11β-Hydroxyandrostenedione
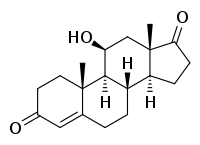
11β-Hydroxyandrostenedione (11β-OHA4), also known as 11β-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and androgen prohormone that is produced primarily, if not exclusively, in the adrenal glands.[1] It is closely related to adrenosterone (11-ketoandrostenedione; 11-KA4), 11-ketotestosterone (11-KT), and 11-ketodihydrotestosterone (11-KDHT), which are also produced in the adrenal glands.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(8S,9S,10R,11S,13S,14S)-11-Hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-dione | |
| Other names
11β-Hydroxy-4-androstenedione; 11β-Hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione; 11β-OHA4 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H26O3 | |
| Molar mass | 302.414 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Pretorius, Elzette; Arlt, Wiebke; Storbeck, Karl-Heinz (2016). "A new dawn for androgens: Novel lessons from 11-oxygenated C19 steroids" (PDF). Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 441: 76–85. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2016.08.014. ISSN 0303-7207. PMID 27519632.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.