COVID-19 pandemic in the Bahamas
The COVID-19 pandemic in the Bahamas is part of the COVID-19 pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).[3] The outbreak was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019,[4] declared to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020,[5] and recognized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization on 11 March 2020.[6] It was confirmed to have reached the Bahamas on 15 March 2020 with the announcement of the first case.[1]
| COVID-19 pandemic in The Bahamas | |
|---|---|
.svg.png) | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | The Bahamas |
| Index case | New Providence[1] |
| Arrival date | 15 March 2020 (5 months and 3 days) |
| Confirmed cases | 1329 [2] |
| Active cases | 1138[2] |
| Recovered | 191[2] |
Deaths | 19[2] |
| Government website | |
COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).[7] The case fatality rate for COVID-19 has been much lower than for other coronavirus respiratory infections such as SARS and MERS, but the transmission has been significantly greater, with a significant total death toll.[8][9]
Timeline
March 2020
On 15 March, Acting Minister of Health Jeffrey Lloyd announced the first confirmed case, a 61-year-old female.[1]
On March 20, Prime Minister Hubert Minnis announced a 9pm to 5am curfew, restrictions on private gatherings, and closure of most in-person businesses, with limited hours for food stores and farmers' markets, pharmacies, gas stations, laundromats, banks, construction, and restaurants (limited to take-out only). Essential workers for the government, utilities, and media were exempted, as were health care providers and suppliers. The airport remained open, but only essential travel was allowed on public buses.[11]
April 2020
On April 19, the prime minister announced that wearing a mask or covering one's face with clothing is mandatory in public. Employers must provide their employees who are serving the general public with masks.[12]
May 2020
