Ofcom
The Office of Communications (Welsh: Y Swyddfa Gyfathrebiadau), commonly known as Ofcom, is the government-approved regulatory and competition authority for the broadcasting, telecommunications and postal industries of the United Kingdom.
 | |
 Ofcom offices at Riverside House, Bankside, next to Southwark Bridge in London | |
| Abbreviation | Ofcom |
|---|---|
| Formation | 29 December 2003 |
| Type | Statutory corporation |
| Legal status | Created by Office of Communications Act 2002[1] |
| Purpose | Regulator and competition authority for broadcasting, postal services, telecommunications and radiocommunications spectrum |
| Headquarters | London, England |
| Location |
|
Region served | United Kingdom |
Official language | English, Welsh |
Chairman | Lord Burns |
Chief Executive | Melanie Dawes |
Main organ | Board of Directors |
| Website | ofcom |
Ofcom has wide-ranging powers across the television, radio, telecoms and postal sectors. It has a statutory duty to represent the interests of citizens and consumers by promoting competition and protecting the public from harmful or offensive material.[2][3]
Some of the main areas Ofcom presides over are licensing, research, codes and policies, complaints, competition and protecting the radio spectrum from abuse (e.g. pirate radio stations).
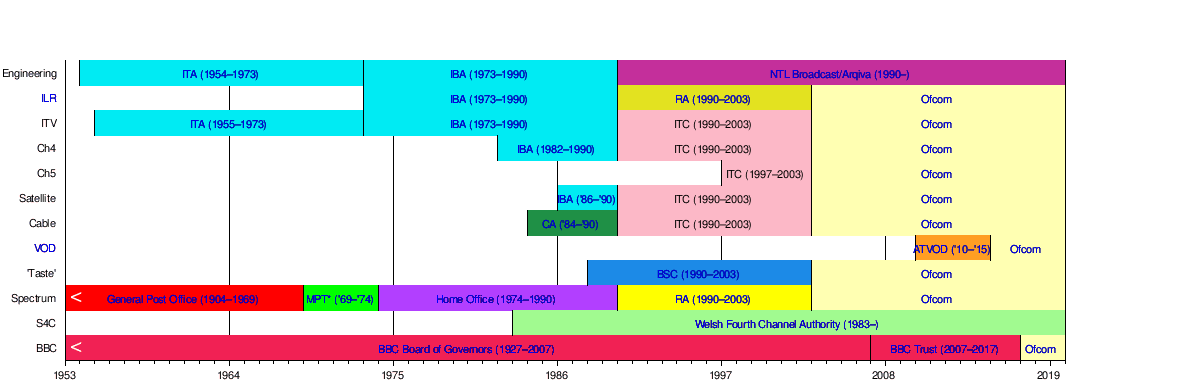
The regulator was initially established by the Office of Communications Act 2002 and received its full authority from the Communications Act 2003.[1]
History
The creation of Ofcom was announced in the Queen's Speech to the UK Parliament, in June 2001. The new body, which would replace several existing authorities, was conceived as a "super-regulator" to oversee media channels that were rapidly converging through digital transmission.[4] Ofcom launched on 29 December 2003, formally inheriting the duties that had previously been the responsibility of five different regulators:[5]
- the Broadcasting Standards Commission
- the Independent Television Commission
- the Office of Telecommunications (Oftel)
- the Radio Authority
- the Radiocommunications Agency
In July 2009, Conservative party opposition leader David Cameron said in a speech against the proliferation of quangos that:
With a Conservative government, Ofcom as we know it will cease to exist… Its remit will be restricted to its narrow technical and enforcement roles. It will no longer play a role in making policy. And the policy-making functions it has today will be transferred back fully to the Department for Culture, Media and Sport.[6][7]
Under Cameron's subsequent premiership of the 2010 UK coalition government, the Public Bodies Act 2011 did remove or modify several of Ofcom's duties, although it did not substantially reduce Ofcom's remit.[8]
On 1 October 2011, Ofcom took over responsibility for regulating the postal services industry from the Postal Services Commission (Postcomm).
