United Kingdom constitutional law
United Kingdom constitutional law concerns the governance of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. With the oldest continuous political system on Earth, the UK constitution is not contained in a single code but principles have emerged over the centuries from statute, case law, political conventions and social consensus. In 1215, Magna Carta required the King to call "common counsel" or Parliament, hold courts in a fixed place, guarantee fair trials, guarantee free movement of people, and free the church from the state; it also enshrined the rights of "common" people to use the land.[1] After the English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution 1688, Parliament won supremacy over the monarch, as well as the church and the courts, and the Bill of Rights 1689 recorded that the "election of members of Parliament ought to be free". The Act of Union 1707 unified England, Wales and Scotland, while Ireland was joined in 1800, but the Republic of Ireland formally separated between 1916 and 1921 through bitter armed conflict. By the Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928, almost every adult man and woman was finally entitled to vote for Parliament. The UK was a founding member of the International Labour Organization (ILO), the United Nations, the Commonwealth, the Council of Europe, the European Union, and the World Trade Organization (WTO).[2] The principles of parliamentary sovereignty, the rule of law, democracy and internationalism guide the UK's modern political system.
The central institutions of modern government are Parliament, the judiciary, the executive, the civil service and public bodies which implement policies, and regional and local governments. Parliament is composed of the House of Commons, elected by voter constituencies, and the House of Lords which is mostly appointed on the recommendation of cross-political party groups. To make a new Act of Parliament, the highest form of law, both Houses must read, amend, or approve proposed legislation three times. The judiciary is headed by a twelve-member UK Supreme Court, and underneath are the Court of Appeal for England and Wales and the Court of Session for Scotland, and a system of high courts, Crown courts, or tribunals depending on the subject in the case. Courts interpret statutes, progress the common law and principles of equity, and can control the discretion of the executive. UK courts are usually thought to have no power to declare an Act of Parliament unconstitutional. The executive is headed by the Prime Minister, who must command a majority in the House of Commons. The Prime Minister appoints a cabinet of people who lead each department, and form Her Majesty's Government. The Queen herself is a ceremonial figurehead, who gives royal assent to new laws. By constitutional convention, the monarch does not usurp the democratic process and has not refused royal assent since the Scottish Militia Bill in 1708. Beyond the Parliament and cabinet, a civil service and a large number of public bodies, from the Department of Education to the National Health Service, deliver public services that implement the law and fulfil political, economic and social rights.
In practice, most constitutional litigation occurs through administrative law disputes, concerning the operation of public bodies, and human rights. The courts have an inherent power of judicial review, to ensure that every institution under law acts according to law. Except for Parliament itself, courts may declare acts of any institution or public figure void, to ensure that discretion is only used reasonably or proportionately. Since it joined the European Convention on Human Rights in 1950, and particularly after the Human Rights Act 1998, courts are required to review whether legislation is compatible with international human rights norms. These protect everyone's rights against government or corporate power, including liberty against arbitrary arrest and detention, the right to privacy against unlawful surveillance, the right to freedom of expression, freedom of association including joining trade unions and taking strike action, and the freedom of assembly and protest. Every public body and private bodies that affect people's rights and freedoms are accountable under the law.
History
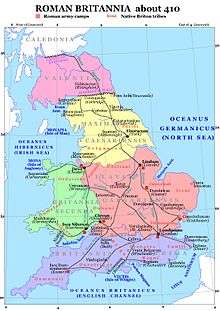
The history of the UK constitution, though officially beginning in 1800, traces back to a time long before the four nations of England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland were fully formed.[3] Before the Roman Empire’s conquest, Britain and Ireland were populated by Celtic migrants from the European continent, but ones who left no recorded history of law.[4] Near the end of the Roman Republic in 55 and 54 BC, the former Consul and legion commander Julius Caesar invaded Britain during the broader Gallic Wars. This did not establish permanent occupation, as Caesar returned to Rome, became dictator and was assassinated. The Republic was transformed into an Empire, when Caesar’s heir Augustus took power in 27 BC. In the reign of Augustus’ grandson, Claudius, Britain was conquered from 43 AD. Under Rome's uncodified constitution, Roman Britain was administered by a governor, usually member of the Senate but appointed by the Emperor for their military record. Londinium was a provincial capital of 60,000 people, and Britain a cosmopolitan society of around 3 million people. Roman law was based upon a slave economy, and highly militarised. Hadrian constructed a wall from 122 as part of the Empire's limits, but this was soon moved north by Antoninus Pius from 142. Constantine the Great was stationed in York in 306 when he left to claim his title to be Emperor. Constantine marched on Rome under the cross in 312, and issued an Edict of Milan in 313. This triggered a series of events where the Church assumed more and more power over the law.[5] But under constant assault, the Empire began to collapse and Britain was abandoned in 407.[6] Neither the Theodosian Code issued in 438, nor the great Corpus Juris Civilis of Justinian I in 534 entered the laws of Britain.[7] In the Dark Ages, during power struggles between Anglo-Saxons, Britons, Danes and Vikings, kings convened regular councils, called the Witan, composed of lords and church leaders.[8] But it was not until the Norman Invasion of 1066 that one common law was established through England under one monarch.

Under William the Conqueror, advised by a King’s Council (Curia Regis), the Domesday Book was compiled in 1086 cataloguing all land and labour to levy taxes. Just 12 per cent of people were free, while the feudal system made others serfs, slaves or bordars and cottars.[10] In 1190 Richard the Lionheart, more closely tied with the Pope in Rome, joined the Third Crusade to invade the Holy land, but at great cost. Taxes levied by Richard I,[11] and his successor King John to pay for the wars led to intense discontent, and the aristocracy forcing the King to sign the Magna Carta 1215. This was a commitment to hold ‘common counsel’ before any taxation, hold courts at a fixed place, hold trials according to law or before an accused’s peers, guarantee free movement of people for trade, and give back common land.[12] Failure to abide by Magna Carta led to the First Barons' war, and the popular legend of Robin Hood emerged: a returned crusader who robbed from the rich to give to the poor.[13] The commitments on common land were soon recast in the Charter of the Forest 1217, signed at St Paul's by Henry III.[14] These documents established that the monarch, even with apparent authority from God, was bound by law, and it remains ‘the nearest approach to an irrepealable “fundamental statute” that England has ever had.’[15] Throughout the Middle Ages, common land was a source of welfare for common people, peasant labourers bound by a feudal system of control. In 1348, the Black Death struck England, and killed around a third of the population. As peasants lost their lords, and there was a shortage of workers, wages rose. The King and Parliament responded with the Statute of Labourers 1351 to freeze wage rises. This led to the Peasants’ Revolt of 1381, where leaders demanded an end to feudalism, and for everything to be held in common.[16] Despite the revolt’s violent repression, slavery and serfdom broke down,[17] yet most people remained without any substantial liberty, in political or economic rights. As sheep farming became more profitable than agricultural work, enclosures of common land dispossessed more people, who turned into paupers and were punished.[18] Under Henry VIII, to seal a divorce from Catherine of Aragon and marry Anne Boleyn (who he soon beheaded for supposed infidelity), the Church of England was declared separate from Rome in the Act of Supremacy 1534, with the King as the head. The Law in Wales Act 1535 united Wales and England in one administrative system, while the King became ever more despotic, executing the Lord Chancellor, Sir Thomas More in 1535, and dissolving the monasteries and murdering those who resisted. After Henry VIII died, and power struggles following the death of his boy Edward VI at age 15,[19] Elizabeth I, the daughter of Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn, took the throne in 1558. Half a century of prosperity followed as Elizabeth I avoided wars, but founded corporations including the East India Company to monopolise trade routes. Under her successor, James I, further companies were created to colonise North America, including the London Company and the Virginia Company in 1606, and the Massachusetts Bay Company in 1628. Many religious dissidents left England to settle the new world.

While Elizabeth I maintained a Protestant church, under her successor James, who unified the Scottish and English Crowns, religious and political tensions grew as he asserted a divine right of Kings.[20] This prompted a series of cases from Sir Edward Coke,[21] the Chief Justice of the Common Pleas and then King's Bench courts, which denied that the King could pass judgment in legal proceedings,[22] and held that the royal prerogative was subject to the law and cannot be expanded.[23] Coke CJ went even further in Dr Bonham's case, holding that even that "the common law will control Acts of Parliament".[24] Though supported by some judges,[25] the idea that common law courts could nullify Acts of Parliament was rejected, and the common law was formally placed under the King's control in the Earl of Oxford’s case, establishing that equity (then administered by the Lord Chancellor in the House of Lords) was above common law.[26] Coke fell from favour,[lower-alpha 1] and was removed from judicial office. When Charles I succeeded to the throne in 1625, and more fervently asserted a divine right, including the ability to levy tax without Parliament,[27] Coke and others presented the Petition of Right 1628.[28] This demanded the King to abide by Magna Carta, levy no tax without Parliament, not arbitrarily commit people to prison, not have martial law in times of peace, and not billet soldiers in private homes. Charles I responded by shutting down or proroguing Parliament and taxing trade (or "ship money") without authority. The country descended into the English Civil War in 1642 culminating in the capture and execution of King Charles I on Whitehall in 1649 by the New Model Army led by Oliver Cromwell.[29] Cromwell, not wishing to become a king, became a de facto dictator. After his death,[30] the monarchy was restored with Charles II in 1660, but his successor James II again attempted to assert divine right to rule. In 1688, Parliament 'invited' a replacement King and Queen, William and Mary of Orange, and after a brief conflict forced James II out.[31] Known as the Glorious Revolution, Parliament proclaimed a new Bill of Rights 1689, with a Claim of Right Act 1689 in Scotland, that cemented parliamentary sovereignty. As well as reaffirming Magna Carta, it says the 'pretended power of suspending laws or the execution of laws by regal authority without consent of Parliament is illegal’, that 'election of members of Parliament ought to be free’, and that 'Parliament ought to be held frequently'.[32] The justification for government itself, encapsulated by John Locke in his Second Treatise on Government was the protection of people's rights: "lives, liberties and estates."[33]
With parliamentary sovereignty as the cornerstone of the new constitution, Parliament proceeded to set up a system of finance in the Bank of England Act 1694 and the Act of Settlement 1700 created an independent system of justice: judges were salaried and could not be removed except by both Houses of Parliament, no member of the House of Commons could be paid by the Crown, and the Crown had to be Anglican. In 1703, Ashby v White established that the right to vote was a constitutional right.[34] The Act of Union 1707 formally joined the parliaments of England and Scotland, by giving Scottish electors representation in Westminster.[35] The new union was soon faced with disaster as in the War of the Spanish Succession, the Spanish promised the right for British ships to trade (mostly slaves) in the seas around South America. The South Sea Company, duly incorporated to monopolise trade routes, became the object of mass financial speculation, provoked by government ministers interested in its rising share price. When it transpired, contrary to promoters' stories, that no trade was done because the Spanish had revoked their promise the stock market crashed, driving economic chaos.[36] This was made worse by the decision of conservative politicians to endorse the company to take over the national debt as an alternative financier to the government over the Whig dominated Bank of England. The result of the crash was that the Chancellor of the Exchequer was imprisoned in the Tower of London for his corruption, the Postmaster General committed suicide, and the disgraced Lord Chancellor was replaced with Lord King LC who promptly ruled that people in a position of trust must avoid any possibility of a conflict of interest.[37] Out of the chaos, Robert Walpole emerged as a stable political figure who for 21 years held a majority of the House of Commons,[38] and is now considered the first "Prime Minister".[39] In 1765, Entick v Carrington established that the government could do nothing but that which was empowered by law,[40] while the first teacher of English law, William Blackstone represented the standard view in his Commentaries on the Laws of England that slavery was unlawful and that "the spirit of liberty is so deeply ingrained in our constitution" any person enslaved in England must be freed. However, the transatlantic slave trade had accelerated to North American colonies. In 1772, when Lord Mansfield ruled in Somerset v Stewart that slavery was unlawful at common law,[41] this set off a wave of outrage in southern, enslavement colonies of America. Together with northern colonies grievances over taxation without representation, this led to the American Revolution and declaration of independence in 1776.[42] The British military failed to hold control. Instead, it began settling Australia from 1788.[43] In 1789, the French Revolution broke out, and the King was deposed with demands for "liberty, equality and fraternity". The British aristocracy reacted with repression on free speech and association to forestall any similar movement.[44] While figures like Jeremy Bentham called natural rights "nonsense upon stilts",[45] Mary Wollstonecraft called for A Vindication of the Rights of Woman as well as men, arguing that unjust gender and class oppression flowed from "the respect paid to property... as from a poisoned fountain".[46] While successful in the Napoleonic wars in defeating France, and cementing union with Ireland in the Act of Union 1800,[47] liberty, freedom and democracy were scarcely protected in the new "United Kingdom".

During this time, with the invention of the steam engine the industrial revolution had begun. Poverty had also accelerated through the Speenhamland system of poor laws by subsidising employers and landowners with parish rates. The Corn Laws from 1815 further impoverished people by fixing prices to maintain landowner profits.[48] While the Great Reform Act 1832 extended the vote slightly, only those with property had any representation in Parliament. Although the Slavery Abolition Act 1833 abolished the slave trade within the British Empire, it only compensated slave owners and made ex-slaves in colonies pay off debts for their freedom for decades after. With the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, further punishment for poverty was inflicted as people were put into workhouses if found to be unemployed. In R v Lovelass a group of agricultural workers who formed a trade union were prosecuted and sentenced to be transported to Australia under the Unlawful Oaths Act 1797,[49] triggering mass protests. A movement called Chartism grew demanding the right to vote for everyone in free and fair elections. As the great famine hit Ireland and millions migrated to the United States, Chartists staged a mass march from Kennington Common to Parliament in 1848 as revolutions broke out across Europe, and the Communist Manifesto was drafted by German revolutionary Karl Marx and Manchester factory owner Friedrich Engels. While the Crimean War distracted from social reform and Viscount Palmerston opposed anything,[50] the American civil war of 1860 to 1865 ended slavery in the US, and the UK gradually enabled greater political freedom. In the Second Reform Act 1867 more middle-class property owners were enfranchised, the Elementary Education Act 1870 provided free primary school, and the Trade Union Act 1871 enabled free association without criminal penalty.[51] The Representation of the People Act 1884 reduced the property qualification further, so that around one third of men could vote. Still, outside the UK liberty and the right to vote were violently repressed across the vast British Empire, in Africa, India, Asia and the Caribbean.[52]
From the start of the 20th century, the UK underwent vast social and constitutional change, beginning with an attempt by the House of Lords to suppress trade union freedom.[53] In response, the labour movement organised to support representatives in Parliament, and in the 1906 general election won 29 seats and supported the Liberal Party's programme of reform. This included a legal guarantee of the right of unions to collectively bargain and strike for fair wages,[54] an old-age pension,[55] a system of minimum wages,[56] a People's Budget with higher taxes on the wealthy to fund spending. After a further election brought by the House of Lords blocking reform, Parliament pass a National Insurance system for welfare,[57] and the Parliament Act 1911 prevented the House of Lords blocking legislation for more than two years, and removed the right to delay any money bills.[58] Despite this, the Liberal government, against the opposition of Labour, armed for and entered World War One. At the end of the War, with millions dead, Parliament passed the Representation of the People Act 1918 which enabled every adult male the vote, although it was only after the mass protest of the Suffragettes that the Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928 enabled all women to vote, and that the UK became democratic. The War also triggered uprising in Ireland, and an Irish War of Independence leading to the partition of the island between the Republic of Ireland in the south and Northern Ireland in the Government of Ireland Act 1920. The Versailles Treaty at the end of the War demanded German reparations, beggaring the country through the 1920s and upon the Great Depression leading to a fascist collapse under Hitler.[59] The failed international law system, after World War Two was replaced with the United Nations where the UK held a permanent seat on the UN Security Council. However the British Empire began to crumble as India, Israel and nations across Africa fought for democracy, human rights, and independence. To prevent any recurrence of the Holocaust and war, the Council of Europe was established to draft the European Convention on Human Rights in 1950. Further, it was seen that the only way to prevent conflict was through economic integration. The European Economic Community, which became the European Union in 1992, was supported by Winston Churchill with the UK to be "at the centre",[60] although it did not enter until the European Communities Act 1972. Under Margaret Thatcher, significant cuts were made to public services, labour rights, and the powers of local government, including abolishing the Greater London Council. However, some powers were restored with extensive devolution of power in the Scotland Act 1998, Northern Ireland Act 1998, Greater London Authority Act 1999 and the Government of Wales Act 2006. After many years of armed conflict in Northern Ireland, the Good Friday Agreement of 1998 brought peace. The Human Rights Act 1998 empowered courts to apply Convention rights without the need for claimants to take cases to the Strasbourg court. The House of Lords Act 1999 reduced but did not fully eliminate hereditary peers. Since a financial crisis of 2007–2008 brought about by bankers' speculation,[61] a Conservative and Liberal Democrat coalition launched a programme of "austerity" cuts, and cemented their term in the Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011. After 2015, however, early elections were held anyway in 2017, following a referendum on EU membership that resulted in 51.9 per cent of people favouring to leave but without any clear plan, and 48.1 per cent of voters favouring to remain. While the United Kingdom formally left the European Union on 31 January 2020, the details of its future relationship with the European Union remain to be negotiated.[62]
Principles

The UK constitution has not been codified in one document, like the Constitution of South Africa or the Grundgesetz in Germany. However, general constitutional principles run through the law,[64] and central statutes have been recognised as holding "constitutional" value.[65] The main sources of law, which "constitute" the body politic of the UK, are Acts of Parliament, cases decided by courts, and conventions on how the Cabinet, the Prime Minister, Parliament and the Monarch conduct themselves.[66] Through legislation, case law and conventions, at least four main principles are usually recognised. First, parliamentary sovereignty is a foundational principle. Through the English Reformation, the Civil War, the Glorious Revolution of 1689 and the Act of the Union 1707, Parliament became the dominant source of law, above the judiciary, executive, monarchy, and church. Parliamentary sovereignty means Parliament can make or unmake any law within its practical power to do so, a fact that is usually justified by Parliament upholding other principles, namely the rule of law, democracy, and internationalism. Second, the rule of law has run through the constitution since the Magna Carta 1215 and the Petition of Right 1628. This means the government may only conduct itself according to legal authority, including respect for human rights.[67] Third, at least since 1928, democracy has become a fundamental constitutional principle. Originally only wealthy, property-owning men held rights to vote for the House of Commons, while the king or queen, and/or a hereditary House of Lords, dominated politics. But from 1832 adult citizens slowly won the right to universal suffrage.[68] Fourth, the UK constitution is international: Parliament has consistently augmented its sovereignty and the practical power of UK citizens through membership of international bodies, including the International Labour Organization,[69] the United Nations, the European Convention on Human Rights, the European Union, the World Trade Organization, and the International Criminal Court. EU membership was challenged by the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, and while the government failed to win the 2017 general election, it is unclear what the outcome will be.
Parliamentary sovereignty
Parliamentary sovereignty is often seen as a central element in the UK constitution, although its extent is contested.[70] It means that an Act of Parliament is the highest form of law, and also that "Parliament cannot bind itself."[71] Historically, Parliament became sovereign through a series of power struggles between the monarch, the church, the courts, and ordinary people. The Magna Carta 1215, which was later annulled leading to the First Barons' War, granted the right of Parliament to exist for "common counsel" before any tax,[72] against the supposedly "divine right of kings" to rule. Common land was also guaranteed to people to farm, graze, hunt or fish, though aristocrats continued to dominate politics. In the Act of Supremacy 1534, King Henry VIII asserted his divine right over the Catholic Church in Rome, declaring himself the supreme leader of the Church of England. Then in the Earl of Oxford's case in 1615,[73] the Lord Chancellor (both the King's representative and head of the judiciary) asserted the supremacy of the Court of Chancery over the common law courts, effectively nullifying Sir Edward Coke's assertion that judges could declare statutes void if they went "against common right and reason".[74] Finally, after the Glorious Revolution of 1688, the Bill of Rights 1689 placed Parliament's power over the monarch (and therefore over the church and courts). Parliament became the "sovereign", and supreme. But power struggles within Parliament continued between the aristocracy and common people. People from the Chartists, to the trade unions fought for the vote in the House of Commons, and finally in the Parliament Act 1911 and Parliament Act 1949 for the Commons to prevail in any conflict over the unelected House of Lords: after 1949, the Lords could only delay legislation by one year,[75] and not delay any budgetary measure over a month.[76] In R (Jackson) v Attorney General, a group of pro-hunting protestors challenged the Hunting Act 2004, arguing it was not valid and could not ban fox hunting, because it was passed avoiding the House of Lords under the Parliament Act 1949, and this was itself invalid, because it was passed using the power in the Parliament Act 1911 to override the Lords in two years and limited the Lords' power of delay to one year. But the Parliament Act 1911 could not be used to amend its own limitation of the Lords power, argued the claimants. It had to be implicitly limited in scope. The House of Lords rejected this argument, holding both the Parliament Act 1949 and the Hunting Act 2004 to be completely valid. However, in obiter dicta Lord Hope did argue that the "rule of law enforced by the courts is the ultimate controlling factor on which our constitution is based", that Parliamentary sovereignty "is no longer, if it ever was, absolute", it cannot be used to defend unconstitutional Acts (as determined by the courts).[77] There remains no settled meaning of "Parliamentary sovereignty", except that it depends upon the principle of representative democracy, and its legal force depends on political legitimacy.

In recent history, four main factors have developed Parliament's sovereignty in practical and legal terms.[79] First, since 1945 international cooperation meant Parliament has augmented its power by working with other sovereign nations, rather than trying to dominate them. The British Empire, which once colonised a quarter of the world's population and a third of its land, was weakened by World War I, and disintegrated after World War II. While the UK's military power before had been largely uncontested, and so was thought by writers of the Imperial period to be able to "make or unmake any law whatever",[80] the UK chose to join in the League of Nations in 1919, and after its failure, the United Nations 1945 to rebuild a system of international law. The Versailles Treaty 1919, in the lasting part that established the International Labour Organization, recalled that "peace can only be established if it is based upon social justice".[81] The UN Charter, which was "based on the principle of the sovereign equality of all its Members", said that "to save succeeding generations from the scourge of war, which twice in our lifetime has brought untold sorrow to mankind", the UN would "reaffirm faith in fundamental human rights", and members should "live together in peace with one another as good neighbours". The Bretton Woods Agreements Act 1945, United Nations Act 1946 and the International Organisations Act 1968 wrote the UK's funding and membership of the United Nations, the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, and other bodies, into statute.[82] For example, the UK bound itself to implement by order UN Security Council resolutions, up to the actual use of force, in return for representation in the General Assembly and Security Council.[83] Although isolated UK governments have infringed international law before,[84] the United Kingdom has always accepted a formal duty that its sovereignty would not be used unlawfully. Second, in 1950 the UK helped to write and join the European Convention on Human Rights. While that convention reflected norms and cases decided under UK statutes and the common law on civil liberties,[lower-alpha 2] the UK accepted that people could appeal to the European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg, if domestic remedies were insufficient. In the Human Rights Act 1998, Parliament decided that the UK judiciary should be both empowered and required to apply human rights norms directly in determining UK cases, to ensure a more speedy, human rights-based resolution to case law, and effectively to influence human rights reasoning more by "bringing rights home".

