Estrogen conjugate
An estrogen conjugate is a conjugate of an endogenous estrogen. They occur naturally in the body as metabolites of estrogens and can be reconverted back into estrogens. They serve as a circulating reservoir for estrogen, particularly in the case of orally administered pharmaceutical estradiol. Estrogen conjugates include sulfate and/or glucuronide conjugates of estradiol, estrone, and estriol:
- Sulfated:
- Estrone 3-sulfate (E1S)
- Estradiol 3-sulfate (E2S, E2-3S) and estradiol 17β-sulfate (E2-17S)
- Estriol 3-sulfate (E3S)
- Estradiol 3,17β-disulfate (E2DS)
- Glucuronidated:
- Estrone 3-glucuronide (E1-G)
- Estradiol 3-glucuronide (E2-3G) and estradiol 17β-glucuronide (E2-17G)
- Estriol 3-glucuronide (E3-3G), estriol 16α-glucuronide (E3-16G)
- Mixed:
- Estradiol 3-glucuronide 17β-sulfate (E2-3G-17βS)
- Estradiol 3-sulfate 17β-glucuronide (E2-3S-17βG)
- Estriol 3-sulfate 16α-glucuronide (E3-3S-16G)
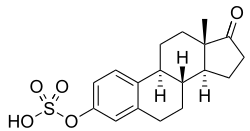
Estrone sulfate, the 3-sulfate conjugate of estrone.
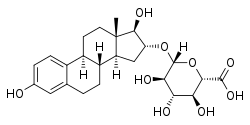
Estriol glucuronide, the 16α-glucuronide conjugate of estriol.
Estrogen conjugates are conjugated at the C3, C16α, and/or C17β positions, where hydroxyl groups are available.[1]
Estrogen conjugates have been used as pharmaceutical estrogens, as in estrone sulfate as estropipate (piperazine estrone sulfate) and in conjugated estrogens (Premarin) and conjugated estriol (Progynon, Emmenin).
| Estrogen | Other names | RBA (%)a | REP (%)b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ERα | ERβ | ||||
| Estradiol | E2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| Estradiol 3-sulfate | E2S; E2-3S | ? | 0.02 | 0.04 | ||
| Estradiol 3-glucuronide | E2-3G | ? | 0.02 | 0.09 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-glucuronide | E2-17G | ? | 0.002 | 0.0002 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | EB; Estradiol 3-benzoate | 10 | 1.1 | 0.52 | ||
| Estradiol 17β-acetate | E2-17A | 31–45 | 24 | ? | ||
| Estradiol diacetate | EDA; Estradiol 3,17β-diacetate | ? | 0.79 | ? | ||
| Estradiol propionate | EP; Estradiol 17β-propionate | 19–26 | 2.6 | ? | ||
| Estradiol valerate | EV; Estradiol 17β-valerate | 2–11 | 0.04–21 | ? | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | EC; Estradiol 17β-cypionate | ?c | 4.0 | ? | ||
| Estradiol palmitate | Estradiol 17β-palmitate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estradiol stearate | Estradiol 17β-stearate | 0 | ? | ? | ||
| Estrone | E1; 17-Ketoestradiol | 11 | 5.3–38 | 14 | ||
| Estrone sulfate | E1S; Estrone 3-sulfate | 2 | 0.004 | 0.002 | ||
| Estrone glucuronide | E1G; Estrone 3-glucuronide | ? | <0.001 | 0.0006 | ||
| Ethinylestradiol | EE; 17α-Ethynylestradiol | 100 | 17–150 | 129 | ||
| Mestranol | EE 3-methyl ether | 1 | 1.3–8.2 | 0.16 | ||
| Quinestrol | EE 3-cyclopentyl ether | ? | 0.37 | ? | ||
| Footnotes: a = Relative binding affinities (RBAs) were determined via in-vitro displacement of labeled estradiol from estrogen receptors (ERs) generally of rodent uterine cytosol. Estrogen esters are variably hydrolyzed into estrogens in these systems (shorter ester chain length -> greater rate of hydrolysis) and the ER RBAs of the esters decrease strongly when hydrolysis is prevented. b = Relative estrogenic potencies (REPs) were calculated from half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50) that were determined via in-vitro β‐galactosidase (β-gal) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression assays in yeast expressing human ERα and human ERβ. Both mammalian cells and yeast have the capacity to hydrolyze estrogen esters. c = The affinities of estradiol cypionate for the ERs are similar to those of estradiol valerate and estradiol benzoate (figure). Sources: See template page. | ||||||
| Ligand | Other names | Relative binding affinities (RBA, %)a | Absolute binding affinities (Ki, nM)a | Action | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERα | ERβ | ERα | ERβ | |||
