Paroxetine
Paroxetine, sold under the brand names Paxil and Seroxat among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class.[5] It is used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder and premenstrual dysphoric disorder.[5] It has also been used in the treatment of premature ejaculation and hot flashes due to menopause.[5][6] It is taken by mouth.[5]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Paxil, Seroxat, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698032 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Extensively absorbed from the GI tract, but extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver[1][2][3][4] |
| Protein binding | 93–95%[1][2][3] |
| Metabolism | Extensive, hepatic (mostly CYP2D6-mediated)[1][2][3] |
| Elimination half-life | 21 hours[1][2][3] |
| Excretion | Renal (64%; 2% unchanged and 62% as metabolites), faecal (36%; <1% unchanged)[1][2][3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.112.096 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H20FNO3 |
| Molar mass | 329.371 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Common side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, loss of appetite, sweating, trouble sleeping, and sexual dysfunction.[5] Serious side effects may include suicide in those under the age of 25, serotonin syndrome, and mania.[5] While the rate of side effects appears similar compared to other SSRIs and SNRIs, antidepressant discontinuation syndromes may occur more often.[7][8] Use in pregnancy is not recommended while use during breastfeeding is relatively safe.[9] It is believed to work by blocking the re-uptake of the chemical serotonin by neurons in the brain.[5]
Paroxetine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1992 and initially sold by GlaxoSmithKline.[5][10] It is available as a generic medication.[11] In 2017, it was the 68th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than eleven million prescriptions.[12][13] The United States Department of Justice fined GlaxoSmithKline $3 billion in 2012, for withholding data, unlawfully promoting use in those under 18, and preparing an article that misleadingly reported the effects of paroxetine in adolescent with depression following its clinical trial study 329.[14][15][16]
Medical uses
Paroxetine is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, social anxiety disorder, panic disorder. It could be used also for agoraphobia, generalized anxiety disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder and menopausal hot flashes.[17][18][19][20][21]
Depression
A variety of meta analyses have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of paroxetine in depression. They have variously concluded that paroxetine is superior or equivalent to placebo and that it is equivalent or inferior to other antidepressants.[22][23][24] Despite this, there was no clear evidence that paroxetine was better or worse compared with other antidepressants at increasing response to treatment at any time point.[25]
Anxiety disorders
Paroxetine was the first antidepressant approved in the United States for the treatment of panic disorder.[26] Several studies have concluded that paroxetine is superior to placebo in the treatment of panic disorder.[24][27]
Paroxetine has demonstrated efficacy for the treatment of social anxiety disorder in adults and children.[28][29] It is also beneficial for people with co-occurring social anxiety disorder and alcohol use disorder.[30] It appears to be similar to a number of other SSRIs.[31]
Paroxetine is used in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder.[32] Comparative efficacy of paroxetine is equivalent to that of clomipramine and venlafaxine.[33][34] Paroxetine is also effective for children with obsessive-compulsive disorder.[35]
Paroxetine is approved for treatment of PTSD in the United States, Japan and Europe.[36][37][38] In the United States it is approved for short term use.[37]
Paroxetine is also FDA-approved for generalized anxiety disorder.[39]
Menopausal hot flashes
In 2013, low-dose paroxetine was approved in the US for the treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats associated with menopause.[6] At the low dose used for menopausal hot flashes, side effects are similar to placebo and dose tapering is not required for discontinuation.[40]
Adverse effects
Common side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, loss of appetite, sweating, trouble sleeping, and sexual dysfunction.[5] Serious side effects may include suicide in those under the age of 25, serotonin syndrome, and mania.[5] While rate of side effects appear similar compared to other SSRIs and SNRIs, antidepressant discontinuation syndromes may occur more often.[7][8] Use in pregnancy is not recommended while use during breastfeeding is relatively safe.[9]
Paroxetine shares many of the common adverse effects of SSRIs, including (with the corresponding rates seen in people treated with placebo in parentheses): nausea 26% (9%), diarrhea 12% (8%), constipation 14% (9%), dry mouth 18% (12%), somnolence 23% (9%), insomnia 13% (6%), headache 18% (17%), hypomania 1% (0.3%), blurred vision 4%(1%), loss of appetite 6% (2%), nervousness 5% (3%), paraesthesia 4% (2%), dizziness 13% (6%), asthenia (weakness; 15% (6%)), tremor 8% (2%), sweating 11% (2%), and sexual dysfunction (≥10% incidence).[4] Most of these adverse effects are transient and go away with continued treatment. Central and peripheral 5-HT3 receptor stimulation is believed to result in the gastrointestinal effects observed with SSRI treatment.[41] Compared to other SSRIs, it has a lower incidence of diarrhea, but a higher incidence of anticholinergic effects (e.g., dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, etc.), sedation/somnolence/drowsiness, sexual side effects, and weight gain.[42]
Due to reports of adverse withdrawal reactions upon terminating treatment, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) at the European Medicines Agency recommends gradually reducing over several weeks or months if the decision to withdraw is made.[43] See also Discontinuation syndrome (withdrawal).