Third, the UK became a member of the European Union after the European Communities Act 1972 and through its ratification of the Maastricht Treaty in 1992. The idea of a Union had long been envisaged by European leaders, including Winston Churchill, who in 1946 had called for a "United States of Europe" with the UK "at the centre".[60] EU law has always been held to prevail in any conflict between member state laws for the limited fields in which it operates,[86] but member states and citizens gain control over the scope and content of EU law, and so extend their sovereignty in international affairs, through joint representation in the European Parliament, Council of Ministers, and the Commission. This means that, as the UK is a member of the club, it voluntarily agrees to play by the club's rules. This principle was tested in R (Factortame Ltd) v SS for Transport, where a fishing business claimed that it should not be required to have 75% of British shareholders, as the Merchant Shipping Act 1988 said.[87] Under EU law, the principle of freedom of establishment states that nationals of any member state can freely incorporate and run a business across the EU without unjustified interference. The House of Lords held that, because the EU law conflicted with the sections of the 1988 Act, those sections would not be enforced, and disapplied, because Parliament had not clearly expressed an intention to renounce the 1972 Act. According to Lord Bridge "whatever limitation of its sovereignty Parliament accepted when it enacted the [1972 Act] was entirely voluntary".[88] It is, therefore, the courts' duty, until Parliament expresses a clear will to leave the EU on certain terms, to apply EU law. On the other hand, in R (HS2 Action Alliance Limited) v Secretary of State for Transport the Supreme Court held that certain fundamental principles of UK constitutional law would not be interpreted by the courts as having been given up by membership of the EU, or probably any international organisation.[89] Here a group protesting against the High Speed 2 rail line from London to Manchester and Leeds claimed that the government had not properly followed the Environmental Impact Assessment Directive 2011 by whipping a vote in Parliament to approve the plan. They argued that the Directive required open and free consultation, a requirement not fulfilled if a party whip compelled party members to vote. The Supreme Court unanimously held the Directive did not prevent a party whip. But if a conflict had existed, a Directive could not compromise the fundamental constitutional principle from the Bill of Rights 1689 that Parliament is free to organise its affairs. In this respect, EU law could not override fundamental principles of UK law.[90]
Fourth, devolution in the United Kingdom has meant Parliament gave power to legislate on specific topics to nations and regions: the Scotland Act 1998 created the Scottish Parliament, the Government of Wales Act 1998 created the Welsh Assembly, and the Northern Ireland Act 1998 created a Northern Ireland Executive following the historic Good Friday Agreement, to bring peace. In addition, the Local Government Act 1972 and the Greater London Authority Act 1999 gives more limited powers to local and London governments. Constitutionally, it has become increasingly accepted that decisions should not be taken for the UK which would override, and run counter to the will of regional governments. However, in Miller v Secretary of State for Exiting the EU, a group of people who sought to remain in the European Union brought the government on whether the Prime Minister could trigger Article 50 to notify the European Commission of the UK's intention to leave, without an Act of Parliament.[91] This followed the Brexit poll of 2016 where 51.9% (of those voting) voted to leave on uncertain terms, comprising 27% of the UK population.[92] The claimants argued that, because "Brexit" would obliterate rights that Parliament had conferred through Acts (e.g. the right of free movement of UK citizens in the EU, the right to fair competition through merger control, or the right to vote for EU institutions) only Parliament could consent to notifying the intention to negotiate to leave under Article 50. They also argued that the Sewel Convention for devolved assemblies, where the assembly passes a motion that the Westminster Parliament can legislate on a devolved matter before it does so, meant the UK could not negotiate to leave without the Scottish or Northern Ireland legislatures' consent. The UK Supreme Court held that Parliament must pass an Act, and could not begin the process of leaving purely through Royal Prerogative. However, the Sewel convention could not be enforced by courts, rather than observed.[93] This led Prime Minister Theresa May to procure the European Union (Notification of Withdrawal) Act 2017, giving her power to notify the intention to negotiate to leave the EU. It remains unclear that the United Kingdom, or Parliament's sovereignty, will survive if EU membership is eventually given up.[94]
Rule of law
The rule of law has been regarded as a fundamental principle of modern legal systems, including the UK.[95] It has been called "as important in a free society as the democratic franchise",[96] and even "the ultimate controlling factor on which our constitution is based",[97] but like parliamentary sovereignty, its meaning and extent is disputed. The most widely accepted meanings speak of several factors: Lord Bingham, formerly the highest judge in the UK, suggested the rule of law ought to mean that law is clear and predictable, not subject to broad or unreasonable discretion, applies equally to all people, with speedy and fair procedures for enforcement, protects fundamental human rights, and works according to international law.[98] Other definitions seek to exclude human rights and international law as relevant, but largely stem from visions of pre-democratic scholars such as Albert Venn Dicey.[99] The rule of law was explicitly recognised as a "constitutional principle" in section 1 of the Constitutional Reform Act 2005, which limited the judicial role of the Lord Chancellor and recast the judicial appointments system to entrench independence, diversity and merit.[100] As statute gives no further definition, the practical meaning of the "rule of law" develops through case law.

At the core of the rule of law, in English and UK law, has traditionally been the principle of "legality". This means that the state, government, and any person acting under government authority (including a corporation),[103] may only act according to law. In 1765, in Entick v Carrington a writer, John Entick, claimed that the King's Chief Messenger, Nathan Carrington, had no legal authority to break into and ransack his home, and remove his papers. Carrington claimed he had authority from the Secretary of State, Lord Halifax who issued a search "warrant", but there was no statute that gave Lord Halifax the authority to issue search warrants. Lord Camden CJ held that the "great end, for which men entered into society, was to secure their property", and that without any authority "every invasion of private property, be it ever so minute, is a trespass."[104] Carrington acted unlawfully and had to pay damages. Today this principle of legality is found throughout the European Convention on Human Rights, which enables infringements of rights as a starting point only if "in accordance with the law".[105] For example, in 1979, in Malone v Metropolitan Police Commissioner a man charged with handling stolen goods claimed the police unlawfully tapped his phone, to get evidence. The only related statute, the Post Office Act 1969 Schedule 5, stated there should be no interference in telecommunications unless the Secretary of State issued a warrant, but said nothing explicit about phone tapping. Megarry VC held there was no wrong at common law, and refused to interpret the statute in light of the right to privacy under the European Convention on Human Rights, article 8.[106] On appeal, the European Court of Human Rights concluded the Convention was breached because the statute did not ‘indicate with reasonable clarity the scope and manner of exercise of the relevant discretion conferred on the public authorities.’[107] The judgment, however, was overshadowed by the government swiftly passing a new Act to authorise phone tapping with a warrant.[108] By itself, the principle of legality is not enough to alone preserve human rights in the face of ever more intrusive statutory powers of surveillance by corporations or government.
.jpg)
The rule of law also requires law is truly enforced, though enforcement bodies may have room for discretion. In R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office a group campaigning against the arms trade, Corner House Research, claimed the Serious Fraud Office acted unlawfully by dropping an investigation into the UK-Saudi Al-Yamamah arms deal. It was alleged that BAE Systems plc paid bribes to Saudi government figures.[109] The House of Lords held the SFO was entitled to take into account the public interest in not pursuing an investigation, including the security threats that might transpire. Baroness Hale remarked that the SFO had to consider "the principle that no-one, including powerful British companies who do business for powerful foreign countries, is above the law", but the decision reached was not unreasonable.[110] When enforcement or court proceedings do take place, they should proceed swiftly: anyone who is detained must be charged and put on trial or released.[111] People must also be able to access justice in practice. In R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor the Supreme Court held the government's imposition of £1200 in fees to bring an Employment Tribunal claim undermined the rule of law, and was void. The Lord Chancellor had statutory authority to create fees for court services, but this led to a 70% drop in claims at Employment Tribunals against employers for breach of labour rights, such as unfair dismissal, unlawful wage deductions or discrimination. Lord Reed held the "constitutional right of access to the courts is inherent in the rule of law". Without access to courts, "laws are liable to become a dead letter, the work done by Parliament may be rendered nugatory, and the democratic election of Members of Parliament may become a meaningless charade."[112] In principle every person is subject to the law, including government ministers, or corporate executives, who may be held in contempt of court for violating an order.[113] In other systems the idea of a separation of powers is seen as an essential part of maintaining the rule of law. In theory, originally advocated by Baron de Montesquieu, there should be a strict separation of the executive, legislature and judiciary.[114] While other systems, notably the United States, attempted to put this into practice (e.g. requiring the executive does not come from the legislature) it is clear that modern political parties may undermine such a separation by capturing all three branches of government. In the UK, democracy has been advanced since the early 20th century despite the fact that "there is no formal separation of powers in the United Kingdom."[115] The Constitutional Reform Act 2005 did, however, end the practice of the Lord Chancellor sitting as the head of the judiciary, while also being a Member of Parliament, and sitting in the cabinet. Since the Act of Settlement 1700, there has been only one instance of a judge being removed, and a suspension cannot happen without the Lord Chief Justice and the Lord Chancellor following a judge being subject to criminal proceedings.[116] There is now a duty on all ministers to "uphold the continued independence of the judiciary", including against assault by powerful corporations or the media.[117]
Democracy

The principle of a "democratic society" is generally seen as a fundamental legitimating factor of both Parliamentary sovereignty and the rule of law. A functioning representative and deliberative democracy, which upholds human rights legitimises the fact of Parliamentary sovereignty,[118] and it is widely considered that "democracy lies at the heart of the concept of the rule of law",[119] because the opposite of arbitrary power exercised by one person is "administration is in the hands of the many and not of the few’".[120] According to the preamble to the European Convention on Human Rights, as drafted by British lawyers following World War II, fundamental human rights and freedoms are themselves "best maintained... by "an effective political democracy".[121] Similarly, this "characteristic principle of democracy" is enshrined by the First Protocol, article 3, which requires the "right to free elections" to "ensure the free expression of the opinion of the people in the choice of the legislature".[122] While there are many conceptions of democracy, such as "direct", "representative" or "deliberative", the dominant view in modern political theory is that democracy requires an active citizenry, not only in electing representatives, but in taking part in political life.[123] Its essence lies not simply majority decision-making, nor referendums that can easily be used as a tool of manipulation,[124] "but in the making of politically responsible decisions" and in "large-scale social changes maximising the freedom" of humankind.[125] The legitimacy of law in a democratic society depends upon a constant process of deliberative discussion and public debate, rather than imposition of decisions.[126] It is also generally agreed that basic standards in political, social and economic rights are necessary to ensure everyone can play a meaningful role in political life.[127] For this reason, the rights to free voting in fair elections and "general welfare in a democratic society" have developed hand-in-hand with all human rights, and form a fundamental cornerstone of international law.[128]
In the UK's "modern democratic constitution",[129] the principle of democracy is manifested through statutes and case law which guarantee the right to vote in fair elections, and through its use as a principle of interpretation by courts. In 1703, in the landmark case of Ashby v White, Lord Holt CJ stated that the right of everyone "to give [their] vote at the election of a person to represent [them] in Parliament, there to concur to the making of laws, which are to bind [their] liberty and property, is a most transcendent thing, and of an high nature".[130] This has meant that the courts actively ensure that votes cast are counted, and that democratic elections are conducted according to law. In Morgan v Simpson the Court of Appeal held that if a vote "was conducted so badly that it was not substantially in accordance with the law as" then it would be declared void, and so would even minor irregularities that would affect the result.[131] A considerable body of regulation, for instance in the Representation of the People Act 1983 or the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000, restrict spending or any foreign interference because, according to Baroness Hale "each person has equal value" and "we do not want our government or its policies to be decided by the highest spenders."[132] More broadly, the concept of a "democratic society" and what is "necessary" for its functioning underpins the entire scheme of interpretation for the European Convention on Human Rights as applied in UK law, particularly after the Human Rights Act 1998, because each right can usually only be restricted if "in accordance with law" and as "necessary in a democratic society". The place of the social welfare state that is necessary to support democratic life is also manifested through courts' interpretation. For instance, in Gorringe v Calderdale MBC Lord Steyn, giving the leading judgment said it was "necessary" to view the law of negligence in the context of "the contours of our social welfare state."[133] More generally, the common law has been increasingly developed to be harmonious with statutory rights,[134] and also in harmony with rights under international law.
Internationalism
Like other democratic countries,[135] the principles of international law are a basic component of the UK constitution, both as a primary tool of interpretation of domestic law, and through the UK's consistent support and membership of major international organisations. As far back as the Magna Carta 1215, English law recognised the right to free movement of people for international trade.[136] By 1608, Sir Edward Coke wrote confidently that international commercial law, or the lex mercatoria, is part of the laws of the realm,[137] while the constitutional crises of the 17th century centred upon Parliament halting the King's attempting to tax international trade without its consent.[138] At the turn of the 18th century, Lord Holt CJ saw international law as a general tool for interpreting the common law,[139] and Lord Mansfield affirmed that the international lex mercatoria "is not the law of a particular country but the law of all nations",[140] and "the law of merchants and the law of the land is the same".[141] In 1774, in Somerset v Stewart, one of the most important cases in legal history, Lord Mansfield held that slavery was lawful "in no country" and therefore in common law.[142] In modern case law it has been consistently accepted that it "is a principle of legal policy that [UK] law should conform to public international law."[143] The House of Lords stressed that "there is a strong presumption in favour of interpreting English law (whether common law or statute) in a way which does not place the United Kingdom in breach of an international obligation."[144] For example, in Hounga v Allen the Supreme Court held that a young lady who had been illegally trafficked to the UK had a right to bring a race discrimination claim against her employers, even though she had herself been in violation of the Immigration Act 1971.[145] In doing so, the court unanimously drew upon international treaties signed by the UK, known as the Palermo Protocols, as well as the European Convention on Human Rights, in interpreting the scope of the common law doctrine of illegality, and held it was no bar for the claimant to assert her legal rights. It has been further debated whether the UK should adopt a theory of that sees international law as part of UK without any further act (a "monist" theory), or whether it should still be required for international law principles to be translated into domestic law (a "dualist" theory).[146] The current position in European Union law is that while international law binds the EU, it cannot undermine fundamental principles of constitutional law or human rights.[147]
.jpg)
Since the World Wars brought an end to the British Empire and physically destroyed large parts of the country, the UK has consistently supported organisations formed under international law. From the Versailles Treaty 1919, the UK was a founding member of the International Labour Organization, which sets universal standards for people's rights at work. After the failure of the League of Nations and following World War Two, the UK became a founding member of the United Nations, recognised by Parliament through the United Nations Act 1946, enabling any resolution of the Security Council except the use of force to be implemented by an Order in Council. Under the Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948, the continued colonial occupation, and suppression of democracy and human rights in the British Empire lost any remaining legitimacy under international law, and combined with independence movements this led to the Empire's rapid dissolution. Two fundamental treaties, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights in 1966 saw the UK ratify most rights from the Universal Declaration. Following the Ponsonby Rule from 1924, the Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010 section 20 stipulates that a treaty is ratified once it is laid before Parliament for 21 days and no adverse resolution is passed against it.
Regionally, the UK participated in drafting the European Convention on Human Rights 1950 which sought to guarantee basic standards of democracy and human rights to preserve peace in post-war Europe. At the same time, following long-held visions for European integration with the UK "at the centre",[149] democratic European countries sought to integrate their economies both to make war impossible, and to advance social progress. In 1972, the UK joined the European Community (renamed the European Union in 1992) and committed to implement EU law in which it participated, in the European Communities Act 1972. In 1995, the UK also became a founding member of the World Trade Organization.[150] To ensure that the European Convention was directly applied by the courts, the Human Rights Act 1998 was passed. It also passed the International Criminal Court Act 2001 to enable prosecution of war criminals, and subjected itself to the jurisdiction of the court. In 2016, however, the UK voted in a referendum on whether to leave the European Union, resulting on a 72.21% turnout in a margin of 48.11% favouring "remain", 51.89% favouring "leave" on unspecified terms (27% of the total UK population).[151] However, large majorities in both Scotland and Northern favoured remaining in the EU, and it was revealed that significant criminal conduct took place in the vote.[152] This led to considerable uncertainty about the UK's future role in the international community.
Institutions

While principles may the basis of the UK constitution, the institutions of the state perform its functions in practice. First, Parliament is the sovereign entity. Its two chambers legislate. In the House of Commons each Member of Parliament is elected by a simple majority in a democratic vote, although outcomes do not always accurately match people's preferences overall. Historically, most elections occurred each four years,[153] but this was fixed at five years in 2011.[154] Election spending is tightly controlled, foreign interference is prohibited, and donations and lobbying are limited in whatever form. The House of Lords reviews and votes upon legislative proposals by the Commons. It can delay legislation by one year, and cannot delay at all if the proposed Act concerns money.[155] Most Lords are appointed by the Prime Minister, through the Queen,[156] on the advice of a Commission which, by convention, offers some balance between political parties. Ninety-two hereditary peers remain.[157] To become law, each Act of Parliament must be read by both houses three times, and given royal assent by the monarch. The monarch cannot veto legislation, by convention, since 1708. Second, the judiciary interprets the law. It can not strike down an Act of Parliament, but the judiciary ensures that any law which may violate fundamental rights has to be clearly expressed, to force politicians to openly confront what they are doing and "accept the political cost".[158] Under the Constitutional Reform Act 2005, the judiciary is appointed by the Judicial Appointments Commission with cross-party and judicial recommendations, to protect judicial independence. Third, the executive branch of government is led by the Prime Minister who must be able to command a majority in the House of Commons. The Cabinet of Ministers is appointed by the Prime Minister to lead the main departments of state, such as the Treasury, the Foreign Office, the Department of Health and the Department of Education. Officially the "head of state" is the monarch, but all prerogative power is exercised by the Prime Minister, subject to judicial review. Fourth, as the UK matured as a modern democracy, an extensive system of civil servants, and public service institutions developed to deliver UK residents economic, social and legal rights. All public bodies, and private bodies that perform public functions, are bound by the rule of law.
Parliament
In the UK constitution, Parliament sits at the apex of power. It emerged through a series of revolutions as the dominant body, over the church, courts, and the monarch,[159] and within Parliament the House of Commons emerged as the dominant chamber, over the House of Lords that traditionally represented the aristocracy.[160] The central justification for Parliamentary sovereignty is usually thought to be its democratic nature, although it was only upon the Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928 that Parliament could be said to have finally become "democratic" in any modern sense (as property qualifications to vote were abolished for everyone over 21), and not until after WW2 that decolonisation, university constituencies and lowering of the voting age took place. Parliament's main functions are to legislate, to allocate money for public spending, and to scrutinise the government.[161] In practice many MPs are involved in Parliamentary committees which investigate spending, policies, laws and their impact, and often report to recommend reform. For instance, the Modernisation Committee of the House of Commons in 2002 recommended publishing draft bills before they became law, and was later found to have been highly successful.[162] There are 650 Members of Parliament (MPs) in the House of Commons, currently elected in five year terms unless two-thirds vote for an early election,[163] and 790 peers in the House of Lords. For a proposed Bill to become an Act, and law, it must be read three times in each chamber, and given royal assent by the monarch.

Today the House of Commons is the primary organ of representative government. The Representation of the People Act 1983 section 1 gives the right to vote for MP in the House of Commons to all Commonwealth citizens, and citizens of the Republic of Ireland, who are over age 18, and registered. Sections 3 and 4 exclude people who are convicted of an offence and in a penal institution, or detained under mental health laws.[164] These restrictions fall below European standards, which require that people who are convicted of very minor crimes (such as petty theft or drug offences) have the right to vote.[165] Since 2013, everyone has to register individually to vote (for instance, at www.gov.uk/register-to-vote), instead of households being able to register collectively, but an annual household canvass is conducted to increase the number of registered people.[166] As far back as 1703,Ashby v White recognised the right to "vote at the election of a person to represent him or [her] in Parliament, there to concur to the making of laws, which are to bind his liberty and property" as "a most transcendent thing, and of an high nature".[167] This originally meant that any interference in that right would lead to damages. If the denial of voting would have changed the result, or if a vote was "conducted so badly that it was not substantially in accordance with the law" the vote would have to be run again.[168] So, in Morgan v Simpson the Court of Appeal declared that an election for a Greater London Council seat was not valid after it was found that 44 unstamped ballot papers were not counted. These common law principles predate statutory regulation, and therefore appear to apply to any vote, including elections and referendums.[169] Election spending is tightly controlled today by statute. A maximum of £20 million can be spent by political parties in national campaigns, plus £10,000 in each constituency.[170] Political advertisements on television are prohibited except for those in certain free time slots,[171] although the internet remains largely unregulated. Any spending over £500 by third parties must be disclosed. While these rules are strict, they were held in Animal Defenders International v UK to be compatible with the Convention because "each person has equal value" and "we do not want our government or its policies to be decided by the highest spenders."[172] Foreign interference in voting is completely prohibited, including any "broadcasting" (also over the internet) "with intent to influence persons to give or refrain from giving their votes".[173] Donations by foreign parties can be forfeited in their entirety to the Electoral Commission.[174] Domestic donations are limited to registered parties, and must be reported, when they are over £7,500 nationally or £1,500 locally, to the Electoral Commission.[175] The system for electing the Commons is based on constituencies, whose boundaries are periodically reviewed to even out populations.[176] There has been considerable debate about the first-past-the-post system of voting the UK uses, as it tends to exclude minority parties. By contrast, in Australia voters may select preferences for candidates, although this system was rejected in a 2011 United Kingdom Alternative Vote referendum staged by the Cameron-Clegg coalition. In the European Parliament, voters choose a party from multi-member regional constituencies: this tends to give smaller parties much greater representation. In the Scottish Parliament, Welsh Assembly and London Assembly, voters have the choice of both constituencies and a party list, which tends to reflect overall preferences best. To be elected as an MP, most people generally become members of political parties, and must be over 18 on the day of nomination to run for a seat,[177] be a qualifying Commonwealth or Irish citizen,[178] not be bankrupt,[179] found guilty of corrupt practices,[180] or be a Lord, judge or employee of the civil service.[181] To limit the government's practical control over Parliament, the Ministerial and Other Salaries Act 1975 restricts higher payment of salaries to a set number of MPs.[182]

Along with a hereditary monarch, the House of Lords remains an historical curiosity in the UK constitution. Traditionally it represented the landed aristocracy, and political allies of the monarch or the government, and has only gradually and incompletely been reformed. Today, the House of Lords Act 1999 has abolished all but 92 hereditary peers, leaving most peers to be "life peers" appointed by the government under the Life Peerages Act 1958, law lords appointed under the Appellate Jurisdiction Act 1876, and Lords Spiritual who are senior clergy of the Church of England.[183] Since 2005, senior judges can only sit and vote in the House of Lords after retirement.[184] The government carries out appointment of most peers, but since 2000 has taken advice from a seven-person House of Lords Appointments Commission with representatives from the Labour, Conservatives and Liberal-Democrat parties.[185] A peerage can always be disclaimed,[186] and ex-peers may then run for Parliament.[187] Since 2015, a peer may be suspended or expelled by the House.[188] In practice the Parliament Act 1949 greatly reduced the House of Lords' power, as can only delay and cannot block legislation by one year, and cannot delay money bills at all.[189] Nevertheless, several options for reform are debated. A House of Lords Reform Bill 2012 proposed to have 360 directly elected members, 90 appointed members, 12 bishops and an uncertain number of ministerial members. The elected Lords would have been elected by proportional representation for 15 year terms, through 10 regional constituencies on a single transferable vote system. However, the government withdrew support after backlash from Conservative backbenches. It has often been argued that if the Lords were elected by geographic constituencies and a party controlled both sides "there would be little prospect of effective scrutiny or revision of government business." A second option, like in Swedish Riksdag, could simply be to abolish the House of Lords: this was in fact done during the English Civil War in 1649, but restored along with the monarchy in 1660. A third proposed option is to elect peers by work and professional groups, so that health care workers elect peers with special health knowledge, people in education elect a fixed number of education experts, legal professionals elect legal representatives, and so on.[190] This is argued to be necessary to improve the quality of legislation.
Judiciary

The judiciary in the United Kingdom has the essential functions of upholding the rule of law, democracy, and human rights. The highest court of appeal, renamed from the House of Lords in 2005, is the UK Supreme Court. Since the 1966 Practice Statement, the judiciary has acknowledged that while a system of precedent, that binds lower courts, is necessary to provide "at least some degree of certainty", the courts should update their jurisprudence and "depart from a previous decision when it appears right to do so."[191] Litigation usually begins in a County Court or the High Court for civil law issues, or a magistrates' court or the Crown Court for criminal law issues. There are also employment tribunals for labour law disputes,[192] and the First-tier Tribunal for public or regulatory disputes, ranging from immigration, to social security, to tax.[193] After the High Court, Crown Court, or appeal tribunals, cases generally may appeal to the Court of Appeal in England and Wales. In Scotland, the Court of Session has an Outer (first instance) and Inner (appeal) House. Appeals then go to the UK Supreme Court, although at any time a court may make a "preliminary reference" to the Court of Justice of the European Union to clarify the meaning of EU law. Since the Human Rights Act 1998, courts have been expressly required to interpret UK law to be compatible with the European Convention on Human Rights. This follows a longer tradition of courts interpreting the law to be compatible with international law obligations.[194] It is generally accepted that the UK courts do not merely apply but also create new law through their interpretative function: this is obvious in the common law and equity, where there is no codified statutory basis for large parts of the law, such as contracts, torts or trusts. This also means an element of retroactivity,[195] since an application of developing rules may differ from at least one party's understanding of the law in any conflict.[196] Although formally the UK judiciary may not declare an Act of Parliament "unconstitutional",[197] in practice the judiciary's power to interpret the law so as to be compatible with human rights can render a statute inoperative, much like in other countries.[198] The courts do so sparingly because they recognise the importance of the democratic process. Judges may also sit from time to time on public inquiries.[199]
The independence of the judiciary is one of the cornerstones of the constitution, and means in practice that judges cannot be dismissed from office. Since the Act of Settlement 1700, no judge has been removed, as to do so the Queen must act on address by both Houses of Parliament.[200] It is very likely that a judge would never be dismissed, not merely because of formal rules but a "shared constitutional understanding" of the importance of the integrity of the legal system.[201] This is reflected, for example, in the sub judice rule that matters awaiting decision in court should not be prejudged in a Parliamentary debate.[202] The Lord Chancellor (once head of the judiciary but now simply a government minister) also has a statutory duty to uphold the independence of the judiciary,[203] for instance, against attacks upon their integrity by media, corporations, or the government itself. Members of the judiciary can be appointed from among any member of the legal profession who has over 10 years of experience having rights of audience before a court: this usually includes barristers, but can also mean solicitors or academics.[204] Appointments should be made "solely on merit" but regard may be had to the need for diversity when two candidates have equal qualifications. For appointments to the Supreme Court, a five-member Judicial Appointments Committee is formed including one Supreme Court judge, three members from the Judicial Appointments Commission, and one lay person.[205] For other senior judges such as those on the Court of Appeal, or for the Lord Chief Justice, Master of the Rolls, or the heads of the High Court divisions, a similar five member panel with two judges is formed.[206] Gender and ethnic diversity is lacking in the UK judiciary compared to other developed countries, and potentially compromises the expertise and administration of justice.[207] Backing up the judiciary is a considerable body of administrative law. The Contempt of Court Act 1981 enables a court to hold anyone in contempt, and commit the person to imprisonment, for violating a court order, or behaviour that could compromise a fair judicial process. In practice this is enforced by the executive. The Lord Chancellor heads the Ministry of Justice, which performs various functions including administering the Legal Aid Agency for people who cannot afford access to the courts. In R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor the government suffered scathing criticism for creating high fees that cut the number of applicants to employment tribunals by 70 per cent.[208] The Attorney General of the UK and the Solicitor General represent the Crown in litigation. The Attorney General also appoints the Director of Public Prosecutions who heads the Crown Prosecution Service, which reviews cases submitted by the police for prosecution, and conducts them on behalf of the Crown.[209]
Executive