In April 2015, Ofcom announced that telephone companies would have to provide customers with a set charge for the cost of calling numbers starting 084, 087 and 09. The streamlining of these charges must be printed in each customer's contract and monthly bills. The change came into force on 1 July 2015 and affected over 175 million phone numbers, making it the biggest overhaul of telephoning in over a decade.[9]
On 1 January 2016, the regulation of video on demand was transferred to Ofcom from ATVOD, the Authority for Television on Demand.[10]
The Digital Economy Act 2017 extended Ofcom's remit and powers. Ofcom were given powers concerning the minimum broadband speed provided by Internet service providers, the ability to financially penalise communications providers for failing to comply with licence commitments and the power to require public service broadcasters to include a minimum quantity of children's programming made in the United Kingdom. The act also transferred to Ofcom the regulation of the BBC, a duty previously undertaken by the BBC Trust,[11][12] and updated the Ofcom Electronic Communications Code to make it easier for telecommunications companies to erect and extend mobile masts.[13]
Following a consultation over the Online Harms White Paper published by the UK government in April 2019, the government announced in February 2020 that it intended Ofcom to have a greater role in Internet regulation to protect users from "harmful and illegal content".[14]
News International phone hacking scandal
In July 2011, in the wake of the News International phone hacking scandal, Ofcom came under pressure to launch an inquiry into whether the parent company of News International, News Corporation, was still the "fit and proper" owner of a controlling stake in the satellite broadcasting company British Sky Broadcasting (BSkyB). On 13 July former Prime Minister Gordon Brown urged Ofcom to launch an investigation.[15][16] On 15 July the Deputy Prime Minister Nick Clegg stated that the Government would launch a review of laws on what constituted a "fit and proper" owner for broadcasting companies in the United Kingdom, and that anyone found not to meet that standard can be forced to give up their current holdings in a company.[17]
On 22 July 2011, it was reported that Ofcom had begun an investigation into whether the phone-hacking scandal may have changed BSkyB's status as the "fit and proper" holder of a UK broadcasting licence.[18] On the same day Ed Richards, the then chief executive of Ofcom, replied to Simon Hughes MP, Don Foster MP and Tim Farron MP following a letter which they had written to him on 8 July concerning News Corporation's shareholding in BSkyB.[19] In the letter Richards confirmed that Ofcom considers that News Corporation's current shareholding of 39.14% in BSkyB does give it a material influence over the company; that Ofcom is not precluded from acting by ongoing police investigations; and that Ofcom's process is not dependent upon a criminal conviction being secured.[19]
In April 2012, Ofcom's probe moved from a monitoring phase to an "evidence gathering" phase.[20]
Activities
Television and radio
Ofcom licenses all UK commercial television and radio services in the UK. Broadcasters must comply by the terms of their licence, or risk having it revoked. Ofcom also publishes the Broadcasting Code, a series of rules which all broadcast content on television and radio must follow.[22] The Broadcasting Code requires that content inappropriate for children should not be broadcast between the hours of 5:30 a.m. and 9:00 p.m. Premium-rate film services may broadcast content equivalent to a BBFC 15 certificate at any time of day provided a PIN-protected system is in place to restrict access to those authorised to view it.[23] The broadcasting of pornography with a BBFC R18 certificate is not permitted.[24] In 2010 Ofcom revoked the licences of four free-to-air television channels for promoting adult chat services during daytime hours and transmitting content that was too sexually explicit. The companies involved were fined £157,250.[25] Ofcom's jurisdiction does not cover television and radio channels which are broadcast in the UK but licensed abroad. In 2012 Ofcom lodged a complaint with the Dutch media regulator regarding the content of adult chat television channels which are broadcast in the UK but licensed in the Netherlands.[26] Based on a survey of 200 British respondents, Ofcom published in 2016 a list of about 50 words classified in four grades of offensiveness, from "milder" to "strongest."[27]
Telephone and broadband
Ofcom regulates the UK telecoms sector, defining and enforcing the conditions by which all mobile and fixed-line phone and broadband companies must abide. These 'general conditions' are wide-ranging rules relating to matters such as telephone numbering, emergency services, sales, marketing and interconnection standards. Ofcom's investigation unit monitors compliance with the conditions and resolves disputes between providers.
Ofcom is also the competition authority for telecoms, enforcing remedies in markets where it believes dominant operators may have a potentially harmful influence on competition or consumers. One of its most high-profile interventions was to require BT to split its wholesale and retail arms into separate companies, bringing about the creation of Openreach which supplies wholesale services to both BT Retail and competing providers.[28]
On 1 July 2015, Ofcom made a number of changes to the way phone calls to UK service numbers would be charged. Under the new legislation, which was promoted by an information campaign entitled UK Calling,[29] call charges must be clearly stated on all materials that advertise a service number. The changes came after research found that callers are often confused about service call charges, and thus can avoid calling these numbers. The July 2015 changes also saw 'freephone numbers' 0800 and 0808 become free to call from both mobiles and landlines.[30]
In March 2016, Ofcom launched an interactive "Mobile coverage and fixed broadband checker",[31] allowing people to check mobile coverage and broadband speeds via their post code.