Mania or hypomania may occur in 1% of patients with depression and up to 12% of patients with bipolar disorder.[44] This side effect can occur in individuals with no history of mania but it may be more likely to occur in those with bipolar or with a family history of mania.[45]
Suicide
Like other antidepressants, paroxetine may increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behaviour in children and adolescents.[46][47] The FDA conducted a statistical analysis of paroxetine clinical trials in children and adolescents in 2004 and found an increase in suicidality and ideation as compared to placebo, which was observed in trials for both depression and anxiety disorders.[48] In 2015 a paper published in The BMJ that reanalysed the original case notes argued that in Study 329,[49] assessing paroxetine and imipramine against placebo in adolescents with depression, the incidence of suicidal behavior had been under-reported and the efficacy exaggerated for paroxetine.[50][51][52][53][54]
Sexual dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction, including loss of libido, anorgasmia, lack of vaginal lubrication, and erectile dysfunction, is one of the most commonly encountered adverse effects of treatment with paroxetine and other SSRIs. While early clinical trials suggested a relatively low rate of sexual dysfunction, more recent studies in which the investigator actively inquires about sexual problems suggest that the incidence is higher than 70%.[55] Symptoms of sexual dysfunction have been reported to persist after discontinuing SSRIs, although this is thought to be occasional.[56][57][58]
Pregnancy
Antidepressant exposure (including paroxetine) is associated with shorter duration of pregnancy (by three days), increased risk of preterm delivery (by 55%), lower birth weight (by 75 g), and lower Apgar scores (by <0.4 points).[59][60] The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that for pregnant women and women planning to become pregnant, "be avoided, if possible", as paroxetine may be associated with increased risk of birth defects.[61][61][62]
Babies born to women who used paroxetine during the first trimester paroxetine have an increased risk of cardiovascular malformations, primarily ventricular and atrial septal defects (VSDs and ASDs). Unless the benefits of paroxetine justify continuing treatment, consideration should be given to stopping or switching to another antidepressant.[63] Paroxetine use during pregnancy is associated with about 1.5–1.7-fold increase in congenital birth defects, in particular, heart defects.[64][65][66][67][68]
Discontinuation syndrome
Many psychoactive medications can cause withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation from administration. Evidence has shown that paroxetine has among the highest incidence rates and severity of withdrawal syndrome of any medication of its class.[69] Common withdrawal symptoms for paroxetine include nausea, dizziness, lightheadedness and vertigo; insomnia, nightmares and vivid dreams; feelings of electricity in the body, as well as rebound depression and anxiety. Liquid formulation of paroxetine is available and allows a very gradual decrease of the dose, which may prevent discontinuation syndrome. Another recommendation is to temporarily switch to fluoxetine, which has a longer half-life and thus decreases the severity of discontinuation syndrome.[70][71][72]
In 2002 the U.S. FDA published a warning regarding "severe" discontinuation symptoms among those terminating paroxetine treatment, including paraesthesia, nightmares, and dizziness. The Agency also warned of case reports describing agitation, sweating, and nausea. In connection with a Glaxo spokesperson's statement that withdrawal reactions occur only in 0.2% of patients and are "mild and short-lived", the International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Associations said GSK had breached two of the Federation's codes of practice.[73]
Paroxetine prescribing information posted at GlaxoSmithKline now acknowledges the occurrence of a discontinuation syndrome, including serious discontinuation symptoms.[63]
Overdose
Acute overdosage is often manifested by emesis, lethargy, ataxia, tachycardia, and seizures. Plasma, serum, or blood concentrations of paroxetine may be measured to monitor therapeutic administration, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized patients or to aid in the medicolegal investigation of fatalities. Plasma paroxetine concentrations are generally in a range of 40–400 μg/L in persons receiving daily therapeutic doses and 200–2,000 μg/L in poisoned patients. Postmortem blood levels have ranged from 1–4 mg/L in acute lethal overdose situations.[74][75] Along with the other SSRIs, sertraline and fluoxetine, paroxetine is considered a low-risk drug in cases of overdose.[76]
Interactions
Interactions with other drugs acting on the serotonin system or impairing the metabolism of serotonin may increase the risk of Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like reaction. Such reactions have been observed with SNRIs and SSRIs alone, but particularly with concurrent use of triptans, MAO inhibitors, antipsychotics, or other dopamine antagonists.
The prescribing information states that paroxetine should "not be used in combination with an MAOI (including linezolid, an antibiotic which is a reversible non-selective MAOI), or within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with an MAOI", and should not be used in combination with pimozide, thioridazine, tryptophan, or warfarin.[63]
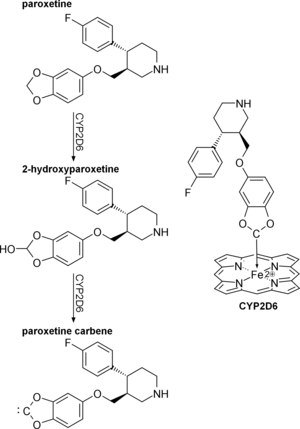
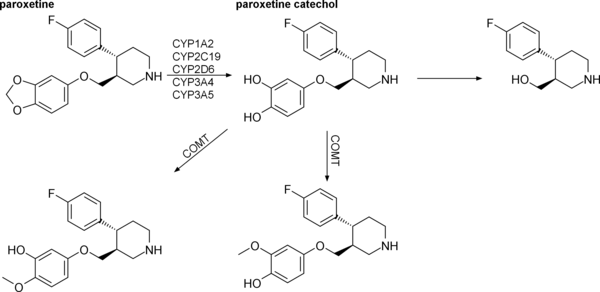
Paroxetine interacts with the following cytochrome P450 enzymes:[42][77]
- CYP2D6 for which it is both a substrate and a potent inhibitor.[1][42]
- CYP2B6 (strong) inhibitor.
