Steroid sulfate
Steroid sulfates are endogenous sulfate esters of steroids.[1] They are formed by steroid sulfotransferases via sulfation of endogenous steroids like cholesterol and steroid hormones.[1] Although steroid sulfates do not bind to steroid hormone receptors and hence are hormonally inert, they can be desulfated by steroid sulfatase and in this way serve as precursors and circulating reservoirs for their active unsulfated counterparts.[1] In addition, some steroid sulfates have biological activity in their own right, for instance acting as neurosteroids and modulating ligand-gated ion channels such as the GABAA and NMDA receptors among other biological targets.[1][2]
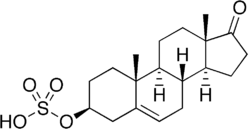
DHEA sulfate, a major endogenous steroid sulfate. Note the steroid ester at the C3β position.
List of endogenous steroid sulfates
Endogenous steroid sulfates include:[1]
- Cholesterol sulfate (formed from cholesterol by SULT2B1b)
- Pregnenolone sulfate (formed from pregnenolone by SULT2A1 and SULT2B1a)
- DHEA sulfate (formed from DHEA by SULT2A1 and SULT1E1)
- Androstenediol sulfate (formed from androstenediol)
- Androsterone sulfate (formed from androsterone by SULT2A1)
- Estrone sulfate (formed from estrone by SULT1E1)
- Estradiol sulfate (formed from estradiol by SULT1A1 and SULT1E1)
- Testosterone sulfate (formed from testosterone)
gollark: ++tel status
gollark: So now it doesn't error but also does not work still.
gollark: Test?
gollark: ???
gollark: Apioform.
See also
References
- Mueller JW, Gilligan LC, Idkowiak J, Arlt W, Foster PA (2015). "The Regulation of Steroid Action by Sulfation and Desulfation". Endocr. Rev. 36 (5): 526–63. doi:10.1210/er.2015-1036. PMC 4591525. PMID 26213785.
- Gibbs TT, Russek SJ, Farb DH (2006). "Sulfated steroids as endogenous neuromodulators". Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 84 (4): 555–67. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2006.07.031. PMID 17023038.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.