Spectrum licensing and protection
Ofcom is responsible for the management, regulation, assignment and licensing of the electromagnetic spectrum in the UK, and licenses portions of it for use in television and radio broadcasts, mobile phone transmissions, private communications networks, wireless devices and so on. The process of licensing varies depending on the type of use required. Some licences simply have to be applied and paid for, other commercial licences are subject to a bidding process. Most of the procedures in place have been inherited from the systems used by the previous regulators. However, Ofcom may change some of these processes in future.
Ofcom protects the radio spectrum in a number of ways:
- Working within international organisations (ITU, CEPT and BEREC).
- Licensing UK-controlled commercial radio spectrum; the Ministry of Defence controls its own spectrum. Within the international framework for frequency use; Ofcom liaises through the UK Government to produce the UKFAT (UK Frequency Allocation Table). The current table was produced in 2017.
- Investigate and, when necessary, carry out enforcement activities to clear interference or illegal use from the spectrum. Until June 2010 Ofcom investigated all interference cases within the UK. Interference reporting has now been transferred to the BBC. This contract specifically excludes any requirement to investigate interference relating to AM radio reception.[32] Commercial and spectrum licence holders report to Ofcom and in all cases illegal ("pirate") radio operations are still reported to Ofcom.
Postal services
In October 2010 the government announced plans for Ofcom to inherit the functions of Postcomm as part of a wider set of public service sell-off measures.[33] Following the Postal Services Act 2011 regulatory responsibility for postal services transferred to Ofcom on 1 October 2011, with its primary duty to maintain the UK's six-day-a-week universal postal service.
Consultations
Ofcom makes extensive use of consultations with industry and the public to help it make decisions based upon the evidence presented. Consultation processes begin with publishing documents on its website,[34] asking for views and responses. If the document is perceived to be long and complicated, a plain English summary is usually published as well. A period, usually of 10 weeks, is allowed for interested persons, companies or organisations to send in their responses to the consultation.
After this consultation period, Ofcom publishes all the responses on its website, excluding any personal or confidential information. Ofcom then prepares a summary of the responses received, and uses this information as a basis for its decisions.[35]
Leadership
Current
Lord (Terry) Burns was appointed as chairman of Ofcom for a four-year term from 1 January 2018.[36]
The current Chief Executive is Melanie Dawes who was appointed on 12 February 2020.[37]
Historical
The first chairman of Ofcom (2002–2009) was David Currie, Dean of Cass Business School at City University and a life peer under the title Lord Currie of Marylebone. The first chief executive (2003–2007) was Stephen Carter, Baron Carter of Barnes, formerly a senior executive of JWT UK and NTL and subsequently a Minister for Communications, Technology and Broadcasting.[38]
Colette Bowe was appointed Ofcom chairman with effect from 11 March 2009.[39][40][41] She was the founding chairman of the Telecoms Ombudsman Council, and chaired Ofcom's Consumer Panel from its inception in 2003 to December 2007.