- CYP3A4 (weak) inhibitor.
- CYP1A2 (weak) inhibitor.
- CYP2C9 (weak) inhibitor.
- CYP2C19 (weak) inhibitor.
Paroxetine has been shown to be an inhibitor of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2).[78][79]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Paroxetine is the most potent and one of the most specific selective serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).[81] It also binds to the allosteric site of the serotonin transporter, similarly, but less potently, than escitalopram.[82] Paroxetine also inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine to a lesser extent (<50 nmol/L).[83] Based on evidence from four weeks of administration in rats, the equivalent of 20 mg paroxetine taken once daily occupies approximately 88% of serotonin transporters in the prefrontal cortex.[77]
| Receptor | Ki (nM) |
|---|---|
| SERT | 0.07 - 0.2 |
| NET | 40 - 85 |
| DAT | 490 |
| D2 | 7,700 |
| 5-HT1A | 21,200 |
| 5-HT2A | 6,300 |
| 5-HT2C | 9,000 |
| α1 | 1,000 - 2,700 |
| α2 | 3,900 |
| M1 | 72 |
| H1 | 13,700 - 23,700 |
Pharmacokinetics
Paroxetine is well-absorbed following oral administration.[77] It has an absolute bioavailability of about 50%, with evidence of a saturable first-pass effect.[87] When taken orally, it achieves maximum concentration in about 6–10 hours[77] and reaches steady-state in 7–14 days.[87] Paroxetine exhibits significant interindividual variations in volume of distribution and clearance.[87] Less than 2% of an oral dose is excreted in urine unchanged.[87]
Paroxetine is a mechanism-based inhibitor of CYP2D6.[80][88]
Society and culture
GlaxoSmithKline has paid substantial fines, paid settlements in class-action lawsuits, and become the subject of several highly critical books about its marketing of paroxetine, in particular the off-label marketing of paroxetine for children, the suppression of negative research results relating to its use in children, and allegations that it failed to warn consumers of substantial withdrawal effects associated with use of the drug.[14][15] Paroxetine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1992 and initially sold by GlaxoSmithKline.[5][89] It is currently available as a generic medication.[11] A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 1.10 £ per month as of 2019.[11] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$2.40.[90] In 2017, it was the 68th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than eleven million prescriptions.[12][13] The United States Department of Justice fined GlaxoSmithKline $3 billion in 2012, for withholding data, unlawfully promoting use in those under 18, and preparing an article that misleadingly reported the effects of paroxetine in adolescents with depression following its clinical trial study 329.[14][15][16]
Marketing
In early 2004, GSK agreed to settle charges of consumer fraud for $2.5 million.[91] The legal discovery process also uncovered evidence of deliberate, systematic suppression of unfavorable Paxil research results. One of GSK's internal documents read, "It would be commercially unacceptable to include a statement that efficacy [in children] had not been demonstrated, as this would undermine the profile of paroxetine".[92]
In 2012 the U.S. Justice Department announced that GSK agreed to plead guilty and pay a $3 billion fine, in part for promoting the use of Paxil for children.[16]
On 12 February 2016, the UK Competition and Markets Authority imposed record fines of £45 million on companies which were found to have infringed European Union and UK Competition law by entering into agreements to delay the market entry of generic versions of the drug in the UK. GlaxoSmithKline received the bulk of the fines, being fined £37,600,757. Other companies, which produce generics, were issued fines which collectively total £7,384,146. UK public health services are likely to claim damages for being overcharged in the period where the generic versions of the drug were illegally blocked from the market, as the generics are over 70% less expensive. GlaxoSmithKline may also face actions from other generics manufacturers who incurred loss as a result of the anticompetitive conduct.[93] On 18 April 2016, appeals were lodged with the Competition Appeal Tribunal by the companies which were fined.[94][95][96][97][98]
GSK marketed paroxetine through television advertisements throughout the late 1990s and early 2000s. Commercials also aired for the CR version of the drug beginning in 2003.[99]
Sales
In 2007, paroxetine was ranked 94th on the list of bestselling drugs, with over $1 billion in sales. In 2006, paroxetine was the fifth-most prescribed antidepressant in the U.S. retail market, with more than 19.7 million prescriptions.[100] In 2007, sales had dropped slightly to 18.1 million but paroxetine remained the fifth-most prescribed antidepressant in the U.S.[101][102]
Research
Several studies have suggested that paroxetine can be used in the treatment of premature ejaculation. In particular, intravaginal ejaculation latency time (IELT) was found to increase with 6–13-fold, which was somewhat longer than the delay achieved by the treatment with other SSRIs (fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, sertraline, and citalopram).[106][107][108] However, paroxetine taken acutely ("on demand") 3–10 hours before coitus resulted only in a "clinically irrelevant and sexually unsatisfactory" 1.5-fold delay of ejaculation and was inferior to clomipramine, which induced a fourfold delay.[108]
There is also evidence that paroxetine may be effective in the treatment of compulsive gambling[109] and hot flashes.[110]
Benefits of paroxetine prescription for diabetic neuropathy[111] or chronic tension headache[112] are uncertain.
