Nomadic empire
Nomadic empires, sometimes also called steppe empires, Central or Inner Asian empires, were the empires erected by the bow-wielding, horse-riding, nomadic people in the Eurasian steppe, from classical antiquity (Scythia) to the early modern era (Dzungars). They are the most prominent example of non-sedentary polities.
Some nomadic empires consolidated by establishing a capital city inside a conquered sedentary state and then exploiting the existing bureaucrats and commercial resources of that non-nomadic society. In such a scenario, the originally nomadic dynasty may become culturally assimilated to the culture of the occupied nation before it is ultimately overthrown.[1] Ibn Khaldun (1332–1406) described a similar cycle on a smaller scale in 1377 in his Asabiyyah theory.
Historians of the early medieval period may refer to these polities as "khanates" (after khan, the title of their rulers). After the Mongol conquests of the 13th century the term orda ("horde") also came into use — as in "Golden Horde".
Background
China was reliant on horses to resist nomadic incursions into their territories but was only able to purchase the needed horses from the nomads. However, purchasing the horses actually gave these nomadic groups the means to acquire goods by commercial means and reduced the number of attacks and raids into Chinese territories. Nomads were generally unable to hold onto conquered territories for long without reducing the size of their cavalry forces because of the limitations of pasture in a settled lifestyle. Therefore settled civilizations usually became reliant on nomadic ones to provide the supply of horse when it was needed because they did not have resources to maintain these numbers of horses themselves.[2]
Ancient history
Cimmeria
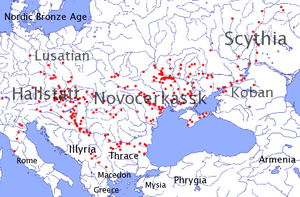
The Cimmerians were an ancient Indo-European people living north of the Caucasus and the Sea of Azov as early as 1300 BCE until they were driven southward by the Scythians into Anatolia during the 8th century BC. Linguistically they are usually regarded as Iranian, or possibly Thracian with an Iranian ruling class.
- The Pontic-Caspian steppe: southern Russia and Ukraine until 7th century BCE.
- The northern Caucasus area, including Georgia and modern day Azerbaijan
- Central, East and North Anatolia 714–626 BCE.
Scythia

Scythia (/ˈsɪθiə/; Ancient Greek: Σκυθική) was a region of Central Eurasia in classical antiquity, occupied by the Eastern Iranian Scythians,[3][4][5] encompassing parts of Eastern Europe east of the Vistula River and Central Asia, with the eastern edges of the region vaguely defined by the Greeks. The Ancient Greeks gave the name Scythia (or Great Scythia) to all the lands north-east of Europe and the northern coast of the Black Sea.[6] The Scythians – the Greeks' name for this initially nomadic people – inhabited Scythia from at least the 11th century BC to the 2nd century AD.[7]
Sarmatia
The Sarmatians (Latin: Sarmatæ or Sauromatæ; Ancient Greek: Σαρμάται, Σαυρομάται) were a large confederation[8] of Iranian people during classical antiquity,[9][10] flourishing from about the 6th century BC to the 4th century AD.[11] They spoke Scythian, an Indo-European language from the Eastern Iranian family. According to authors Arrowsmith, Fellowes and Graves Hansard in their book A Grammar of Ancient Geography published in 1832, Sarmatia had two parts, Sarmatia Europea [12] and Sarmatia Asiatica [13] covering a combined area of 503,000 sq mi or 1,302,764 km2. Sarmatians were basically Scythian veterans (Saka, Iazyges, Skolotoi, Parthians...) returning to the Pontic-Caspian steppe after the siege of Nineveh. Many noble families of Polish Szlachta claimed a direct descent from Sarmatians as a part of Sarmatism.