| Estradiol | E2; 17β-Estradiol | 100 | 100 | 0.115 (0.04–0.24) | 0.15 (0.10–2.08) | Estrogen |
| Estrone | E1; 17-Ketoestradiol | 16.39 (0.7–60) | 6.5 (1.36–52) | 0.445 (0.3–1.01) | 1.75 (0.35–9.24) | Estrogen |
| Estriol | E3; 16α-OH-17β-E2 | 12.65 (4.03–56) | 26 (14.0–44.6) | 0.45 (0.35–1.4) | 0.7 (0.63–0.7) | Estrogen |
| Estetrol | E4; 15α,16α-Di-OH-17β-E2 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.9 | 19 | Estrogen |
| Alfatradiol | 17α-Estradiol | 20.5 (7–80.1) | 8.195 (2–42) | 0.2–0.52 | 0.43–1.2 | Metabolite |
| 16-Epiestriol | 16β-Hydroxy-17β-estradiol | 7.795 (4.94–63) | 50 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 17-Epiestriol | 16α-Hydroxy-17α-estradiol | 55.45 (29–103) | 79–80 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 16,17-Epiestriol | 16β-Hydroxy-17α-estradiol | 1.0 | 13 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 2-OH-E2 | 22 (7–81) | 11–35 | 2.5 | 1.3 | Metabolite |
| 2-Methoxyestradiol | 2-MeO-E2 | 0.0027–2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Hydroxyestradiol | 4-OH-E2 | 13 (8–70) | 7–56 | 1.0 | 1.9 | Metabolite |
| 4-Methoxyestradiol | 4-MeO-E2 | 2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Hydroxyestrone | 2-OH-E1 | 2.0–4.0 | 0.2–0.4 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Methoxyestrone | 2-MeO-E1 | <0.001–<1 | <1 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Hydroxyestrone | 4-OH-E1 | 1.0–2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Methoxyestrone | 4-MeO-E1 | <1 | <1 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 16α-Hydroxyestrone | 16α-OH-E1; 17-Ketoestriol | 2.0–6.5 | 35 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Hydroxyestriol | 2-OH-E3 | 2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Methoxyestriol | 4-MeO-E3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol sulfate | E2S; Estradiol 3-sulfate | <1 | <1 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol disulfate | Estradiol 3,17β-disulfate | 0.0004 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol 3-glucuronide | E2-3G | 0.0079 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol 17β-glucuronide | E2-17G | 0.0015 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol 3-gluc. 17β-sulfate | E2-3G-17S | 0.0001 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estrone sulfate | E1S; Estrone 3-sulfate | <1 | <1 | >10 | >10 | Metabolite |
| Estradiol benzoate | EB; Estradiol 3-benzoate | 10 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Estradiol 17β-benzoate | E2-17B | 11.3 | 32.6 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Estrone methyl ether | Estrone 3-methyl ether | 0.145 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| ent-Estradiol | 1-Estradiol | 1.31–12.34 | 9.44–80.07 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Equilin | 7-Dehydroestrone | 13 (4.0–28.9) | 13.0–49 | 0.79 | 0.36 | Estrogen |
| Equilenin | 6,8-Didehydroestrone | 2.0–15 | 7.0–20 | 0.64 | 0.62 | Estrogen |
| 17β-Dihydroequilin | 7-Dehydro-17β-estradiol | 7.9–113 | 7.9–108 | 0.09 | 0.17 | Estrogen |
| 17α-Dihydroequilin | 7-Dehydro-17α-estradiol | 18.6 (18–41) | 14–32 | 0.24 | 0.57 | Estrogen |
| 17β-Dihydroequilenin | 6,8-Didehydro-17β-estradiol | 35–68 | 90–100 | 0.15 | 0.20 | Estrogen |
| 17α-Dihydroequilenin | 6,8-Didehydro-17α-estradiol | 20 | 49 | 0.50 | 0.37 | Estrogen |
| Δ8-Estradiol | 8,9-Dehydro-17β-estradiol | 68 | 72 | 0.15 | 0.25 | Estrogen |
| Δ8-Estrone | 8,9-Dehydroestrone | 19 | 32 | 0.52 | 0.57 | Estrogen |
| Ethinylestradiol | EE; 17α-Ethynyl-17β-E2 | 120.9 (68.8–480) | 44.4 (2.0–144) | 0.02–0.05 | 0.29–0.81 | Estrogen |
| Mestranol | EE 3-methyl ether | ? | 2.5 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Moxestrol | RU-2858; 11β-Methoxy-EE | 35–43 | 5–20 | 0.5 | 2.6 | Estrogen |