Although the evidence is conflicting, paroxetine may be effective for the treatment of dysthymia, a chronic disorder involving depressive symptoms for most days of the year.[113]
There is evidence to support that paroxetine selectively binds to and inhibits G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2). Since GRK2 regulates the activity of the beta adrenergic receptor, which becomes desensitized in cases of heart failure, paroxetine (or a paroxetine derivative) could be used as a heart failure treatment in the future.[78][79]
See also
References
- Sandoz Pty Ltd (18 January 2012). "PRODUCT INFORMATION PAROXETINE SANDOZ 20mg FILM-COATED TABLETS" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Therapeutic Goods Administration. Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- Mylan Institutional Inc. (January 2012). "PAROXETINE (paroxetine hydrochloride hemihydrate) tablet, film coated". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 23 October 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- Sandoz Limited (21 March 2013). "Paroxetine 20 mg Tablets – Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium. Datapharm Ltd. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- "Paxil, Paxil CR (paroxetine) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 10 November 2015. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- "Paroxetine Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- Fischer A (June 28, 2013). "FDA approves the first non-hormonal treatment for hot flashes associated with menopause" (Press release). Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on January 18, 2017.
- Hosenbocus S, Chahal R (February 2011). "SSRIs and SNRIs: A review of the Discontinuation Syndrome in Children and Adolescents". Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 20 (1): 60–7. PMC 3024727. PMID 21286371.
- Pae CU, Patkar AA (February 2007). "Paroxetine: current status in psychiatry". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 7 (2): 107–20. doi:10.1586/14737175.7.2.107. PMID 17286545. S2CID 34636522.
- "Paroxetine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 3 December 2018. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- Food and Drug Administration (2011). Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations – FDA Orange Book 31st Edition (2011): FDA Orange Book 31st Edition (2011). DrugPatentWatch.com. p. 344. ISBN 9781934899816. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 2019-03-04.
- British national formulary: BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 363. ISBN 9780857113382.
- "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 2020-03-18. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Paroxetine - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "GlaxoSmithKline to Plead Guilty and Pay $3 Billion to Resolve Fraud Allegations and Failure to Report Safety Data" (Press release). United States Department of Justice, Office of Public Affairs. 2 July 2012. Archived from the original on 9 September 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2015.
The United States alleges that, among other things, GSK participated in preparing, publishing and distributing a misleading medical journal article that misreported that a clinical trial of Paxil demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of depression in patients under age 18, when the study failed to demonstrate efficacy.
- United States ex rel. Greg Thorpe, et al. v. GlaxoSmithKline PLC, and GlaxoSmithKline LLC, pp. 3–19 (D. Mass. 26 October 2011). Text
- Thomas K, Schmidt MS (2 July 2012). "Glaxo Agrees to Pay $3 Billion in Fraud Settlement". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 March 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- Wagstaff AJ, Cheer SM, Matheson AJ, Ormrod D, Goa KL (March 2002). "Paroxetine: an update of its use in psychiatric disorders in adults". Drugs. 62 (4): 655–703. doi:10.2165/00003495-200262040-00010. PMID 11893234.
- Lotke P, Garcia F, Stearns V, Beebe KL, Iyengar M (2004-01-01). "Paroxetine controlled release was effective and tolerable for treating menopausal hot flash symptoms in women". Evidence Based Medicine. 9 (1): 23. doi:10.1136/ebm.9.1.23. ISSN 1473-6810. Archived from the original on 2016-02-14. Retrieved 2017-01-20.
- "Paroxetine: an antidepressant". nhs.uk. 2018-08-29. Archived from the original on 2020-05-14. Retrieved 2020-03-15.
- "Paroxetine 20 mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) - (emc)". www.medicines.org.uk. Retrieved 2020-03-15.
- "TGA eBS - Product and Consumer Medicine Information". www.ebs.tga.gov.au. Retrieved 2020-03-15.
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, Geddes JR, Higgins JP, Churchill R, Watanabe N, Nakagawa A, Omori IM, McGuire H, Tansella M, Barbui C (February 2009). "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis". Lancet. 373 (9665): 746–58. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5. PMID 19185342. S2CID 35858125.
- Fava M, Amsterdam JD, Deltito JA, Salzman C, Schwaller M, Dunner DL (December 1998). "A double-blind study of paroxetine, fluoxetine, and placebo in outpatients with major depression". Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 10 (4): 145–50. doi:10.3109/10401239809147030. PMID 9988054.