Xiongnu
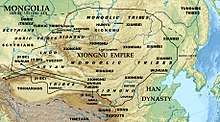
The Xiongnu were a confederation of nomadic tribes from Central Asia with a ruling class of unknown origin and other subjugated tribes. They lived on the Mongolian Plateau between the 3rd century BC and the 460s AD, their territories including modern day Mongolia, southern Siberia, western Manchuria, and the modern Chinese provinces of Inner Mongolia, Gansu, and Xinjiang. The Xiongnu was the first unified empire of nomadic peoples. Relations between early Chinese dynasties and the Xiongnu were complicated and included military conflict, exchanges of tribute and trade, and marriage treaties. When Emperor Qin Shihuang drove them away from the south of the Yellow River, he built the famous Great Wall to prevent the Xiongnu from coming back.
Kushan Empire
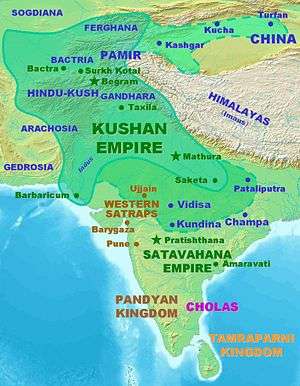
The Kushan Empire (Bactrian: Κυϸανο, Kushano; Sanskrit: कुषाण राजवंश Kuṣāṇ Rājavaṃśa, BHS: Guṣāṇa-vaṃśa; Parthian: 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓 Kušan-xšaθr[14]) was a syncretic empire, formed by Yuezhi under the pressure of the Xiongnu, in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of Afghanistan,[15] and then the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath near Varanasi (Benares), where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great.[16]
Xianbei
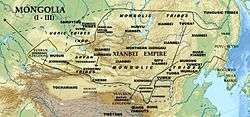
The Xianbei state or Xianbei confederation was a nomadic empire which existed in modern-day Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, northern Xinjiang, Northeast China, Gansu, Buryatia, Zabaykalsky Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, Tuva, Altai Republic and eastern Kazakhstan from 156–234 AD. Like most ancient peoples known through Chinese historiography, the ethnic makeup of the Xianbei is unclear.[17] The Xianbei were a northern branch of the earlier Donghu and it is likely at least some were proto-Mongols. After it collapsed, the tribe immigrated to China and founded the Northern Wei Dynasty.[18]
Hephthalite Empire
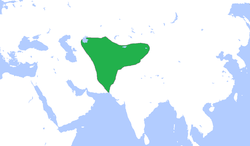
The Hephthalites, Ephthalites, Ye-tai, White Huns, or, in Sanskrit, the Sveta Huna, were a confederation of nomadic and settled[19] people in Central Asia who expanded their domain westward in the 5th century.[20] At the height of its power in the first half of the 6th century, the Hephthalite Empire controlled territory in present-day Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, India and China.[21][22]
Hunnic Empire
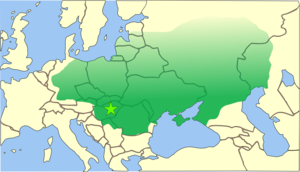
The Huns were a confederation of Eurasian tribes from the Steppes of Central Asia. Appearing from beyond the Volga River some years after the middle of the 4th century, they conquered all of eastern Europe, ending up at the border of the Roman Empire in the south, and advancing far into modern day Germany in the north. Their appearance in Europe brought with it great ethnic and political upheaval and may have stimulated the Great Migration. The empire reached its largest size under Attila between 447 and 453.