| Methylestradiol | 17α-Methyl-17β-estradiol | 70 | 44 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Diethylstilbestrol | DES; Stilbestrol | 129.5 (89.1–468) | 219.63 (61.2–295) | 0.04 | 0.05 | Estrogen |
| Hexestrol | Dihydrodiethylstilbestrol | 153.6 (31–302) | 60–234 | 0.06 | 0.06 | Estrogen |
| Dienestrol | Dehydrostilbestrol | 37 (20.4–223) | 56–404 | 0.05 | 0.03 | Estrogen |
| Benzestrol (B2) | – | 114 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Chlorotrianisene | TACE | 1.74 | ? | 15.30 | ? | Estrogen |
| Triphenylethylene | TPE | 0.074 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Triphenylbromoethylene | TPBE | 2.69 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Tamoxifen | ICI-46,474 | 3 (0.1–47) | 3.33 (0.28–6) | 3.4–9.69 | 2.5 | SERM |
| Afimoxifene | 4-Hydroxytamoxifen; 4-OHT | 100.1 (1.7–257) | 10 (0.98–339) | 2.3 (0.1–3.61) | 0.04–4.8 | SERM |
| Toremifene | 4-Chlorotamoxifen; 4-CT | ? | ? | 7.14–20.3 | 15.4 | SERM |
| Clomifene | MRL-41 | 25 (19.2–37.2) | 12 | 0.9 | 1.2 | SERM |
| Cyclofenil | F-6066; Sexovid | 151–152 | 243 | ? | ? | SERM |
| Nafoxidine | U-11,000A | 30.9–44 | 16 | 0.3 | 0.8 | SERM |
| Raloxifene | – | 41.2 (7.8–69) | 5.34 (0.54–16) | 0.188–0.52 | 20.2 | SERM |
| Arzoxifene | LY-353,381 | ? | ? | 0.179 | ? | SERM |
| Lasofoxifene | CP-336,156 | 10.2–166 | 19.0 | 0.229 | ? | SERM |
| Ormeloxifene | Centchroman | ? | ? | 0.313 | ? | SERM |
| Levormeloxifene | 6720-CDRI; NNC-460,020 | 1.55 | 1.88 | ? | ? | SERM |
| Ospemifene | Deaminohydroxytoremifene | 2.63 | 1.22 | ? | ? | SERM |
| Bazedoxifene | – | ? | ? | 0.053 | ? | SERM |
| Etacstil | GW-5638 | 4.30 | 11.5 | ? | ? | SERM |
| ICI-164,384 | – | 63.5 (3.70–97.7) | 166 | 0.2 | 0.08 | Antiestrogen |
| Fulvestrant | ICI-182,780 | 43.5 (9.4–325) | 21.65 (2.05–40.5) | 0.42 | 1.3 | Antiestrogen |
| Propylpyrazoletriol | PPT | 49 (10.0–89.1) | 0.12 | 0.40 | 92.8 | ERα agonist |
| 16α-LE2 | 16α-Lactone-17β-estradiol | 14.6–57 | 0.089 | 0.27 | 131 | ERα agonist |
| 16α-Iodo-E2 | 16α-Iodo-17β-estradiol | 30.2 | 2.30 | ? | ? | ERα agonist |
| Methylpiperidinopyrazole | MPP | 11 | 0.05 | ? | ? | ERα antagonist |
| Diarylpropionitrile | DPN | 0.12–0.25 | 6.6–18 | 32.4 | 1.7 | ERβ agonist |
| 8β-VE2 | 8β-Vinyl-17β-estradiol | 0.35 | 22.0–83 | 12.9 | 0.50 | ERβ agonist |
| Prinaberel | ERB-041; WAY-202,041 | 0.27 | 67–72 | ? | ? | ERβ agonist |
| ERB-196 | WAY-202,196 | ? | 180 | ? | ? | ERβ agonist |
| Erteberel | SERBA-1; LY-500,307 | ? | ? | 2.68 | 0.19 | ERβ agonist |
| SERBA-2 | – | ? | ? | 14.5 | 1.54 | ERβ agonist |
| Coumestrol | – | 9.225 (0.0117–94) | 64.125 (0.41–185) | 0.14–80.0 | 0.07–27.0 | Xenoestrogen |
| Genistein | – | 0.445 (0.0012–16) | 33.42 (0.86–87) | 2.6–126 | 0.3–12.8 | Xenoestrogen |
| Equol | – | 0.2–0.287 | 0.85 (0.10–2.85) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Daidzein | – | 0.07 (0.0018–9.3) | 0.7865 (0.04–17.1) | 2.0 | 85.3 | Xenoestrogen |
| Biochanin A | – | 0.04 (0.022–0.15) | 0.6225 (0.010–1.2) | 174 | 8.9 | Xenoestrogen |
| Kaempferol | – | 0.07 (0.029–0.10) | 2.2 (0.002–3.00) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Naringenin | – | 0.0054 (<0.001–0.01) | 0.15 (0.11–0.33) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| 8-Prenylnaringenin | 8-PN | 4.4 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Quercetin | – | <0.001–0.01 | 0.002–0.040 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Ipriflavone | – | <0.01 | <0.01 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Miroestrol | – | 0.39 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Deoxymiroestrol | – | 2.0 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| β-Sitosterol | – | <0.001–0.0875 | <0.001–0.016 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Resveratrol | – | <0.001–0.0032 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| α-Zearalenol | – | 48 (13–52.5) | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| β-Zearalenol | – | 0.6 (0.032–13) | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Zeranol | α-Zearalanol | 48–111 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Taleranol | β-Zearalanol | 16 (13–17.8) | 14 | 0.8 | 0.9 | Xenoestrogen |
