Geography of Turkmenistan
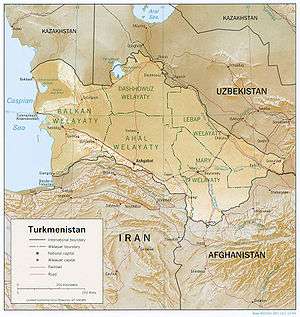
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea to the west, Iran and Afghanistan to the south, Uzbekistan to the north-east, and Kazakhstan to the north-west. It is the southernmost republic of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the loose federation created at the end of 1991 by most of the Post-Soviet states.

Its longest border is with the Caspian Sea (1,786 km (1,110 mi)). The other borders are with Iran (to the south, 992 km (616 mi)), Afghanistan (to the south, 744 km (462 mi)), Uzbekistan (to the north and east, 1,621 km (1,007 mi)) and Kazakhstan (to the north, 379 km (235 mi)). Turkmenistan is slightly larger than the US state of California in territory, occupying 488,100 km². By area, Turkmenistan ranks fourth among the former Soviet republics, after Russia, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine. The country's greatest extent from west to east is 1,100 km (680 mi), and its greatest north-to-south distance is 650 km (400 mi).
Physical features
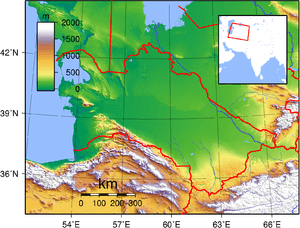
Terrain of Turkmenistan consists of a flat-to-rolling sandy desert, the Karakum, with its dunes slowly rising to the south; by the time they reach the border with Iran, they become the low mountains known as the Kopet Dag. The Caspian Sea washes the western shores of this mostly arid country.
Turkmenistan's average elevation is 100 to 220 meters above sea level, with its highest point being Mount Aýrybaba (3,139 m) in the Köýtendag Range of the Pamir-Alay chain in the south-east, and its lowest point being the Akjagaýa Depression in Sarygamysh Lake, close to 100 meters below sea level (the actual water level in Sarygamysh Lake fluctuates widely from –110 m at its shallowest to –60 m).[1]. The Mount Arlan rises sharply above sea level in the Great Balkhan Range in western Turkmenistan (Balkan Province). Nearly 80% of the republic lies within the Turan Depression, which slopes from south to north and from east to west.
Turkmenistan's mountains include 600 km of the northern reaches of the Kopet Dag Range, which it shares with Iran. The Kopet Dag Range is a region characterized by foothills, dry and sandy slopes, mountain plateaus, and steep ravines; Mount Şahşah (2,912 m), also known as Mount Rizeh, southwest of Ashgabat, is the highest elevation of the Kopet Dag Range in Turkmenistan. The Kopet Dag is undergoing tectonic transformation, meaning that the region is threatened by earthquakes such as the one that destroyed Ashgabat in 1948. The Krasnovodsk and Üstýurt plateaus are the prominent topographical features of northwestern Turkmenistan.
A dominant feature of the republic's landscape is the Garagum Desert (also known as Karakum), which occupies about 350,000 square kilometers (see Environmental Issues). Shifting winds create desert mountains that range from two to twenty meters in height and may be several kilometers in length. Chains of such structures are common, as are steep elevations and smooth, concrete-like clay deposits formed by the rapid evaporation of flood waters in the same area for a number of years. Large marshy salt flats, formed by capillary action in the soil, exist in many depressions, including the Garaşor, which occupies 1,500 square kilometers in the northwest. The Sandykly Desert west of the Amu Darya river is the southernmost extremity of the Qizilqum Desert, most of which lies in Uzbekistan to the northeast.
Climate
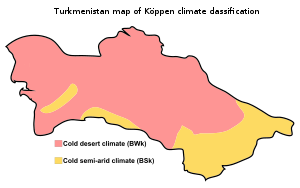
Turkmenistan has a cold desert climate that is severely continental. Summers are long (from May through September), hot, and dry, while winters generally are mild and dry, although occasionally cold and damp in the north. Most precipitation falls between January and May; precipitation is slight throughout the country, with annual averages ranging from 300 millimeters (11.8 in) in the Kopet Dag to 80 millimeters (3.15 in) in the northwest. The capital, Ashgabat, close to the Iranian border in south-central Turkmenistan, averages 225 millimeters (8.9 in) of rainfall annually. Average annual temperatures range from 17.1 °C (62.8 °F) in Ashgabat to 12.8 °C (55.0 °F) in Daşoguz, on the Uzbek border in north-central Turkmenistan. The almost constant winds are northerly, northeasterly, or westerly.
Hydrological conditions
Almost 80% of the territory of Turkmenistan lacks a constant source of surface water flow. Its main rivers are located only in the southern and eastern peripheries; a few smaller rivers on the northern slopes of the Kopetdag are diverted entirely to irrigation. The most important river is the Amu Darya, which has a total length of 2,540 km from its farthest tributary, making it the longest river in Central Asia. The Amu Darya flows across northeastern Turkmenistan, thence eastward to form the southern borders of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan. Damming and irrigation uses of the Amu Darya have had severe environmental effects on the Aral Sea, into which the river flows (see Environmental Issues). The river's average annual flow is 1,940 cubic meters per second. Other major rivers are the Tejen (1,124 km); the Murgab (852 km); and the Atrek (660 km).
