Geography of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a partially recognized country in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, known historically in English as Formosa, makes up 99% of the area controlled by the ROC, measuring 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi) and lying some 180 kilometres (112 mi) across the Taiwan Strait from the southeastern coast of mainland China. The East China Sea lies to its north, the Philippine Sea to its east, the Luzon Strait directly to its south and the South China Sea to its southwest. Smaller islands include a number in the Taiwan Strait including the Penghu archipelago, the Kinmen and Matsu Islands near the Chinese coast, and some of the South China Sea Islands.
 Taiwan is mostly mountainous in the east, with gently sloping plains in the west. The Penghu Islands appear in the Taiwan Strait to the west of the main island. | |
.svg.png) | |
| Region | East Asia |
|---|---|
| Area | Ranked 139[1] |
| • Total | 35,980 km2 (13,890 sq mi) |
| • Land | 89.7% |
| • Water | 10.3% |
| Coastline | 1,566.3 km (973.3 mi) |
| Highest point | Yu Shan, 3,952 m (12,966 ft) |
| Climate | tropical, marine[1] |
| Natural Resources | small deposits of coal, natural gas, limestone, marble, asbestos, arable land[1] |
| Environmental Issues | air pollution; water pollution from industrial emissions, raw sewage; contamination of drinking water; trade in endangered species; low-level radioactive waste disposal[1] |
| Exclusive economic zone | 83,231 km2 (32,136 sq mi) |
| Taiwan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 臺灣 or 台灣 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 台湾 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Taiwan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Portuguese: (Ilha) Formosa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 福爾摩沙 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 福尔摩沙 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | beautiful island | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The main island is a tilted fault block, characterized by the contrast between the eastern two-thirds, consisting mostly of five rugged mountain ranges parallel to the east coast, and the flat to gently rolling plains of the western third, where the majority of Taiwan's population reside. There are several peaks over 3,500 m, the highest being Yu Shan at 3,952 m (12,966 ft), making Taiwan the world's fourth-highest island. The tectonic boundary that formed these ranges is still active, and the island experiences many earthquakes, a few of them highly destructive. There are also many active submarine volcanoes in the Taiwan Straits.
The climate ranges from tropical in the south to subtropical in the north, and is governed by the East Asian Monsoon. The main island is struck by an average of four typhoons in each year. The eastern mountains are heavily forested and home to a diverse range of wildlife, while land use in the western and northern lowlands is intensive.
Physical boundaries
| Disputed island Other names: Formosa | |
|---|---|
 Map of the Taiwan archipelago | |
| Geography | |
| Rank | 38 |
| Length | 394 km (244.82 mi) |
| Width | 144 km (89.48 mi) |
| Administered by | |
| Province and special municipalities |
|
| Capital city | Taipei City |
| Largest city | New Taipei City (3,976,313) |
| Claimed by | |
| Province | Taiwan Province |
| Demographics | |
| Population | (as of 2017.[2]) |
| Density | 648.49[2]/km² |
| Ethnic groups | Han Taiwanese (>95%) ∟ Hoklo people (70%) ∟ Hakka people (14%) ∟ Mainland Chinese (14%)[lower-alpha 1][3] Taiwanese aborigines (2.3%) |
The total land area of Taiwan is 32,260 km2 (12,456 sq mi),[1] making it intermediate in size between Belgium and the Netherlands. It has a coastline of 1,566.3 km (973.3 mi).[1] The ROC claims an exclusive economic zone of 83,231 km2 (32,136 sq mi) with 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi) and a territorial sea of 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi).[1][4]
Taiwan proper, the main island of the archipelago, was known in the West until after World War II as Formosa, from the Portuguese Ilha Formosa ([ˌiʎɐ fuɾˈmɔzɐ]), "beautiful island".[5] It is 394 km (245 mi) long and 144 km (89 mi) wide,[6] and has an area of 35,808 km2 (13,826 sq mi).[7] The northernmost point of the island is Cape Fugui in New Taipei's Shimen District. The central point of the island is in Puli Township, Nantou County. The southernmost point on the island is Cape Eluanbi in Hengchun Township, Pingtung County.