Post-classical history
Mongolic people and Turkic expansion
Bulgars

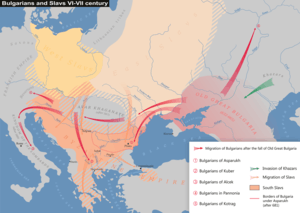
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari,[23] Proto-Bulgarians[24]) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. Emerging as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, according to some researchers their roots can be traced to Central Asia.[25] During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe the Bulgars absorbed other ethnic groups and cultural influences, including Hunnic and Indo-European peoples.[26][27][28][29][30][31] Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations.[31][32][33] The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch.[34] They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes,[35] as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra.[36]
After Dengizich's death, the Huns seem to have been absorbed by other ethnic groups such as the Bulgars.[37] Kim, however, argues that the Huns continued under Ernak, becoming the Kutrigur and Utigur Hunno-Bulgars.[38] This conclusion is still subject to some controversy. Some scholars also argue that another group identified in ancient sources as Huns, the North Caucasian Huns, were genuine Huns.[39] The rulers of various post-Hunnic steppe peoples are known to have claimed descent from Attila in order to legitimize their right to the power, and various steppe peoples were also called "Huns" by Western and Byzantine sources from the fourth century onward.[40]
The first clear mention and evidence of the Bulgars was in 480, when they served as the allies of the Byzantine Emperor Zeno (474–491) against the Ostrogoths.[41] Anachronistic references about them can also be found in the 7th-century geography work Ashkharatsuyts by Anania Shirakatsi, where the Kup'i Bulgar, Duč'i Bulkar, Olxontor Błkar and immigrant Č'dar Bulkar tribes are mentioned as being in the North Caucasian-Kuban steppes.[42] An obscure reference to Ziezi ex quo Vulgares, with Ziezi being an offspring of Biblical Shem, is in the Chronography of 354.[42][43]
The Bulgars became semi-sedentary during the 7th century in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, establishing the polity of Old Great Bulgaria c. 635, which was absorbed by the Khazar Empire in 668 AD.
In c. 679, Khan Asparukh conquered Scythia Minor, opening access to Moesia, and established the First Bulgarian Empire, where the Bulgars became a political and military elite. They merged subsequently with established Byzantine populations,[44][45] as well as with previously settled Slavic tribes, and were eventually Slavicized, thus forming the ancestors of modern Bulgarians.[46]
Rouran
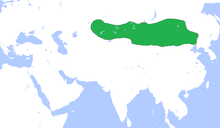
The Rouran (柔然), Juan Juan (蠕蠕), or Ruru (茹茹) were a confederation of Mongolic speaking[47] nomadic tribes on the northern borders of China from the late 4th century until the late 6th century. They controlled the area of Mongolia from the Manchurian border to Turpan and, perhaps, the east coast of Lake Balkhash, and from the Orkhon River to China Proper.
Göktürks
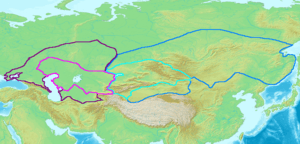
The Göktürks or Kök-Türks were a Turkic people of ancient North and Central Asia and northwestern China. Under the leadership of Bumin Khan and his sons they established the first known Turkic state around 546, taking the place of the earlier Xiongnu as the main power in the region. They were the first Turkic tribe to use the name Türk as a political name. The empire was split into a western and an eastern part around 600 and was conquered by the Tang Dynasty, but merged again in 680, and finally declined after 734 following the establishment of Uyghur Khaganate.
Uyghurs

The Uyghur Empire was a Turkic empire that existed in present-day Mongolia and surrounding areas for about a century between the mid 8th and 9th centuries. It was a tribal confederation under the Orkhon Uyghur nobility. It was established by Kutlug I Bilge Kagan in 744, taking advantage of the power vacuum in the region after the fall of the Gökturk Empire. It collapsed after a Kyrgyz invasion in 840.
Khitans
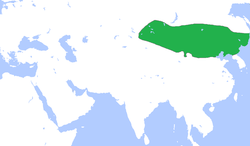
The Liao dynasty (/ljaʊ/;[48] Khitan: Mos Jælud; traditional Chinese: 遼朝; simplified Chinese: 辽朝; pinyin: Liáo cháo),[49] also known as the Liao Empire, officially the Great Liao (大遼; 大辽; Dà Liáo), or the Khitan (Qidan) State (Khitan: Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur),[50] was an empire and imperial dynasty in East Asia that ruled from 916 to 1125 over present-day Northern and Northeast China, Mongolia and portions of the Russian Far East and North Korea.[51] The empire was founded by Yelü Abaoji (Emperor Taizu of Liao), Khagan of the Khitans around the time of the collapse of the Tang dynasty and was the first state to control all of Manchuria.[52] The Liao dynasty was ruled by the Khitan Yelü clan.