Environmental issues
Background
Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union, environmental regulation is largely unchanged in Turkmenistan. The new government created the Ministry of Natural Resources Use and Environmental Protection in July 1992, with departments responsible for environmental protection, protection of flora and fauna, forestry, hydrometeorology, and administrative planning. Like other CIS republics, Turkmenistan has established an Environmental Fund based on revenues collected from environmental fines, but the fines generally are too low to accumulate significant revenue. Thanks to the former Soviet system of game preserves and the efforts of the Society for Nature Conservation and the Academy of Sciences, flora and fauna receive some protection in the republic; however, "hard-currency hunts" by wealthy Western and Arab businesspeople already are depleting animals on preserves.
Environment - current issues
Contamination of soil and groundwater with agricultural chemicals, pesticides; salination, water-logging of soil due to poor irrigation methods; Caspian Sea pollution; diversion of a large share of the flow of the Amu Darya into irrigation contributes to that river's inability to replenish the Aral Sea; desertification
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Desertification
According to estimates, as a result of desertification processes and pollution, biological productivity of the ecological systems in Turkmenistan has declined by 30% to 50% in recent decades. The Karakum and Kyzyl Kum deserts are expanding at a rate surpassed on a planetary scale only by the desertification process in the Sahara and Sahel regions of Africa. Between 8,000 and 10,000 km² of new desert now appears each year in Central Asia.
The most irreparable type of desertification is the salinization process that forms marshy salt flats. A major factor that contributes to these conditions is inefficient use of water because of weak regulation and failure to charge for water that is used. Efficiency in application of water to the fields is low, but the main problem is leakage in main and secondary canals, especially Turkmenistan's main canal, the Karakum Canal. Nearly half of the canal's water seeps out into lakes and salt swamps along its path. Excessive irrigation brings salts to the surface, forming salt marshes that dry into unusable clay flats. In 1989 Turkmenistan's Institute for Desert Studies claimed that the area of such flats had reached 10,000 km².
The type of desertification caused by year-round pasturing of cattle has been termed the most devastating in Central Asia, with the gravest situations in Turkmenistan and the Kazakh steppe along the eastern and northern coasts of the Caspian Sea. Wind erosion and desertification also are severe in settled areas along the Garagum Canal; planted windbreaks have died because of soil waterlogging and/or salinization. Other factors promoting desertification are the inadequacy of the collector-drainage system built in the 1950s and inappropriate application of chemicals.
The Aral Sea
Turkmenistan both contributes to and suffers from the consequences of the desiccation of the Aral Sea. Because of excessive irrigation, Turkmen agriculture contributes to the steady drawdown of sea levels. In turn, the Aral Sea's desiccation, which had shrunk that body of water by an estimated 59,000 square kilometers by 1994, profoundly affects economic productivity and the health of the population of the republic. Besides the cost of ameliorating damaged areas and the loss of at least part of the initial investment in them, salinization and chemicalization of land have reduced agricultural productivity in Central Asia by an estimated 20 to 25%. Poor drinking water is the main health risk posed by such environmental degradation. In Dashhowuz Province, which has suffered the greatest ecological damage from the Aral Sea's desiccation, bacteria levels in drinking water exceeded ten times the sanitary level; 70% of the population has experienced illnesses, many with hepatitis, and infant mortality is high. Experts have warned that inhabitants will have to evacuate the province by the end of the century unless a comprehensive cleanup program is undertaken. Turkmenistan has announced plans to clean up some of the Aral Sea fallout with financial support from the World Bank.
Chemical pollution
The most productive cotton lands in Turkmenistan (the middle and lower Amu Darya and the Murgap oasis) receive as much as 250 kilograms of fertilizer per hectare, compared with the average application of thirty kilograms per hectare. Furthermore, most fertilizers are so poorly applied that experts have estimated that only 15 to 40% of the chemicals can be absorbed by cotton plants, while the remainder washes into the soil and subsequently into the groundwater. Cotton also uses far more pesticides and defoliants than other crops, and application of these chemicals often is mishandled by farmers. For example, local herdsmen, unaware of the danger of DDT, have reportedly mixed the pesticide with water and applied it to their faces to keep away mosquitoes. In the late 1980s, a drive began in Central Asia to reduce agrochemical usage. In Turkmenistan the campaign reduced fertilizer use 30% between 1988 and 1989. In the early 1990s, use of some pesticides and defoliants declined drastically because of the country's shortage of hard currency.
Area and boundaries
Area:
total: 488,100 km²
land: 469,930 km²
water: 18,170 km²
Area - comparative: slightly larger than the US state of California
Land boundaries:
total: 3,736 km
border countries: Afghanistan 744 km, Iran 992 km, Kazakhstan 379 km, Uzbekistan 1,621 km
Coastline: 0 km
Note: Turkmenistan borders the Caspian Sea. Its coastline with the Caspian Sea is 1,768 km.
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
Resources
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, sulfur, salt
Land use:
arable land: 3.89%
permanent crops: 0.12%
other: 95.98% (2011)
Irrigated land: 19,910 km² (2006)
Total renewable water resources: 24.77 km2 (2011)
References