The island of Taiwan is separated from the southeast coast of China by the Taiwan Strait, which ranges from 220 km (140 mi) at its widest point to 130 km (81 mi) at its narrowest. Part of the continental shelf, the Strait is no more than 100 m (330 ft) deep, and has become a land bridge during glacial periods.[8]
To the south, the island of Taiwan is separated from the Philippine island of Luzon by the 250 km (155 mi)-wide Luzon Strait. The South China Sea lies to the southwest, the East China Sea to the north, and the Philippine Sea to the east.[9] Niushan Island in Nanlai village, Aoqian town, Pingtan County, Fuzhou, Fujian is the closest China (PRC)-administered island to Taiwan (main island).[10]
Smaller islands of the archipelago include the Penghu islands in the Taiwan Strait 50 km (31 mi) west of the main island, with an area of 127 km2 (49 sq mi), the tiny islet of Xiaoliuqiu off the southwest coast, and Orchid Island and Green Island to the southeast, separated from the northernmost islands of the Philippines by the Bashi Channel. The islands of Kinmen and Matsu near the coast of Fujian across the Taiwan Strait have a total area of 180 km2 (69 sq mi);[11] the Pratas and Taiping islets in the South China Sea are also administered by the ROC, but are not part of the Taiwanese archipelago.
Geology
The island of Taiwan was formed approximately 4 to 5 million years ago at a complex convergent boundary between the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate. In a boundary running the length of the island and continuing southwards in the Luzon Volcanic Arc (including Green Island and Orchid Island), the Eurasian Plate is sliding under the Philippine Sea Plate.
Most of the island comprises a huge fault block tilted to the west.[12] The western part of the island, and much of the central range, consists of sedimentary deposits scraped from the descending edge of the Eurasian Plate. In the northeast of the island, and continuing eastwards in the Ryukyu Volcanic Arc, the Philippine Sea Plate slides under the Eurasian Plate.[13][14]
The tectonic boundary remains active, and Taiwan experiences 15,000 to 18,000 earthquakes each year, of which 800 to 1,000 are noticed by people. The most catastrophic recent earthquake was the magnitude-7.3 Chi-Chi earthquake, which occurred in the center of Taiwan on 21 September 1999, killing more than 2,400 people.[15] On 4 March 2010 at about 01:20 UTC, a magnitude 6.4 earthquake hit southwestern Taiwan in the mountainous area of Kaohsiung County.[16] Another major earthquake occurred on 6 February 2016, with a magnitude of 6.4. Tainan was damaged the most, with 117 deaths, most of them caused by the collapse of a 17-story apartment building.[17]
Terrain
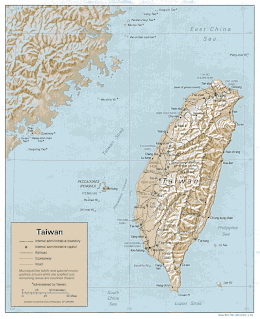
The terrain in Taiwan is divided into two parts: the flat to gently rolling plains in the west, where 90% of the population lives, and the mostly rugged forest-covered mountains in the eastern two-thirds.
The eastern part of the island is dominated by five mountain ranges, each running from north-northeast to south-southwest, roughly parallel to the east coast of the island. As a group, they extend 330 km (210 mi) from north to south and average about 80 kilometres (50 mi) from east to west. They include more than two hundred peaks with elevations of over 3,000 m (9,800 ft).[7]
The Central Mountain Range extends from Su'ao in the northeast to Eluanbi at the southern tip of the island, forming a ridge of high mountains and serving as the island's principal watershed. The mountains are predominantly composed of hard rock formations resistant to weathering and erosion, although heavy rainfall has deeply scarred the sides with gorges and sharp valleys. The relative relief of the terrain is usually extensive, and the forest-clad mountains with their extreme ruggedness are almost impenetrable. The east side of the Central Mountain Range is the steepest mountain slope in Taiwan, with fault scarps ranging in height from 120 to 1,200 m (390 to 3,900 ft). Taroko National Park, on the steep eastern side of the range, has good examples of mountainous terrain, gorges and erosion caused by a swiftly flowing river.
The East Coast Mountain Range extends down the east coast of the island from the mouth of the Hualien River in the north to Taitung County in the south, and chiefly consist of sandstone and shale. It is separated from the Central Range by the narrow Huatung Valley, at an altitude of 120 m (390 ft). Although Hsinkangshan (新港山), the highest peak, reaches an elevation of 1,682 m (5,518 ft), most of the range is composed of large hills. Small streams have developed on the flanks, but only one large river cuts across the range. Badlands are located at the western foot of the range, where the ground water level is the lowest and rock formations are the least resistant to weathering. Raised coral reefs along the east coast and the frequent occurrences of earthquakes in the rift valley indicate that the fault block is still rising.
