Battle of Dover Strait (1916)
The Battle of Dover Strait that occurred on 26–27 October 1916 was a naval battle of the First World War between Great Britain and the German Empire. Two and a half flotillas of German torpedo boats from the Flanders Flotilla launched a raid into the Dover Strait in an attempt to disrupt the Dover Barrage and destroy whatever Allied shipping could be found in the strait.
| Battle of Dover Strait (1916) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the First World War | |||||||
 HMS Nubian beached on the South Foreland, after her bow had been blown off in battle with German torpedo boats in the Dover Strait. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
7 destroyers 1 armed yacht 1 naval trawler 1 troopship 28 naval drifters | 23 torpedo boats[1] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
1 destroyer sunk 6 naval drifters sunk 1 troopship sunk 3 destroyers damaged 1 naval trawler damaged 3 naval drifters damaged | 1 torpedo boat damaged[2] | ||||||
Upon approaching the barrage, the German torpedo boats were challenged by the British destroyer HMS Flirt and an engagement broke out. The Germans were able to destroy Flirt and successfully assault the barrage′s drifters, but were once more engaged when a flotilla of British destroyers was sent to repel them. The Germans were able to fight off the additional British units before successfully withdrawing. By the end of the night, the British had lost one destroyer, a transport, and several drifters while the Germans themselves suffered only minor damage to a single torpedo boat.
Background
In October 1916, the Flanders Flotilla was finally reinforced by the German Admiralty with two full torpedo boat flotillas. The transfer of the 3rd and 9th Torpedo Boat Flotillas to Flanders had immediate consequences to the balance of power in the Dover Strait. Whereas before, the Flanders Flotilla had been equipped with only three large torpedo boats and several of the smaller inferior A-class torpedo boats, they now possessed 23 large torpedo boats capable of meeting the British Dover Patrol in combat. Due to the lack of large torpedo boats, the Flanders Flotilla had not sortied against the Dover Patrol in several months and as a result British defences were quite lax in the area.[1]
With his newly acquired flotillas, the Flanders Flotilla′s commander - Admiral Ludwig von Schröder - decided to launch a raid in the Dover Strait against the Dover Barrage as well as any Allied shipping that could be found in the Channel. Although the British had prohibited transports from being in the Channel at night in anticipation of a German raid, the Dover Barrage was not prepared to meet such an attack. Facing Schröder′s 23 boats, the Dover Barrage was guarded by only the old destroyer HMS Flirt, the yacht Ombra, and the naval trawler H. E. Straud.[3] The four divisions of drifters manning the barrage′s anti-submarine nets were armed with only a single rifle each for defence. In addition to the forces guarding the Barrage, there were six Tribal-class destroyers at Dover that could be called upon in the event of a raid as well as several units of Harwich Force dispersed at the Downs.[4]
Battle
The German torpedo boats split into five groups, with each attacking a different section of the shipping in the channel. The German 5th Half-Flotilla sailed into the Dover Barrage and soon came into contact with five drifters of the 10th Drifter Division tending the anti-submarine nets and attacked.[5] After hearing gunfire, Flirt—the drifters' escort—approached the unidentified vessels and challenged them. The boats responded to the British signal with a similar signal. Confused, Flirt's commander decided that the approaching vessels were Allied destroyers and that drifters had been attacked by a submarine. An open boat was also launched from Flirt to rescue survivors from the sinking drifters.[3] The German boats attacked the destroyer, surprising the crew. Outnumbered, Flirt tried to ram one of the German boats; after a brief engagement it was sunk by gunfire and torpedoes. After sinking Flirt, the Germans continued the attack on the barrage, sinking two drifters each from the 8th and 16th Drifter Divisions. Six drifters were sunk and three others damaged, as well as the trawler H. E. Straud, before the Fifth Half-Flotilla withdrew.[6]
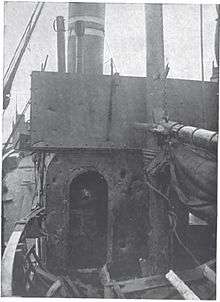
When Admiral Reginald Bacon - the commander of the Dover Patrol - heard about the raid, he sent six Tribal-class destroyers—HMS Amazon, Mohawk, Viking, Tartar, Cossack and Nubian—to engage the Germans. Due to a misinterpretation of his orders, the British commander of the destroyer division—Commander Henry Oliphant of Viking—deployed his destroyers in two loose groups, one consisting of Viking, Mohawk, and Tartar and the other Nubian, Amazon and Cossack. Nubian soon steamed far ahead of her group and was the first vessel to reach the scene of Flirt's sinking.[7] Another half-flotilla of German boats had caught the empty British transport Queen off Goodwin Sands as it returned from the French coast, boarded it and removed her crew before sinking her.[6]
Upon Nubian's contact with the German 17th Half Flotilla, she made the same error as Flirt and mistook the German boats for Allied vessels. Surprised with a hail of gunfire, Nubian attempted to ram the last boat in the German line of battle but was struck by a torpedo that blew off her bow and reduced her to a drifting hulk.[2] Amazon and Cossack soon arrived to aid Nubian and engaged the German boats. The Germans scored several hits on Amazon, knocking out two of her boilers before withdrawing. Viking's division of boats also clashed with Kaiserliche Marine torpedo boats. The German 18th Half Flotilla was heading back to Zeebrugge when it sailed into Oliphant's group of destroyers, engaging them as they passed. Although Viking escaped unscathed, Mohawk suffered several hits, before the Germans were able to break away to the safety of the coast.[8] Near the end of the action, Admiral Bacon dispatched the Dunkirk Division to intercept the German torpedo boats before they could return to Flanders but the Germans were able to successfully withdraw before being caught by these further reinforcements.[6]
Aftermath
The British had failed to stop the raiders from destroying the drifters and 45 men were killed, four wounded and 10 taken prisoner. Six ships were sunk in addition to Flirt, the transport Queen and three destroyers, three drifters and a naval trawler were damaged. Of the German torpedo boats, only SMS G91 suffered any damage and no German vessel suffered any casualties. The success of the raid encouraged the Germans to plan more sorties into the English Channel and the raids continued until the 3rd and 9th Torpedo Boat Flotillas were redeployed to the High Seas Fleet in November 1916.[9]
Notes
- Karau, p. 81
- Karau, p. 84
- Bacon, p. 27
- Bacon, p. 26
- Karau, p. 83
- Bacon, p. 28
- Kemp, p. 107
- Kemp, p. 108
- Karau, p. 86
References
- Bacon, Reginald (1919). The Dover Patrol 1915–1917. II. New York: George H. Doran Company. OCLC 1136826. Retrieved 18 January 2016.
- Karau, Mark (2003). Wielding the Dagger: The Marinekorps Flandern and the German War Effort, 1914–1918. Westport: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 0-313-32475-1.
- Karau, M. D. (2014). The Naval Flank of the Western Front: The German MarineKorps Flandern 1914–1918. First published as Wielding the Dagger: The Marinekorps Flandern and the German War Effort, 1914–1918 (2003). Barnsley: Seaforth (Pen & Sword). ISBN 978-1-84832-231-8.
- Kemp, Peter (1956). H. M. Destroyers. London: H. Jenkins. OCLC 7719395.