, pp. 188–89
- Renan, Ernest. 1882. "Qu'est-ce qu'une nation?"
- Mill, John Stuart. 1861. Considerations on Representative Government.
- Kymlicka 1995, p. 34.
- For criticism, see: Patten, Alan (1999). "The Autonomy Argument for Liberal Nationalism". Nations and Nationalism. 5 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1111/j.1354-5078.1999.00001.x.
- Miller 1995, p. 136
- For criticism, see: Abizadeh, Arash (2002). "Does Liberal Democracy Presuppose a Cultural Nation? Four Arguments". American Political Science Review. 96 (3): 495–509. doi:10.1017/s000305540200028x.; Abizadeh, Arash (2004). "Liberal Nationalist versus Postnational Social Integration". Nations and Nationalism. 10 (3): 231–50. doi:10.1111/j.1354-5078.2004.00165.x.
- Singley, Carol J. (2003). "Race, Culture, Nation: Edith Wharton and Ernest Renan". Twentieth Century Literature. 49 (1): 32–45. doi:10.2307/3176007. JSTOR 3176007.
- Monika Kirloskar-Steinbach, "Liberal Nationalism-A Critique" Trames 5#2 (June 2001) pp. 107–19 online
- D. A. Brading, The First America: The Spanish Monarchy, Creole Patriots and the Liberal State 1492–1866 (1991)
- "The Website of Political Research Associates". PublicEye.org. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- Muller, Jerry Z. "Us and Them." Current Issue 501 Mar/Apr 2008 9–14
- Timothy Baycroft, Nationalism in Europe 1789–1945 (1998) p. 56.
- Baycroft, Nationalism in Europe 1789–1945 (1998) p. 58.
- Schwarzmantel, J. J (2006). "Class and Nation: Problems of Socialist Nationalism". Political Studies. 35 (2): 239–55. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9248.1987.tb01886.x. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017.
- Robert Zuzowski, "The Left and Nationalism in Eastern Europe" East European Quarterly, 41#4 (2008) online
- Alexander J. Motyl, ed., Encyclopedia of Nationalism (2 vol. 2000).
- Smith, Anthony D. 1986. The Ethnic Origins of Nations London: Basil Blackwell. pp. 6–18. ISBN 0-631-15205-9.
- Middle East and North Africa: Challenge to Western Security by Peter Duignan and L.H. Gann, Hoover Institution Press, 1981, ISBN 978-0-8179-7392-6 p. 22
- Leoussi 2001, p. 62.
- Brown, David (2003). Contemporary Nationalism. ISBN 978-1-134-69541-6.
- Integral nationalism is one of five types of nationalism defined by Carlton Hayes in his 1928 book The Historical Evolution of Modern Nationalism.
- Ivo Banac, The National Question in Yugoslavia (Cornell University Press, 1984).
- Grant, Moyra. "Politics Review" (PDF). Politics Review. Retrieved 16 April 2011.
- Anderson 1983, pp. 37–46.
- Velychenko, Stephen (October 2012). "Ukrainia Anticolonialist Thought in Comparative Perspective". Ab Imperio (4): 339. doi:10.1353/imp.2012.0109.
- Grant Jarvie and Wray Vamplew, Sport, nationalism and cultural identity (1993).
- Andrew Jennings, The Dirty Game: Uncovering the Scandal at FIFA (2015).
- Jeff Kingston, Nationalism in Asia: A History Since 1945 (2016).
- H. Fernández L’Hoeste et al. Sports and Nationalism in Latin/o America (2015).
- Alan Bairner, Sport, nationalism, and globalization: European and North American perspectives (2001).
- Gwang Ok, Transformation of Modern Korean Sport: Imperialism, Nationalism, Globalization (2007).
- P. McDevitt, May the Best Man Win: Sport, Masculinity, and Nationalism in Great Britain and the Empire, 1880–1935 (2008).
- Harold Perkin, "Teaching the nations how to play: sport and society in the British empire and Commonwealth." International Journal of the History of Sport 6#2 (1989): 145–55.