Dame Patricia Hodgson DBE was appointed as chairman of Ofcom for a three-year term from April 2014. She was a member of the Ofcom board from July 2011 and became deputy chairman in January 2012.[42] On 18 July 2016 it was announced that her term would be extended for a further year until 2018.[43]
Sharon White was Ofcom's chief executive from 2015 to 2019, having replaced Ed Richards in the role.[44]
After Sharon White was appointed the Chief Executive of John Lewis in June 2019[45], the office of Chief Executive remained open until Jonathan Oxley was appointed as Interim Chief Executive.[46] In February 2020 it was announced that Melanie Dawes would become the new Chief Executive.[47]
On 15 March 2016 it was announced that Steve Gettings would become Corporation Secretary in succession to Graham Howell.[48]
Key personnel
Ofcom's key personnel are:[49]
- Chief Executive, Melanie Dawes, appointed February 2020
- Board members:
- Maggie Carver, Deputy Chair, appointed September 2018
- Jonathan Oxley, appointed January 2015
- Graham Mather, appointed June 2014
- Ben Verwaayen, appointed January 2016
- Tim Suter, appointed September 2017[50]
- Bob Downes, appointed February 2018
- Angela Dean, appointed September 2018
- David Jones, appointed April 2019
Ofcom publishes a register of disclosable interests of the Ofcom board.[51]
Ofcom committees
Ofcom has a number of committees and advisory bodies which inform the Ofcom Board and Executive. These include:[52]
- Communications Consumer Panel (CCP)
- Advisory Committee for Older and Disabled People (ACOD)
- Risk and Audit Committee
- Nominations Committee
- Remuneration Committee
- Election Committee
- Non-Executive Remuneration Committee
- Nations Committee
- Advisory Committee for England
- Advisory Committee for Northern Ireland
- Advisory Committee for Scotland
- Advisory Committee for Wales
- Community Radio Fund Panel
- Ofcom Spectrum Advisory Board (OSAB)
- Broadcast Licensing Committee
Controversies
Expenditure
Ofcom has received criticism for incurring unnecessary costs as a result of "extravagant Thames-side offices" and a "top-heavy salary bill",[53] for inflexibility in its regulation of commercial radio,[54] and for "poor service".[55] In response to ongoing expenditure concerns, Ofcom made the following statement regarding the 2017/2018 budget: "Ofcom has delivered 12 consecutive years of like-for-like real-terms budget reductions, and we will continue to reduce spending wherever we can."[56]
Al Jazeera
The Qatar-based newsmedia outlet was reported[57] to Ofcom in January 2017, following an exposé about Israeli diplomatic[58] corp irregularities and influence peddling amongst political and student groups in the UK. After investigations exceeding eight months, Ofcom reported that Al Jazeera was in line with journalism standards and cleared the filmmakers of the allegations.[59]
Press TV
In May 2011, Ofcom ruled that Press TV, an Iranian English-language satellite channel, was responsible for a serious breach of UK broadcasting rules and could face a fine for airing an interview with Maziar Bahari, the Newsweek journalist arrested covering the Iranian presidential election in 2009, that was obtained by force while he was held in a Tehran jail.[60]
Upon the release of Ofcom's findings, Press TV claimed that Maziar Bahari was "an MI6 contact person"[61] taking guidance from "The Protocols of the Learned Elders of Zion, protocol No. 7".[62] Press TV called Ofcom's ruling "part of an anti-Iranian campaign," and that "A quick look at senior decision makers at OFCOM demonstrates that the regulator is mostly made up of former Channel 4 and BBC executives, some of whom are well-linked to and influenced by powerful pro-Israeli politicians."[63][64]
Sitefinder database and freedom of information
The Sitefinder database is a national database of mobile phone base stations in the UK.[65] In September 2007 an Information Tribunal ruled that the public should have access to the database under the Freedom of Information Act 2000.[66] However, as Ofcom has no legal power to force mobile phone operators to add information to the database, UK mobile phone operators consequently ceased updating it.[28] Ofcom appealed against the Freedom of Information Act ruling, together with one UK mobile operator – T-Mobile.[67] This has led to accusations of the organisation's complicity with the mobile telecommunications industry in keeping information about mast locations secret.[68] Ofcom's stated reasons for the appeal have ranged from "preventing terrorist attacks" on the sites of phone masts to "protecting the intellectual property" of the mobile telecommunications industry.[67]
In April 2008, the High Court found in favour of the Information Commissioner's Office and over-ruled Ofcom's objections. Ofcom appealed to the Supreme Court, who in turn referred a point of law to the European Court of Justice, and then in October 2011 ordered that the matter should be remitted to the Information Rights Tribunal to reconsider the public interest balancing exercise.[69] On 12 December 2012, the Information Rights Tribunal upheld its decision of 4 September 2007.[70]
Deryn Consulting controversy
In 2017 Ofcom’s advisory committee for Wales awarded Deryn Consulting a contract to monitor the National Assembly for Wales and Welsh Government. It was subsequently reported that the contract had not been put out to tender and that Huw Roberts and Nerys Evans held positions for both Deryn and Ofcom.[71][72] The contract was terminated[73] and Ofcom concluded that it had broken its own procurement rules.[74]
See also
- Advertising Standards Authority
- Annan Committee, that in 1977 recommended the establishment of a Broadcasting Complaints Commission
- BOCRA
- Broadband stakeholder group
- Office of Fair Trading
- Press Complaints Commission
- ATVOD
- ITSPA
- ISPA
- Commonwealth Telecommunications Organisation (CTO)
- International Telecommunication Union
- List of telecommunications regulatory bodies
References
- "Office of Communications Act 2002 – 2002 CHAPTER 11". Office of Public Sector Information. 19 March 2002. Retrieved 23 February 2010.