- Sugarman MA, Loree AM, Baltes BB, Grekin ER, Kirsch I (2014-08-27). "The efficacy of paroxetine and placebo in treating anxiety and depression: a meta-analysis of change on the Hamilton Rating Scales". PLOS ONE. 9 (8): e106337. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j6337S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106337. PMC 4146610. PMID 25162656.
- Purgato M, Papola D, Gastaldon C, Trespidi C, Magni LR, Rizzo C, Furukawa TA, Watanabe N, Cipriani A, Barbui C (April 2014). "Paroxetine versus other anti-depressive agents for depression". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD006531. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006531.pub2. PMID 24696195.
- Turner FJ (2005). Social Work Diagnosis in Contemporary Practice. Oxford University Press US. ISBN 978-0-19-516878-5.
- Ballenger JC, Wheadon DE, Steiner M, Bushnell W, Gergel IP (January 1998). "Double-blind, fixed-dose, placebo-controlled study of paroxetine in the treatment of panic disorder". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 155 (1): 36–42. doi:10.1176/ajp.155.1.36. PMID 9433336.
- Stein MB, Liebowitz MR, Lydiard RB, Pitts CD, Bushnell W, Gergel I (August 1998). "Paroxetine treatment of generalized social phobia (social anxiety disorder): a randomized controlled trial". JAMA. 280 (8): 708–13. doi:10.1001/jama.280.8.708. PMID 9728642.
- Manassis K (May 2005). "Paroxetine improves social anxiety disorder in children and adolescents". Evidence-Based Mental Health. 8 (2): 43. doi:10.1136/ebmh.8.2.43. PMID 15851806. Archived from the original on 2017-08-27. Retrieved 2017-01-20.
- Randall CL, Johnson MR, Thevos AK, Sonne SC, Thomas SE, Willard SL, Brady KT, Davidson JR (2001-01-01). "Paroxetine for social anxiety and alcohol use in dual-diagnosed patients". Depression and Anxiety. 14 (4): 255–62. doi:10.1002/da.1077. PMID 11754136.
- Blanco C, Bragdon LB, Schneier FR, Liebowitz MR (February 2013). "The evidence-based pharmacotherapy of social anxiety disorder". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 16 (1): 235–49. doi:10.1017/S1461145712000119. PMID 22436306.
There were no significant differences between the three SSRIs that had been tested in placebo-controlled studies: paroxetine; sertraline; fluvoxamine.
- Germann D, Ma G, Han F, Tikhomirova A (2013). Brittain HG (ed.). Paroxetine hydrochloride. Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients, and Related Methodology. Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances and Excipients. 38. pp. 367–406. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-407691-4.00008-3. ISBN 978-0-12-407691-4. PMID 23668408.
- Zohar J, Judge R (October 1996). "Paroxetine versus clomipramine in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. OCD Paroxetine Study Investigators". The British Journal of Psychiatry. 169 (4): 468–74. doi:10.1192/bjp.169.4.468. PMID 8894198.
- Denys D, van der Wee N, van Megen HJ, Westenberg HG (December 2003). "A double blind comparison of venlafaxine and paroxetine in obsessive-compulsive disorder". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 23 (6): 568–75. doi:10.1097/01.jcp.0000095342.32154.54. PMID 14624187. S2CID 23260081.
- Ipser JC, Stein DJ, Hawkridge S, Hoppe L (July 2009). "Pharmacotherapy for anxiety disorders in children and adolescents". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD005170. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005170.pub2. PMID 19588367.
- Alexander W (January 2012). "Pharmacotherapy for Post-traumatic Stress Disorder In Combat Veterans: Focus on Antidepressants and Atypical Antipsychotic Agents". P & T. 37 (1): 32–8. PMC 3278188. PMID 22346334.
- Ipser JC, Stein DJ (July 2012). "Evidence-based pharmacotherapy of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 15 (6): 825–40. doi:10.1017/S1461145711001209. PMID 21798109.
- "Search results detail| Kusurino-Shiori(Drug information Sheet)". www.rad-ar.or.jp. Retrieved 2019-03-15.
- "FDA Approves Antidepressant For Generalized Anxiety Disorder". Psychiatric News. 36 (10): 14. 2001-05-18. doi:10.1176/pn.36.10.0014b.
- Orleans RJ, Li L, Kim MJ, Guo J, Sobhan M, Soule L, Joffe HV (May 2014). "FDA approval of paroxetine for menopausal hot flushes". The New England Journal of Medicine. 370 (19): 1777–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1402080. PMID 24806158.
- Brunton L, Chabner B, Knollman B (2010). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (12th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-162442-8.
- Ciraulo DA, Shader RI, eds. (2011). Pharmacotherapy of Depression (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Humana Press. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-435-7. ISBN 978-1-60327-434-0.
- "Press release, CHMP meeting on Paroxetine and other SSRIs" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 2004-12-09. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-09-04. Retrieved 2007-08-24.
- "www.accessdata.fda.gov" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-05-03.