- Driss Abbassi, "Le sport dans l'empire français: un instrument de domination?." Outre-mers 96.364 (2009): 5–15. online
- Banerjee, Sikata (2003). "Gender and nationalism: the masculinization of hinduism and female political participation in india". Women's Studies International Forum. 26 (2): 167–79. doi:10.1016/s0277-5395(03)00019-0.
- Mackay, Eva (2000). "Death by Landscape: Race, Nature and Gender in the Canadian Nationalist Mythology". Canadian Woman Studies. 20: 125–30 – via Journals.Yorku.
- Peterson, Spike V. (1998). "Gendered nationalism: Reproducing "Us" versus "Them"". In Turpin, Jennifer; Lorentzen, Lois Ann (eds.). The Woman and War Reader. New York: New York University Press. pp. 41–49. ISBN 978-0-8147-5145-9.
- Mayer, Tamar (2000). Gender Ironies of Nationalism. Psychology Press.
- Robidoux, Michael A. (2002). "Imagining a Canadian Identity through Sport: A Historical Interpretation of Lacrosse and Hockey". The Journal of American Folklore. 115 (456): 209–25. doi:10.2307/4129220. JSTOR 4129220.
- Said, Edward (1979). Orientalism. New York: Vintage Books. pp. 1–368. ISBN 978-0-394-74067-6.
- Waetjen, Thembisa (2001). "The Limits of Gender Rhetoric for Nationalism: A Case Study from Southern Africa". Theory and Society. 30 (1): 121–52. doi:10.1023/a:1011099627847. JSTOR 658064.
- Alison, Miranda (2007). "Wartime Sexual Violence: Women's Human Rights and Questions of Masculinity". Review of International Studies. 33 (1): 75–90. doi:10.1017/s0260210507007310. JSTOR 20097951.
- Heywood, Andrew (1999). Political Theory: An Introduction (2nd ed.). London: Macmillan Press. pp. 97–98. ISBN 978-0-333-76091-8.
- Grayling, A.C. (2001). The Meaning of Things: Applying Philosophy to Life. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. pp. 78–79. ISBN 978-0-297-60758-8.
- Heywood, Andrew (2000). Key Concepts in Politics. London: Macmillan Press. p. 256. ISBN 978-0-333-77095-5.
- World Book Encyclopedia, 2018 ed., s.v. "Muslims"
- Cliff, Tony (1959). "Rosa Luxemburg and the national question". Marxists Internet Archive. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- George Orwell, Notes on Nationalism, orwell.ru.
- Lang, Timothy (2002). "Lord Acton and 'the Insanity of Nationality'". Journal of the History of Ideas. 63 (1): 129–49. doi:10.2307/3654261. JSTOR 3654261.
- Motyl 1:298
- Russell Speaks His Mind, 1960. Fletcher and son Ltd., Norwich, United Kingdom
- Russell, Bertrand (1915). "The ethics of war". International Journal of Ethics. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- Viereck, George Sylvester (26 October 1929). "What Life Means to Einstein" (PDF). The Saturday Evening Post. p. 117. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
References
| Library resources about Nationalism |
- Anderson, Benedict (1983). Imagined Communities: Reflections on the Origin and Spread of Nationalism. London: Verso. ISBN 978-0-86091-059-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Billig, Michael (1995). Banal Nationalism. London: Sage. ISBN 978-0-8039-7525-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Delanty, Gerard; Kumar, Krishan, eds. (2006). The Sage Handbook of Nations and Nationalism. London: Sage Publications. ISBN 978-1-4129-0101-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Hayes, Carlton J. The Historical Evolution of Modern Nationalism (1928) the first major scholarly survey.
- Hobsbawm, Eric J. (1992). Nations and Nationalism Since 1780: Programme, Myth, Reality (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-43961-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- James, Paul (1996). Nation Formation: Towards a Theory of Abstract Community. London: Sage Publications. ISBN 978-0-7619-5072-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- James, Paul (2006). Globalism, Nationalism, Tribalism: Bringing Theory Back In. London: Sage Publications.
