Tampramine
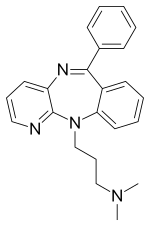
Tampramine (AHR-9,377) is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which was developed in the 1980s but was never marketed.[1][2] Despite being a TCA, it acts as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and has negligible affinity for adrenergic, histaminergic, and muscarinic receptors.[1] It was found to be effective in the forced swim test (FST) model of depression in animal studies but is not known to have ever been trialed in humans.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H24N4 |
| Molar mass | 356.473 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
See also
References
- Kinnier WJ, Tabor RD, Norrell LY (October 1984). "Neurochemical properties of AHR-9377: a novel inhibitor of norepinephrine reuptake". Biochemical Pharmacology. 33 (19): 3001–5. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(84)90600-2. PMID 6548381.
- O'Donnell JM, Seiden LS (1985). "Effect of the experimental antidepressant AHR-9377 on performance during differential reinforcement of low response rate". Psychopharmacology. 87 (3): 283–5. doi:10.1007/BF00432708. PMID 3936083.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.