The executive branch, while subservient to Parliament and judicial oversight, exercises day to day power of the UK government. In form, the UK remains a constitutional monarchy. The formal head of state is Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II, a hereditary monarch since 1952. In reality, no Queen or King has attempted to usurp the will of Parliament since 1708, and all constitutional duties and power are accepted by binding convention to have shifted to the Prime Minister, Parliament or the courts.[210] Over the 17th century, the Petition of Right 1628 was asserted by Parliament to prevent any taxation by the monarch without Parliament's consent, and the Habeas Corpus Act 1640 denied the monarch any power to arrest people for failing to pay taxes. The monarch's continued assertion of the divine right to rule led to Charles I being executed in the English Civil War, and finally the settlement of power in the Bill of Rights of 1689. Following the Act of Union 1707 and an early financial crisis as South Sea Company shares crashed, Robert Walpole emerged as a dominant political figure. Leading the House of Commons from 1721 to 1742, Walpole is generally acknowledged to be the first Prime Minister (Primus inter pares). The PM's modern functions include leading the dominant political party, setting policy priorities, creating Ministries and appointing ministers, judges, peers, and civil servants. The PM also has considerable control through the convention of collective responsibility (that ministers must publicly support the government even when they privately disagree, or resign), and control over the government's communications to the public. By contrast in law, as is necessary in a democratic society,[211] the monarch is a figurehead with no political power,[212] but a series of ceremonial duties, and considerable funding. Aside from private wealth and finance,[213] the monarchy is funded under the Sovereign Grant Act 2011, which reserves 25 per cent of the net revenue from the Crown Estate.[214] The Crown Estate is a public, government corporation,[215] which in 2015 held £12 billion in investments, mostly land and property, and therefore generates income by charging rent to businesses or people for homes.[216] The monarch's major ceremonial duties are to appoint the Prime Minister who can command the majority of the House of Commons,[217] to give royal assent to Acts of Parliament, and to dissolve Parliament upon the calling of an election.[218] Minor ceremonial duties include giving an audience to the Prime Minister, as well as visiting ministers or diplomats from the Commonwealth, and acting on state occasions, such as delivering the "Queen's speech" (written by the government, outlining its political platform) at the opening of Parliament. It has frequently been debated whether the UK should abolish the monarchy, on the ground that hereditary inheritance of political office has no place in a democracy. On the other hand, there are powerful attachments of emotion and tradition: in Australia a referendum was held in 1999 on becoming a Republic, but failed to get a majority.[219]

Although called the royal prerogative, a series of important powers that were once vested in the King or Queen are now exercised by government, and the Prime Minister in particular. These are powers of day-to-day management, but tightly constrained to ensure that executive power cannot usurp Parliament or the courts. In the Case of Prohibitions in 1607,[220] it was held that the royal prerogative could not be used to determine court cases, and in the Case of Proclamations in 1610 it was held new prerogative powers could not be created by the executive.[23] It is also clear that no exercise of the prerogative can compromise any right contained in an Act of Parliament. So, for instance, in R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the EU the Supreme Court held that the Prime Minister could not notify the European Commission of an intention to leave under Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union without an Act of Parliament, because it could result in rights being withdrawn that were granted under the European Communities Act 1972, such as the right to work in other EU member states or vote in European Parliament elections.[221] Royal prerogative powers can be categorised in different ways,[222] there are around 15.[223] First, the executive may create hereditary titles, confer honours and create peers.[224] Second, the executive can legislate by an Order in Council, though this has been called an 'anachronistic survival'.[225] Third, the executive can create and administer financial benefits schemes.[226] Fourth, through the Attorney General the executive can stop prosecutions or pardon convicted offenders after taking advice.[227] Fifth, the executive may acquire more territory or alter limits of British territorial waters.[228] Sixth, the executive may expel aliens and theoretically restrain people from leaving the UK.[229] The executive can sign treaties, although before it is considered ratified the treaty must be laid before Parliament for 21 days and there must be no resolution against it.[230] Eighth, the executive governs the armed forces and can do "all those things in an emergency which are necessary for the conduct of war".[231] The executive cannot declare war without Parliament by convention, and in any case has no hope in funding war without Parliament.[232] Ninth, the Prime Minister can appoint ministers, judges, public officials or royal commissioners. Tenth, the monarch needs to pay no tax, unless statute states it expressly.[233] Eleventh, the executive may by royal charter create corporations, such as the BBC,[234] and franchises for markets, ferries and fisheries.[235] Twelfth, the executive has the right to mine precious metals, and to take treasure troves. Thirteenth, it may make coins. Fourteenth, it can print or license the authorised version of the Bible, Book of Common Prayer and state papers. And fifteenth, subject to modern family law, it may take guardianship of infants.[236] In addition to these royal prerogative powers, there are innumerable powers explicitly laid down in statutes enabling the executive to make legal changes. This includes a growing number of Henry VIII clauses, which enable a Secretary of State to alter provisions of primary legislation. For this reason it has often been argued that executive authority should be reduced, written into statute, and never used to deprive people of rights without Parliament. All uses of the prerogative, however, are subject to judicial review: in the GCHQ case the House of Lords held that no person could be deprived of legitimate expectations by use of the royal prerogative.[237]
Although the Prime Minister is the head of Parliament, Her Majesty's Government is formed by a larger group of Members of Parliament, or peers. The "cabinet" is a still smaller group of 22 or 23 people, though only twenty ministers may be paid.[238] Each minister typically heads a Department or Ministry, which can be created or renamed by prerogative.[239] Cabinet committees are usually organised by the Prime Minister. Every minister is expected to follow collective responsibility,[240] and the Ministerial Code 2010. This includes rules that Ministers are "expected to behave in a way that upholds the highest standards of propriety", "give accurate and truthful information to Parliament", resign if they "knowingly mislead Parliament", to be "as open as possible", have no possible conflicts of interest and give a full list of interests to a permanent secretary, and only "remain in office for so long as they retain the confidence of the Prime Minister". Assisting ministers is a modern civil service and network of government bodies, who are employed at the pleasure of the Crown.[241] The Civil Service Code requires civil servants to show "high standards of behaviour", uphold core values of "integrity, honesty, objectivity and impartiality", and never put themselves in a position that "might reasonably be seen to compromise their personal judgment or integrity". Since the Freedom of Information Act 2000, it has been expected that government should be open about information, and should disclose it upon a request unless disclosure would compromise personal data, security or may run against the public interest.[242] In this way the trend has been to more open, transparent and accountable governance.
Civil and public service
- UK tax law
- European Social Charter 1961
- Social Security Contributions and Benefits Act 1992
- National Health Service Act 2006
- Further and Higher Education Act 1992
- Education Reform Act 1988
- Bank of England Act 1998
- Financial Services and Markets Act 2000
- Consumer Credit Act 1974
- Climate Change Act 2008
- Electricity Act 1989
- Utilities Act 2000
- Water Industry Act 1991
- Railways Act 1993
- Transport Act 1983
- Transport Act 2000
- Communications Act 2003
- Wireless Telegraphy Act 2006
- Reserve Forces Act 1996
- Armed Forces Act 2006
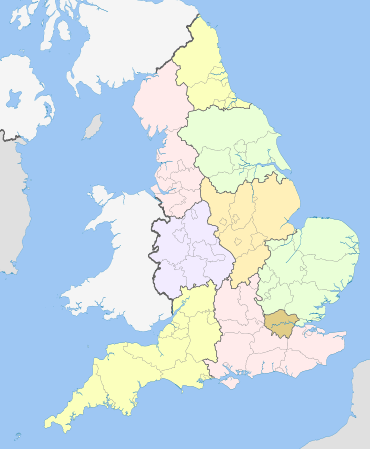
Regional government
.jpg)
The constitution of UK regional governments is an uncodified patchwork of authorities, mayors, councils and devolved assemblies.[245] In Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland and London unified district or borough councils have local government powers, and since 1998 to 2006 new regional assemblies or Parliaments exercise extra powers devolved from Westminster. In England, there are 55 unitary authorities in the larger towns (e.g. Bristol, Brighton, Milton Keynes) and 36 metropolitan boroughs (surrounding Liverpool, Manchester, Leeds, Birmingham, Sheffield, and Newcastle) which function as unitary local authorities. But in other parts of England, local government is split between two tiers of authority: 32 larger County Councils, and within those 192 District Councils, each sharing different functions. Since 1994, England has had eight regions for administrative purposes at Whitehall, yet these have no regional government or democratic assembly (like in London, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland) after a 2004 referendum on a North East Assembly failed. This means that England has among the most centralised, and disunified systems of governance in the Commonwealth or Europe.
Three main issues in local government are the authorities' financing, their powers, and the reform of governance structures. First, councils raise revenue from council tax (charged on local residents according to property values in 1993[247]) and business rates charged on businesses with operations in the locality. These powers are, compared to other countries, extreme in limiting local government autonomy, and taxes can be subjected to a local referendum if the Secretary of State determines they are excessive.[248] In real terms since 2010, central government cut local council funding by nearly 50 per cent, and real spending fell by 21 per cent, as councils failed to make up cuts through business rates.[249] Unitary authorities and district councils are responsible for administering council tax and business rates.[250] The duties of UK local governments are also extremely limited compared to other countries, but also uncodified so that in 2011 the Department for Communities and Local Government enumerated 1340 specific duties of local authorities.[251] Generally, the Localism Act 2011 section 1 states local authorities may do anything an individual person may do, unless prohibited by law, but this provision has little effect because human beings or companies cannot tax or regulate other people in the way that governments must.[252] The Local Government Act 1972 section 101 says that a local authority can discharge its functions through a committee or any officer, and can transfer functions to another authority, while section 111 gives authorities the power to do any thing including spending or borrowing 'which is calculated to facilitate, or is conducive or incidental to, the discharge of any of their functions'. However the real duties of local council are found in hundreds of scattered Acts and statutory instruments. These include duties to administer planning consent,[253] to carry out compulsory purchasing according to law,[254] to administer school education,[255] libraries,[256] care for children,[257] roads or highway maintenance and local buses,[258] provide care for the elderly and disabled,[259] prevent pollution and ensure clean air,[260] ensure collection, recycling and disposal of waste,[261] regulate building standards,[262] provide social and affordable housing,[263] and shelters for the homeless. Local authorities do not yet have powers common in other countries, such as setting minimum wages, regulating rents, or borrowing and taxing as is necessary in the public interest, which frustrates objectives of pluralism, localism and autonomy.[264] Since 2009, authorities have been empowered to merge into 'combined authorities' and to have an elected mayor.[265] This has been done around Manchester, Sheffield, Liverpool, Newcastle, Leeds, Birmingham, the Tees Valley, Bristol and Peterborough. The functions of an elected mayor are not substantial, but can include those of Police and Crime Commissioners.[266]

In Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and London there are also regional assemblies and Parliaments, similar to state or provincial governments in other countries. The extent of devolution differs in each place. The Scotland Act 1998 created a unicameral Scottish Parliament with 129 elected members each four years: 73 from single member constituencies with simple majority vote, and 56 from additional member systems of proportional representation. Under section 28, the Scottish Parliament can make any laws except for on 'reserved matters' listed in Schedule 5. These powers, reserved for the UK Parliament, include foreign affairs, defence, finance, economic planning, home affairs, trade and industry, social security, employment, broadcasting, and equal opportunities. By convention, members of the UK Parliament from Scottish constituencies do not vote on issues that the Scottish Parliament has exercised power over.[267] This is the most powerful regional government so far. The Northern Ireland Act 1998 lists which matters are transferred, but the Northern Ireland Assembly has been suspended since 2017 because of basic disagreements among its members, stemming from long-standing violence and civil conflict, before a delicate peace deal was brokered in the Good Friday Agreement.[268] The Government of Wales Act 2006 requires a 40-member assembly with elections each four years, and sets out in Schedule 5 twenty fields of government competence, with some exceptions. The fields include agriculture, fisheries, forestry and rural development, economic development, school education, environmental policy, highways and transport, housing, planning, and some aspects of social welfare.[269] The Supreme Court has tended to interpret these powers in favour of devolution.[270]
Human rights
.jpg)
Codification of human rights is recent, but before the Human Rights Act 1998 and the European Convention on Human Rights, UK law had one of the world's longest human rights traditions. The Magna Carta 1215 bound the King to require Parliament's consent before any tax, respect the right to a trial "by lawful judgment of his Peers, or by the Law of the Land", stated that "We will sell to no man, we will not deny or defer to any man either Justice or Right", guaranteed free movement for people, and preserved common land for everyone.[272] After the English Civil War the Bill of Rights 1689 in England and Wales, and the Claim of Rights Act 1689 in Scotland, enshrined principles of representative democracy, no tax without Parliament, freedom of speech in Parliament, and no "cruel and unusual punishment". By 1789, these ideas evolved and inspired both the US Bill of Rights, and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen after the American and French Revolutions. Although some labelled natural rights as "nonsense upon stilts",[273] more legal rights were slowly developed by Parliament and the courts. In 1792, Mary Wollstonecraft began the British movement for women's rights and equality,[274] while movements behind the Tolpuddle martyrs and the Chartists drove reform for labour and democratic freedom.[275] Upon the catastrophe of World War Two and the Holocaust, the new international law order put the Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 at its centre, enshrining civil, political, economic, social and cultural rights.[276] In 1950, the UK co-authored the European Convention on Human Rights, enabling people to appeal to the European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg even against Acts of Parliament: Parliament has always undertaken to comply with basic principles of international law.[277] Because this appeals process was long, Parliament legislated to "bring rights home" with the Human Rights Act 1998, so that people can raise human rights claims in UK courts based on the Convention directly. The Convention contains the rights to life, rights against torture, against forced labour, to marry, to an effective remedy, and the right to suffer no discrimination in those rights.[278] Most case law concerns the rights to liberty, privacy, freedom of conscience and expression, and to freedom of association and assembly.[279] The UK also enshrines rights to fair labour standards, social security, and a multitude of social and economic rights through its legislation.
Liberty and a fair trial
The right to liberty of the person, to be free from the domination or servitude of others, and only to lose one's liberty 'by lawful judgment of his Peers, or by the Law of the Land' has been fundamental to UK and English law since the Magna Carta.[280] This said, slavery and serfdom took until the 16th century to break down in England, and was maintained at least until 1833 within the British Empire, before full abolition of forced labour was passed, extending the writ of habeas corpus (the right to one's own body) to everyone.[281] Benjamin Franklin's adage, that people who sacrifice liberty for security will lose both and deserve neither,[282] is reflected in human rights law. Like international law,[283] the European Convention on Human Rights article 5 states no 'one shall be deprived of [their] liberty' unless law expressly allows that person's detention after conviction, a lawful arrest or detention on suspicion of an offence, detention of a minor for education, detention for health or stopping infectious diseases spreading, or for lawful deportation or extradition.[284] People must be told reasons for any detention, be put on trial in a reasonable time, or released immediately with compensation if detention was unlawful.[285] Article 6 requires a fair trial, with a presumption of innocence, and legal aid if justice requires it, according to principles of natural justice. Article 7 prohibits criminal offences applying retroactively to acts done before something was made criminal. In practice, every power of the police or the state to maintain order and security 'inevitably means a corresponding reduction in the liberty of the individual',[286] and the UK has among the highest spending on policing in the world.[287] For this reason the Police and Criminal Evidence Act 1984, and the limits to police powers, is a key legislative guardian of liberty in the UK today.
.jpg)
Three main issues of police power and liberty are (1) powers of arrest, detention and questioning, (2) powers to enter, search or seize property, and (3) the accountability of the police for abuse of power. First, the Police and Criminal Evidence Act 1984 section 1 allows a constable to stop and search people if a constable 'has reasonable grounds for suspecting' that they will 'find stolen or prohibited articles', they may seize the articles, and they may use reasonable force.[289] The constable must give their name, police station, and grounds for the search. People cannot be made to remove clothing in public, except an outer coat, jacket or gloves.[290] Because of the widespread problem of race discrimination in stop and search, the Home Office Code A says that 'reasonable suspicion cannot be based on generalisations or stereotypical images' of people being involved in crime.[291] It was formerly seen as 'contrary to constitutional principle' to search someone to find whether or not there are grounds for arrest.[292] But since 1994, there is no need for police to show reasonable suspicion to search someone to prevent violence or the carrying of offensive weapons.[293] In 2015 the Supreme Court held suspicionless searches were held to be compatible with ECHR article 5.[294] Under section 24, constables can arrest people without a warrant if they are committing an offence, or if there are reasonable grounds for suspecting they will.[295] The meaning of 'reasonable grounds' is not exacting, but a police officer must not arrest someone in bad faith, or irrationally, or if a suspect is cooperating and arrest is therefore unnecessary.[296] Otherwise, a justice of the peace may issue a warrant for arrest, require attendance at court, in writing, and it can be executed by a constable.[297] With a warrant, a constable can enter and search premises to make an arrest, or enter and search after an arrest. In addition, any person can make a 'citizens' arrest of another person who is in the act of committing an indictable offence.[298] Anyone being arrested mus be told the fact of arrest, and the reasons, or be told as soon as practicable, and if they are not the arrest is unlawful.[299] People who are arrested must be brought to a police station as soon as practicable, and there must either be released, charged or detained for questioning.[300] People can only be detained without charge for 24 hours, but this can be extended to 36 hours for an indictable offence, or another 36 hours (i.e. 72 hours in total) but only with approval of a magistrate's court where the detainee has a right to legal representation.[301] People can be searched at a police station with an inspector's authority, but can only do intimate searches of orifices if there are reasonable grounds for thinking there is a class A drug or article that could cause injury. A detainee has the right to inform a friend or relative, and consult a solicitor, but this right can be delayed by 36 hours if arrested for an indictable offence or 48 hours for terrorism.[302] Interviews should be recorded, people can be photographed and drug tested without their consent. 'Intimate' samples of bodily fluids, blood and swabs cannot be taken without consent, but courts may draw adverse inferences.[303] When being questioned by police, it is acknowledged that the right to silence is ultimately 'at the heart' of a fair trial,[304] and ‘particular caution [is] required before a domestic court [should] invoke an accused’s silence against him.’[305] No statement or confession is admissible unless it is voluntarily given.[306] A clear exception, however, is that a vehicle owner can be required to reveal the identity of a driver, and this does not breach ECHR article 6.[307]
Entick v Carrington [1765] EWHC KB J98, Lord Camden CJ
Second, police officers have no right to trespass upon property without a lawful warrant, because as Lord Camden said in Entick v Carrington by 'the law of England every invasion of private property, be it ever so minute, is a trespass.' Here a sheriff searched and seized property at the home of a journalist, John Entick, but the 'warrant' used by the sheriff had no legal basis. The Court held that the sheriff had to pay damages. Today, under the Police and Criminal Evidence Act 1984 section 8 enables officers to enter premises and search but only based on a warrant granted by a justice of the peace. There is no right to search communications between lawyer and a client, or confidential personal records, some medical materials, and confidential journalistic material, unless there is an order of a judge.[308] A common law power to enter premises to stop a breach of peace[309] was held in McLeod v UK to have unjustifiably violated the right to privacy under ECHR article 8, because the police used it to help an ex-husband recover property when an ex-wife was absent from a home.[310] Under section 19, an officer can seize material if they have reasonable grounds to believe it was obtained by committing an offence, or if it is evidence, but not if it is subject to legal privilege.[311] Third, although 'the law does not encourage' someone to 'resist the authority of... an officer of the law', there is an inherent right to resist an unlawful arrest,[312] but it is an offence to resist a lawful arrest.[313] By contrast, before being formally arrested, in R v Iqbal a man accused of drug offences was detained and handcuffed by police while attending a friend's trial, but before being arrested he broke free and escaped. He was caught again, and convicted for escaping lawful custody, but the Lord Chief Justice overturned the conviction because there was no lawful arrest, and the offence could not be widened 'by making it apply to those whose arrest has been deliberately postponed.'[314] Anyone can bring a claim against police for unlawful conduct, the chief constable is vicariously liable for constables' conduct, and exemplary damages are available for 'oppressive, arbitrary or unconstitutional actions'.[315] Evidence illegally obtained, such as a confession, and certainly anything through 'torture, inhuman or degrading treatment and the use or threat of violence' must be excluded, and a court can refuse evidence if it would have an adverse effect on the fairness of proceedings.[316] Since 2011, Police and Crime Commissioners are directly elected in England and Wales (on low turnouts) and have a duty to 'secure that the police force is efficient and effective'.[317] The Home Secretary is meant to issue a 'strategic policing document' that chief constables pay regard to, but can intervene and require 'special measures' if there is mismanagement.[318] This means the Home Secretary is ultimately politically responsible, but administration is largely local. Commissioners have a duty to enforce the law, but decisions about how to allocate scarce resources mean that police forces can choose to prioritise tackling some kinds of crime (e.g. violence) over others (e.g. drugs).[319] Generally police forces will not be liable in tort for failing to stop criminal acts,[320] but positive duties do exist to take preventative measures or properly investigate allegations.[321]
Privacy
The constitutional importance of privacy, of one’s home, belongings, and correspondence, has been recognised since 1604, when Sir Edward Coke wrote that the ‘house of every one is to him as his castle and fortress’.[322] While rights to liberty and a fair trial also protect against unjustified search or seizure, the European Convention on Human Rights article 8 enshrines the right to one’s ‘private and family life’, ‘home’ and ‘correspondence’ unless interference is ‘in accordance with the law’ and ‘necessary in a democratic society’ for public security, safety, economic well-being, preventing crime, protecting health or morals or rights of others.[323] The law of trespass, as in Entick v Carrington,[324] traditionally protected against unjustified physical violations of people’s homes, but given extensive powers of entry,[325] and with modern information technology the central concerns of privacy are electronic surveillance, both by the state and by private corporations aiming to profit from data or 'surveillance capitalism'.[326] The four main fields of law relating to privacy concern (1) listening devices and interference with private property, (2) interception of mail, email or web communications by government, (3) mass data storage and processing by corporations or state bodies, and (4) other breaches of confidence and privacy, particularly by the press.