Mongol Empire
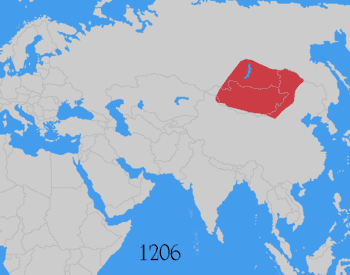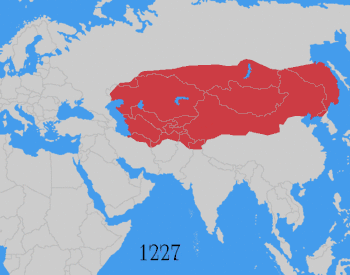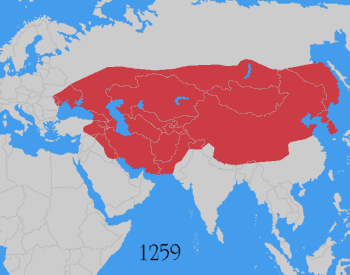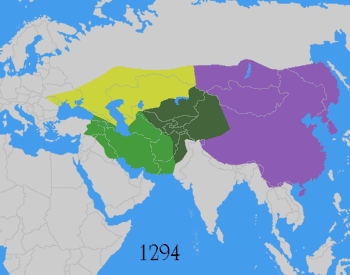
The Mongol Empire was the largest contiguous land empire in history at its peak, with an estimated population of over 100 million people. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan in 1206, and at its height, it encompassed the majority of the territories from Southeast Asia to Eastern Europe.
After unifying the Turco-Mongol tribes, the Empire expanded through conquests throughout continental Eurasia. During its existence, the Pax Mongolica facilitated cultural exchange and trade on the Silk Route between the East, West, and the Middle East in the period of the 13th and 14th centuries. It had significantly eased communication and commerce across Asia during its height.[53][54]
After the death of Möngke Khan in 1259, the empire split into four parts (Yuan dynasty, Ilkhanate, Chagatai Khanate and Golden Horde), each of which was ruled by its own Khan, though the Yuan rulers had nominal title of Khagan. After the disintegration of the western khanates and the fall of the Yuan dynasty in China in 1368, the empire finally broke up.
Timurid Empire
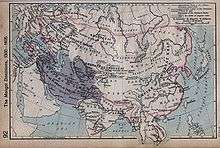
The Timurids, self-designated Gurkānī, were a Turko-Mongol dynasty, established by the warlord Timur in 1370 and lasting until 1506. At its zenith, the Timurid Empire included the whole of Central Asia, Iran and modern Afghanistan, as well as large parts of Mesopotamia and the Caucasus.
Modern history
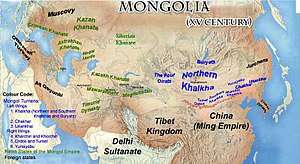
Later Mongol khanates

Later Mongol khanates such as the Northern Yuan dynasty based in Mongolia and the Dzungar Khanate based in Xinjiang were also nomadic empires. Right after the fall of the Yuan dynasty in 1368, the succeeding Ming dynasty established by Han Chinese rebuilt the Great Wall, which had been begun many hundreds of years earlier to keep the northern nomads out of China proper. During the subsequent centuries the Mongols, who were then based in Mongolia as the Northern Yuan dynasty, tended to continue their independent, nomadic way of life as much as possible.[55] On the other hand, the Dzungars were a confederation of several Oirat tribes who formed and maintained the last horse archer empire from the early 17th century to the middle 18th century. They emerged in the early 17th century to fight the Altan Khan of the Khalkha, the Jasaghtu Khan and their Manchu patrons for dominion and control over the Mongolian people and territories. In 1756 this last nomadic power was dissolved due to the Oirat princes' succession struggle and costly war with the Qing dynasty.