The ranges to the west of the Central range are divided into two groups separated by the Sun Moon Lake Basin in the centre of the island. The Dadu and Zhuoshui Rivers flow from the western slopes of the Central Range through the basin to the west coast of the island.
The Xueshan Range lies to the northwest of the Central Mountain Range, beginning at Sandiaojiao, the northeast tip of the island, and gaining elevation as it extends southwest towards Nantou County. Xueshan, the main peak, is 3,886 m (12,749 ft) high.

The Yushan Range runs along the southwestern flank of the Central Range. It includes the island's tallest peak, the 3,952 m (12,966 ft) Yu Shan ('Jade Mountain')[1][18][19] which makes Taiwan the world's fourth-highest island, and is the highest point in the western Pacific region outside of the Kamchatka Peninsula, New Guinea Highlands and Mount Kinabalu.[20]
The Alishan Range lies west of the Yushan Range, across the valley of the south-flowing Kaoping River. The range has major elevations between 1,000 and 2,000 m (3,300 and 6,600 ft). The main peak, Data Mountain (大塔山), towers 2,663 m (8,737 ft).
Below the western foothills of the ranges, such as the Hsinchu Hills and the Miaoli Hills, lie raised terraces formed of material eroded from the ranges. These include the Linkou Plateau, the Taoyuan Plateau and the Dadu Plateau. About 23% of Taiwan's land area consists of fertile alluvial plains and basins watered by rivers running from the eastern mountains. Over half of this land lies in the Chianan Plain in southwest Taiwan, with lesser areas in the Pingtung Plain, Taichung Basin and Taipei Basin. The only sizable plain on the east coast is the Yilan Plain in the northeast.[21]
Climate
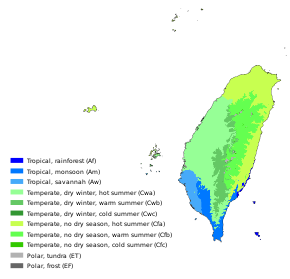
The island of Taiwan lies across the Tropic of Cancer, and its climate is influenced by the East Asian Monsoon. Northern Taiwan has a humid subtropical climate, with substantial seasonal variation of temperatures, while parts of central and most of southern has a tropical monsoon climate where seasonal temperature variations are less noticeable with temperatures typically varying from warm to hot. During the winter (November to March), the northeast experiences steady rain, while the central and southern parts of the island are mostly sunny. The summer monsoon (from May to October) accounts for 90% of the annual precipitation in the south, but only 60% in the north.[22] The average rainfall is approximately 2,600 mm per year.[22]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Typhoons are most likely to strike between July and October, with on average about four direct hits per year. Intensive rain from typhoons often leads to disastrous mudslides.[22]
Records
| Area | Max. temperature | Date | Earliest recording | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | °F | |||
| Taipei City | 39.3 | 102.7 | 8 August 2013[23] | 1896 |
| Kaohsiung City | 37.6 | 99.7 | 15 September 2014[24] | 1932 |
| Taitung County | 40.2 | 104.4 | 9 May 2004[23] | |
| Taoyuan City | 37.9 | 100.2 | 15 September 2014[25] | |
Flora and fauna
Before extensive human settlement, the vegetation on Taiwan ranged from tropical rainforest in the lowlands through temperate forests, boreal forest and alpine plants with increasing altitude.[26] Most of the plains and low-lying hills of the west and north of the island have been cleared for agricultural use since the arrival of the Chinese immigrants during the 17th and 18th century. However the mountain forests are very diverse, with several endemic species such as Formosan cypress (Chamaecyparis formosensis) and Taiwan fir (Abies kawakamii), while the camphor laurel (Cinnamomum camphora) was once also widespread at lower altitudes.

Taiwan is a center of bird endemism (see List of endemic birds of Taiwan).
Prior to the country's industrialization, the mountainous areas held several endemic animal species and subspecies, such as the Swinhoe's pheasant (Lophura swinhoii), Taiwan blue magpie (Urocissa caerulea), the Formosan sika deer (Cervus nippon taiwanensis or Cervus nippon taiouanus) and the Formosan landlocked salmon (Oncorhynchus masou formosanus). A few of these are now extinct, and many others have been designated endangered species.