First, the Police Act 1997 sections 92 prohibits 'interference with property or with wireless telegraphy' without authorisation by a chief constable or others.[327] Such listening or bugging devices may only be used 'for the prevention or detection of serious crime' that could lead to over 3 years of jail. A judicial commissioner's approval is further needed if a dwelling, bedroom or office is being bugged, and if refused the police can appeal to the Investigatory Powers Commissioner.[328] On top of this, the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 which also generally allows surveillance by police, intelligence, HMRC and councils to obtain private information ('directed'), or surveillance of a residence or vehicle ('intrusive') if for the purpose of national security, preventing serious crime, or protecting UK economic well-being. Only 'intrusive' surveillance requires approval by a judicial commissioner.[329] This has frequently led to abuse, for instance, in one case with a family being put under surveillance to see if they lived in a catchment area of an oversubscribed school,[330] and in another an intelligence officer infiltrating a protest group and fathering a child, after taking a dead child's identity.[331] Surveillance in public places does not engage the human right to privacy, according to Kinloch v HM Advocate, where evidence of the defendant money laundering was gathered by police following the suspect in public spaces.[332] Second, although the Investigatory Powers Act 2016 section 2 creates a duty to consider whether means less intrusive to privacy could be used, warrants can be issue for targeted or bulk interception of any data, including to assist other governments, but only to detect serious crime, protect national security, or protect the UK's economic well-being, and this must be proportionate.[333] Applications are made to the Home Secretary or other appropriate ministers, and must be approved by a judicial commissioner with written reasons for any refusal.[334] Warrants can also be issued against Members of Parliament with the consent of the Prime Minister.[335] Interception should not be disclosed in judicial proceedings.[336] Local councils are able to carry out interceptions, albeit with authority of a justice of the peace. Journalists' material can be intercepted, though only with authority of a judicial commissioner. The government can also require internet service providers retain data, including bulk data, for up to a year. Judicial commissioners must have held high judicial office, while the Investigatory Powers Commissioner audits, inspects and investigates the exercise of public body powers. In 2015, over 3059 warrants were granted, and it is argued by MI5 that bulk data enables security services to 'make the right connections between disparate pieces of information'.[337] The fact of bulk data collection, however, inevitably means people who have nothing to do with serious crime remain under state surveillance.
Third, it has been recognised that the 'right to keep oneself to oneself, to tell other people that certain things are none of their business, is under technological threat' also from private corporations, as well as the state.[339] Through standard form contracts, tech corporations routinely appropriate users' private data for targeted advertising, particularly Google (e.g. search and browsing history, email, locations), Facebook (e.g. personal interactions, hobbies, messages), Microsoft (e.g. emails, or cloud documents) and others. Because people have no choice but to agree to the terms and conditions, consent is defective and contract terms are often unfair, legislation has been increasing in strength to reflect the fundamental 'right to the protection of personal data' in the European Union.[340] The General Data Protection Regulation 2016 requires that all data is processed lawfully, fairly and transparently, and on the basis of 'consent' or a contract.[341] The meaning of 'consent' requires more than the basic rules for commercial contracts, and must be clearly and distinctly identifiable, and revocable at any time.[342] Contract terms may be subject to more protective rights contained in UK law.[343] Whenever a 'data subject' has personal data processed or stored, they have basic rights to be provided with transparent information about the data stored including when they have not given that information themselves,[344] to access the data and rectify any inaccuracies, and to demand that the data is erased when it is no longer necessary for the purpose for which it was originally given.[345] There is a further right that data must be portable 'to another controller without hindrance',[346] for instance in switching phone contacts. Data may be disclosed for legitimate reasons, so in Rugby Football Union v Consolidated Information Services Ltd the Supreme Court held that a ticketing agency had no data protection defence against disclosing information to the Rugby Football Union about people who touted tickets against its rules, because the legitimate interest in stopping theft was stronger.[347] Article 32 states a data controller must ensure the security of people's data, and notify supervisory authorities of any breach, including transfers to 'third countries' where the rule of law is defective. However, during the 2016 Brexit referendum the House of Commons fake news committee found that Facebook enabled massive breaches of users' data, being sold onto third parties including Cambridge Analytica, which psychologically targeted voters with political adverts, and this data spread into Russia.[348] The penalties for breach of GDPR rules, since it came into force in May 2018, can be up to 4% of a company's worldwide turnover, or €20m, whichever is higher.[349] There are also databases kept by UK state bodies, including the National Domestic Extremism Database, a DNA Database,[350] and a Police National Computer,[351] Related to this, the Supreme Court held in R(L) v Metropolitan Police Commissioner that there was no breach of privacy when a primary school's enhanced criminal record check on an applicant for a teaching assistant job showed the applicant's son was put on a child protection register because of neglect, and she was refused a job.[352] A planned NHS patients' database, care.data, was abandoned because of protests about confidentiality and security of data.[353] Finally, claimants may sue any private party on the grounds of breach of confidence, an old equitable action,[354] although one that may be giving way to a tort of misuse of private information.[355] For instance, it was held that it was an unlawful breach of privacy for the Daily Mail to publish private journals of the Prince of Wales about the handover of Hong Kong to China stolen and leaked by a former employee.[356] It was also held to be unlawful for a newspaper to publish details of an applicant's private sexual life, even though in other countries the story had spread around the internet, because there was no 'public interest... in the disclosure or publication of purely private sexual encounters, even though they involve adultery or more than one person at the same time'.[357] In this way the common law has developed to uphold human rights.
Conscience and expression
The rights to freedom of conscience, and freedom of expression, are generally seen as being the 'lifeblood of democracy.'[358] The trial and executions of Socrates in ancient Athens for 'corrupting the youth',[359] of Jesus Christ in ancient Rome for blasphemy and sedition,[360] of Sir Thomas More for refusing to bless Henry VIII's remarriage and split from the Catholic Church, or the house arrest of Galileo Galilei in the Inquisition for heresy, exemplified how people's conscience and expression in the ancient and medieval worlds were crushed for challenging people in political and economic power. After the English Civil War, it was established that a jury could acquit a Quaker who preached to a crowd even against the judge's direction and ‘against full and manifest evidence’.[361] The Bill of Rights 1689 article 9 guaranteed the 'freedom of speech and debates or proceedings in Parliament' and stated they were 'not to be impeached or questioned in any court or place out of Parliament', but the first full, legal guarantees for free speech came from the American Revolution, when the First Amendment to the US Constitution guaranteed 'freedom of speech'. The government and employers suppressed free speech through the French revolution and after the Napoleonic wars,[362] until the repeal of the anti-Catholic laws,[363] and the abolition of restraints on trade union organising, as well as throughout the British Empire. But after World War Two, the UK signed the Universal Declaration on Human Rights and joined the European Convention. Article 9 states that everyone has the right to freedom of conscience, including religion and belief. Only the manifestation of a belief can be limited on justifiable legal grounds as strictly necessary in a democracy.[364] Article 10 enshrines the right to freedom of expression which includes the rights 'to hold opinions and to receive and impart information and ideas without interference by public authority and regardless of frontiers.' This does not prevent 'the licensing of broadcasting, television or cinema enterprises.' Like all other rights these are subject to restrictions set out in law, and as necessary in a democratic society, to stop crime, or protect security, territorial integrity, safety, health, morals, the rights of others, and to maintain the judiciary's impartiality.[lower-alpha 3]

The practical right to free expression is limited by (1) unaccountable ownership in the media, (2) censorship and obscenity laws, (3) public order offences, and (4) the law of defamation and breach of confidence. First, although anybody can stand on Speakers’ Corner, in Parliament Square, or in Trafalgar Square and speak freely to a crowd,[lower-alpha 5] the communication channels with the biggest audiences are owned by large corporate entities:[366] three internet media networks,[lower-alpha 6] five television networks,[lower-alpha 7] and six corporate-owned newspaper groups,[lower-alpha 8] almost all of which aim have shareholders that demand to make a profit.[368][lower-alpha 9] This means that most speech, with most reach, is designed to be compatible with generating advertising revenue and shareholder profit for the newspaper, TV, or Internet corporation, and controllers choose which speech or images are acceptable, unless the law creates different rights. While there are loose limits on cross-ownership of TV and newspapers,[370][371][372] there is no regulation yet separate advertising business and internet media platforms where their interests conflict with public goals. The Communications Act 2003 sections 319-321, regulates television (but not explicitly Internet broadcasts, or newspapers) to ensure that diverse views are heard, and to restrict discriminatory viewing, or the stop misleading information, and allows a complaints procedure.[lower-alpha 10] An Independent Press Standards Organisation operates for newspapers,[373] but this has no publicly accountable legal basis after the industry chose to boycott one. The UK's transparent, and publicly accountable system of TV media regulation is consistently held to be compatible with freedom of expression.[lower-alpha 11] Two of the UK’s TV networks, the BBC and Channel 4, are publicly owned and accountable, through an arm’s length appointment process overseen by the government. However, most television channels are funded through advertising revenue. There is also effectively no regulation of standards on Internet media, although the House of Commons committee on fake news called for the same regulation as on TV to be applied after Facebook data theft and psychologically targeted political ads were used by ‘Vote Leave’ in the 2016 Brexit poll.[338]
Second, censorship and obscenity laws have been a highly traditional limit on freedom of expression. The Theatres Act 1968 prohibits obscenity in plays, that is 'indecent, offensive, disgusting or injurious to morality' but with a defence in the public good, while the Video Recordings Act 1984 section 9 makes it illegal to supply of a video without a classification certificate, which is graded according to sexual or violent activity. Obscene publications, since early common law,[374] have been banned although the idea of what is 'obscene' has changed from Victorian values.[375] The Obscene Publications Act 1959 defines 'obscene' as having the effect to 'deprave and corrupt' people, and allows police or the Director of Public Prosecutions to search and seize obscene material, subject to a defence for literary, artistic, scientific or other merit. Pornography, but also non-sexual gay literature, was suppressed until the 1990s,[376][377] There are around 70 cases each year, but today the Criminal Prosecution Service guidelines only recommend charges for 'extreme' cases. The controversial Digital Economy Act 2017, which would have required age verification on the basis of protecting children to access all pornographic websites, by requiring companies take bank card details, has been repeatedly delayed. Third, there are three main public order offences, based on incitement to disaffection, racial hatred, and terrorism.[lower-alpha 12] Disaffection means attempting to persuade the armed forces,[378] police,[379] or others,[380] to revolt or even withhold services. Racial hatred means 'hatred against a group of persons defined by reference to colour, race, nationality (including citizenship) or ethnic or national origins', and it is an offence to threaten, abuse or insult anyone, including through displays, to stir up racial hatred.[381] The same idea extends to religious hatred, sexual orientation and in practice disability.[382] In international law, it is also explicit, that advocacy of hatred includes 'incitement to discrimination' (as well as hostility or violence).[383] The Terrorism Act 2006 defines incitement to terrorism as 'direct or indirect encouragement or other inducement' for 'commission, preparation or instigation of acts of terrorism', as well as glorifying terrorist acts (that is 'any form of praise or celebration') punishable with 7 years in prison.[384] Fourth, the laws of defamation and breach of confidence are designed to balance people's reputations and rights to privacy. The Defamation Act 2013 states that defamation means a statement that has or would 'cause serious harm to the reputation of the claimant', and if that claimant is a profit-making body this requires 'serious financial loss'.[lower-alpha 13] The truth is always a defence for stating something factual, and a defendant may always show their statement 'is substantially true', or that they made a statement of honest opinion, rather than an assertion of fact. Further, if the statement is in the public interest, it will not be unlawful. Connected to this, news outlets should ask someone who is a subject of a story for their side.[385] Internet operators are liable for statements on their websites that are defamatory if the poster is hard to identify, and they fail on a notice by the claimant to remove the statement within 48 hours.[386] There can be no claim for defamation if a defendant has the 'absolute privilege' of making a statement in Parliament or reports, in the course of high state duty, internal documents or a foreign embassy, or reports of courts' proceedings.[387] There is also 'qualified privilege' which gives a defence to defamation, but only if the writer asks the subject for an explanation or contradiction, for any legislative proceedings outside the UK, public enquiries, non-UK government documents, and matters of an international organisation.[388] Given the global nature of media, a claim in the UK must ensure that the UK is the 'most appropriate place', there is no long trial by jury, and courts can order removal of claims from many websites if it has spread.[389] Claims for breach of confidence are meant to protect the right to privacy. Examples have included an injunction against a retired security service officer who wrote a book called Spycatcher that revealed official secrets.[390] But the government lost its claim to have an injunction against a newspaper on the effects of thalidomide on new births.[391]
Association and assembly
The rights to freedom of association and freedom of assembly are central to the functioning of democracy because they are the basis for political organisation and discourse.[392] Political parties, trade unions, social campaign groups, and businesses all associate freely in democratic societies, and take action upon that freedom, including through assemblies, strikes, or protests. Also protected in international law,[393] the European Convention on Human Rights article 11 states: "Everyone has the right to freedom of peaceful assembly and to freedom of association with others" including joining "trade unions for the protection of" one's interests. Like with other rights, freedom of association cannot be restricted without a lawful justification that is further than necessary in a democratic society, to protect security, safety, health or other people's rights. Freedom of association involves three main principles.[394] First, there is a right to suffer no disadvantage for associating with others, for instance, because if an employer penalises workers for joining a trade union.[395] Second, one must be able to associate with others on the terms one wishes so that, for example, a political party or a trade union must be able to admit or expel members based on their political values and actions.[396] Third, there is a right to act upon the goals of the association, for instance by campaigning for election as a political party, or as a trade union collectively bargaining with an employer for better wages or if necessary going on strike.[397] UK law generally imposes no restriction on people forming groups for political purposes, with the significant exception of organisations banned under the Terrorism Act 2000, such as the neo-Nazi white hate group National Action or Jihadi fundamentalists in Al Qaeda.[398]
.jpg)
Like freedom of association,[399] the right of peaceful assembly was recognised at common law. For instance, in Beatty v Gillbanks the Salvation Army wanted to march against alcohol. The march was halted by the police over concerns that a rival 'skeleton army' of local brewers would violently disrupt them, and result in a breach of the peace. The court held that nobody could 'say that such an assembly [was] in itself an unlawful one' and said there was 'no authority' for saying anyone 'may be convicted for doing a lawful act'.[400] Any procession in the streets or highways is lawful,[401] although there is a duty to inform police 6 days in advance if it is to demonstrate for a cause.[402] This said, in Kay v Metropolitan Police Commissioner the House of Lords held that a regular cycling protest called Critical Mass required no notification because under the Public Order Act 1986 section 11(2) it was "commonly or customarily held" and it did not have a planned route.[403] Although the Highways Act 1980 section 137 makes it an offence to obstruct a highway,[404] in DPP v Jones the House of Lords held that protestors who assembled on roads around Stonehenge despite police ordering them to disperse from a four-mile radius,[405] could not be lawfully arrested or convicted, because their occupation was 'not inconsistent with the primary right of the public to pass and repass.'[406] As well as rights to use public spaces, the law creates positive rights to use public property, such as school halls, for public political meetings.[407] Universities also have a special duty, imposed in 1986, to 'ensure that freedom of speech within the law is secured for members... and for visiting speakers' and people are not denied use of premises based on their views or objectives.[408] This does not mean, however, that student societies cannot protest or that universities cannot prohibit speakers based on likely threats to property or good order.[409] Anomalously it was held in Hubbard v Pitt that an estate agent might be able to sue a group of protestors in the tort of private nuisance for giving out leaflets and displaying placards opposed to it, on the ground that frustrated its business. Lord Denning MR dissented, and would have held the protestors used the highway reasonably, there was no nuisance at common law, and any picket was lawful if to obtain or communicate information for peaceful persuasion.[410] Whenever a picket is made in the "contemplation or furtherance of a trade dispute" it is lawful,[411] so mushroom workers leafleting customers outside a supermarket to boycott their employers' mushrooms acted lawfully even though it caused the employers economic loss.[412]
The right to assembly does not yet extend to private property. In Appleby v UK the Court of Human Rights held there was no interference in ECHR article 11 when the owners of a private shopping mall in Washington, Tyne and Wear excluded protestors collecting signatures to stop the loss of open space from their mall.[413] Although UK law could provide more protection than the minimum European level, it does not, and makes it an offence under the Criminal Law Act 1977 to enter 'any premises' without leave, or threaten violence to secure entry. For 'residential premises' it is also an offence to remain as a trespasser after being required to leave. Further, a law dating from 1875, still makes it an offence to 'wrongfully and without legal authority... watch and beset' premises.[414] In R v Jones, Jones entered a Royal Air Force base intending to damage military equipment during the 2003 invasion of Iraq, which was itself a violation of international law.[415] The House of Lords held that it was no defence even if the invasion was itself unlawful in international law, and there was still a conspiracy to cause criminal damage in violation of the Criminal Law Act 1977 section 1.[416] The Criminal Justice and Public Order Act 1994 also makes it an offence to trespass and reside, disrupt or quat on premises without the owner's consent.[417] Genuine beliefs in the importance of the cause is no defence,[418] and an injunction can be obtained for violations. However, in all of these offences, the human right of freedom of assembly or expression of the protestors must be taken into account.[419] There are also four further significant public order offences. First, it is unlawful to riot, where 12 or more people use or threaten unlawful violence.[420] Second, using threatening, abusive or insulting words or behaviour, including on signs, is an offence if this could make people believe they will suffer immediate unlawful violence,[421] or if it causes or is likely to cause "harassment, alarm or distress."[422] Insults did not include anti-apartheid protests at Wimbledon that spectators resented,[423] and did not include books, such as Salman Rushdie's The Satanic Verses where the immediacy of any result is lacking.[424] Third, harassment is an offence under the Protection from Harassment Act 1997 section 4 if it causes someone to fear on two or more occasions that violence will be used against them.[425] Fourth, while breach of peace is not an offence itself, the apprehension that it is about to happen is grounds for arrest. This has included selling a National Front paper outside a football ground,[426] and a homophobic preacher holding signs in Bournemouth saying ‘Stop Immorality’, ‘Stop Homosexuality’ and ‘Stop Lesbianism’.[427] Generally the police may arrest people who they honestly and reasonably think will risk a breach of the peace,[428] but in R (Laporte) v Gloucestershire Chief Constable the House of Lords held it was unlawful for police to stop a coach of demonstrators from travelling to RAF Fairford and turn it back to London. There was no evidence that a breach of peace was imminent.[429] By contrast, in Austin v United Kingdom the European Court of Human Rights held there was no breach of article 5, the right to liberty, when protestors were kettled in Oxford Circus without food or drink for 7 hours. They were held not to have been falsely imprisoned and the conduct was justified to stop breach of the peace. Arguments were not, however, made under article 11.[430] This said, the police must use their 'operational discretion' at all times with regard to human rights.[431]
Social and economic rights
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 art 22 (social security), art 25 (health, medical care, food, clothing, housing), art 26 (education), art 27 (share in scientific advancement and its benefits)
- International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights arts 9-14
- ECHR Protocol 1, article 2, education
- CFREU art 14 (education), art 34 (social security), art 35 (health care), art 36 (public services)
- (1) health and social care (2) education (3) social security, income, pension (4) housing (5) employment on fair wages and holidays (6) equal treatment, (7) clean environment, (8) fair competition, (9) benefits of science, culture and art (10) development of personality.
- NHS Act 2006
- Education Reform Act 1988, School Standards and Framework Act 1998 and Further and Higher Education Act 1992
- Social Security Contributions and Benefits Act 1992, Pensions Act 2008
- Gorringe v Calderdale Metropolitan Borough Council [2004] UKHL 15, it was "necessary" to view negligence in the context of "the contours of our social welfare state."
- Social Security (Scotland) Act 2018
Security and intelligence
- article 3 (no torture), article 2 (life)
- Counter-Terrorism and Security Act 2015
- Terrorism Prevention and Investigation Measures Act 2011
- Protection of Freedoms Act 2012 s 59
- Prevention of Terrorism Act 2005 s 1
- Anti-terrorism, Crime and Security Act 2001 s 23
- A v Home Secretary [2004] UKHL 56
- A v Home Secretary (No 2) [2005] UKHL 71
- Home Secretary v JJ [2007] UKHL 45
- Home Secretary v AP [2010] UKSC 24
- Gillan v United Kingdom [2009] ECHR 28
Administrative law
.jpg)
Administrative law, through judicial review, is essential to hold executive power and public bodies accountable under the law. In practice, constitutional principles emerge through cases of judicial review, because every public body, whose decisions affect people's lives, is created and bound by law. A person can apply to the High Court to challenge a public body's decision if they have a "sufficient interest",[432] within three months of the grounds of the cause of action becoming known.[433] By contrast, claims against public bodies in tort or contract, where the Limitation Act 1980 usually sets the period as 6 years.[434] Almost any public body, or private bodies exercising public functions,[435] can be the target of judicial review, including a government department, a local council, any Minister, the Prime Minister, or any other body that is created by law. The only public body whose decisions cannot be reviewed is Parliament, when it passes an Act. Otherwise, a claimant can argue that a public body's decision was unlawful in five main types of case:[436]
- it exceeded the lawful power of the body, used its power for an improper purpose, or acted unreasonably,[437]
- it violated a legitimate expectation,[438]
- it failed to exercise relevant and independent judgement,[439]
- it exhibited bias or a conflict of interest, or failed to give a fair hearing,[440] and
- it violated a human right.[441]
As a remedy, a claimant can ask for the public body's decisions to be declared void and quashed (via a quashing order), or it could ask for an order to make the body do something (via a mandatory order), or prevent the body from acting unlawfully (via a prohibiting order). A court may also declare the parties' rights and duties, give an injunction, or compensation could also be payable in tort or contract.[442]
Substantive judicial review
Applications for judicial review are generally divided into claims about the 'substance' of a public body's decision, and claims about the 'procedure' of a decision, although the two overlap, and there is not yet a codified set of grounds as is found in other countries or in other fields of law.[443] First, a claimant may allege that a public body's decision was outside the 'letter and spirit of the law': that an act was ultra vires or did not follow the 'proper purpose' for which the public body's powers were conferred. For example, in R (McCarthy and Stone Ltd) v Richmond Council the House of Lords held that Richmond Council had no statutory power to charge residents a £25 fee to consult its planning officers, because deciding planning permission was a statutory duty, and no charge can be levied by a public body without clear statutory authority.[444] Similarly, in Hazell v Hammersmith and Fulham LBC the House of Lords held that the council acted beyond its powers in the Local Government Act 1972 by entering interest rate swaps transactions, a functional equivalent of borrowing money, which was limited by statute.[445] The courts particularly guard against the executive's attempt to overreach its power. In Ahmed v HM Treasury the Supreme Court held that the United Nations Act 1946 section 1 did not confer on the Prime Minister the right to pass two orders that froze or seized funds of people designed by the UN Security Council as suspected terrorists without any possibility for review. The Act could not have left the definition of what was 'necessary' or 'expedient' to the uncontrolled judgement of the Prime Minister, which affected the rights of citizens without the clear authority of Parliament.[446] A public body may also act unlawfully by misinterpreting its own powers. In Anisminic Ltd v Foreign Compensation Commission the House of Lords held that the Foreign Compensation Commission (a body to compensate British persons who lost property when Gamal Abdel Nasser nationalised the Suez canal during the Suez crisis of 1956) made an error of law by interpreting its powers narrowly. The FCC thought an Order in Council about its powers, which excluded claims by anyone whose 'successor in title' was not a British company, applied to Anisminic Ltd, whose assets were acquired by an Egyptian company after 1956. But the House of Lords held that the Egyptian company was not Anisminic Ltd's 'successor' in title, that the FCC had therefore taken an irrelevant factor into account (its own error of law) in denying a claim, and that the decision had to be a nullity. It was also not possible for an ouster clause in the Act, saying nothing should question the FCC's decisions, to prevent judicial review.[447]