Medieval Turkic khanates
The Kazakh Khanate (Kazakh: Қазақ Хандығы, Qazaq Handyǵy, قازاق حاندىعى) was a successor of the Golden Horde existing from the 15th to 19th century, located roughly on the territory of the present-day Republic of Kazakhstan. At its height, the khanate ruled from eastern Cumania (modern-day West Kazakhstan) to most of Uzbekistan, Karakalpakstan and the Syr Darya river with military confrontation as far as Astrakhan and Khorasan Province, which are now in Russia and Iran, respectively. The Khanate also engaged in slavery and raids in its neighboring countries of Russia and Central Asia, and was later weakened by a series of Oirat and Dzungar invasions. These resulted in a decline and further disintegration into three Jüz-es, which gradually lost their sovereignty and were incorporated to the expanding Russian Empire. Its establishment marked the beginning of Kazakh statehood[56] whose 550th anniversary was celebrated in 2015.[57]
Popular misconceptions
The Qing dynasty is mistakenly confused as a nomadic empire by people who wrongly think that the Manchus were a nomadic people,[58] when in fact they were not nomads,[59][60] but instead were a sedentary agricultural people who lived in fixed villages, farmed crops, and practiced hunting and mounted archery.
The Sushen used flint headed wooden arrows, farmed, hunted, and fished, and lived in caves and trees.[61] The cognates Sushen or Jichen (稷真) again appear in the Shan Hai Jing and Book of Wei during the dynastic era referring to Tungusic Mohe tribes of the far northeast.[62] The Mohe enjoyed eating pork, practiced pig farming extensively, and were mainly sedentary,[63] and also used both pig and dog skins for coats. They were predominantly farmers and grew soybean, wheat, millet, and rice, in addition to engaging in hunting.[64]
The Jurchens were sedentary,[65] settled farmers with advanced agriculture. They farmed grain and millet as their cereal crops, grew flax, and raised oxen, pigs, sheep, and horses.[66] Their farming way of life was very different from the pastoral nomadism of the Mongols and the Khitan on the steppes.[67][68] "At the most", the Jurchen could only be described as "semi-nomadic" while the majority of them were sedentary.[69]
The Manchu way of life (economy) was described as agricultural, farming crops and raising animals on farms.[70] Manchus practiced Slash-and-burn agriculture in the areas north of Shenyang.[71] The Haixi Jurchens were "semi-agricultural, the Jianzhou Jurchens and Maolian (毛怜) Jurchens were sedentary, while hunting and fishing was the way of life of the "Wild Jurchens".[72] Han Chinese society resembled that of the sedentary Jianzhou and Maolian, who were farmers.[73] Hunting, archery on horseback, horsemanship, livestock raising, and sedentary agriculture were all practiced by the Jianzhou Jurchens as part of their culture.[74] In spite of the fact that the Manchus practiced archery on horse back and equestrianism, the Manchu's immediate progenitors practiced sedentary agriculture.[75] Although the Manchus also partook in hunting, they were sedentary.[76] Their primary mode of production was farming while they lived in villages, forts, and towns surrounded by walls. Farming was practiced by their Jurchen Jin predecessors.[77][78]
— 据魏焕《皇明九边考》卷二《辽东镇边夷考》[79] Translation from Sino-J̌ürčed relations during the Yung-Lo period, 1403–1424 by Henry Serruys[80]
For political reasons, the Jurchen leader Nurhaci chose variously to emphasize either differences or similarities in lifestyles with other peoples like the Mongols.[81] Nurhaci said to the Mongols that "The languages of the Chinese and Koreans are different, but their clothing and way of life is the same. It is the same with us Manchus (Jušen) and Mongols. Our languages are different, but our clothing and way of life is the same." Later Nurhaci indicated that the bond with the Mongols was not based in any real shared culture. It was for pragmatic reasons of "mutual opportunism", since Nurhaci said to the Mongols: "You Mongols raise livestock, eat meat and wear pelts. My people till the fields and live on grain. We two are not one country and we have different languages."[82]