Taiwan had relatively few carnivores, 11 species in total, of which the Formosan clouded leopard is likely extinct and the otter restricted to Kinmen island[27]. The largest carnivore is the Formosan black bear (Selanarctos thibetanus formosanus), a rare and endangered species.[28]
Nine national parks in Taiwan showcase the diverse terrain, flora and fauna of the archipelago. Kenting National Park on the southern tip of Taiwan contains uplifted coral reefs, moist tropical forest and marine ecosystems. Yushan National Park has alpine terrain, mountain ecology, forest types that vary with altitude, and remains of ancient road. Yangmingshan National Park has volcanic geology, hot springs, waterfalls, and forest. Taroko National Park has marble canyon, cliff, and fold mountains. Shei-Pa National Park has alpine ecosystems, geological terrain, and valley streams. Kinmen National Park has lakes, wetlands, coastal topography, flora and fauna-shaped island. Dongsha Atoll National Park has the Pratas reef atolls for integrity, a unique marine ecology, biodiversity, and is a key habitat for the marine resources of the South China Sea and Taiwan Strait.[29]
Natural resources

Natural resources on the islands include small deposits of gold, copper,[30] coal, natural gas, limestone, marble, and asbestos.[1] The island is 55% forest and woodland (mostly on the mountains) and 24% arable land (mostly on the plains), with 15% going to other purposes. 5% is permanent pasture and 1% is permanent crops.
Because of the intensive exploitation throughout Taiwan's pre-modern and modern history, the island's mineral resources (e.g. coal, gold, marble), as well as wild animal reserves (e.g. deer), have been virtually exhausted. Moreover, much of its forestry resources, especially firs were harvested during Japanese rule for the construction of shrines and have only recovered slightly since then. To this day, forests do not contribute to significant timber production mainly because of concerns about production costs and environmental regulations.
Agriculture
The few natural resources with significant economic value remaining in Taiwan are essentially agriculture-associated. Sugarcane and rice have been cultivated in western Taiwan since the 17th century. Camphor extraction and sugarcane refining played an important role in Taiwan's exportation from the late 19th century through the first half of the 20th century.[31] The importance of these industries subsequently declined not because of the exhaustion of related natural resources but mainly due to the decline of international demand.
Domestic agriculture (rice being the dominant kind of crop) and fisheries retain importance to a certain degree, but they have been greatly challenged by foreign imports since Taiwan's accession to the World Trade Organization in 2001. Consequently, upon the decline of subsistent importance, Taiwan's agriculture now relies heavily on the marketing and exportation of specialty crops, such as banana, guava, lychee, bell fruit, and high-mountain tea.[32]
Energy resources

Taiwan has significant coal deposits and some insignificant petroleum and natural gas deposits. As of 2010, oil accounts for 49.0% of the total energy consumption. Coal comes next with 32.1%, followed by nuclear energy with 8.3%, natural gas (indigenous and liquefied) with 10.2%, and energy from renewable sources with 0.5%. Taiwan has six nuclear reactors and two under construction.[33] Nearly all oil and gas for transportation and power needs must be imported, making Taiwan particularly sensitive to fluctuations in energy prices. Taiwan is rich in wind energy resources, with wind farms both onshore and offshore, though limited land area favors offshore wind resources.[34] By promoting renewable energy, Taiwan's government hopes to also aid the nascent renewable energy manufacturing industry, and develop it into an export market.