- Morishita S, Arita S (October 2003). "Induction of mania in depression by paroxetine". Human Psychopharmacology. 18 (7): 565–8. doi:10.1002/hup.531. PMID 14533140.
- "www.fda.gov" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-03-11.
- "FDA Launches a Multi-Pronged Strategy to Strengthen Safeguards for Children Treated With Antidepressant Medications". Archived from the original on 2017-01-18.
- Hammad TA (2004-08-16). "Review and evaluation of clinical data: relationship between psychotropic drugs and pediatric suicidality" (PDF). Joint Meeting of the Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee and Pediatric Advisory Committee. September 13–14, 2004. Briefing Information. FDA. p. 30. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-06-25. Retrieved 2009-01-27.
- Keller MB, Ryan ND, Strober M, Klein RG, Kutcher SP, Birmaher B, Hagino OR, Koplewicz H, Carlson GA, Clarke GN, Emslie GJ, Feinberg D, Geller B, Kusumakar V, Papatheodorou G, Sack WH, Sweeney M, Wagner KD, Weller EB, Winters NC, Oakes R, McCafferty JP (July 2001). "Efficacy of paroxetine in the treatment of adolescent major depression: a randomized, controlled trial". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 40 (7): 762–72. doi:10.1097/00004583-200107000-00010. PMID 11437014. S2CID 2125130.
- Le Noury J, Nardo JM, Healy D, Jureidini J, Raven M, Tufanaru C, Abi-Jaoude E (September 2015). "Restoring Study 329: efficacy and harms of paroxetine and imipramine in treatment of major depression in adolescence". BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 351: h4320. doi:10.1136/bmj.h4320. PMC 4572084. PMID 26376805.
- Godlee F (17 September 2015). "Study 329". BMJ. 351: h4973. doi:10.1136/bmj.h4973.
- Doshi P (September 2015). "No correction, no retraction, no apology, no comment: paroxetine trial reanalysis raises questions about institutional responsibility". BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 351: h4629. doi:10.1136/bmj.h4629. PMID 26377109. S2CID 44921667.
- Henry D, Fitzpatrick T (September 2015). "Liberating the data from clinical trials". BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 351: h4601. doi:10.1136/bmj.h4601. PMID 26377210. S2CID 41871189.
- Boseley S (16 September 2015). "Seroxat study under-reported harmful effects on young people, say scientists". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 27 May 2016. Retrieved 16 December 2016.
- Clark MS, Jansen K, Bresnahan M (November 2013). "Clinical inquiry: How do antidepressants affect sexual function?". The Journal of Family Practice. 62 (11): 660–1. PMID 24288712.
- Csoka AB, Csoka A, Bahrick A, Mehtonen OP (January 2008). "Persistent sexual dysfunction after discontinuation of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 5 (1): 227–33. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00630.x. PMID 18173768.
- Csoka AB, Shipko S (2006). "Persistent sexual side effects after SSRI discontinuation" (PDF). Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics. 75 (3): 187–8. doi:10.1159/000091777. PMID 16636635. S2CID 33448116. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-02-05. Retrieved 2016-01-10.
- http://pi.lilly.com/us/prozac.pdf Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine Page 14.
- Ross LE, Grigoriadis S, Mamisashvili L, Vonderporten EH, Roerecke M, Rehm J, Dennis CL, Koren G, Steiner M, Mousmanis P, Cheung A (April 2013). "Selected pregnancy and delivery outcomes after exposure to antidepressant medication: a systematic review and meta-analysis". JAMA Psychiatry. 70 (4): 436–43. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.684. PMID 23446732.
- Lattimore KA, Donn SM, Kaciroti N, Kemper AR, Neal CR, Vazquez DM (September 2005). "Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) use during pregnancy and effects on the fetus and newborn: a meta-analysis". Journal of Perinatology. 25 (9): 595–604. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7211352. PMID 16015372.
- ACOG Committee on Obstetric Practice (December 2006). "ACOG Committee Opinion No. 354: Treatment with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors during pregnancy". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 108 (6): 1601–3. doi:10.1097/00006250-200612000-00058. PMID 17138801.
- Yonkers KA, Blackwell KA, Glover J, Forray A (2014). "Antidepressant use in pregnant and postpartum women". Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 10: 369–92. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032813-153626. PMC 4138492. PMID 24313569.
- "PAXIL (paroxetine hydrochloride) Tablets and Oral Suspension: PRESCRIBING INFORMATION" (PDF). Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmithKline. August 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-04. Retrieved 2007-08-14.
- Thormahlen GM (October 2006). "Paroxetine use during pregnancy: is it safe?". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 40 (10): 1834–7. doi:10.1345/aph.1H116. PMID 16926304. S2CID 28814479.
- Way CM (April 2007). "Safety of newer antidepressants in pregnancy". Pharmacotherapy. 27 (4): 546–52. doi:10.1592/phco.27.4.546. PMID 17381382.
- Bellantuono C, Migliarese G, Gentile S (April 2007). "Serotonin reuptake inhibitors in pregnancy and the risk of major malformations: a systematic review". Human Psychopharmacology. 22 (3): 121–8. doi:10.1002/hup.836. PMID 17397101.