Similarly the Indo-European dominions, as the Cimmerian, Scythian, Sarmatian or Kushan ones, were not strictly nomadic nor strictly empires. They were organized in small Kšatrapies/Voivodeships sometimes uniting into a bigger Mandala to repel surrounding despotic empires trying to annex their homelands. Only the pastoral part of the population and military troops migrated frequently but most of the population lived in organized agricultural and industrial small scale townships, called in Europe grods, e.g. the oases of Sogdia and Sparia along the Silk Road (Śaka, Tokarians/Tokharians…) and around the Tarim Basin (Tarim mummies, Kingdom of Khotan) or the rural areas of Europe (Sarmatia, Pannonia, Vysperia, Spyrgowa/Spirgovia, Boioaria/Boghoaria…) and Indian subcontinent (Kaśperia, Pandžab…). Due to growing (since the 2nd century BC) number of Turkic nomads and invaders among them, who adopted their horse-riding, metallurgy, technologies, clothing and customs, they were also often confused with the later, which mostly occurs in the case of the Scythians (Śaka, Sarmatians, Skolotoi, Iazyges…). In India the Śaka, although known earlier as Śakya as well as Kambojas, forming now the Kushan Empire were confused with the Xionites invading them and were called Mleccha. The Turkic invaders exploit the subdued sedentary Indo-Europeans in agriculture, industry and warfare (Mamluk, Janissaries). In some rare cases the enslaved Indo-Europeans may rise to power, e.g. Aleksandra (Iškandara) Lisowska alias Roxelana.
Further reading
- Amitai, Reuven; Biran, Michal (editors). Mongols, Turks, and others: Eurasian nomads and the sedentary world (Brill's Inner Asian Library, 11). Leiden: Brill, 2005 (ISBN 90-04-14096-4).
- Drews, Robert. Early riders: The beginnings of mounted warfare in Asia and Europe. N.Y.: Routledge, 2004 (ISBN 0-415-32624-9).
- Grousset, Rene. The Empire of the Steppes: a History of Central Asia, Naomi Walford, (tr.), New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1970.
- Hildinger, Erik. Warriors of the steppe: A military history of Central Asia, 500 B.C. to A.D. 1700. New York: Sarpedon Publishers, 1997 (hardcover, ISBN 1-885119-43-7); Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 2001 (paperback, ISBN 0-306-81065-4).
- Kradin, Nikolay. Nomadic Empires: Origins, Rise, Decline. In Nomadic Pathways in Social Evolution. Ed. by N.N. Kradin, Dmitri Bondarenko, and T. Barfield (p. 73–87). Moscow: Center for Civilizational Studies, Russian Academy of Sciences, 2003.
- Kradin, Nikolay. Nomads of Inner Asia in Transition. Moscow: URSS, 2014 (ISBN 978-5-396-00632-4).
See also
References
- Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples: Ethnogenesis and State Formation in the Medieval and Early Modern Eurasia and the Middle East. Southgate Publishers. p. 75.
- [https://www.google.com/books/edition/The_Cambridge_History_of_Early_Inner_Asi/ST6TRNuWmHsC?hl=en&gbpv=0 The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia Volume 1]
- "Scythian". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- "Scythia". Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia. Columbia University Press. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- "The Scythians". history-world.org.
- "Scythia", Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854), William Smith, LLD, Ed.
- Lessman, Thomas. "World History Maps". 2004. Thomas Lessman. Archived from the original on 8 December 2013. Retrieved 23 October 2013.