Determining the legality of a public body's action also extends to the purpose and therefore the policy objectives behind the legislation. In Padfield v Minister of Agriculture milk producers successfully argued that the Minister for Agriculture had wrongly exercised his power in the Agricultural Marketing Act 1958 section 19 by not raising subsidies for milk when transport costs changed. The country was divided into eleven milk regions, with different milk prices based on estimates of how much it cost to transport milk. The House of Lords held the Minister was wrong to refuse an investigation into milk price disparities because this frustrated a central policy of the Act: to ensure fair milk subsidies were paid, taking into account costs of production.[448] If public bodies take into account factors outside those necessary for exercising their judgment, a decision will also be quashed. So in R v Home Secretary ex parte Venables and Thompson the House of Lords held that the Home Secretary (Michael Howard) unlawfully took into account the irrelevant consideration of a petition organised by The Sun newspaper to not allow two men release from prison. Instead he should have taken into account the prisoners' progress during detention.[449] In the best known case, Associated Provincial Picture Houses v Wednesbury Corporation, a cinema claimed that the council's requirement that it stop admitting children aged under 15 on Sundays after a local poll was unreasonable. The Court of Appeal (in 1948) held that this was not an unreasonable, irrational or absurd condition and therefore lawful.[450] Lord Greene MR said that the different grounds of judicial review (including an error of law, regarding only relevant considerations, and absurd decisions) all 'run into one another', but that as a general concept a decision would only be unlawful if 'no sensible person could ever dream that it lay within the powers of the authority'.[451] One established ground by which decisions will automatically be unreasonable is if they have a discriminatory impact, violating the principle of equality. In Kruse v Johnson, Lord Russell CJ held that if a public body's actions 'were found to be partial and unequal in their operation as between different classes' it would be unreasonable and ultra vires.[452] However, this test of "Wednesbury unreasonableness" has been repeatedly criticised as having little principled meaning, unless it is coupled with the purpose or policy of the law.[453] The 'proportionality' test has been increasingly favoured, and sometimes said to reach similar outcomes.[454] The proportionality test asks whether a public body's act has a legitimate aim, and then is appropriate, necessary, and reasonably balances individual and social interests, in achieving that aim.[455] This test is routinely used in human rights, discrimination law, and trade law reasoning.
The second major group of cases concern claims that a public body defeated an applicant's 'legitimate expectations'. This is similar to a contract (without the need for consideration) or estoppel, so that if a public body promises or assures somebody something, but does not deliver, they will be able to claim a 'legitimate expectation' was defeated.[456] For example, in R v North and East Devon Health Authority, ex p Coughlan, Miss Coughlan claimed that she should be able to remain in social housing, a care home for people with severe disabilities after the health authority had assured her it was a 'home for life'. Coughlan had become tetraplegic after a severe road accident. The Court of Appeal held that it would be an abuse of power, breaking the assurance was 'equivalent to a breach of contract in private law', and it 'was unfair because it frustrated her legitimate expectation of having a home for life'.[457] By contrast, in Council of Civil Service Unions v Minister for the Civil Service the House of Lords held that the trade union at GCHQ had been given the assurance through the 'existence of a regular practice' that the employer would negotiate over a fair pay scale. However, Margaret Thatcher's decision to stop negotiation through an Order in Council on pay was justified (ostensibly) on grounds of 'national security'. On this point, and while the prerogative was also subject to judicial review, security was 'par excellence a non-justiciable question', their Lordships saying they were 'totally inept to deal with the sort of problems which it involves.'[458] This has been criticised on the basis that the courts should have required reasons as to why workers bargaining for fair pay threatened national security. A third group of cases concern a failure of a public body to exercise independent judgement,[459] for instance by fettering their discretion. In British Oxygen Co Ltd v Minister of Technology the Minister had a rule in handing out capital grants to firms that it would not fund claims under £25. An oxygen cylinder company claimed it should receive the grants it has spent £4m on gas cylinders: they unfortunately just cost £20 each. The House of Lords held that while a government department was entitled to make a rule or policy in exercising its discretion, it must be 'always willing to listen to anyone with something new to say' and to make an exception,[460] a principle akin to equity (mitigating strict legal rules) in administrative law.
Procedural review
As well as reviewing the substance of a decision, judicial review has developed to ensure that public bodies follow lawful and just procedures in making all decisions. First, like the substance of a decision may go beyond the powers of a public body, a procedure actually followed by a public official may not follow what was required by law. In Ridge v Baldwin a chief constable was summarily dismissed by a Brighton police committee, even though the disciplinary regulations made under the Police Act 1919 required an inquiry into charges against someone before they were dismissed. The House of Lords held the regulations applied, and should have been followed, so the dismissal was ultra vires. But in addition, basic principles of natural justice required the constable should have had a hearing before being dismissed. According to Lord Hodson, the ‘irreducible minimum’ of natural justice is (1) the right to decision by an unbiased tribunal, (2) notice of any charges, and (3) a right to be heard.[461] The same principles with regard to dismissal have been applied to a wide range of public servants, while the law of unfair dismissal and the common law quickly developed to protect the same right to job security.[462]