- "Your rights – Ofcom". The Liberty Guide to Human Rights. Liberty. 12 August 2010. Archived from the original on 11 January 2014. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- Lunt, Peter; Livingstone, Sonia (2007). "Regulating markets in the interest of consumers?: on the changing regime of governance in the financial service and communications sectors.". Governance, consumers and citizens: agency and resistance in contemporary politics (PDF). Basingstoke, UK: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 139–161. Retrieved 11 January 2014. Footnote 15.
- "Queen announces media shake-up". BBC News. 20 June 2001.
- "'Super-regulator' Ofcom launches". BBC News. 29 December 2003.
- Chris Williams (6 July 2009). "Ofcom top of Tory deathlist – Quangogeddon". The Register. Retrieved 23 February 2010.
- Leigh Holmwood (6 July 2009). "Ofcom hits back at David Cameron". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- "Ofcom". Politics.co.uk.
- "Ofcom cracks down on hidden charges in TV phone-ins". The Daily Telegraph. 27 April 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- Jasper Jackson (14 October 2015). "Ofcom to take on regulation of video-on-demand services". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- Jamie Rigg (3 May 2017). "How the Digital Economy Act will come between you and porn". engadget. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- "Digital Economy Bill: Networks and porn sites face fines". BBC News. 6 July 2016. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- Paul Carter (18 October 2016). "Small cells and 5G: What the Digital Economy Bill changes mean for operators". Telecoms Tech. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- Alex Hern; Jim Waterson (12 February 2020). "Ofcom to be put in charge of regulating internet in UK". The Guardian.
- "Brown Urges Ofcom to Probe News Corp.'s Existing BSkyB Stake". San Francisco Chronicle. 13 July 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- Hutton, Robert (14 July 2011). "Brown Calls on Regulator to Probe News Corp.'s Existing BSkyB Shareholding". Bloomberg L.P. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- Kirkup, James (15 July 2011). "Phone Hacking: Murdoch's grip on BSkyB may be threatened, warns Clegg". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- "UK regulator begins probe into BSkyB's status". Financial Times. 22 July 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- "Letter to Simon Hughes, Don Foster and Tim Farron MP from Ed Richards July 22, 2011". Ofcom. Archived from the original on 20 September 2011. Retrieved 25 July 2011.
- Katherine Rushton Ofcom steps up 'fit and proper' probe into BSkyB, The Daily Telegraph. 26 April 2012
- "Regulator archives". Ofcom. 24 June 2010.
- "Ofcom broadcasting". Ofcom.
- "Appendix 3: International Comparison of Classification and Content Regulation – The United Kingdom". Australian Law Reform Commission. 1 March 2012. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- Joe Lepper (25 May 2005). "Ofcom to consider product placement on TV and radio". Brand Republic. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- "Adult TV channels become first to lose licences". BBC News. 26 November 2010. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- Del Crookes (8 March 2012). "Ofcom lodges porn TV complaint with Dutch regulator". BBC newsbeat. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- Will Butler (3 October 2016). "Ofcom Have Officially Ranked Every British Swear Word". Look Magazine.
- "Overview of UK telecommunications regulation". Chartered Institute for IT.
- "UK Calling". Ofcom.
- burton, Tony. "July number Change". 0345 Numbers.
- "Mobile coverage and fixed broadband checker". maps.ofcom.org.uk. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- "About Us". Radio & Television Investigation Service. 8 April 2013.
- Tim Bradshaw (21 October 2010). "Ofcom to cut staff by a fifth". Financial Times.
- "List of Ofcom consultations". Stakeholders.ofcom.org.uk. 24 May 2010. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- "Ofcom – Official Website – Homepage".
- "Lord (Terry) Burns". DCMS. 13 December 2017.
- "Ofcom Selects Melanie Dawes As Chief Executive". The Guardian. 12 February 2020.
- "Lord Carter of Barnes". Department for Business, Information and Skills. 6 November 2009. Archived from the original on 14 July 2009. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- "Colette Bowe". Ofcom. Archived from the original on 30 April 2012. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- Colette Bowe Institute of Competition Law. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- Sweney, Mark (17 December 2008). "Colette Bowe appointed as Ofcom chair". The Guardian. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- "Dame Patricia Hodgson DBE". Ofcom. 1 February 2012. Archived from the original on 21 April 2014. Retrieved 20 April 2014.