- Sinor 1990, p. 113
- "Sarmatian". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- Waldman & Mason 2006, pp. 692–694
- J.Harmatta: "Scythians" in UNESCO Collection of History of Humanity – Volume III: From the Seventh Century BC to the Seventh Century AD. Routledge/UNESCO. 1996. pg. 182
- Arrowsmith, Fellowes, Hansard, A, B & G L (1832). A Grammar of Ancient Geography,: Compiled for the Use of King's College School (3 April 2006 ed.). Hansard London. p. 9. Retrieved 20 August 2014.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Arrowsmith, Fellowes, Hansard, A, B & G L (1832). A Grammar of Ancient Geography,: Compiled for the Use of King's College School (3 April 2006 ed.). Hansard London. p. 15. Retrieved 20 August 2014.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- The Dynasty Arts of the Kushans, University of California Press, 1967, p. 5
- and Si-Yu-Ki, Buddhist Records of the Western World, (Tr. Samuel Beal: Travels of Fa-Hian, The Mission of Sung-Yun and Hwei-Sang, Books 1–5), Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner & Co. Ltd. London. 1906 and Hill (2009), pp. 29, 318–350
- which began about 127 CE. "Falk 2001, pp. 121–136", Falk (2001), pp. 121–136, Falk, Harry (2004), pp. 167–176 and Hill (2009), pp. 29, 33, 368–371.
- Wyatt 2004, p. 8.
- Chen, Sanping (1996). "A-Gan Revisited — The Tuoba's Cultural and Political Heritage". Journal of Asian History. 30 (1): 46–78. JSTOR 41931010.
- Prokopios, Historien I 3,2–7.
- Grousset, Rene (1970). The Empire of the Steppes. Rutgers University Press. pp. 67–72. ISBN 978-0-8135-1304-1.
- Unesco Staff 1996, pp. 135–163
- West 2009, pp. 274–277
- Waldman, Mason 2006, p. 106.
- Gi︠u︡zelev, Vasil (1979). The Proto-Bulgarians: Pre-history of Asparouhian Bulgaria text. p. 15, 33, 38.
- Hyun Jin Kim (2013). The Huns, Rome and the Birth of Europe. Cambridge University Press. pp. 58–59, 150–155, 168, 204, 243. ISBN 9781107009066.
- Golden 1992, p. 253, 256: "[Pontic Bulgars] With their Avar and Türk political heritage, they assumed political leadership over an array of Turkic groups, Iranians and Finno-Ugric peoples, under the overlordship of the Khazars, whose vassals they remained." ... "The Bulgars, whose Oguric ancestors ..."
- McKitterick, Rosamond (1995). The New Cambridge Medieval History. Cambridge University Press. p. 229. ISBN 9780521362924.
The exact ethnic origins of the Danubian Bulgars is controversial. It is in any case most probable that they had enveloped groupings of diverse origins during their migration westwards across the Eurasian steppes, and they undoubtedly spoke a form of Turkic as their main language. The Bulgars long retained many of the customs, military tactics, titles and emblems of a nomadic people of the steppes.
- Sophoulis 2011, pp. 65–66, 68–69: "The warriors who founded the Bulgar state in the Lower Danube region were culturally related to the nomads of Eurasia. Indeed, their language was Turkic, and more specifically Oğuric, as is apparent from the isolated words and phrases preserved in a number of inventory inscriptions." ... "It is generally believed that during their migration to the Balkans, the Bulgars brought with them or swept along several other groups of Eurasian nomads whose exact ethnic and linguistic affinities are impossible to determine... Sarmato-Alanian origin... Slav or Slavicized sedentary populations."
- Brook 2006, p. 13: "Thus, the Bulgars were actually a tribal confederation of multiple Hunnic, Turkic, and Iranian groups mixed together."
- "Bulgaria: Arrival of the Bulgars". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
The name Bulgaria comes from the Bulgars, a people who are still a matter of academic dispute with respect to their origin (Turkic or Indo-European) as well as to their influence on the ethnic mixture and the language of present-day Bulgaria.
- "Bulgar". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
Although many scholars, including linguists, had posited that the Bulgars were derived from a Turkic tribe of Central Asia (perhaps with Iranian elements), modern genetic research points to an affiliation with western Eurasian populations.
- Cenghiz, Ilhan (2015). "Y-DNA Haplogroups in Turkic People". yhaplogroups.wordpress.com.