If statutes are silent, the courts readily apply principles of natural justice, to ensure there is no bias and a fair hearing. These common law principles are reinforced by the European Convention on Human Rights article 6, which in determining anyone’s ‘civil rights and obligations’,[463] or ‘any criminal charge’, requires ‘a fair and public hearing within a reasonable time by an independent and impartial tribunal established by law.’ The rule against bias includes, for example, not allowing a judge to sit on any case in which he is financially interested, such as being a shareholder in a company that is a litigant.[464] This rule, which reflects a principle of equity that there must be no possibility of a conflict of interest,[465] was applied in R v Bow Street Stipendiary Magistrate, ex p Pinochet (No 2) after the ex-dictator General Pinochet had been ordered by the House of Lords to be extradited to Chile to stand criminal trial. The charity, Amnesty International had argued in the appeal to support extradition, and Lord Hoffmann had not disclosed that he was a director of the charity. The House of Lords, after a complaint, held that its decision could not stand and had to be heard again. According to Lord Nolan, even if there was no actual bias or conflict, ‘in any case where the impartiality of a judge is in question the appearance of the matter is just as important as the reality.’[466] Justice ‘should not only be done but should manifestly and undoubtedly be seen to be done’.[467] Where conflicts of interest taint any public body’s decision, they may be quashed. In Porter v Magill the Conservative majority in Westminster City Council had a policy of selling off council houses in parts of the city where they believed new owners would be more likely to vote conservative. For this reason, the House of Lords held that the councillors had exercised their powers for improper purposes, and were motivated by bias.[468]
The requirements of a fair hearing are that each side knows the case against them,[469] can present their version of the facts, makes submissions on the rules of law, comments on material considered by the judge, and does not communicate with the judge without the other having the same opportunity. For instance, in Cooper v Wandsworth Board of Works, Mr Cooper failed to notify his intention to build a house. The Board of Works decided to demolish the house without giving him any hearing. Byles J held that although ‘there are no positive words in a statute requiring that the party shall be heard, yet the justice of the common law shall supply the omission of the legislature.’[470] The right to know any case against you was illustrated in R v Secretary of State for the Home Department, ex p Doody, where prisoners who received life sentences were told a minimum period they had to stay in prison before any review, but not the judiciary’s recommendations. The House of Lords held that they had to be able to know the recommended period, and to be able to make representations, before any time was fixed.[471] Often, although there is no hard right to them, a failure to give reasons for a decision will be regarded as unfair,[472] because giving reasons ‘is one of the fundamentals of good administration’.[473] In all cases where human rights are at stake, the standards are higher.[474]
Human rights review
Like the common law grounds (that public bodies must act within lawful power, uphold legitimate expectations, and natural justice), human rights violations are a major ground for judicial review. Since World War Two, the Holocaust, and the end of the British Empire, ensuring compatibility between international human rights and UK law has generally been considered a binding duty of the courts,[475] but it was only since the Human Rights Act 1998 that the courts have had structured, statutory guidance for how to do this. The Supreme Court has, at least since 2014, adopted a practice of giving indirect effect to international law, to which the UK has acceded through binding treaties.[476] The post-war 'international Magna Carta', the Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 was expanded into two human rights Conventions, ratified by the UK, in 1966: the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights. Within Europe, the UK was a founding signatory to the European Convention on Human Rights 1950 and the European Social Charter 1961. These documents were not also written into UK statute, because it was generally thought that the ordinary mechanisms of judicial review were sufficient. However, to establish a violation of the Convention, claimants had to exhaust the judicial process within the UK before making another application to the Strasbourg court system, and there was no guarantee that UK courts would explicitly engage with human rights reasoning in their decisions. The Human Rights Act 1998 was eventually passed to 'bring rights home' in order to make the judicial process quicker, and to ensure greater influence by the UK judiciary in formulating what human rights meant.
Under the Human Rights Act 1998 section 3, courts have a duty to interpret legislation so 'far as it is possible to do so' to be compatible with the European Convention on Human Rights.[477] This is a strong duty, and courts must, if a compatible interpretation is possible, use it because the Act presumes Parliament cannot have intended to violate international human rights law. For instance, in Ghaidan v Godin-Mendoza an applicant argued that he should have the right to succeed in title to a flat of his recently deceased homosexual, because the Rent Act 1977 said there was a right of succession if two people lived together 'as his or her wife or husband'.[478] The landlord argued this did not apply, because Godin-Mendoza was gay. This was clearly discriminatory in violation of ECHR article 14, and also an interference in the right to private life and one's home under ECHR article 8. The House of Lords held they could interpret the Act compatibly with the right to equal treatment and one's home, by reading the Rent Act 1977 like it said that they lived together 'as if they were his wife or husband'.[479] If a compatible interpretation is impossible, a court must under section 4 issue a 'declaration of incompatibility', a (rare) notice to Parliament that the law does not match the Convention and should be changed. Parliament has always, since it was written in 1950, ultimately upheld the Convention. Under section 10(2) a Minister may if 'there are compelling reasons' amend legislation to remove the inconsistency, although Parliament often passes a new Act.[480] For instance, in Bellinger v Bellinger a transsexual woman, Elizabeth, married a man called Michael and sought a declaration that this was a lawful marriage under the Matrimonial Causes Act 1973 section 11, which described marriage as being between a 'male' and a 'female'. The judge refused because Elizabeth was classified as male at her birth, and the House of Lords held that, despite being 'profoundly conscious of the humanitarian considerations underlying Mrs Bellinger's claim', they could not interpret the statute compatibly (to give the word 'woman' a non-biological meaning), and so they instead issued a declaration of incompatibility.[481] Parliament soon amended the law in the Gender Recognition Act 2004. Section 6 requires all public bodies to act compatibly with the Convention, and this includes courts in developing common law and equity. Section 8 enables the courts to give any 'relief or remedy' that is 'just and appropriate'.[482] Despite indirect effect, there is not yet direct effect codified in statute for important economic and social rights, such as the right to work, fair pay, increased leisure time, and social security.[483]
A central difference between judicial review based on human rights, and judicial review based on common law ground that a decision is "Wednesbury unreasonable" and ultra vires, is that infringements of rights can only be defended if the infringement is 'proportionate'. If the infringement is disproportionate, the right is violated. The proportionality test requires the court to ask, first, if the public body had a legitimate aim. For most rights, the legitimate aims are set out in sub-article 2, such as infringements for the purpose of national security, health, morals, or the rights of others. Second, the court asks whether the public body's conduct was 'appropriate' or 'suitable' to achieve the aim. Third, it asks if the public body's conduct was 'necessary', and particularly whether it could have taken an alternative course of action that would not have interfered with the applicant's human rights. For instance, in R (Daly) v Secretary of State for the Home Department the House of Lords held that searches of a prisoner's cells which contained legally privileged correspondence with the prisoner's solicitor went further than necessary to achieve the aim of maintaining security and preventing crime, because it was a blanket policy that could be tailored to individual prisoners' circumstances, depending on whether they had been disruptive, a result the same as the common law.[484] Fourth, the court asks whether the action was 'reasonable' in striking a balance between the interests of the individual and society.[485] If anything is lacking, if there is no legitimate aim, or the public body's actions are not appropriate, necessary, and reasonable, its actions will be disproportionate and violate the applicant's right.
Standing and remedies
Judicial review applications are more limited than other forms of legal claims, particularly those in contract, tort, unjust enrichment or criminal law, although these may be available against public bodies as well. Judicial review applications must be brought promptly, by people with a 'sufficient interest' and only against persons exercising public functions. First, unlike the typical limitation period of six years in contract or tort,[486] the Civil Procedure Rules, rule 54.5 requires that judicial review applications must be made within 'three months after the grounds to make the claim first arose'.[487] Often, however, the same set of facts could be seen as giving rise to concurrent claims for judicial review. In O'Reilly v Mackman prisoners claimed that a prison breached rules of natural justice in deciding they lost the right to remission after a riot. The House of Lords held that, because they had no remedy in 'private law' by itself, and there was merely a 'legitimate expectation' that the prison's statutory obligations would be fulfilled, only a claim for judicial review could be brought, and the three month time limit had expired. It was an abuse of process to attempt a claim in tort for breach of statutory duty.[488]
Second, according to the Senior Courts Act 1981 section 31 an applicant must have a 'sufficient interest' to bring a case.[489] In R (National Federation of Self-Employed and Small Businesses Ltd) v Inland Revenue Commissioners a taxpayer group (the NFSE) claimed that the Revenue should collect tax from 6000 casual Fleet Street newspaper workers, after they had decided to end a practice of tax evasion over many years by collecting for a previous two years and not investigate earlier infringements. The House of Lords held the NFSE did not have a sufficient interest in the issue because this would interfere with the Revenue's general management powers.[490] It was also held that a theatre preservation group had no standing to review a minister's decision refusing to designate a site as an historic monument.[491] On the other hand, it has been consistently recognised that public interest groups have standing to challenge decisions of public bodies, such as a respected and expert environmental group over pollution concerns,[492] a development campaign group over excessive spending in an international dam project,[493] and the government equality watchdog, the Equal Opportunities Commission, for whether UK legislation complied with EU law on redundancy protection.[494] Occasionally, the government has attempted to exclude judicial review through putting an ouster clause in an Act, providing that a public body's decisions should not be 'called into question'. However, in R (Privacy International) v Investigatory Powers Tribunal the Supreme Court suggested that ouster clauses cannot restrict the right to judicial review without the most express words, because of a strong common law presumption that Parliament intends for public bodies to act lawfully and within their jurisdiction.[495]
A third issue is which bodies are subject to judicial review. This clearly includes any government department, minister, council, or entity set up under a statute to fulfil public functions. However, the division between 'public' and 'private' bodies has become increasingly blurred as more regulatory and public actions have been outsourced to private entities. In R (Datafin plc) v Panel on Take-overs and Mergers the Court of Appeal held that the Takeover Panel, a private association organised by companies and financial institutions in the City of London to enforce standards in takeover bids, was subject to judicial review because it exercised 'immense power de facto by devising, promulgating, amending and interpreting the City Code' with 'sanctions are no less effective because they are applied indirectly and lack a legally enforceable base'.[496] By contrast, the Jockey Club was not thought to exercise sufficient power to be subject to judicial review.[497] Nor was the Aston Cantlow Parochial Church Council, because although a public authority, it was not a 'core' public authority with any significant regulatory function.[498] In a controversial decision, YL v Birmingham CC held that a large private corporation called Southern Cross was not a public authority subject to judicial review, even though it was contracted by the council to run most nursing homes in Birmingham.[499] This decision was immediately reversed by statute,[500] and in R (Weaver) v London and Quadrant Housing Trust the Court of Appeal held that a housing trust, supported by government subsidies, could be subject to judicial review for unjust termination of a tenancy.[501]
Finally, the Supreme Court Act 1981 section 31 sets out the main remedies available through judicial review: a mandatory order (previously called mandamus) to make a public body do something, a prohibiting order (prohibition) to stop a public body doing something, a quashing order (certiorari) to cancel an act, an injunction, or a declaration. The old writ of habeas corpus also remains available, to require that a person be delivered to court and freed.[502] Further, in contract, tort or unjust enrichment claims against public bodies, the courts may order standard remedies of compensation for loss, restitution of gains, or an award of specific performance. In Chief Constable of the North Wales Police v Evans, however, the House of Lords held that although a police officer was unlawfully dismissed in violation of statute, compensatory damages were a more appropriate remedy than a mandatory order for reinstatement given the rarity (at the time) of specific performance in employment contracts.[503] Occasionally the law makes provision for special privileges or immunities of public bodies from the ordinary law, but these are generally construed restrictively.[504]
See also
- English contract law
- English trusts law
- English land law
- English tort law
- English criminal law
- European Union law
- UK enterprise law
- UK labour law
- UK company law
Explanatory notes
- Compounded by a ruling in Peacham's Case (1614) that held it would not be treason to advocate the King's death.
- For instance, preceding art. 8 of that convention, see Entick v Carrington [1765] EWHC KB J98. On Article 11, see Crofter Hand Woven Harris Tweed Co Ltd v Veitch [1941] UKHL 2, but note the severe limitations of judicial clarity, apparent in Malone v UK [1984] ECHR 10 and Wilson v United Kingdom [2002] ECHR 552.
- In international law, the duty to stop war propaganda and incitement of discrimination is made explicit.[365]
- The oldest free speech and debating society in the world is Cogers (est 1755), while The Cambridge Union was established in 1815, and the Oxford Union in 1823. Most universities have student debating societies.
- Generally the same laws apply to these places of free speech as in the whole country: see Redmond-Bate v DPP [2000] HRLR 249 (Speakers' Corner), Bailey v Williamson (1873) 8 QBD 118 (Hyde Park), and DPP v Haw [2007] EWHC 1931 (Admin).
- In 2019, these were
- Youtube and Google, owned by Alphabet, which is controlled by Larry Page and Sergey Brin
- Facebook, controlled by Mark Zuckerberg, and
- Twitter, controlled by Jack Dorsey.
- In 2019, these were
- the BBC, owned by an arms-length public corporation ultimately accountable to the UK government
- Channel 4, a public corporation set up under the Department for Culture, Media and Sport,
- ITV, owned by asset managers such as Capital Group Companies, Ameriprise Financial and BlackRock
- Channel 5, owned by Viacom Inc, where 80% of votes on shares are controlled by Sumner Redstone, and
- Sky, owned by Comcast which is controlled by Brian L. Roberts.
- In 2019, the largest by website and circulation were
- the Daily Mail, Metro and Evening Standard, largely owned by Jonathan Harmsworth, 4th Viscount Rothermere through Daily Mail and General Trust plc,
- The Times, and The Sun, controlled by Rupert Murdoch through Newscorp,
- the Daily Mirror, Daily Express and Daily Star, controlled by Reach plc
- the Guardian and the Observer, owned by Scott Trust Limited which has a board must guard editorial independence, but which appoints itself,[367]
- the Daily Telegraph, controlled by the Barclay Brothers, and
- The Independent and The i, controlled by Alexander Lebedev (who also has a majority stake with Lord Rothermere in the Evening Standard.
- There is no formal legal duty to maximise shareholder returns under the Companies Act 2006 s 172, but in practice where shareholders monopolise votes to dismiss the board under CA 2006 s 168, this becomes the duty in practice, and the culture.[369]
- This is detailed by the Ofcom Broadcasting Code (2017)
- For example, R (Pro-Life Alliance) v BBC [2003] UKHL 23 finding that a ban on an anti-abortion group showing 'prolonged and deeply disturbing' images of an aborted foetus for a TV campaign advert did not violate ECHR article 10. cf R v Central Independent Television plc [1994] Fam 192
- Old offences of seditious libel and blasphemous libel were removed by the Criminal Justice and Coroners Act 2009 s 73. See previously R v Burns (1886) 16 Cox CC 355, R v Aldred (1909) 22 Cos CC 1, R v Lemon [1979] AC 617, and Gay News Ltd v UK (1982) 5 EHRR 123 (linking Jesus Christ to homosexuality).
- Trade unions, central and local government appear unable to bring defamation claims: EETPU v Times Newspapers [1980] 1 All ER 1097 (trade unions), Derbyshire CC v Times Newspapers Ltd [1993] AC 534 (local government).
Notes
- Magna Carta 1215 clauses 1 ('... the English church shall be free...'), 12 and 14 (no tax 'unless by common counsel of our kingdom...'), 17 ('Common pleas shall... be held in some fixed place'), 39-40 ('To no one will we sell, to no one will we refuse or delay, right or justice'), 41 ('merchants shall have safe and secure exit from England, and entry to England') and 47-48 (land taken by the King 'shall forthwith be disafforested').
- The ILO was formed as part of the (now defunct) League of Nations in the Versailles Treaty 1919 Part XIII. The UN was formed in 1945. The Commonwealth of Nations was formally established by the London Declaration of 1949. The Council of Europe was created in 1950. The European Union was formed by the Maastricht Treaty 1992, succeeding the European Community which the UK joined by the European Communities Act 1972. The WTO was created in 1994.
- See AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) ch 2, 32–48, on historic structure, and devolution.
- See F Pollock and FW Maitland, The history of English law before the time of Edward I (1899) Book I, ch I, 1, ‘Such is the unity of all history that anyone who endeavours to tell a piece of it must feel that his first sentence tears a seamless web.’
- Pollock and Maitland (1899) 4–5
- cf E Gibbon, The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire (1789) arguing Christianity led to weakness that caused Rome’s fall.
- Pollock and Maitland (1899) 5-6
- FW Maitland, The constitutional history of England (1909) 6
- J Froissart, Froissart's Chronicles (1385) translated by GC Macaulay (1895) 251–252.
- DD McGarry, Medieval History and Civilization (1976) 242, 12% free, 30% serfs, 35% bordars and cottars, 9% slaves.
- T Purser, Medieval England, 1042–1228 (2004) 161, this included a 25% tax on income and property, all the year's wool, and all churches gold and silver, to pay a ransom after Richard I was captured when returning from the crusades by Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor.
- Magna Carta 1215 clauses 12 (Parliament), 17 (court), 39 (fair trial), 41 (free movement), 47 (common land).
- See W Langland, Piers Plowman (1370) Passus 5, 3278, "But I kan rymes of Robyn Hood" is the first mention of the tales, notably in the run up to the Peasants' revolt of 1381. As ballads and poems evolved, see John Stow, Annales of England (1592)
- Charter of the Forest 1217. This allowed, for example, in clause 9, ‘Every freeman shall at his own pleasure provide agistment' or grazing rights, and in clause 12, ‘Henceforth every freeman, in his wood or on his land that he has in the forest, may with impunity make a mill, fish-preserve, pond, marl-pit, ditch, or arable in cultivated land outside coverts, provided that no injury is thereby given to any neighbour.’
- Pollock and Maitland (1899) Book I, 173
- J Froissart, The Chronicles of Froissart (1385) translated by GC Macaulay (1895) 250–52, "What have we deserved, or why should we be kept thus in servage? We be all come from one father and one mother, Adam and Eve: whereby can they say or shew that they be greater lords than we be, saving by that they cause us to win and labour for that they dispend? They are clothed in velvet and camlet furred with grise, and we be vestured with poor cloth: they have their wines, spices and good bread, and we have the drawing out of the chaff and drink water: they dwell in fair houses, and we have the pain and travail, rain and wind in the fields; and by that that cometh of our labours they keep and maintain their estates: we be called their bondmen, and without we do readily them service, we be beaten; and we have no sovereign to whom we may complain, nor that will hear us nor do us right."
- EP Cheyney, ‘The Disappearance of English Serfdom’ (1900) 15(57) English Historical Review 20 and A Fitzherbert, Surueyenge (1546) 31, servitude was ‘the greatest inconvenience that nowe is suffred by the lawe. That is to have any christen man bounden to an other, and to have the rule of his body, landes, and goodes, that his wyfe, children, and servantes have laboured for, all their life tyme, to be so taken, lyke as it were extorcion or bribery’.
- See Inclosure Acts and Vagrancy Act 1547. cf T More, Utopia (1516) Book I, "wherever it is found that the sheep of any soil yield a softer and richer wool than ordinary, there the nobility and gentry, and even those holy men, the abbots not contented with the old rents which their farms yielded... stop the course of agriculture, destroying houses and towns, reserving only the churches, and enclose grounds that they may lodge their sheep in them... Stop the rich from cornering markets and establishing virtual monopolies. Reduce the number of people who are kept doing nothing. Revive agriculture and the wool industry, so that there is plenty of honest, useful work for the great army of unemployed – by which I mean not only existing thieves, but tramps and idle servants who are bound to become thieves eventually."
- On his behalf Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset ruled as Lord Protector until he was replaced and executed by John Dudley, 1st Duke of Northumberland. Somerset House was transferred to the crown, and Elizabeth was allowed to live there by Mary, Queen of Scots as she killed Lady Jane Grey (1554) and ruled until 1558. Mary then died without children, after killing hundreds of protestants.
- James, The True Law of Free Monarchies (1598)
- Coke had already reported on many significant constitutional judgments, often adding his own style, including Heydon's Case (1584) 76 ER 637, that the task of a court in construing any statute is to find its mischief and the intention of Parliament, and Semayne's Case (1604) 5 Coke Rep 91, that nobody can enter another's property without lawful authority and that "the house of every one is to him as his castle and fortress, as well for his defence against injury and violence as for his repose." See also Calvin's Case Calvin's Case (1572) , 77 ER 377 that a person born in Scotland is entitled to all rights in England.
- Case of Prohibitions [1607] EWHC J23 (KB)
- Case of Proclamations [1610] EWHC KB J22
- (1610) 77 Eng Rep 638
- e.g. Day v Savadge (1614) Hob 85, 80 ER 235, Hobart CJ, ‘even an Act of Parliament, made against natural equity, as to make a man judge in his own case, is void in itself, for jura nutrae sunt immutabilia, and they are leges legu.’ R v Love (1653) 5 State Tr 825, 828, Keble J, ‘Whatsoever is not consonant to the law of God, or to right reason which is maintained by scripture... be it Acts of Parliament, customs, or any judicial acts of the Court, it is not the law of England.’ City of London v Wood (1701) 12 Mod 669 per Holt CJ. cf W Blackstone, Commentaries on the Laws of England (1765) "if the parliament will positively enact a thing to be done which is unreasonable, I know of no power that can control it..." In the US, Coke CJ's argument was applied in Marbury v Madison 5 US (1 Cranch) 137 (1803).
- (1615) 21 ER 485
- Five Knights' case (1627) 3 How St Tr 1
- Petition of Right 1628 (3 Car 1 c 1)
- Debates on the proper nature of liberty were held at the Putney debates, October to November 1647, summarised in ASP Woodhouse, Puritanism and Liberty (1938) 52. By contrast, a bitter opponent of the civil war was T Hobbes, Leviathan (1651)
- Richard Cromwell, Oliver's son, briefly succeeded but lacking support swiftly renounced power after nine months.
- The conflict ended at Battle of the Boyne.
- Bill of Rights 1689 and Claim of Right 1689 arts 2, 8 and 13
- John Locke, Second Treatise on Government (1689) Chapter IX
- (1703) 92 ER 126, per Holt CJ confirmed by the House of Lords.
- Union with Scotland Act 1706 arts 18 and 19, stipulate that Scottish private law would continue under a Scottish court system.
- A Smith, The Wealth of Nations (1776) Book V, ch 1, §107
- Keech v Sandford [1726] EWHC J76, an English trust law case following Lord Macclesfield LC, disgraced by his role on the South Sea Company, impeached by the House of Lords and found guilty of taking bribes in 1725. Keech reversed Bromfield v Wytherley (1718) Prec Ch 505 that a fiduciary could take money from a trust and keep profits if they restored the principal afterwards.
- Attorney General v Davy (1741) 26 ER 531 established that any body of assembled people can do a corporate act by a majority.
- Walpole's tenure lasted from 1721-1742.
- Entick v Carrington [1765] EWHC KB J98
- (1772) 98 ER 499 Charles Stewart from Boston, Massachusetts had bought James Somerset as a slave and taken him to England. With the help of abolitionists, Somerset escaped and sued for a writ of habeas corpus (that "holding his body" had been unlawful). Lord Mansfield, after declaring he should "let justice be done whatever be the consequence", held that slavery was "so odious" that nobody could take "a slave by force to be sold" for any "reason whatever".
- AW Blumrosen, 'The Profound Influence in America of Lord Mansfield's Decision in Somerset v Stuart' (2007) 13 Texas Wesleyan Law Review 645
- Using the Transportation Act 1717 and then the Transportation Act 1790.
- See the Combination Acts, etc.
- J Bentham, Anarchical Fallacies; Being an examination of the Declaration of Rights issued during the French Revolution (1796)
- M Wollstonecraft, A Vindication of the Rights of Woman (1792) Chapter IX
- Union with Ireland Act 1800 arts 3–4 gave Irish representation at Westminster.
- T Malthus, An Essay on the Principle of Population (1798) supported this, arguing that working class "vice" and overpopulation was the cause of poverty.
- (1834) 172 ER 1380
- Letter to Lord Russell (October 1862) 'Power in the Hands of the Masses throws the Scum of the Community to the Surface. ... Truth and Justice are soon banished from the Land.'
- See also the Conspiracy and Protection of Property Act 1875 and Allen v Flood [1898] AC 1
- See S Tharoor, Inglorious Empire (2018)
- Taff Vale Railway Co v Amalgamated Society of Railway Servants [1901] UKHL 1
- Trade Disputes Act 1906
- Old Age Pensions Act 1908
- Trade Boards Act 1909
- National Insurance Act 1911
- Parliament Act 1949 reduced the power to delay to one year.
- Predicted by JM Keynes, The Economic Consequences of the Peace (1919)
- e.g. 'Speech to the 69th Annual Conservative Party Conference at Llandudno' (9 October 1948). See J Danzig 'Winston Churchill: A founder of the European Union' (10 November 2013) EU ROPE
- JC Coffee, ‘What Went Wrong? An Initial Inquiry into the Causes of the 2008 Financial Crisis’ (2009) 9(1) Journal of Corporate Law Studies 1. For problems starting in US regulation, see E Warren, ‘Product Safety Regulation as a Model for Financial Services Regulation’ (2008) 43(2) Journal of Consumer Affairs 452, and contrast the Consumer Credit Act 1974 or the Unfair Terms in Consumer Contracts Directive 93/13/EEC arts 3–6.
- "The Future Relationship between the UK and the EU". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
- See AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) chs 1-6
- AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) chs 1-6
- R (HS2 Action Alliance Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport [2014] UKSC 3, [207] per Lord Neuberger and Lord Mance, "The United Kingdom has no written constitution, but we have a number of constitutional instruments. They include Magna Carta, the Petition of Right 1628, the Bill of Rights and (in Scotland) the Claim of Rights Act 1689, the Act of Settlement 1701 and the Act of Union 1707. The European Communities Act 1972, the Human Rights Act 1998 and the Constitutional Reform Act 2005 may now be added to this list."
- On conventions, see Attorney General v Jonathan Cape Ltd [1975] 3 All ER 484
- See T Bingham, The Rule of Law (2011) and Entick v Carrington [1765] EWHC KB J98
- Great Reform Act 1832 (common property qualification rules for all boroughs and counties), Representation of the People Act 1867 (extended the franchise to around 1/3 of men), Representation of the People Act 1884 (extended the male franchise), Representation of the People Act 1918 (enabled all men to vote over 21, and women over 30 with property), and Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928 (enabled equal suffrage of men at women age 21). The Representation of the People Act 1948 further abolished multiple votes for graduates of London, Cambridge and Oxford, and other University constituencies, and the Representation of the People Act 1969 lowered the voting age to 18. Restrictions on prisoner voting were inserted by the Representation of the People Act 1983. British citizens abroad can vote under the Representation of the People Act 1985, but millions of UK residents, who pay taxes but do not have citizenship, cannot vote.
- See the Appropriation Act 1923 Sch 4
- See generally, AW Bradley, ‘The Sovereignty of Parliament – Form or Substance?’ in J Jowell, The Changing Constitution (7th edn 2011) ch 2
- cf AW Bradley and KD Ewing, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2015) 65, it ‘is not possible to predict the outcome of changes made by Parliament to the ‘manner and form’ of the legislative process since, depending on the nature and reasons for such changes, the courts might still be influenced by a deep-seated belief in the proposition that Parliament cannot bind itself.’
- Magna Carta 1215 cl 12, ‘No scutage [tax on knight's land or fee] nor aid shall be imposed on our kingdom, unless by common counsel of our kingdom...’
- Earl of Oxford’s case (1615) 21 ER 485, Lord Ellesmere LC, ‘... when a Judgment is obtained by Oppression, Wrong and a hard Conscience, the Chancellor will frustrate and set it aside, not for any error or Defect in the Judgment, but for the hard Conscience of the Party.’
- Dr Bonham’s case (1610) 8 Co Rep 114a
- Parliament Act 1949 s 1.
- Parliament Act 1911 s 1.
- [2005] UKHL 56, [120] 'Parliamentary sovereignty is an empty principle if legislation is passed which is so absurd or so unacceptable that the populace at large refuses to recognise it as law'.
- See also a photo of the first General Assembly.
- cf Leslie Stephen, The Science of Ethics (1882) 145, "Lawyers are apt to speak as though the legislature were omnipotent, as they do not require to go beyond its decisions. It is, of course, omnipotent in the sense that it can make whatever laws it pleases, inasmuch as a law means any rule which has been made by the legislature. But from the scientific point of view, the power of the legislature is of course strictly limited. It is limited, so to speak, both from within and from without; from within, because the legislature is the product of a certain social condition, and determined by whatever determines the society; and from without, because the power of imposing laws is dependent upon the instinct of subordination, which is itself limited. If a legislature decided that all blue-eyed babies should be murdered, the preservation of blue-eyed babies would be illegal; but legislators must go mad before they could pass such a law, and subjects be idiotic before they could submit to it."