- Kohn, Hans. The idea of nationalism: A study in its origins and background (1944; 2nd ed. 2005 with introduction by Craig Calhoun). 735 pp; an often-cited classic
- Kymlicka, Will (1995). Multicultural Citizenship: A Liberal Theory of Minority Rights. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-827949-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Leoussi, Athena S., ed. (2001). Encyclopedia of Nationalism. New Brunswick, N.J: Transaction Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7658-0002-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Miller, David (1995). On Nationality. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-828047-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Motyl, Alexander, ed. (2001). Encyclopedia of Nationalism. San Diego: Academic Press 2 vol. ISBN 978-0-12-227230-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Snyder, Louis L. (1990). Encyclopedia of Nationalism. New York: Paragon House. ISBN 978-1-55778-167-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
Further reading
- Baycroft, Timothy. Nationalism in Europe 1789–1945 (1998), textbook; 104 pp.
- Breuilly, John (1994). Nationalism and the State (2nd ed.). University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-07414-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Breuilly, John, ed. The Oxford handbook of the history of nationalism (Oxford UP, 2013).
- Brubaker, Rogers (1996). Nationalism Reframed: Nationhood and the National Question in the New Europe. Cambridge UP. ISBN 978-0-521-57224-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Day, Graham (2004). Theorizing Nationalism. Palgrave. ISBN 978-0-333-96265-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- De Benoist, Alain (Summer 2004). "On Identity". Telos. 2004 (128).
- Gellner, Ernest. Nations and Nationalism (2nd ed. 2009).
- Gerrits, Nationalism in Europe since 1945 (2015).
- Greenfeld, Liah (1992). Nationalism: Five Roads to Modernity. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-60318-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Guibernau, Montserrat 2007 (The Identity of Nations) Polity Press, Cambridge UK
- Guibernau, Montserrat 2013 (Belonging: solidarity and division in modern societies) Polity Press, Cambridge
- Jusdanis, Gregory (2001). The Necessary Nation. Princeton UP. ISBN 978-0-691-07029-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kingston, Jeff. Nationalism in Asia: A History Since 1945 (2016).
- Kohn, Hans. Nationalism: Its Meaning and History (1955) 192 pp, with primary sources online
- Kramer, Lloyd. Nationalism in Europe and America: Politics, Cultures, and Identities since 1775 (2011). excerpt
- Malesevic, Sinisa (2006). Identity As Ideology: Understanding Ethnicity and Nationalism. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-8786-0.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Malesevic, Sinisa (2013). Nation-States and Nationalisms:Organization, Ideology and Solidarity. Polity. ISBN 978-0-7456-5339-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Malesevic, Sinisa (2019). Grounded Nationalisms. Cambridge University Press.
- Miscevic, Nenad (1 June 2010). "Nationalism". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford University.
- "Nations and Nationalism". Harvard Asia Pacific Review. 11 (1). Spring 2010. ISSN 1522-1113.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Özkirimli, Umut (2010). Theories of Nationalism: A Critical Introduction (2nd ed.). Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-57732-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Anthony D. (1981). The Ethnic Revival in the Modern World. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521232678.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Anthony D. (1995). Nations and Nationalism in a Global Era. Cambridge: Polity Press. ISBN 9780745610191.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Anthony D. (2000). The Nation in History: Historiographical Debates about Ethnicity and Nationalism. Hanover: University Press of New England. ISBN 9781584650409.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Anthony D. (2010) [2001]. Nationalism: Theory, Ideology, History (2. ed.). Cambridge: Polity Press. ISBN 9780745651279.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Anthony D. (2009). Ethno-symbolism and Nationalism: A Cultural Approach. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 9781135999483.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Smith, Anthony D. (2013). The Nation Made Real: Art and National Identity in Western Europe, 1600-1850. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199662975.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Spira, Thomas, ed. (1999). Nationalism and Ethnicity Terminologies: An Encyclopedic Dictionary and Research Guide. Gulf Breeze, FL: Academic International Press. ISBN 978-0-87569-205-0.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- White, Philip L.; White, Michael Lee (2008). "Nationality: The History of a Social Phenomenon". Nationality in World History.
External links
- Nationalism — entry at Encyclopædia Britannica
- "Nationalism". Internet Modern History Sourcebook. Fordham University.
- "The Nationalism Project". Association for Research on Ethnicity and Nationalism in the Americas. University of South Carolina.
- Nationalism : selected references