- Suslova; et al. (October 2012). "HLA gene and haplotype frequencies in Russians, Bashkirs and Tatars, living in the Chelyabinsk Region (Russian South Urals)". International Journal of Immunogenetics. Blackwell Publishing Ltd. 39 (5): 375–392. doi:10.1111/j.1744-313X.2012.01117.x. PMID 22520580.
- Waldman, Mason 2006, p. 106–107.
- Waldman, Mason 2006, p. 108–109.
- Waldman, Mason 2006, p. 109.
- Maenchen-Helfen 1973, p. 168.
- Kim 2013, p. 123.
- Kim 2015, p. 136; Sinor 2005, p. 4228.
- Róna-Tas 1999, p. 309.
- Golden 1992, p. 104.
- Golden 1992, p. 103.
- Bowersock, Brown, Grabar 1999, p. 354.
- Waldman, Mason 2006, p. 108.
- Golden 2011, p. 145, 158, 196.
- Fiedler 2008, p. 151: "...ethnic symbiosis between Slavic commoners and Bulgar elites of Turkic origin, who ultimately gave their name to the Slavic-speaking Bulgarians."
- William Montgomery McGovern – early empires of Central Asia, p. 421
- "Liao". Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.
- Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun (2009). 《愛新覚羅烏拉熙春女真契丹学研究》 [Research into Jurchen and Khitan Studies by Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun] (in Chinese). Shōkadō (松香堂). Chapter: 〈遼朝國號非「哈喇契丹(遼契丹)」考:兼擬契丹大字
- Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun (2009). "〈契丹文dan gur與「東丹國」國號:兼評劉浦江「再談"東丹國"國号問題」〉(Original Meaning of Dan gur in the Khitai Scripts: with a Discussion of the State Name of the Dongdanguo)" (PDF). 《愛新覚羅烏拉熙春女真契丹学研究》 [Research into Jurchen and Khitan Studies by Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun] (in Chinese). Shōkadō (松香堂).
- Ledyard, 1983, 323
- Ruins of Identity: Ethnogenesis in the Japanese Islands By Mark Hudson
- Gregory G.Guzman – the barbarians a negative or positive factor in ancient and medieval history?, The historian 50 (1988), 568–70
- Thomas T. Allsen – and conquest in Mongol Eurasia, 211
- Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Asia and Oceania, by Barbara A. West, p. 558
- "Kazakh Khanate – 550th anniversary". e-history.kz.
- "Kazakhstan to Celebrate 550th Kazakh Statehood Anniversary in 2015". Astana Times.
- Pamela Crossley, The Manchus, p. 3
- Patricia Buckley Ebrey et al., East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History, 3rd edition, p. 271
- Frederic Wakeman, Jr., The Great Enterprise: The Manchu Reconstruction of Imperial Order in the Seventeenth Century, p. 24, note 1
- Huang 1990 p. 246.
- "逸周書". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- Gorelova 2002, pp. 13–4.
- Gorelova 2002, p. 14.
- Vajda Archived 2010-06-01 at the Wayback Machine
- Sinor 1996, p. 416.
- Twitchett, Franke, Fairbank 1994, p. 217.
- de Rachewiltz 1993, p. 112.
- Breuker 2010, p. 221.
- Wurm 1996, p. 828.
- Reardon-Anderson 2000, p. 504.
- Mote, Twitchett & Fairbank 1988, p. 266.
- Twitchett & Mote 1998, p. 258.
- Rawski 1996, p. 834.
- Rawski 1998, p. 43.
- Allsen 2011, p. 215.
- Transactions, American Philosophical Society (vol. 36, Part 1, 1946). American Philosophical Society. pp. 10–. ISBN 978-1-4223-7719-2.
- Karl August Wittfogel; Chia-shêng Fêng (1949). History of Chinese Society: Liao, 907–1125. American Philosophical Society. p. 10.
- 萧国亮 (2007-01-24). "明代汉族与女真族的马市贸易". 艺术中国(ARTX.cn). p. 1. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- Serruys 1955, p. 22.
- Perdue 2009, p. 127.
- Peterson 2002, p. 31.
.png)