- AV Dicey, The Law of the Constitution (1885) 39-40, Parliament has ‘under the English constitution, the right to make or unmake any law whatever; and further... no person or body is recognised by the law of England as having a right to override or set aside the legislation of Parliament.’
- Treaty of Versailles 1919 Part XIII, statute of the International Labour Organization
- See the International Organisations Act 1968 ss 1-8
- United Nations Act 1946 s 1
- See, for example, the Legality of the Iraq War page.
- Treaty on European Union Article 2
- Van Gend en Loos v Nederlandse Administratie der Belastingen (1963) Case 26/62, [94] member states "have limited their sovereign rights, albeit within limited fields, and have thus created a body of law which binds both their nationals and themselves" on the "basis of reciprocity".
- [1990] UKHL 7
- [1990] UKHL 7
- [2014] UKSC 3
- See further, P Craig and G de Búrca, EU Law: Text, Cases, and Materials (6th edn 2015) chs 9-10. See also, by analogy in German constitutional law, Solange II or Re Wünsche Handelsgesellschaft (22 October 1986) BVerfGE, [1987] 3 CMLR 225
- [2017] UKSC 5
- See Opinion polling for the United Kingdom European Union membership referendum#Post–referendum polling
- [2017] UKSC 5, [146] "Judges, therefore, are neither the parents nor the guardians of political conventions; they are merely observers. As such, they can recognise the operation of a political convention in the context of deciding a legal question (as in the Crossman diaries case - Attorney General v Jonathan Cape Ltd [1976] 1 QB 752), but they cannot give legal rulings on its operation or scope, because those matters are determined within the political world. As Professor Colin Munro has stated, “the validity of conventions cannot be the subject of proceedings in a court of law” - (1975) 91 LQR 218, 228."
- cf MacCormick v Lord Advocate 1953 SC 396, Lord Cooper, "The principle of the unlimited sovereignty of Parliament is a distinctively English principle which has no counterpart in Scottish constitutional law." However this view was disapproved in R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the EU [2017] UKSC 5, [43] "Parliamentary sovereignty is a fundamental principle of the UK constitution" and at [50] "it is a fundamental principle of the UK constitution that, unless primary legislation permits it, the Royal prerogative does not enable ministers to change statute law or common law... This is, of course, just as true in relation to Scottish, Welsh or Northern Irish law."
- cf Aristotle, Politics (330 BCE) 3.16, ‘It is more proper that law should govern than any one of the citizens’.
- X v Morgan-Grampian Ltd [1991] AC 1, 48, per Lord Bridge, ‘The maintenance of the rule of law is in every way as important in a free society as the democratic franchise. In our society the rule of law rests upon twin foundations: the sovereignty of the Queen in Parliament in making the law and the sovereignty of the Queen's courts in interpreting and applying the law.’
- R (Jackson) v Attorney General [2005] UKHL 56, [104] per Lord Hope
- T Bingham, ‘The Rule of Law’ (2007) 66(1) Cambridge Law Journal 67 and see also T Bingham, Rule of Law (2008) 8, ‘all persons and authorities within the state, whether public or private should be bound by and entitled to the benefit of laws publicly made, taking effect (generally) in the future and publicly administered in the courts.’ Lord Bingham, ‘The Rule of Law and the Sovereignty of Parliament’ (31 October 2007) King's College, London also remarked, ‘democracy lies at the heart of the concept of the rule of law’.
- AV Dicey, Introduction to the Study of the Law of the Constitution (3rd edn 1889) Part II, ch IV, 189, first "absolute supremacy or predominance of regular law as opposed to the influence of arbitrary power", second "equality before the law, or the equal subjection of all classes to the ordinary law of the land administered by the ordinary law courts" and third, "principles of private law have with us been by the action of the courts and Parliament so extended as to determine the position of the Crown and of its servants". See also J Raz, ‘The Rule of Law and its Virtue’ (1977) 93 Law Quarterly Review 195. Contrast D Lino, ‘The Rule of Law and the Rule of Empire: A.V. Dicey in Imperial Context’ (2018) 81(5) Modern Law Review 739. Previously, discourse among international finance followed a restrictive ideal: M Stephenson, ‘Rule of Law as a Goal of Development Policy’ (2008) World Bank Research
- Constitutional Reform Act 2005 ss 1, 63-65 and Schs 8 and 12
- Entick v Carrington [1765] EWHC KB J98
- Malone v United Kingdom (1984) 7 EHRR 14
- T Bingham, Rule of Law (2008) 8, ‘all persons and authorities within the state, whether public or private should be bound by and entitled to the benefit of laws publicly made, taking effect (generally) in the future and publicly administered in the courts.’
- [1765] EWHC KB J98
- European Convention on Human Rights Article 8 (1) Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home and his correspondence. (2) There shall be no interference by a public authority with the exercise of this right except such as is in accordance with the law and is necessary in a democratic society in the interests of national security, public safety or the economic well-being of the country, for the prevention of disorder or crime, for the protection of health or morals, or for the protection of the rights and freedoms of others."
- [1979] Ch 344
- [1984] ECHR 10, (1984) 7 EHRR 14
- Originally the Interception of Communications Act 1985, and now the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 ss 1-11, as amended by the Data Retention and Investigatory Powers Act 2014.
- [2008] UKHL 60, [2]-[7]
- R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office [2008] UKHL 60, [55]
- See A v Home Secretary [2004] UKHL 56, Lord Nicholls, ‘indefinite imprisonment without charge or trial is anathema in any country which observes the rule of law’.
- [2017] UKSC 51, [66]-[68]
- e.g. M v Home Office [1993] UKHL 5, holding the Home Secretary, Kenneth Baker, in contempt of court for failing to return a Zaire teacher to the UK on refugee status, despite a High Court judge ordering it be done.
- Montesquieu, The Spirit of the Laws (1748) Book XI, ch 6, ‘When legislative power is united with executive power in a single person or in a single body of the magistracy, there is no liberty.’
- AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2014) 94. cf W Bagehot, The English Constitution 65, the ‘efficient secret’ of the UK constitution was ‘the close union, the nearly complete fusion, of the legislative and executive powers’.
- Constitutional Reform Act 2005 ss 108-9
- Constitutional Reform Act 2005 s 3.
- cf A Bradley, ‘The Sovereignty of Parliament – Form or Substance?’ in Jowell, The Changing Constitution (7th edn 2011) 35, ‘A further question is whether the democratic process in the UK works so well as to justify the absence of any limit on the authority of Parliament to legislate.’ Criticising AV Dicey, The Law of the Constitution (10th edn 1959) 73, who said ‘The electors in the long run can always enforce their will’, on the basis that executive dominance over Parliament might require revisions of the extent of the concept.
- Lord Bingham, ‘The Rule of Law and the Sovereignty of Parliament’ (31 October 2007) Speech given at King's College, London. It is also a considered that the rule of law is necessary for democracy, e.g. X v Morgan-Grampian Ltd [1991] AC 1, 48, per Lord Bridge, ‘The maintenance of the rule of law is in every way as important in a free society as the democratic franchise." Lord Woolf [1995] PL 57, ‘Our Parliamentary democracy is based on the Rule of Law.... If Parliament did the unthinkable then I would say that the courts would also be required to act in a manner which would be unprecedented." Reference on Quebec (1998) 161 DLR (4th) 385, 416, "democracy in any real sense of the word cannot exist without the rule of law." R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor [2017] UKSC 51, [68] "Without such access [to courts], laws are liable to become a dead letter, the work done by Parliament may be rendered nugatory, and the democratic election of Members of Parliament may become a meaningless charade."
- See Thucydides, History of the Peloponnesian War (c 411 BC) Book 2, para 37. Contrast Aristotle, Nicomachean Ethics, Book V, Parts 3 and 4, translated by DP Chase (favouring aristocracy, by equating it with appointment according "excellence", supposedly), and Plato, The Republic, Book IV, Part V, 139, translated by D Lee (arguing that philosopher kings should rule over a rigid hierarchy where there was "no interchange of jobs").
- ECHR 1950 Preamble
- See Mathieu-Mohin and Clerfayt v Belgium (1987) 10 EHRR 1, [47] on ECHR 1950 Prot 1, art 3
- A Lincoln, Gettysburg Address (1863) "that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the Earth".
- cf AJ Zurcher, 'The Hitler Referenda' (1935) 29(1) American Political Science Review 91
- See FL Neumann, The Democratic and the Authoritarian State (1957) 186-193
- J Habermas, Between Facts and Norms (1996) 135, ‘the only law that counts as legitimate is one that could be rationally accepted by all citizens in a discursive process of opinion- and will-formation.’
- e.g. R Dworkin, ‘Constitutionalism and Democracy’ (1995) 3(1) European Journal of Philosophy 2-11, 4-5, a constitutional democracy means: (1) ‘a majority or plurality of people’ (2) ‘all citizens have the moral independence necessary to participate in the political decision as free moral agents’ (3) ‘the political process is such as to treat all citizens with equal concern’. D Feldman, Civil Liberties and Human Rights in England and Wales (2002) 32-33 ‘it would be perverse to argue that there is anything undemocratic about a restriction on the capacity of decision-makers to interfere with the rights which are fundamental to democracy itself’. See also Matadeen v Pointu [1999] 1 AC 98, Lord Hoffmann, “Their Lordships do not doubt that such a principle [of equality] is one of the building blocks of democracy and necessarily permeates any democratic constitution."
- See Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 Articles 21 and 29(2), International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights 1966 Article 25, International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights 1966, Article 4
- Archie v Law Association of Trinidad and Tobago [2018] UKPC 23, [18] Lady Hale, "A vital element in any modern democratic constitution is the independence of the judiciary from the other arms of government, the executive and the legislature. This is crucial to maintaining the rule of law: the judges must be free to interpret and apply the law, in accordance with their judicial oaths, not only in disputes between private persons but also in disputes between private persons and the state. The state, in the shape of the executive, is as much subject to the rule of law as are private persons." cf KD Ewing, ‘The Resilience of the Political Constitution’ [2013] 14(12) German Law Journal 2111, 2116, suggesting the current political constitution of the UK is not necessarily the same as a fully democratic constitution.
- (1703) 2 Ld Raym 938, dissent approved by the House of Lords.
- [1975] QB 151
- Animal Defenders International v United Kingdom [2008] UKHL 15, [48] and see also [2013] ECHR 362
- Gorringe v Calderdale Metropolitan Borough Council [2004] UKHL 15, [2]. See also O'Rourke v Camden London Borough Council [1998] AC 188, "the [Housing] Act [1985] is a scheme of social welfare, intended to confer benefits at the public expense on grounds of public policy."
- e.g. Johnson v Unisys Limited [2001] UKHL 13, and Gisda Cyf v Barratt [2010] UKSC 41, [39]
- See, for example, J Lobel, 'The Limits of Constitutional Power: Conflicts between Foreign Policy and International Law' (1985) 71(7) Virginia Law Review 1071. J Habermas, 'The Constitutionalization of International Law and the Legitimation Problems of a Constitution for World Society' (2008) 15(4) Constellations 444. In Germany, see Grundgesetz 1949 Article 25, "The general rules of international law shall be an integral part of federal law. They shall take precedence over the laws and directly create rights and duties for the inhabitants of the federal territory." In the EU, see Kadi and Al Barakaat International Foundation v Council and Commission (2008) C-402/05, holding that international law binds EU law unless it requires an act that would run contrary to basic human rights.
- e.g. Magna Carta 1215, ch 41, ‘All merchants shall have safe and secure exit from England, and entry to England, with the right to tarry there and to move about as well by land as by water, for buying and selling by the ancient and right customs, quit from all evil tolls, except (in time of war) such merchants as are of the land at war with us...’
- Coke, 1 Institutes 182
- See Bate's case or Case of Impositions (1606) 2 St Tr 371, John Bate claimed he did not need to pay a duty on imported currants imposed by the Crown, as contrary to the Confirmation of Charters, Weirs, Taxation Act 1371, 45 Edw 3 c 4, which prohibited indirect taxation without consent of Parliament. The Court of Exchequer held the Crown could impose the duty as he pleased to regulate trade. The Court could not go behind the King's statement that the duty was indeed imposed for the purpose of regulating trade. Then, the Case of Ship Money or R v Hampden (1637) 3 St Tr 825 held that the King could raise money from trade without Parliament. This was reversed by the Shipmoney Act 1640, and after the civil war and glorious revolution, once again by the Bill of Rights 1689 art 4.
- Lethulier's Case (1692) 2 Salk 443, "we take notice of the laws of merchants that are general, not of those that are particular."
- Luke v Lyde (1759) 97 Eng Rep 614, 618; (1759) 2 Burr 882, 887
- Pillans v Van Mierop (1765) 3 Burr 1663
- Somerset v Stewart (1772) 98 ER 499, "The state of slavery is of such a nature, that it is incapable of now being introduced by Courts of Justice upon mere reasoning or inferences from any principles, natural or political; it must take its rise from positive law; the origin of it can in no country or age be traced back to any other source: immemorial usage preserves the memory of positive law long after all traces of the occasion; reason, authority, and time of its introduction are lost..."
- Saad v SS for the Home Department [2001] EWCA Civ 2008, [15] Lord Phillips MR, quoting Bennion on Statutory Interpretation (3rd ed) p 630 that: “It is a principle of legal policy that the municipal law should conform to public international law. The court, when considering, in relation to the facts of the instant case, which of the opposing constructions of the enactment would give effect to the legislative intention, should presume that the legislator intended to observe this principle.”
- R v Lyons [2002] UKHL 44, [27] Lord Hoffmann
- [2014] UKSC 47
- See further R (SG) v SS for Work and Pensions [2015] UKSC 16, on the benefits cap, Lord Kerr, dissenting, at [247]-[257] argued the dualist theory of international law should be abandoned, and international law should be directly effective in UK law.
- Kadi and Al Barakaat International Foundation v Council and Commission (2008) C-402/05
- See the Venice Commission, Code of Practice on Referendums (2007) on asking questions with concrete, determinative choices.
- e.g. Winston Churchill, 'Speech to the 69th Annual Conservative Party Conference at Llandudno' (9 October 1948). See J Danzig 'Winston Churchill: A founder of the European Union' (10 November 2013) EU ROPE
- cf World Trade Organization (Immunities and Privileges) Order 1995
- On the post-referendum crisis, see R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the European Union [2017] UKSC 5 and European Union (Notification of Withdrawal) Act 2017 s 1, giving power to the PM to notify intention to negotiate to leave the EU.
- See House of Commons, Digital, Culture, Media and Sport Committee, Disinformation and ‘fake news’: Interim Report (29 July 2018) HC 363 and Electoral Commission, Report of an investigation in respect of Vote Leave Limited, Mr Darren Grimes, BeLeave, Veterans for Britain (17 July 2018). Litigated in R (Wilson) v Prime Minister [2018] EWHC 3520 (Admin), and see E McGaughey, 'Could Brexit be Void?' (2018) King's Law Journal.
- The Parliament Act 1911 set elections to take place at a maximum of each five years, but elections usually occurred in a fourth year. Before this the maximum was seven years, but in practice governments called votes sooner.
- Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 s 1(3). By contrast, Australia has elections each 3 years, and the US has presidential elections each 4 years.
- Parliament Act 1911 and Parliament Act 1949.
- Life Peerages Act 1958 s 1
- House of Lords Act 1999 ss 1-2, or 90 plus the "Lord Great Chamberlain" and the "Earl Marshal".
- R (Simms) v SS for the Home Department [1999] UKHL 33, [2000] 2 AC 115, 131, Lord Hoffmann
- Following Magna Carta 1215, see the Acts of Supremacy 1534, the Earl of Oxford's case (1615) 21 ER 485, and the Bill of Rights 1689
- This was represented by the Parliament Act 1911, following the People's Budget of 1909.
- See JS Mill, Considerations on Representative Government (1861) ch 5. AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) ch 8.
- HC Modernisation Committee (2001-2) HC 1168, recommended publishing draft bills, and (2005-6) HC 1097, 'one of the most successful Parliamentary innovations of the last ten years' and 'should become more widespread'.
- Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 s 1(3)
- Mental Health Act 1983 or Criminal Procedure (Insanity) Act 1964
- See Hirst v United Kingdom (No 2) [2005] ECHR 681 (blanket disqualification of convicted prisoners from voting breached ECHR Prot 1, art 3. After this the UK failed to change its laws. Green v United Kingdom [2010] ECHR 868 reaffirmed the position. HL Paper 103, HC 924 (2013-14) recommended prisoners serving under 12 months should be entitled to vote. Parliament still did not act. McHugh v UK [2015] ECHR 155, reaffirmed breach but awarded no compensation or costs.However, Moohan v Lord Advocate [2014] UKSC 67 and Moohan v UK (13 June 2017) App No 22962/15, denial of prisoner voting in the Scottish independent referendum was not a breach of art 3.
- Electoral Registration and Administration Act 2013 ss 1-5
- (1703) 2 Ld Raym 938
- Morgan v Simpson [1975] QB 151, per Lord Denning MR
- cf R (Wilson) v Prime Minister [2018] EWHC 3520 (Admin), and E McGaughey, 'Could Brexit be Void?' (2018) King's Law Journal
- PPERA 2000 ss 72-131 and Schs 8-13, in referendums, the limit has traditionally been set at £600,000 for the official campaigns on each side.
- Communications Act 2003 ss 319-333.
- Animal Defenders International v United Kingdom [2008] UKHL 15, [48] per Baroness Hale. Confirmed in [2013] ECHR 362.
- Representation of the People Act 1983 ss 92. Furthermore, any "trading" with hostile foreign parties with whom the UK is "at war" may lead to seven years in prison. Trading with the Enemy Act 1939 (c 89) ss 1-2, seven years prison for trading with an enemy who is "at war with His majesty".
- R (Electoral Commission) v City of Westminster Magistrate's Court and UKIP [2010] UKSC 40, holding that a partial forfeiture of £349,216 donations by a non-UK resident was appropriate.
- Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000 ss 12-69 and 149
- Parliamentary Constituencies Act 1986, setting up the Boundary Commission. See also, R (McWhirter) v Home Secretary (21 October 1969) The Times, elector in Enfield sought mandamus ('we command') to require Home Secretary to perform statutory duty of laying before Parliament Commission reports with draft orders in Council.
- Electoral Administration Act 2006 s 17
- Act of Settlement 1700 s 3 unless ‘qualifying Commonwealth and Irish citizens, British Nationality Act 1981 Sch 7 and Electoral Administration Act 2006 s 18
- Insolvency Act 1986 s 426A(5)
- RPA 1983 ss 160 and 173
- House of Commons Disqualification Act 1957 ss 1 and 5 and House of Commons Disqualification Act 1975 give further exceptions.
- Ministerial and Other Salaries Act 1975 ss 1-2
- House of Lords Act 1999 ss 1-2
- Constitutional Reform Act 2005 s 24
- See the Lords Appointments webpage.
- Now confirmed in the House of Lords Reform Act 2014
- Peerages Act 1963 and Re Parliamentary Election for Bristol South East [1964] 2 QB 257, Viscount Stansgate or Tony Benn challenged the law disqualifying peers standing for Parliament.
- House of Lords (Expulsion and Suspension) Act 2015
- Parliament Act 1911 ss 1-3 and Parliament Act 1949
- cf GDH Cole, Self-Government in Industry (5th edn 1920) ch V, 134-135. S Webb, Reform of the House of Lords (1917) Fabian Tract No. 183, 7, at 12, preferring a chamber of around 100 people elected by proportional representation. E McGaughey, 'A Twelve Point Plan for Labour, and A Manifesto for Labour Law' (2017) 46(1) Industrial Law Journal 169
- Practice Statement [1966] 3 All ER 77
- Employment Tribunals Act 1996, appealing to the Employment Appeal Tribunal.
- Tribunals, Courts and Enforcement Act 2007, appealing to the appropriate Upper Tribunal division.
- e.g. Hounga v Allen [2014] UKSC 47
- "The power to interpret is the power to destroy." O Kahn-Freund, 'The Impact of Constitutions on Labour Law” (1976) 35 Cambridge Law Journal 240, 244, paraphrasing Marshall CJ in McCulloch v Maryland (1819) 17 US (4 Wheat) 316
- See Re Spectrum Plus Ltd [2005] UKHL 41.
- See Pickin v British Railways Board [1974] AC 765
- R (Simms) v SS for the Home Department [1999] UKHL 33, per Lord Hoffmann, "In this way the courts of the United Kingdom, though acknowledging the sovereignty of Parliament, apply principles of constitutionality little different from those which exist in countries where the power of the legislature is expressly limited by a constitutional document."
- Inquiries Act 2005
- See now the Constitutional Reform Act 2005 s 33 and Senior Courts Act 1981 s 11(3)
- AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2014) 329, ‘whatever the theoretical position, there are a number of reasons which help to ensure that these latter powers are unlikely ever to be used, with the security of judicial tenure relying not so much on legal rules as on a shared constitutional understanding which these rules reflect.’
- Codified in 1963, updated in 1972 and 2001, HC Deb (15 December 2001) col 1012.
- Constitutional Reform Act 2005 s 3
- Courts and Legal Services Act 1990
- CRA 2005 s 27A and SI 2013/2193. See also Judicial Appointments Regulations 2013 (SI 2192)
- CRA 2005 ss 70-79
- cf 'Baroness Brenda Hale: "I often ask myself 'why am I here?'" (17 September 2010) Guardian "I'm quite embarrassed to be the only justice to tick a lot of the diversity boxes, for example the gender one, the subject areas in which I'm interested (which are not ones that most of my colleagues have had much to do with up until now), the fact that I went to a non-fee-paying school and the fact that I wasn't a practitioner for any great length of time. I'm different from most of my colleagues in a number of respects (and they're probably at least as conscious of this as I am). I think we could do with more of that sort of diversity."
- [2017] UKSC 51
- See the Prosecution of Offences Act 1985
- See R Blackburn, ‘Monarchy and the personal prerogatives’ [2004] Public Law 546, explaining that the "personal prerogative" of the monarch is a set of powers that must be exercised according to law, and must follow the advice of the Prime Minister, or in accordance with Parliament and the courts.
- n.b. the Monarch continued to withhold royal assent for laws in British colonies leading, for example, to the American Revolution and US Declaration of Independence in 1776.
- cf W Bagehot, The English Constitution (1867) 111, suggesting the monarch has a right to be consulted, to encourage and to warn.
- The Sunday Times Rich List 2015 estimated the Queen's personal wealth at £340 million, making her the 302nd richest person in the UK: H Nianias, 'The Queen drops off the top end of the Sunday Times Rich List for the first time since its inception' (26 April 2015) The Independent
- Sovereign Grant Act 2011 ss 1-6. This was raised from 15% by SI 2017/438 art 2.
- Crown Estate Act 1961 s 1, up to eight Crown Estate Commissioners are appointed by the monarch on PM advice.
- 'Crown Estate makes record £304m Treasury payout' (28 June 2016) BBC News. See map.whoownsengland.org and the colour purple for the Crown Estate. This includes (1) retail property such as Regent Street in London, commercial property in Oxford, Milton Keynes, Nottingham, Newcastle, etc., and a right to receive 23% of the income from the Duchy of Lancaster's Savoy Estate in London (2) 116,000 hectares of agricultural land and forests, together with minerals and residential and commercial property (3) rights to extract minerals covers some 115,500 hectares (4) 55% of the UK's foreshore, and all of the UK's seabed from mean low water to the 12-nautical-mile (22 km) limit, plus sovereign rights of the UK in the seabed and its resources vested by the Continental Shelf Act 1964.
- I Jennings, Cabinet Government (3rd edn 1959) ch 2
- Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011
- The vote was 45.13% in favour of becoming a republic, but on a model of having a directly elected president. 54..87% of voters opposed this. See [2000] Public Law 3.
- Case of Prohibitions [1607] EWHC J23 (KB), per Coke CJ, "true it was, that God had endowed His Majesty with excellent science, and great endowments of nature; but His Majesty was not learned in the laws of his realm of England, and causes which concern the life, or inheritance, or goods, or fortunes of his subjects".
- R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the EU [2017] UKSC 5
- cf AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) ch 10 258-265, listing 9 categories.
- HC Deb (21 April 1993) col 490 and HC 422 (2003-4) Treasury Solicitor, suggesting an exhaustive catalogue of powers is probably not possible, but listing major categories.
- Subject to the Life Peerages Act 1958 and House of Lords Act 1999 s 1
- See R v Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs, ex p Bancoult (No 2) [2008] UKHL 61, [69] per Lord Bingham
- R (Lain) v Criminal Injuries Compensation Board [1967] 2 QB 864, 886. R (Harrison) v Home Secretary [1988] 3 All ER 86. R (FBU) v Home Secretary [1995] 2 AC 513, Re Lord Bishop of Natal (1864) 3 Moo PC (NS) 115
- Allen (1862) 1 B&S 850 and Criminal Appeal Act 1995 s 16
- e.g. the Island of Rockall was seized in 1955, and later recognised in the Island of Rockall Act 1972. See R (Lye) v Kent JJ [1967] 2 QB 153 on alterations.
- Nissan v AG [1970] AC 179, now regulated by Immigration Act 1971 s 33(5). The power of expulsion is considered 'doubtful' outside statute: AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) ch 10, 261
- Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010 s 20, codifying the previous Ponsonby Rule.
- Burmah Oil Co Ltd v Lord Advocate [1965] AC 75, 101
- This convention was established through the Iraq war, where Parliament backed an invasion contrary to international law in 2003, and a vote against an invasion of Syria in 2013.
- Bank voor Handel en Scheepvaart NV v Administrator of Hungarian Property [1954] AC 584
- e.g. MoJ, Rev of the Exec Royal Prer Powers (2009) 23
- Spook Erection Ltd v Environment Secretary [1989] QB 300 (beneficiary of market franchise not entitled to Crown’s exemption from planning control)
- e.g. Butler v Freeman (1756) Amb 302, In re a Local Authority [2003] EWHC 2746, Scott v Scott [1913] AC 417.
- Council of Civil Service Unions v Minister for the Civil Service [1985] AC 374
- Ministerial Salaries Act 1975. See also, recognising the PM's position, the Chequers Estate Act 1917, Chevening Estate Act 1959, Ministerial and other Pensions and Salaries Act 1991
- Ministers of the Crown Act 1975 s 5. Under the Crown Proceedings Act 1947 s 17 the Minister for Civil Service (i.e. the PM) maintains a list of govt departments (for the purpose of proceedings against the Crown).
- See AG v Jonathan Cape Ltd [1976] QB 752, suggesting the duty of confidentiality expires after a number of years out of government.
- Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010 s 3, putting management of the civil service into statute. Civil Service Management Code s 11.1.1, civil servants employed at pleasure of the Crown, theoretically lacking a wrongful dismissal remedy according to somewhat outdated case law: Dunn v R [1896] 1 QB 116 and Riordan v War Office [1959] 1 WLR 1046, but under the Employment Rights Act 1996 s 191, civil servants expressly have the right to claim unfair dismissal.
- Freedom of Information Act 2000 ss 1 and 21-44. Sch 1 lists public bodies that are subject. The BBC can only be required to disclose information held for non-journalistic purposes, to protect freedom of expression: Sugar v BBC [2012] UKSC 4 and BBC v Information Commissioner [2009] UKHL 9
- "Budget 2016" (PDF). HM Treasury. March 2016. p. 5.
- Greater London Authority Act 1999 ss 31, 141, 180 and 333 (with highly limited powers except in transport)
- See S Bailey, Cross on Local Government Law (2004). J Loughlin (ed), The Oxford Handbook of Local and Regional Democracy (2012). S Webb, English Local Government (1929) Volumes I–X.
- See Greater London Authority Act 1999 ss 31, 141, 180 and 333 (with highly limited powers except in transport) the Scotland Act 1998 ss 28-29 and Sch 5 (with full legislative power except 'reserved matters'), the Government of Wales Act 2006 Sch 5 (setting a list of devolved 'fields'), and the Norther Ireland Act 1998 s 4 and Schs 2 and 3 (listing excepted and reserved matters, but the Assembly can legislate in all other fields).
- Local Government Finance Act 1992 set up property value bands, but despite proposals in 1995, these have never been altered despite drastic shifts in house prices.
- Local Government Finance Act 1992 ss 52ZA-ZY, introduced by the Localism Act 2011. Also under ss 52A-Y in Wales the Secretary can cap council tax if deemed excessive.
- N Amin-Smith and D Phillips, 'English council funding: what’s happened and what’s next?' (2019) IFS, BN 250
- See further Local Government Finance Act 1992 ss 65-68. Council Tax (Administration and Enforcement) Regulations 1992 regs 8-31
- See DCLG duties and other duties.
- Localism Act 2011 ss 1-5, which add that the Secretary of State can remove restrictions through secondary legislation.
- Town and Country Planning Act 1990 ss 65-223
- Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004 ss 13-39
- Education Act 1996 ss 3A-458
- Public Libraries and Museums Act 1964 ss 1-13
- Childcare Act 2006 ss 6-13
- Highways Act 1980 ss 25-31A
- egNHS Act 2006 ss 74-82. NHS and Community Care Act 1990 ss 46-47. Carers and Disabled Children Act 2000 s 1-6A
- Environmental Protection Act 1990 ss 45-73A
- e.g. Household Recycling Act 2003
- Building Act 1984 ss 59-106
- eg Housing Act 1985 ss 8-43 and 166-8
- cf Widdicombe Committee, Committee of Inquiry into the Conduct of Local Authority Business (1986) Cmnd 9797
- Local Democracy, Economic Development and Construction Act 2009 s 107A and Sch 5A
- Cities and Local Government Devolution Act 2016 s 15. cf M Elliot, Public Law (2016) 320, ‘The net result, over time, will be a patchwork of combined authorities with elected mayors, supplying a mezzanine layer of government that sits between individual local authorities and central government.’ HC 369 (2015-16) [53] criticised the lack of actual public consultation in creating combined authorities. See also 2012 English mayoral referendums and List of lord mayoralties and lord provostships in the United Kingdom.
- cf Sir Kenneth Calman Report, Serving Scotland Better (2009)
- Belfast or Good Friday Agreement (10 April 1998)
- Government of Wales Act 2006 Sch 5 listing (1) agriculture, fisheries, forestry and rural development) (2) ancient monuments and historic buildings (3) culture (4) economic development (5) education and training (6) environment (7) fire and rescue services and promotion of fire safety (8) food (9) health and health services (10) highways and transport (11) housing (12) local government (13) National Assembly for Wales (14) public administration (15) social welfare (16) sport and recreation (17) tourism (18) town and country planning (19) water and flood defence (20) Welsh language.
- See Agricultural Sector (Wales) Bill - Reference by the Attorney General for England and Wales [2014] UKSC 43
- Eleanor Roosevelt: Address to the United Nations General Assembly 10 December 1948 in Paris, France
- Magna Carta 1215 clauses 12 (no tax without consent), 39 (fair trial), 40 (justice), 41 (free movement of merchants), and 47 (disafforesting common land). The Petition of Right 1628 reasserted these values from the Magna Carta against King Charles I.
- J Bentham, Anarchical Fallacies; Being an Examination of the Declarations of Rights Issued During the French Revolution (1789) art II
- M Wollstonecraft, A Vindication of the Rights of Woman: with Strictures on Political and Moral Subjects (1792). See also O de Gouges, Declaration of the Rights of Woman and of the Female Citizen (1791)
- Turning points were the Second Reform Act 1867 and the Trade Union Act 1871.
- Though a UN General Assembly Declaration, not a treaty, the rights are binding jus cogens norms in international law, since two treaties, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 recast the UDHR.
- This is qualified, as in the EU, by the position that international law must be compatible with basic principles of the UK constitution: see R (HS2 Action Alliance Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport [2014] UKSC 3 (for the UK), Kadi and Al Barakaat International Foundation v Council and Commission (2008) C-402/05 (for the EU) and Re Wünsche Handelsgesellschaft (22 October 1986) BVerfGE 73, 339 (first setting out the basic concepts).