Human geography
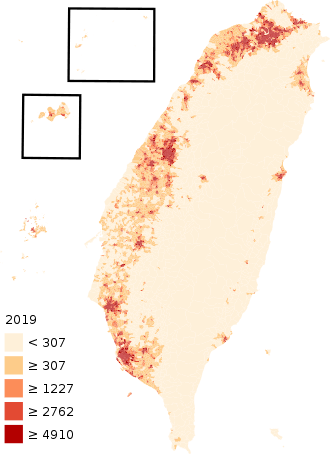
Taiwan has a population of over 23 million, the vast majority of whom live in the lowlands near the western coast of the island.[6] The island is highly urbanized, with nearly 9 million people living in the Taipei–Keelung–Taoyuan metropolitan area at the northern end, and over 2 million each in the urban areas of Kaohsiung and Taichung.[35]
Taiwanese aborigines comprise approximately 2% of the population, and now mostly live in the mountainous eastern part of the island.[36][37] Most scholars believe their ancestors arrived in Taiwan by sea between 4000 and 3000 BC, probably from the mainland.[38]
Han Chinese make up over 95% of the population.[39] Immigrants from southern Fujian began to farm the area around modern Tainan and Kaohsiung from the 17th century, later spreading across the western and northern plains and absorbing the aboriginal population of those areas. Hakka people from eastern Guangdong arrived later and settled the foothills further inland, but the rugged uplands of the eastern half of the island remained the exclusive preserve of the aborigines until the early 20th century.[40] A further 1.2 million people from throughout mainland China entered Taiwan at the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949.[41]
Environmental issues

Some areas in Taiwan with high population density and many factories are affected by heavy pollution. The most notable areas are the southern suburbs of Taipei and the western stretch from Tainan to Lin Yuan, south of Kaohsiung. By the late 20th century, Taipei suffered from extensive vehicle and factory air pollution, but after the government required mandatory use of unleaded petrol and established the Environmental Protection Administration in 1987 to regulate air quality, the air quality of Taiwan has improved dramatically.[42] Motor scooters, especially older or cheaper two-stroke versions, which are ubiquitous in Taiwan, contribute disproportionately to urban air pollution.[43][44]
Other environmental issues include water pollution from industrial emissions and raw sewage, contamination of drinking water supplies, trade in endangered species, and low-level radioactive waste disposal.[1] Though regulation of sulfate aerosol emissions from petroleum combustion is becoming stringent, acid rain remains a threat to the health of residents and forests. Atmospheric scientists in Taiwan estimate that more than half of the pollutants causing Taiwan's acid rain are carried from mainland China by monsoon winds.[45]
Notes
- Mainland Chinese on Taiwan refers to people who retreated to Taiwan from mainland China due to the Chinese Communist Revolution after 1945 and their descendants. That does not include citizens of the People's Republic of China who are living on Taiwan. Not all Mainland Chinese on Taiwan are Han people; among those who retreated to Taiwan, Pai Hsien-yung is a Hui, Xi Murong is a Mongolian, and Puru is a Manchu.
References
Citations
- "Taiwan". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- "人口統計資料" (in Chinese). Ministry of the Interior of the Republic of China. May 2018.
- Government Information Office (2009). The Republic of China Yearbook 2009 / CHAPTER 2: People and Language. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- "Law on the Exclusive Economic Zone and the Continental Shelf of the Republic of China (中華民國專屬經濟海域及大陸礁層法)". Retrieved 21 May 2007.
- "Chapter 3: History" (PDF). The Republic of China Yearbook 2011. Government Information Office, Republic of China (Taiwan). 2011. p. 46. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2012..
- "1.1 Number of Villages, Neighborhoods, Households and Resident Population". Monthly Bulletin of Interior Statistics. Ministry of the Interior, Republic of China (Taiwan). November 2012. Archived from the original (XLS) on 29 March 2014.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 40.
- Chang, K.C. (1989). translated by W. Tsao, ed. by B. Gordon. "The Neolithic Taiwan Strait" (PDF). Kaogu. 6: 541–550, 569. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 April 2012. Retrieved 30 November 2017.
- National Taiwan Normal University, Geography Department. "Geography of Taiwan: A Summary". Archived from the original on 14 December 2007. Retrieved 21 May 2007.
- 台灣海峽——平潭島東端的牛山島 (in Chinese). 13 May 2019. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
仔細研究地圖發現大陸與台灣兩地最接近的地方至少也有125海里,這個地點就是福建省平潭縣海壇島(即平潭島)東端的——牛山島。
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 46.
- Williams, Jack Francis; Chang, David (2008). Taiwan's Environmental Struggle: Toward a Green Silicon Island. Routledge. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-415-44723-2.
- "The Geology of Taiwan". Department of Geology, National Taiwan Normal University. Archived from the original on 22 February 2008.
- "Geology of Taiwan". Department of Geology, University of Arizona.
- "GSHAP Region 8: Eastern Asia". Global Seismic Hazard Assessment Program. Archived from the original on 30 May 2012. Retrieved 12 February 2012.
- Theodorou, Christine; Lee, Andrew (3 March 2010). "6.4-magnitude quake hits southern Taiwan". CNN.com. Retrieved 4 March 2010.