On May 21, authorities are maintaining various restrictions across the islands in order to slow the spread of COVID-19. A daily 24-hour curfew on weekdays and weekend lockdowns are from 2100 on Fridays to 0500 on Mondays. The island of Bimini is under complete lockdown at least through May 30. Under the 24 hour curfew, the residents can only leave their homes for essential purposes or for an emergency.[13]
Statistics
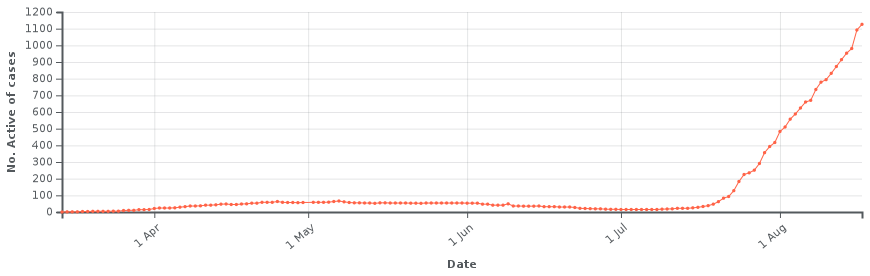
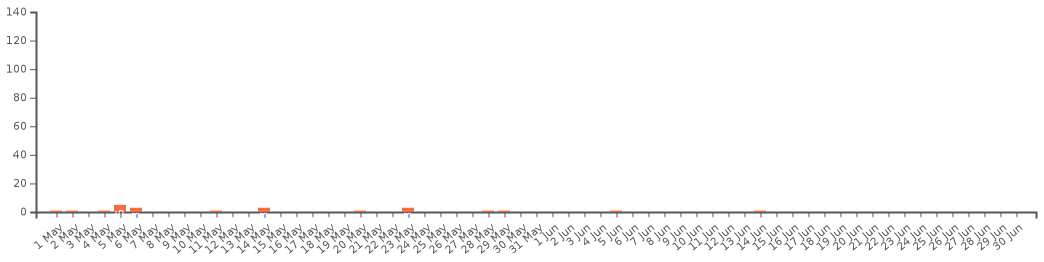
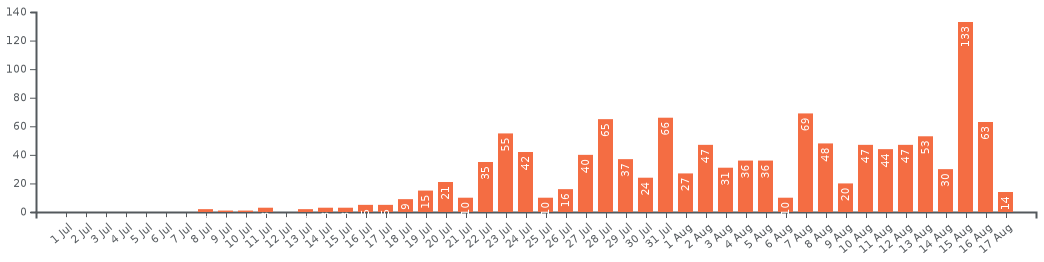
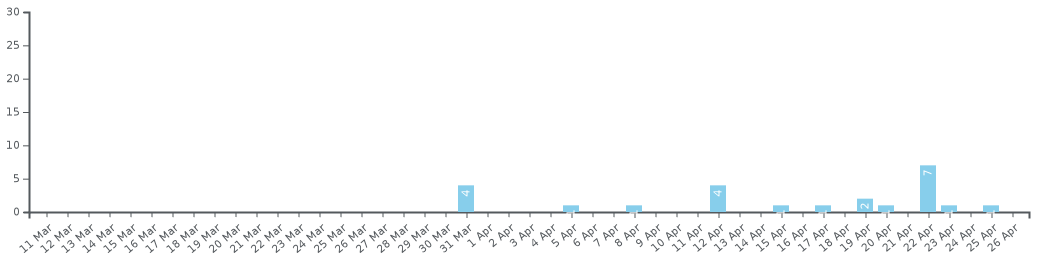
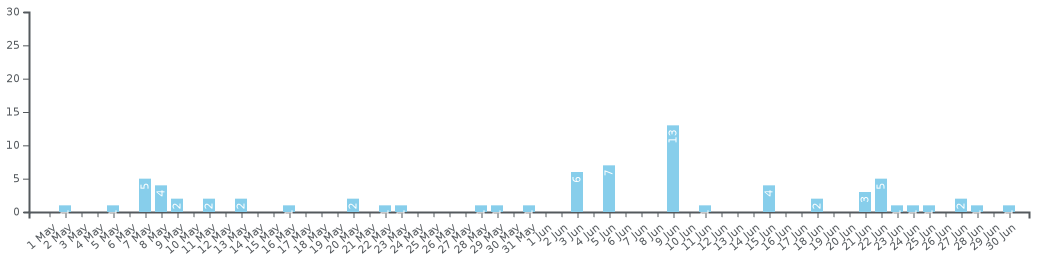
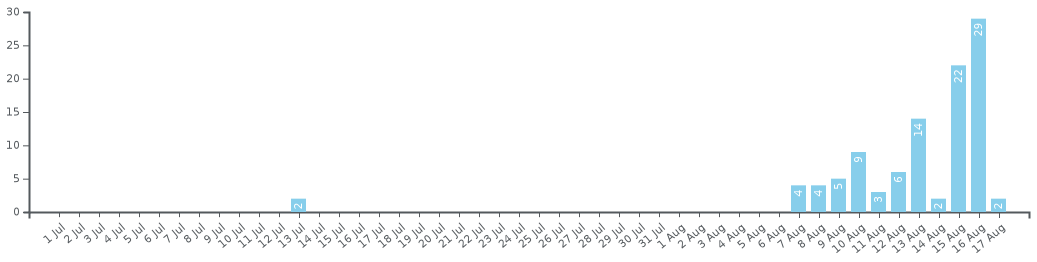
Chronology of the number of active cases in the Bahamas

See also
References
- "61-Year-Old Woman Is The First Confirmed Case Of Covid-19 In The Bahamas". The Tribune. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2020.
- "Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)". Bahamas Ministry of Health. 9 August 2020. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
- "Coronavirus disease 2019". World Health Organization. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "WHO | Novel Coronavirus – China". World Health Organization. 12 January 2020.
- "Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)". World Health Organization. 30 January 2020. Archived from the original on 31 January 2020.
- "WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 – 11 March 2020". World Health Organization. 11 March 2020.
- "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "Crunching the numbers for coronavirus". Imperial News. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "World Federation Of Societies of Anaesthesiologists – Coronavirus". World Federation of Societies of Anesthesiologists. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "News and Press Release". GOVERNMENT OF THE BAHAMAS. 10 August 2020. Retrieved 12 August 2020.
- Updated: Pm Puts Nation In Lockdown, Confirmed Covid-19 Cases Now Stand At Four
- "Bahamas PM's National Press Conference: Update on COVID-19 Response". Eleutheran Newspaper. 19 April 2020.
- "COVID-19 Alert: Bahamas Maintains Curfew & Port Closures as of May 21". WorldAware. 21 May 2020. Retrieved 1 July 2020.