- ECHR arts 2 (right to life). Article 3 (right against torture). Article 4, right against forced labour, see Somerset v Stewart (1772) 98 ER 499. Articles 12-14 are the right to marriage, effectiveness and to equal treatment.
- ECHR arts 5-11.
- Magna Carta 1215 ch XXIX, 'NO Freeman shall be taken or imprisoned, or be disseised of his Freehold, or Liberties, or free Customs, or be outlawed, or exiled, or any other wise destroyed; nor will We not pass upon him, nor condemn him, but by lawful judgment of his Peers, or by the Law of the Land. We will sell to no man, we will not deny or defer to any man either Justice or Right.'
- cf Somerset v Stewart (1772) 98 ER 499, and now article 4. See also the Habeas Corpus Act 1679 and Bird v Jones (1845) 7 QB 742.
- cf Benjamin Franklin, Objections to Barclay’s Draft Articles of February 16 (1775) 'They who can give up essential Liberty to obtain a little temporary Safety, deserve neither Liberty nor Safety.'
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 arts 3 and 9-11. International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights 1966 arts 9-16
- ECHR art 5(1)
- ECHR art 5(2)-(5)
- AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) 398, ‘Every power conferred on police officers inevitably means a corresponding reduction in the liberty of the individual, and brings us face to face with Convention obligations.'
- Home Affairs Committee, Policing in the 21st Century (2007-8) HC 364-I, para 67, the UK spent 2.5% of GDP on police, the OECD’s highest.
- Police Reform Act 2002 s 40
- PACEA 1984 ss 1 and 117
- PACEA 1984 s 2, and s 3 requires details are recorded.
- Home Office Code A, para 2.2B(b). The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 s 23 enables stop and search powers for unlawful drugs. M Townsend, 'Racial bias in police stop and search getting worse, report reveals' (13 October 2018) Guardian, finds black people are 9 times more likely than white people to be searched. In 2019, 43% of searches in London were on black people: (26 January 2019) Guardian. See also K Rawlinson, 'Bristol race relations adviser Tasered by police is targeted again' (19 October 2018) Guardian.
- Jackson v Stevenson (1879) 2 Adam 255, per the Lord Justice General
- Criminal Justice and Public Order Act 1994 s 60(5) and see B Bowling and E Marks, 'The rise and fall of suspicionless searches' (2017) 28 KLJ 62.
- R (Roberts) v MPC [2015] UKSC 79.
- PACEA 1984 s 24
- Alanov v Sussex CC [2012] EWCA Civ 235, ‘the “threshold” for the existence of “reasonable grounds” for suspicion is low... small, even sparse.’ Also R (TL) v Surrey CC [2017] EWHC 129
- Magistrates’ Courts Act 1980 s 1 and 125D-126. nb Constables’ Protection Act 1750 s 6 means a constable who arrests someone in good faith is protected from liability from arrest if it turns out the warrant was beyond the jurisdiction of the person who issued it.
- PACEA 1984 s 24A
- PACEA 1984 s 28. Hill v Chief Constable of South Yorkshire [1990] 1 All ER 1046, s 28 is a rule ‘laid down by Parliament to protect the individual against the excess or abuse of the power of arrest’. Christie v Leachinsky [1947] AC 573, ‘the arrested man is entitled to be told what is the act for which he is arrested.’
- PACEA 1984 ss 30-39
- PACEA 1984 ss 41-45ZA.
- PACEA 1984 ss 54-58 and Terrorism Act 2000 s 41 and Sch 8 para 9. Ibrahim v UK [2016] ECHR 750, suggests that damages were recoverable for denial of access to a solicitor in breach of Convention rights. cf Cullen v Chief Constable of the RUC [2003] UKHL 39, held there was no right to damages for failure to permit legal representatives, but evidence may be inadmissible.
- PACEA 1984 ss 60-64A.
- Condron v UK (2000) 31 EHRR 1, 20 the right to silence is in ECHR art 6, ‘at the heart’. But drawing adverse inferences is not an infringement.
- Beckles v UK (2003) 36 EHRR 162
- Ibrahim v R [1914] AC 599, a confession or statement of an accused person is not admissible unless it is voluntary, not obtained by fear of prejudice or hope of advantage, exercised by the person in authority: PACEA 1984 ss 76-78.
- Brown v Stott [2001] 1 AC 681, on the Road Traffic Act 1988
- PACEA 1984 ss 9-14 and Sch 1, paras 4-12. See R v Singleton (1995) 1 Cr App R 431.
- Thomas v Sawkins [1935] 2 KB 249, power to enter to stop breach of peace: controversial. KD Ewing and C Gearty, The Struggle for Civil Liberties (2000) ch 6.
- McLeod v UK (1998) 27 EHRR 493
- PACEA 1984 ss 19 and 21, a record must be provided to the occupier, and a person has a right of access under police supervision unless this would prejudice investigation.
- Christie v Leachinsky [1947] AC 573, 599, per Lord du Parcq, and at 591, Lord Simonds, ‘it is the corollary of the right of every citizen to be thus free from arrest that he should be entitled to resist arrest unless that arrest is lawful’. See also Abbassy v MPC [1990] 1 All ER 193, Woolf LJ
- Police Act 1996 s 89
- R v Iqbal [2011] EWCA Crim 273
- Police Act 1996 s 88, Police Reform Act 2002 s 42 and Kuddus v Chief Constable of Leicestershire Constabulary [2001] UKHL 29
- PACEA 1984 ss 76-78 and see R v Khan [1997] AC 558, an illegally placed surveillance device evidence was admissible, even with probable ECHR art 8 breach, but merely ‘a consideration which may be taken into account for what it is worth’. Schenck v Switzerland (1988) 13 EHRR 242, irregularly obtained evidence can be admitted. R v Loosely [2001] UKHL 53, no need to change s 78 for the ECHR.
- Police Reform and Social Responsibility Act 2011 s 1
- Police Act 1996 ss 37A-54
- e.g. R v MPC ex p Blackburn (No 3) [1973] QB 241
- Hill v CC of West Yorkshire [1989] AC 53
- Osman v UK (2000) 29 EHRR 245, ECHR art 2 requires the state ‘to take preventive operational measures to protect an individual whose life is at risk from the criminal acts of another individual.’ But breach hard to establish. DSD v MPC [2018] UKSC 11
- Semayne’s case (1604) 77 Eng Rep 194, Sir Edward Coke, ‘The house of every one is to him as his castle and fortress, as well for his defence against injury and violence as for his repose.’
- ECHR article 8
- (1765) 19 St Tr 1030
- Protection of Freedoms Act 2012 explanatory notes stated over 1300 statutory provisions enable entry into people's homes, and while ss 39-47 and Sch 2 enable a Minister to repeal and replace these powers, the government continued to add them, eg Scrap Metal Dealers Act 2013 s 16(1)
- See AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) ch 16, 429, not just the state but private parties violate privacy, highlighting ‘newspapers engaged in a desperate circulation war, or employers checking on employees’. S Zuboff, The Age of Surveillance Capitalism: The Fight for a Human Future at the New Frontier of Power (2019)
- Police Act 1997 s 92, following R v Khan [1997] AC 558, (2001) 31 EHRR 1016 which found there was no legal basis for police bugging, and therefore a violation of ECHR article 8.
- Police Act 1997 s 104
- RIPA 2000 ss 26-36.
- Investigatory Powers Tribunal, Report 2010 (2011) 28.
- R v Barkshire [2011] EWCA Crim 1885.
- [2012] UKSC 62, [21] Lord Hope, 'He took the risk of being seen and of his movements being noted down. The criminal nature of what he was doing, if that was what it was found to be, was not an aspect of his private life that he was entitled to keep private.'
- Investigatory Powers Act 2016 ss 6 and 20
- IPA 2016 ss 19 and 23
- IPA 2016 s 26
- IPA 2016 s 56
- Privacy International v Foreign Secretary [2016] UKIPTrib 15_110-CH
- House of Commons, Digital, Culture, Media and Sport Committee, Disinformation and ‘fake news’: Final Report (2019) HC 1791
- R v Brown [1996] 1 AC 541, 556, per Lord Hoffmann
- See the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union 2000 art 8
- GDPR 2016 arts 5-6
- GDPR 2016 arts 6-7
- See the Consumer Rights Act 2015 at present.
- GDPR 2016 arts 12-14
- GDPR 2016 art 17. Also art 18 gives the right to restrict processing.
- GDPR 2016 art 20
- [2012] UKSC 55
- House of Commons, Digital, Culture, Media and Sport Committee, Disinformation and ‘fake news’: Final Report (2019) HC 1791, [150] and [255]-[256]
- GDPR 2016 art 83.
- S and Marper [2008] ECHR 1581, limits to retain DNA information
- Police and Criminal Evidence Act 1984 s 27(4) and National Police Records (Recordable Offences) Regulations 2000/1139, recording people's convictions, cautions, reprimands, and warnings for any offence punishable with prison or in the Schedule.
- [2009] UKSC 3
- cf J Kollewe, 'NHS data is worth billions – but who should have access to it?' (10 June 2019) Guardian and S Boseley, 'NHS to scrap single database of patients' medical details' (6 July 2016) Guardian
- Prince Albert v Strange (1849) 1 Mac&G 25
- R (Ingenious Media Holdings plc) v HMRC [2016] UKSC 54 and Campbell v MGN Ltd [2004] UKHL 22, [14] per Lord Nicholls, and [2005] UKHL 61
- Associated Newspapers Ltd v Prince of Wales [2006] EWCA Civ 1776
- PJS v News Group Newspapers Ltd [2016] UKSC 26, [32]
- R v Home Secretary, ex p Simms [2000] 2 AC 115, 126
- Plato, Crito (ca 350 BC) and JS Mill, On Liberty (1859) ch 1
- Book of Matthew 26-27. Book of John 18. Book of Luke 23.
- R v Penn and Mead or Bushell’s case (1670) 6 St Tr 951, prosecuting Quakers under the Religion Act 1592 (offence to not attend church) and the Conventicle Act 1664 and Conventicles Act 1670 (prohibitions on religious gatherings over five people outside the Church of England).
- eg R v Lovelass (1834) 172 ER 1380 on the transportation of the Tolpuddle martyrs under the Unlawful Oaths Act 1797.
- Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829, and contrast the Gordon Riots following the Papists Act 1778.
- cf Ahmad v Inner London Education Authority [1978] QB 38, and Redfearn v Serco Ltd [2012] ECHR 1878
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights 1966 Articles 18-20
- cf Leveson Report (2012-13) HC 779 discussing media concentration and competition.
- "article 63" (PDF).
- AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) 464, ‘most newspapers are commercial enterprises whose first duty is one arising under private law to maximise shareholder return.’
- S Deakin, 'The Coming Transformation of Shareholder Value' (2005) 13(1) Corporate Governance 11
- Communications Act 2003 s 3 requires Ofcom to maintain 'sufficient plurality'
- Communications Act 2003 s 391 requires regular reviews of media ownership, by Ofcom, to be sent to Secretary of State
- The Broadcasting Act 1990 Sch 2, and CA 2003 Sch 14, para 1, states a person cannot hold a Channel 3 (ITV) licence if he runs a national newspaper/s with market share over 20% over a six month period.
- R (News Media Association) v Press Recognition Panel [2017] EWHC 2527
- eg Curl’s case (1727) 17 St Tr 153
- In the Obscene Publications Act 1857 debate, Lord Campbell, HL Deb (25 June 1857) col 329 said obscene meant ‘exclusively to works written for the single purpose of corrupting the morals of youth, and of a nature calculated to shock the common feelings of decency in any well regulated mind’. In R v Hicklin (1868) LR 3 QB 360, Lord Cockburn CJ (a notorious womaniser) held that immunity for a medical treatise depended on the circumstances, and the author's intent could be taken into account.
- Shaw v DPP [1962] AC 220, finding obscene an illustrated magazine with contacts for prostitutes, and convicting the publisher, Shaw, for conspiracy, Lord Reid dissenting.
- Knuller Ltd v DPP [1973] AC 435 finding a gay magazine for men to meet other men was involved in a 'conspiracy' to 'corrupt public morals' even though homosexuality ceased to be criminal in the Sexual Offences Act 1967, Lord Reid and Lord Diplock dissenting.
- Incitement to Disaffection Act 1934, makes it an offence to maliciously and advisedly endeavour to seduce a member of the armed forces from that person’s duty or allegiance.
- Police Act 1996 s 91 prohibits causing disaffection among police officers or inducing them to withhold services or commit breaches of discipline. This effectively prohibits strikes, or calling for them, although it appears unenforceable in practice.
- Aliens Restriction (Amendment) Act 1919 s 3 prohibits an 'alien' from causing sedition or disaffection among civil population and armed forces.
- Public Order Act 1986 ss 17-27, first introduced in the Race Relations Act 1965.
- Racial and Religious Hatred Act 2006 s 1, inserted POA 1986 ss 29A-29N. Criminal Justice and Immigration Act 2008 s 74, Sch 16. College of Policing, Hate Crime Operational Guidance (2014) on disability.
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights 1966 Article 20 '(1) Any propaganda for war shall be prohibited by law. (2) Any advocacy of national, racial or religious hatred that constitutes incitement to discrimination, hostility or violence shall be prohibited by law.' In the UK this would engage the Equality Act 2010, and could include incitement to discriminate against immigrants.
- Terrorism Act 2006 ss 1-3 and 20
- Reynolds v Times Newspapers Ltd [2001] 2 AC 127
- Defamation Act 2013 s 5 and The Defamation (Operators of Websites) Regulations 2013 Schedule
- Prebble v Television New Zealand Ltd [1995] 1 AC 321, Chatterton v Secretary of State of India [1895] 2 QB 189, Parliamentary Commissioner Act 1967 s 10(5), Al-Fayed v Al-Tajir [1988] QB 712, Defamation Act 1996 s 14(3)
- Webb v Times Publishing Co [1960] 2 QB 535, Tsikata v Newspaper Publishing plc [1997] 1 All ER 655, Curistan v Times Newspapers Ltd [2008] EWCA Civ 432, and Defamation Act 1996 Sch 1, part 1.
- Defamation Act 2013 ss 9-13
- Attorney General v Guardian Newspapers Ltd (1992) 14 EHRR 153
- Sunday Times v United Kingdom (1979–80) 2 EHRR 245
- AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) ch 18 and E McGaughey, A Casebook on Labour Law (2019) ch 8, 324, stating freedom of association "is fundamental to democratic society... workers taking collective action were major... factors contributing to the deposition of German Kaiser in 1918, Indian independence in 1948, the victory of the US civil rights movement in 1964, the collapse of the Iron Curtain in 1989, and the end of apartheid South Africa in 1994".
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948 arts 20 and 23. Also, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights 1966 arts 21-22 and International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights 1966 art 8, both ratified by the UK.
- KD Ewing, ‘The Implications of Wilson and Palmer’ (2003) 32(1) Industrial Law Journal 1-22
- Wilson v United Kingdom [2002] ECHR 552, where an employee for the Daily Mail who was not given a raise after he refused to give up trade union membership was held to have suffered an unlawful detriment, violating his freedom of association.
- e.g. ASLEF v UK [2007] ECHR 184, where the European Court of Human Rights held that a union, ASLEF, could expel a member of the fascist group, the British National Party, because it was committed to equality.
- cf RMT v United Kingdom [2014] ECHR 366, where the ECtHR held that although a union had the right to strike, and the UK's laws were at the outer limits (with Russia and Turkey) in restricting union freedoms, it was within the margin of appreciation to have restricting balloting rules, and possibly to limit secondary action.
- Terrorism Act 2000 s 3 and Sch 2, with a growing list of banned organisations.
- eg Crofter Hand Woven Harris Tweed Co Ltd v Veitch [1941] UKHL 2 and Mogul Steamship Co Ltd v McGregor, Gow & Co [1892] AC 25
- (1882) 9 QBD 308, approved in Redmond-Bate v Director of Public Prosecutions [2000] HRLR 249
- AL Goodhart, ‘Public Meetings and Processions’ (1937) 6 CLJ 161, 169
- Public Order Act 1986 ss 11-16. Police can impose conditions on duration and numbers, and may apply for a banning order but only if serious public disorder could not be controlled with conditions. In Scotland, the Civic Government (Scotland) Act 1982 ss 62-64 requires 28 days notification.
- [2008] UKHL 69
- Highways Act 1980 s 137 is inconsistent with many other EU member state and Commonwealth country rules, see e.g. Eugen Schmidberger, Internationale Transporte und Planzüge v Austria (2003) C-112/00
- Public Order Act 1980 s 14A
- [1999] UKHL 5, [1999] 2 AC 240, a 3 to 2 decision.
- Representation of the People Act 1983 ss 95-96, and case law such as Wheeler v Leicester CC [1985] AC 1054 and Webster v Southwark Council [1983] QB 698. But contrast the Anti-social Behaviour, Crime and Policing Act 2014 s 59, that enables public space protection orders, requiring application for a public assembly.
- Education (No 2) Act 1986 s 43
- R v University of Liverpool, ex p Caesar-Gordon [1987] PL 344, a university was not entitled to stop a talk by secretaries of the South African Embassy, from the apartheid government, because of fears about violence on the nearby Toxteth estate, but could have done if there was concern about 'disorder on university premises and among university members'.
- Hubbard v Pitt [1976] QB 142
- TULRCA 1992 s 220. cf Broome v DPP [1974] AC 587, holding there was no right to stop traffic.
- Middlebrook Mushrooms Ltd v TGWU [1993] ICR 612
- [2003] ECHR 222
- Trade Union and Labour Relations (Consolidation) Act 1992 s 241, originally in the Conspiracy and Protection of Property Act 1875 s 7. This fell into disuse, but was revived for miners’ strike: Wallington (1985) 14 Industrial Law Journal 145.
- See J Crawford, Brownlie's Principles of Public International Law (2019) ch 33
- [2006] UKHL 16, also Criminal Damage Act 1971 s 3(b)
- Criminal Justice and Public Order Act 1994 ss 61-77, also Serious Organised Crime and Police Act 2005 s 128.
- DPP v Bayer [2003] EWHC 2567
- On injunctions, see NWL Ltd v Woods [1979] ICR 867, 881, Lord Diplock, stating the test concerns ‘the degree of likelihood the plaintiff would have succeeded in establishing his right to an injunction if the action had gone to trial, is a factor to be brought into the balance.’ AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) chs 18, 501, where human rights are at stake, HRA 1998 s 12 means that ‘courts ought to give more weight to the respondent’s defence than might otherwise have been the case.’
- Public Order Act 1986 s 1, with up to 10 years prison. The famous Riot Act 1714 is now repealed, and the Seditious Meetings Act 1817, which allowed police to disperse meetings lapsed. The Riot Compensation Act 2016 entitles victims who suffer damage from rioting to compensation for uninsured property.
- Public Order Act 1986 s 4
- Public Order Act 1986 s 4A-5
- Brutus v Cozens [1973] AC 854
- R v Horseferry Road Magistrate, ex p Siadatan [1991] 1 QB 260
- Oxford University v Broughton [2004] EWHC 2543, injunctions against animal rights activists.
- Alexander v Smith 1984 SLT 176
- Hammond v Director of Public Prosecutions [2004] EWHC 69 (Admin)
- eg Piddington v Bates [1960] 3 All ER 660, a police officer instructed at a trade dispute in a North London factory there should only be two pickets at each entrance. The appellant insisted on joining, and was arrested for obstruction. Divisional Court upheld the conviction, the restriction to 2 pickets was not unlawful and arbitrary. Lord Parker CJ, ‘a police officer charged with the duty of preserving the Queen’s peace must be left to take such steps as, on the evidence before him, he thinks are proper.’ Moss v McLachlan [1985] IRLR 76, defendants were stopped at a motorway exit, suspected of travelling to attend a picket at a colliery. They refused to go back and were arrested for obstructing a police officer. Skinner J upheld convictions, saying provided officers ‘honestly and reasonably form the opinion that there is a real risk of a breach of the peace in the sense that it is in close proximity both in place and time, then the conditions exist for reasonable preventive action including, if necessary, the measures taken in this case.’
- [2006] UKHL 55
- R (Hicks) v Metropolitan Police Commissioner [2017] UKSC 9 holding arrests and release of protestors on the royal wedding day was not unlawful. Contrast AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018) 515-6.
- cf DB v PSI Chief Constable [2017] UKSC 7, [72] ‘The area of discretion available to the police was also constrained by the positive obligation to protect the appellant’s article 8 rights’.
- Senior Courts Act 1981 s 31(3)
- Civil Procedure Rules rule 54.5 claims can be made up to 'three months after the grounds to make the claim first arose', but the period can be shorter if legislation says so.
- Limitation Act 1980 ss 2 and 5. But under s 11, the period is three years for personal injury or death, under s 11A ten years for defective products, and under s 15 twelve years to recover land.
- R (Datafin) v Panel on Takeovers and Mergers [1987] QB 815
- Different books and cases categorise the grounds to review administrative discretion differently, as do different fields of law such as directors' duties in UK company law, unfair dismissal in UK labour law or implied terms in English contract law. Lord Diplock in the GCHQ case said the grounds were "illegality", "irrationality" and "procedural impropriety". A Le Sueur, M Sunkin and J Murkens, Public Law Text, Cases, and Materials (3rd edn 2016) ch 16 follows this. It is often, however, unclear how a procedural requirement of the law can be separated from substance, and it was thought that "irrationality" is too restrictive. AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2014) ch 24 now suggests substantive grounds, legitimate expectations and procedural grounds. In R (Baker) v Devon CC [1995] 1 All ER 73, 88, Sir Robin Cooke said "The administrator must act fairly, reasonably and according to law. That is the essence and the rest is mainly machinery." M Elliott and R Thomas, Public Law (3rd edn 2017) ch 12 generally follows this. Another categorisation of Lord Bingham, Rule of Law (2010), was "Ministers and public officers at all levels must exercise the powers conferred on them in good faith, fairly, for the purposes for which the powers were conferred, without exceeding the limits of such powers and not unreasonably." Contrast the Companies Act 2006 ss 171-177, codifying directors' duties.
- Ridge v Baldwin [1964] AC 40 (following law). Padfield v Minister of Agriculture [1968] AC 997 (improper purpose), R v Home Secretary ex p Venables and Thompson [1998] AC 407 (irrelevant consideration).
- Associated Provincial Picture Houses v Wednesbury Corporation [1948] 1 KB 223 (unreasonableness loosely defined); Council of Civil Service Unions v Minister for the Civil Service [1985] AC 374 (legitimate expectation rejected). R v North and East Devon Health Authority, ex p Coughlan [2001] QB 213 (legitimate expectation upheld)
- R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office [2008] UKHL 60 (independent judgement)
- Porter v Magill [2001] UKHL 67 (bias). R v Bow Street Stipendiary Magistrate, ex p Pinochet (No 2) [2000] 1 AC 119 (possibility of a conflict of interest).
- Human Rights Act 1998 ss 3–6
- Senior Courts Act 1981 s 31(1)
- In Germany, see the Administrative Procedure Act 1976, Verwaltungsverfahrensgesetz 1976, or in UK company law see the Companies Act 2006 ss 170-177 and 260-263.
- [1992] 2 AC 48
- Hazell v Hammersmith and Fulham LBC [1992] 2 AC 1
- [2010] UKSC 2
- [1969] 2 AC 147
- [1968] AC 997, upholding Lord Denning MR's dissent in the Court of Appeal.
- [1998] AC 407
- [1948] 1 KB 223
- Contrast in company law Re Smith and Fawcett Ltd [1942] Ch 304, per Lord Greene MR
- [1898] 2 QB 91, 98-100, '... unreasonable in what sense? If, for instance, they were found to be partial and unequal in their operation as between different classes; if they were manifestly unjust; if they disclosed bad faith; if they involved such oppressive or gratuitous interference with the rights of those subject to them as could find no justification in the minds of reasonable men, the Court might well say, “Parliament never intended to give authority to make such rules; they are unreasonable and ultra vires.”' here a council's bylaw prohibited playing music or singing within 50 years of a public house or highway, but this was held to be valid.
- eg R (Daly) v Secretary of State for the Home Department [2001] UKHL 26, per Lord Cooke, ‘an unfortunately retrogressive decision’ because it ‘suggested that there are degrees of unreasonableness and that only a very extreme degree can bring an administrative decision within the legitimate scope of judicial invalidation’.
- R (Alconbury Developments Ltd) v SS for Environment, Transport and the Regions [2001] UKHL 23, [51]. R (Daly) v Secretary of State for the Home Department [2001] UKHL 26, [27]-28] per Lord Steyn.
- Huang v Home Secretary [2007] UKSC 11, [13]-[22] per Lord Bingham
- Contrast Crabb v Arun DC [1975] EWCA Civ 7 and O'Neill v Phillips [1999] UKHL 24
- [2001] QB 213
- [1985] AC 374
- cf R (Corner House Research) v Director of the Serious Fraud Office [2008] UKHL 60 held that taking into account a threat of the Saudi Arabia government to not investigate allegations of fraud was lawful on the fact.
- [1971] AC 610
- [1964] AC 40
- See Wilson v Racher [1974] ICR 428, Employment Rights Act 1996 s 94, and Chhabra v West London Mental Health NHS Trust [2013] UKSC 80
- cf Tomlinson v Birmingham CC [2010] UKSC 8, applicants who argued they had a right to homeless accommodation under the Housing Act 1996 s 193(5), and never received letters rejecting them, had violated the right to a fair trial in determination of their 'civil rights' in ECHR article 6. The Supreme Court held that no 'civil rights' were at stake because benefits in kind were not a right that an applicant held, rather than a right that depended upon a public body's evaluation.
- Dimes v Grand Junction Canal (1852) 3 HLC 759, the parties may, however, consent. Also R v Mulvihill [1990] 1 WLR 438, and contrast a controversial decision in R (United Cabbies Group (London) Ltd) v Westminster Magistrates' Court [2019] EWHC 409 (Admin) finding that a judge's husband doing consulting work for a firm, which had Uber as a client, posed no actual or potential conflict of interest.
- See Keech v Sandford EWHC Ch J76 following the disgrace of Lord Macclesfield in the South Sea Bubble.
- [2000] 1 AC 119, 139
- R (McCarthy) v Sussex Justices [1924] 1 KB 256, per Lord Hewart
- [2001] UKHL 67
- Dr Bentley’s Case (1723) 1 Stra 557, the right to know charges against you, and a right to reply, used in a university.
- (1863) 14 CBNS 180
- [1994] 1 AC 531
- [1994] 1 AC 531, 564-5, per Lord Mustill, ‘The giving of reasons may be inconvenient, but I can see no grounds at all why it should be against the public interest: indeed, rather the reverse. That being so, I would ask simply: Is refusal to give reasons fair? I would answer without hesitation that it is not.
- Breen v AEU [1971] 2 QB 175, 191, Lord Denning MR.
- eg Hadjianastassiou v Greece (1992) 16 EHRR 219.
- e.g. Seaford Court Estates Ltd v Asher [1949] 2 KB 481, 498-499, Denning LJ, a judge ‘must set to work on the constructive task of finding the intention of Parliament, and he must do this not only from the language of the statute, but also from a consideration of the social conditions which gave rise to it, and of the mischief which it was passed to remedy, and then he must supplement the written word so as to give “force and life” to the intention of the legislature.’ Ahmad v Inner London Education Authority [1978] QB 38, Lord Denning MR, 'The convention is not part of our English law, but, as I have often said, we will always have regard to it. We will do our best to see that our decisions are in conformity with it.' Congreve v Home Office [1976] QB 69 (need for judiciary to control any executive's abuse of power). 'The convention is not part of our English law, but, as I have often said, we will always have regard to it. We will do our best to see that our decisions are in conformity with it.'
- e.g. Hounga v Allen [2014] UKSC 47, interpreting the common law illegality doctrine according to the Palermo Protocol. FHR European Ventures LLP v Cedar Capital Partners LLC [2014] UKSC 45, [42] referring to the United Nations Convention against Corruption 2003 in interpreting remedies for breach of fiduciary duty. The Christian Institute v Lord Advocate [2016] UKSC 51, [72]-[73], ' As is well known, it is proper to look to international instruments... as aids to the interpretation of the ECHR', going on to examine the UNCRC, the UDHR and the ICCPR. cf R (SG) v SS for Work and Pensions [2015] UKSC 16, Lord Kerr, dissenting, at [247]-[257] arguing the dualist theory of international law should be abandoned, and international law should be directly effective in UK law.
- Human Rights Act 1998 s 3 and Sch 1 lists provisions of the ECHR to be followed.
- Rent Act 1977 Sch 1, para 2(2)
- [2004] UKHL 30, [50] per Lord Steyn.
- HRA 1998 s 10(2)
- [2003] UKHL 21. See also, R (Wright) v Secretary of State for Health [2009] UKHL 3, [39] per Baroness Hale, ‘It is not for us to attempt to rewrite the legislation.’ Here a nurse could not be suspended under the Care Standards Act 2000 s 82(4) without a hearing compatibly with ECHR article 6, leading to a declaration of incompatibility.
- HRA 1998 s 8
- eg in the European Social Charter 1961 and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights 1966
- [2001] UKHL 26, [18]-[19] and [23] per Lord Bingham.
- Huang v Home Secretary [2007] UKSC 11, [19] noting that proportionality analysis involves 'the need to balance the interests of society with those of individuals and groups... [and] should never be overlooked or discounted'.
- Limitation Act 1980 ss 2 and 4
- Civil Procedure Rules, rule 54.5(1)(b). This was six months before 1977. See further R (Burkett) v Hammersmith and Fulham LBC [2002] UKHL 23 time begins running when a formal decision is made by a public body, not when such a body resolves to make a decision. cf R (Wilson) v Prime Minister [2019] EWCA Civ 304 (on time to bring a claim where conduct is concealed and fraudulent).
- [1983] UKHL 1, [1983] 2 AC 237
- Senior Courts Act 1981 s 31
- [1982] AC 617, 633
- R v Secretary of State for the Environment, ex p Rose Theatre Trust Co Ltd [1990] 1 QB 504
- R v Inspectorate of Pollution, ex p Greenpeace Ltd (No 2) [1994] 4 All ER 329, Otton J, classing 'the applicants as eminently respectable and responsible in their genuine interest in the issues raised', and referring to the fact that if Greenpeace were denied standing, a less organised group could claim which could stretch a court's resources.
- R v Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs, ex p World Development Movement [1995] 1 WLR 386
- R (Equal Opportunities Commission) v Secretary of State for Employment [1995] 1 AC 1
- [2019] UKSC 22, Lord Carnwath, Lady Hale, Lord Kerr, Lord Lloyd-Jones holding that ouster clause applied only to a legally valid decision relating to jurisdiction. Lord Sumption, Lord Reed, Lord Wilson dissented. See also R (Cart) v The Upper Tribunal [2011] UKSC 28.
- [1987] QB 815
- R v Disciplinary Committee of the Jockey Club, ex p Aga Khan [1992] EWCA Civ 7, [1993] 1 WLR 909
- Aston Cantlow Parochial Church Council v Wallbank [2003] UKHL 37
- [2007] UKHL 27. YL claimed the company violated her right to a home under ECHR article 8 by giving her just 28 days notice to leave after a disagreement.
- Health and Social Care Act 2008 s 145
- [2009] EWCA Civ 587, per Elias LJ.
- See R (Khawaja) v Home Secretary [1984] AC 74 and Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs v Rahmatullah [2012] UKSC 48
- [1982] 1 WLR 1155
- cf Duncan v Cammell Laird & Co [1942] AC 624
References
- Articles
- V Bogdanor, T Khaitan and S Vogenauer, 'Should Britain have a written constitution?' (2007) 78(4) Political Quarterly 499
- KD Ewing, 'The Resilience of the Political Constitution' (2013) 14(12) German Law Journal 2111
- JAW Griffith, 'The Political Constitution' (1979) 42(1) Modern Law Review 1
- F Kessler, 'Natural Law, Justice and Democracy—Some Reflections on Three Types of Thinking About Law and Justice' (1944) 19 Tulane Law Review 32
- Lord Hoffmann, (2013) 17 Oxford Law News 8-9, from a tribute at St John's Smith Square on 5 June 2013
- O Kahn-Freund, 'Autobiographical Memories of the Weimar Republic: A Conversation with Wolfgang Luthardt' (February 1978) KCL Law School Research Paper No. 2016-34
- J Laws, 'Law and Democracy' [1995] Public Law 72
- E McGaughey, 'Fascism-lite in America (or the Social Ideal of Donald Trump)' (2018) British Journal of American Legal Studies
- S Webb, 'Socialism: true and false. A lecture delivered to the Fabian Society' (21 January 1894) Fabian Tract, 51
- S Webb, 'The reform of the House of Lords' (1917) Fabian Tract, 183
- Books
- W Bagehot, The English Constitution (1867)
- Lord Bingham, Rule of Law (2010)
- AV Dicey, Introduction to the Study of the Law of the Constitution (3rd edn 1889)
- J Froissart, Froissart's Chronicles (1385) translated by GC Macaulay (1895)
- I Jennings, A Federation for Western Europe (1940)
- J Locke, Two Treatises of Government (1689) Book II, An Essay Concerning the True Origin, Extent, and End of Civil Government]
- FW Maitland, The Constitutional History of England (CUP 1919)
- JS Mill, On Liberty (1859)
- JS Mill, Considerations on Representative Government (1861)
- T More, Utopia (1516) translated by Gilbert Burnet (1901)
- FL Neumann, Behemoth: The Structure and Practice of National Socialism, 1933-1944 (1944)
- FL Neumann, The Democratic and the Authoritarian State: Essays in Political and Legal Theory (1957)
- S Webb and B Webb, Industrial Democracy (1890)
- S Webb, English Local Government (1906 through 1929) Volumes I–X
- Textbooks
- AW Bradley, KD Ewing and CJS Knight, Constitutional and Administrative Law (2018)
- H Kelsen, Principles of International Law (1952)
- A Le Sueur, M Sunkin and J Murkens, Public Law Text, Cases, and Materials (3rd edn 2016)
- M Elliott and R Thomas, Public Law (3rd edn 2017)