- "Dame Patricia Hodgson to remain Ofcom Chairman until 2018". Ofcom. Retrieved 22 May 2017.
- "Ofcom Board appoints Sharon White as Chief Executive". Ofcom. 16 December 2014.
- "Sharon White Leaves Ofcom to Join John Lewis Partnership". The Guardian. 6 June 2019.
- "Jonathan Oxley Appointed Interim Chief Executive". Ofcom. 12 February 2020.
- "Ofcom Selects Melanie Dawes As Chief Executive". The Guardian. 12 February 2020.
- "Note of the 225th Meeting of the Ofcom Board, held on 15 March 2016" (PDF). Ofcom. 22 March 2016.
- "Ofcom Board". Ofcom. 25 June 2010. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- "New Ofcom board member appointed". Ofcom. 29 September 2017. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- "Register of disclosable interests". Ofcom. Retrieved 22 May 2017.
- "Ofcom committees". Ofcom. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- David Rowan (31 December 2003). "Interview: Stephen Carter & David Currie, Ofcom (Evening Standard)". davidrowan.com. Archived from the original on 13 October 2008.
- Plunkett, John (5 June 2007). "Ofcom accused of 'Nero approach'". The Guardian. London.
- "Poor Service from OFCOM". Letsfixbritain.com. Archived from the original on 3 November 2004. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- "Ofcom confirms priorities for 2017/18". ofcom.org.uk. 30 March 2017.
- "Israel moves against Al Jazeera". BBC News. 6 August 2017. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- Lizzie Dearden (12 January 2017). "Israeli embassy official caught discussing 'take down' of pro-Palestinian MPs quits". The Independent. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- Ruddick, Graham (9 October 2017). "Ofcom clears al-Jazeera of antisemitism in exposé of Israeli official". The Guardian. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- Sweney, Mark (23 May 2011). "Iran's Press TV censured for interview with arrested journalist". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- "PressTV – A British game against PressTV". Press TV. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2012.
- "PressTV – Empire continues to sweat over Press TV". Press TV. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2012.
- "PressTV – OfCom, UK Office of Miscommunication". Press TV. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2012.
- "PressTV – The OFCOM sitcom". Press TV. Archived from the original on 18 October 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2012.
- "Ofcom | Frequently Asked Questions". Stakeholders.ofcom.org.uk. 21 June 2010. Retrieved 20 April 2014.
- "Data row hits mobile mast website". Technology. BBC News. 2 October 2007. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
- Bill Ray (13 September 2007). "Ofcom fails to prevent release of cell locations – But operators might not play ball". Networks. Retrieved 23 February 2010.
- Geoffrey Lean, Environment Editor (27 May 2007). "Phone mast locations kept from public". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 21 December 2008. Retrieved 23 February 2010.
- "Sitefinder: Frequently Asked Questions". Ofcom. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
- "EIR Exemptions and Aggregation : a round trip". Panopticon Blog. 17 December 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2014.
- Private Eye, March 9th, 2018. p13.
- Martin Shipton (24 February 2017). "Ofcom Wales under fire after contract awarded to insiders' company". Wales Online.
- Martin Shipton (21 August 2017). "A controversial contract awarded by Ofcom to a Welsh lobbying firm has been terminated". Wales Online.
- Martin Shipton (23 October 2017). "Ofcom admits it broke its own rules in giving contract to lobbying firm run by its own advisors". Wales Online.
External links
| Preceded by BBC Trust |
Regulation of BBC 1 January 2017–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Independent Television Commission |
Regulation of ITV 29 December 2003–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Independent Television Commission |
Regulation of Channel 4 29 December 2003–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Independent Television Commission |
Regulation of Satellite Television 29 December 2003–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Independent Television Commission |
Regulation of Cable Television 29 December 2003–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Radio Authority |
Regulation of Independent Local Radio 29 December 2003–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Radiocommunications Agency |
Regulation of use of the Radio Spectrum 29 December 2003–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Broadcasting Standards Commission |
Monitoring of 'Taste and Decency' 29 December 2003–present |
Succeeded by Current |
| Preceded by Postal Services Commission |
Regulation of Postal services 1 October 2011–present |
Succeeded by Current |