- Källén B (July 2007). "The safety of antidepressant drugs during pregnancy". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 6 (4): 357–70. doi:10.1517/14740338.6.4.357. PMID 17688379. S2CID 20167648.
- Bar-Oz B, Einarson T, Einarson A, Boskovic R, O'Brien L, Malm H, Bérard A, Koren G (May 2007). "Paroxetine and congenital malformations: meta-Analysis and consideration of potential confounding factors". Clinical Therapeutics. 29 (5): 918–926. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.05.003. PMID 17697910.
- Fava GA, Gatti A, Belaise C, Guidi J, Offidani E (2015). "Withdrawal Symptoms after Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Discontinuation: A Systematic Review". Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics. 84 (2): 72–81. doi:10.1159/000370338. PMID 25721705.
- Haddad PM (March 2001). "Antidepressant discontinuation syndromes". Drug Safety. 24 (3): 183–97. doi:10.2165/00002018-200124030-00003. PMID 11347722. S2CID 26897797.
- Haddad PM, Anderson IM (November 2007). "Recognising and managing antidepressant discontinuation symptoms". Advances in Psychiatric Treatment. 13 (6): 447–457. doi:10.1192/apt.bp.105.001966.
- Healy D. "Dependence on Antidepressants & Halting SSRIs". benzo.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2013-05-10. Retrieved 2013-04-23.
- Tonks A (February 2002). "Withdrawal from paroxetine can be severe, warns FDA". BMJ. 324 (7332): 260. doi:10.1136/bmj.324.7332.260. PMC 1122195. PMID 11823353.
- Goeringer KE, Raymon L, Christian GD, Logan BK (May 2000). "Postmortem forensic toxicology of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: a review of pharmacology and report of 168 cases". Journal of Forensic Sciences. 45 (3): 633–48. doi:10.1520/JFS14740J. PMID 10855970.
- R. Baselt,Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 8th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, 2008, pp. 1190–1193.
- White N, Litovitz T, Clancy C (December 2008). "Suicidal antidepressant overdoses: a comparative analysis by antidepressant type". Journal of Medical Toxicology. 4 (4): 238–50. doi:10.1007/BF03161207. PMC 3550116. PMID 19031375.
- Sanchez C, Reines EH, Montgomery SA (July 2014). "A comparative review of escitalopram, paroxetine, and sertraline: Are they all alike?". International Clinical Psychopharmacology. 29 (4): 185–96. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000023. PMC 4047306. PMID 24424469.
- Thal DM, Homan KT, Chen J, Wu EK, Hinkle PM, Huang ZM, Chuprun JK, Song J, Gao E, Cheung JY, Sklar LA, Koch WJ, Tesmer JJ (November 2012). "Paroxetine is a direct inhibitor of g protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and increases myocardial contractility". ACS Chemical Biology. 7 (11): 1830–9. doi:10.1021/cb3003013. PMC 3500392. PMID 22882301.
- Waldschmidt HV, Homan KT, Cato MC, Cruz-Rodríguez O, Cannavo A, Wilson MW, Song J, Cheung JY, Koch WJ, Tesmer JJ, Larsen SD (April 2017). "Structure-Based Design of Highly Selective and Potent G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 Inhibitors Based on Paroxetine". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 60 (7): 3052–3069. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00112. PMC 5641445. PMID 28323425.
- Stepan AF, Mascitti V, Beaumont K, Kalgutkar AS (2013). "Metabolism-guided drug design". MedChemComm. 4 (4): 631. doi:10.1039/C2MD20317K.
- Mellerup ET, Plenge P (July 1986). "High affinity binding of 3H-paroxetine and 3H-imipramine to rat neuronal membranes". Psychopharmacology. 89 (4): 436–9. doi:10.1007/BF02412117. PMID 2944152. S2CID 6037759.
- Mansari ME, Wiborg O, Mnie-Filali O, Benturquia N, Sánchez C, Haddjeri N (February 2007). "Allosteric modulation of the effect of escitalopram, paroxetine and fluoxetine: in-vitro and in-vivo studies". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 10 (1): 31–40. doi:10.1017/S1461145705006462. PMID 16448580.
- Owens JM, Knight DL, Nemeroff CB (2002-08-01). "[Second generation SSRIS: human monoamine transporter binding profile of escitalopram and R-fluoxetine]". L'Encephale. 28 (4): 350–5. PMID 12232544.
- Owens MJ, Knight DL, Nemeroff CB (September 2001). "Second-generation SSRIs: human monoamine transporter binding profile of escitalopram and R-fluoxetine". Biological Psychiatry. 50 (5): 345–50. doi:10.1016/s0006-3223(01)01145-3. PMID 11543737.
- Roth BL, Driscol J (12 January 2011). "PDSP Ki Database". Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP). University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the United States National Institute of Mental Health. Archived from the original on November 8, 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- Sanchez, Connie; Reines, Elin H.; Montgomery, Stuart A. (2014). "A comparative review of escitalopram, paroxetine, and sertraline: are they all alike?". International Clinical Psychopharmacology. 29 (4): 185–196. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000023. PMC 4047306.