- Yang, Ssu-jui; Huang, Frances (18 February 2016). "Body of last victim of apartment collapse in Tainan found". Focus Taiwan.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 43.
- Reported by Taiwan's National Geographic Information System Steering Committee (NGISSC)
- "Tallest Islands of the World – World Island Info web site". Worldislandinfo.com. Retrieved 1 August 2010.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), pp. 2, 43.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 45.
- Shan, Shelley; Mo, Yan-chih (9 August 2013). "Taipei bakes on hottest day in 117 years". Taipei Times. p. 1. Retrieved 27 February 2015.
- Huang, Chiao-wen; Liu, Kay (15 September 2014). "Taiwan's electricity supplies hit tightest point of the year". Focus Taiwan. Central News Agency. Retrieved 27 February 2015.
- Shan, Shelley (16 September 2014). "Nation sees record high temperatures". Taipei Times. p. 3. Retrieved 27 February 2015.
- Tsukada, Matsuo (1966). "Late Pleistocene vegetation and climate of Taiwan (Formosa)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 55 (3): 543–548. Bibcode:1966PNAS...55..543T. doi:10.1073/pnas.55.3.543. PMC 224184. PMID 16591341.
- "Otter Conservation in Kinmen". Kinmen County Government. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- Chiang, Po-Jen; Kurtis Jai-Chyi Pei; Michael R. Vaughan; Ching-Feng Li (2012). "Niche relationships of carnivores in a subtropical primary forest in southern Taiwan" (PDF). Zoological Studies. 51: 500–511.
- National Parks of Taiwan Archived 16 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Construction and Planning Agency, Ministry of the Interior, ROC (Taiwan).
- Taiwan Panorama (17 July 2008). "Chinkuashih's Gold Ecological Park brings history to life". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China (Taiwan). Taiwan Today. Retrieved 3 December 2019.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 304.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), pp. 160–168.
- Energy Statistics Handbook Archived 25 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Bureau of Energy, Ministry of Economic Affairs, 2010.
- "Taiwan's Energy Policy and Supply-Demand Situation". Bureau of Energy, Ministry of Economic Affairs. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012.
- "Taiwan: metropolitan areas". World Gazetteer. Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 49.
- Thomson, John (1898), English: Through China with a camera, retrieved 5 December 2017, see: Appendix- The Aboriginal Dialects of Formosa, page 275 - 284
- Jiao, Tianlong (2007). The Neolithic of southeast China: cultural transformation and regional interaction on the coast. Cambria Press. pp. 91–94. ISBN 978-1-934043-16-5.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 36.
- Knapp, Ronald G. (1999). "The shaping of Taiwan's landscapes". In Rubinstein, Murray A. (ed.). Taiwan: a new history. Armonk, N.Y.: M.E. Sharpe. pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-0-7656-1494-0.
- Exec. Yuan (2014), p. 48.
- "Taiwan: Environmental Issues". Country Analysis Brief – Taiwan. United States Department of Energy. October 2003. Archived from the original on 7 October 2006. Retrieved 8 March 2006.
The government credits the APC system with helping to reduce the number of days when the country's pollution standard index score exceeded 100 from 7% of days in 1994 to 3% of days in 2001.
- "Taiwan Country Analysis Brief". United States Department of Energy. August 2005. Archived from the original on 2 February 2007.
Taipei has the most obvious air pollution, primarily caused by the motorbikes and scooters used by millions of the city's residents.
- Tso, Chunto (July 2003). "A Viable Niche Market–Fuel Cell Scooters in Taiwan" (PDF). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 28 (7): 757–762. doi:10.1016/S0360-3199(02)00245-8.
In Taiwan's cities, the main source of air pollution is the waste gas exhausted by scooters, especially by the great number of two-stroke engine scooters.
- Chiu, Yu-Tzu (26 January 2005). "Forests in Taiwan jeopardized by acid rain: EPA". Taipei Times.
Works cited
- The Republic of China Yearbook 2014 (PDF). Taipei: Executive Yuan, R.O.C. 2014. ISBN 978-986-04-2302-0.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Formosa (China). |
- Taiwan datums, Open Source Geospatial Foundation Wiki
- National Parks of Taiwan, Construction and Planning Agency, Ministry of the Interior, Taiwan (ROC)
- Taiwan Pass, Tourism Bureau, Ministry of Transportation and communications, Taiwan (ROC)