| Zearalenone | ZEN | 7.68 (2.04–28) | 9.45 (2.43–31.5) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Zearalanone | ZAN | 0.51 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Bisphenol A | BPA | 0.0315 (0.008–1.0) | 0.135 (0.002–4.23) | 195 | 35 | Xenoestrogen |
| Endosulfan | EDS | <0.001–<0.01 | <0.01 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Kepone | Chlordecone | 0.0069–0.2 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| o,p'-DDT | – | 0.0073–0.4 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| p,p'-DDT | – | 0.03 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Methoxychlor | p,p'-Dimethoxy-DDT | 0.01 (<0.001–0.02) | 0.01–0.13 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| HPTE | Hydroxychlor; p,p'-OH-DDT | 1.2–1.7 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Testosterone | T; 4-Androstenolone | <0.0001–<0.01 | <0.002–0.040 | >5000 | >5000 | Androgen |
| Dihydrotestosterone | DHT; 5α-Androstanolone | 0.01 (<0.001–0.05) | 0.0059–0.17 | 221–>5000 | 73–1688 | Androgen |
| Nandrolone | 19-Nortestosterone; 19-NT | 0.01 | 0.23 | 765 | 53 | Androgen |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone | DHEA; Prasterone | 0.038 (<0.001–0.04) | 0.019–0.07 | 245–1053 | 163–515 | Androgen |
| 5-Androstenediol | A5; Androstenediol | 6 | 17 | 3.6 | 0.9 | Androgen |
| 4-Androstenediol | – | 0.5 | 0.6 | 23 | 19 | Androgen |
| 4-Androstenedione | A4; Androstenedione | <0.01 | <0.01 | >10000 | >10000 | Androgen |
| 3α-Androstanediol | 3α-Adiol | 0.07 | 0.3 | 260 | 48 | Androgen |
| 3β-Androstanediol | 3β-Adiol | 3 | 7 | 6 | 2 | Androgen |
| Androstanedione | 5α-Androstanedione | <0.01 | <0.01 | >10000 | >10000 | Androgen |
| Etiocholanedione | 5β-Androstanedione | <0.01 | <0.01 | >10000 | >10000 | Androgen |
| Methyltestosterone | 17α-Methyltestosterone | <0.0001 | ? | ? | ? | Androgen |
| Ethinyl-3α-androstanediol | 17α-Ethynyl-3α-adiol | 4.0 | <0.07 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Ethinyl-3β-androstanediol | 17α-Ethynyl-3β-adiol | 50 | 5.6 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Progesterone | P4; 4-Pregnenedione | <0.001–0.6 | <0.001–0.010 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| Norethisterone | NET; 17α-Ethynyl-19-NT | 0.085 (0.0015–<0.1) | 0.1 (0.01–0.3) | 152 | 1084 | Progestogen |
| Norethynodrel | 5(10)-Norethisterone | 0.5 (0.3–0.7) | <0.1–0.22 | 14 | 53 | Progestogen |
| Tibolone | 7α-Methylnorethynodrel | 0.5 (0.45–2.0) | 0.2–0.076 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| Δ4-Tibolone | 7α-Methylnorethisterone | 0.069–<0.1 | 0.027–<0.1 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| 3α-Hydroxytibolone | – | 2.5 (1.06–5.0) | 0.6–0.8 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| 3β-Hydroxytibolone | – | 1.6 (0.75–1.9) | 0.070–0.1 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| Footnotes: a = (1) Binding affinity values are of the format "median (range)" (# (#–#)), "range" (#–#), or "value" (#) depending on the values available. The full sets of values within the ranges can be found in the Wiki code. (2) Binding affinities were determined via displacement studies in a variety of in-vitro systems with labeled estradiol and human ERα and ERβ proteins (except the ERβ values from Kuiper et al. (1997), which are rat ERβ). Sources: See template page. | ||||||
References
- Bhavnani, BR (January 1998). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of conjugated equine estrogens: chemistry and metabolism". Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine (New York, N.Y.). 217 (1): 6–16. doi:10.3181/00379727-217-44199. PMID 9421201.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.