- Kaye CM, Haddock RE, Langley PF, Mellows G, Tasker TC, Zussman BD, Greb WH (1989). "A review of the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of paroxetine in man". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. Supplementum. 350: 60–75. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1989.tb07176.x. PMID 2530793.
- Jornil J, Jensen KG, Larsen F, Linnet K (March 2010). "Identification of cytochrome P450 isoforms involved in the metabolism of paroxetine and estimation of their importance for human paroxetine metabolism using a population-based simulator". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 38 (3): 376–85. doi:10.1124/dmd.109.030551. PMID 20007670. S2CID 1795852.
- Food and Drug Administration (2011). Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations – FDA Orange Book 31st Edition (2011): FDA Orange Book 31st Edition (2011). DrugPatentWatch.com. p. 344. ISBN 9781934899816. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 2019-03-04.
- "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- Angell M (15 January 2009). "Drug Companies & Doctors: A Story of Corruption". New York Review of Books. 56 (1).
- Kondro W, Sibbald B (March 2004). "Drug company experts advised staff to withhold data about SSRI use in children". CMAJ. 170 (5): 783. doi:10.1503/cmaj.1040213. PMC 343848. PMID 14993169.
- "CMA fines pharma companies £45 million". Archived from the original on 2016-07-13. Retrieved 2016-07-15.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-12. Retrieved 2016-07-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-12. Retrieved 2016-07-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-12. Retrieved 2016-07-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-12. Retrieved 2016-07-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-12. Retrieved 2016-07-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2020-02-24. Retrieved 2020-02-24.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- The paroxetine prescriptions were calculated as a total of prescriptions for Paxil CR and generic paroxetine using data from the charts for generic and brand-name drugs."Top 200 generic drugs by units in 2006. Top 200 brand-name drugs by units". Drug Topics, Mar 5, 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-08.
- The paroxetine prescriptions were calculated as a total of prescriptions for Paxil CR and generic paroxetine using data from the charts for generic and brand-name drugs."Top 200 generic drugs by units in 2007". Drug Topics. February 18, 2008. Archived from the original on 2009-07-18. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
- "Top 200 brand drugs by units in 2007". Drug Topics, Feb 18, 2008. Archived from the original on 2009-06-29. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
- Nevels, RM; Gontkovsky, ST; Williams, BE (1 March 2016). "Paroxetine-The Antidepressant from Hell? Probably Not, But Caution Required". Psychopharmacology Bulletin. 46 (1): 77–104. ISSN 0048-5764. PMC 5044489. PMID 27738376.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Coleman A (2006). Dictionary of Psychology (Second ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 552.
- Coleman A (2006). Dictionary of Psychology (Second ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 161.
- Waldinger MD, Hengeveld MW, Zwinderman AH, Olivier B (August 1998). "Effect of SSRI antidepressants on ejaculation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study with fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 18 (4): 274–81. doi:10.1097/00004714-199808000-00004. PMID 9690692.
- Waldinger MD, Zwinderman AH, Olivier B (December 2001). "SSRIs and ejaculation: a double-blind, randomized, fixed-dose study with paroxetine and citalopram". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 21 (6): 556–60. doi:10.1097/00004714-200112000-00003. PMID 11763001. S2CID 36888042.
- Waldinger MD, Zwinderman AH, Olivier B (October 2004). "On-demand treatment of premature ejaculation with clomipramine and paroxetine: a randomized, double-blind fixed-dose study with stopwatch assessment". European Urology. 46 (4): 510–5, discussion 516. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2004.05.005. PMID 15363569.
- Kim SW, Grant JE, Adson DE, Shin YC, Zaninelli R (June 2002). "A double-blind placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of paroxetine in the treatment of pathological gambling". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 63 (6): 501–7. doi:10.4088/JCP.v63n0606. PMID 12088161.
- Weitzner MA, Moncello J, Jacobsen PB, Minton S (April 2002). "A pilot trial of paroxetine for the treatment of hot flashes and associated symptoms in women with breast cancer". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 23 (4): 337–45. doi:10.1016/S0885-3924(02)00379-2. PMID 11997203.
- Sindrup SH, Gram LF, Brøsen K, Eshøj O, Mogensen EF (August 1990). "The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine is effective in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy symptoms". Pain. 42 (2): 135–44. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(90)91157-E. PMID 2147235. S2CID 42327989.
- Langemark M, Olesen J (January 1994). "Sulpiride and paroxetine in the treatment of chronic tension-type headache. An explanatory double-blind trial". Headache. 34 (1): 20–4. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.1994.hed3401020.x. PMID 8132436.
- Gartlehner G, Gaynes BN, Hansen RA, Thieda P, DeVeaugh-Geiss A, Krebs EE, Moore CG, Morgan L, Lohr KN (November 2008). "Comparative benefits and harms of second-generation antidepressants: background paper for the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine. 149 (10): 734–50. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-149-10-200811180-00008. PMID 19017592.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Paroxetine. |
- "Paroxetine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Detailed Paroxetine Consumer Information: Uses, Precautions, Side Effects from medlibrary.org