South African locomotive history
In South Africa, as elsewhere in the world, the railways played a huge part in development and growth on nearly all terrains in the country. Conversely, events in South Africa and its neighbours over the years had a huge influence on the development of railways.
When the articles on the locomotives of South Africa are read sequentially in the order of their years of entering railway service, much of the history of the country becomes apparent between the lines. At the same time, the development of steam locomotives can be followed from the basic 0-4-0 to the mighty 4-8-4 wheel arrangements, and articulated steam locomotives from the Fairlies and the Kitson-Meyer to the Mallets and ultimately to the Garratts. Likewise with the development of modern traction such as electric, gas-electric, diesel-hydraulic, electro-diesel and diesel-electric locomotives.
This article consists of links to articles on South African locomotives, arranged in the order of their years of entering service, with the links embedded in the applicable pictures. In addition, the opening dates of new railway lines are shown.
Railway construction
In South Africa and South West Africa, where the South African Railways operated, all early mainline railway construction took place working inland from harbours and ports. Construction on these lines began in the years from 1859 to 1887 in South Africa and from 1897 to 1908 in South West Africa.
- Cape Western – The Cape Town–Wellington line in 1859.[1]
- Namaqualand – The Port Nolloth–O'okiep line in 1869.[2]
- Cape Midland – The Port Elizabeth–Uitenhage line in 1872.[3]
- Cape Midland – The Swartkops–Alicedale line in 1875.[1][4]
- Natal – The Durban–Pietermaritzburg line in 1876.[1]
- Cape Eastern – The East London–King William's Town line in 1876.[1][4]
- Kowie – The Port Alfred–Grahamstown line in 1881.[1][5]
- Transvaal – The Delagoa Bay–Pretoria line in 1887.[1]
- South West Africa Central – The Swakopmund–Windhoek line in 1897.[1]
- South West Africa Northern – The Swakopmund–Otavi line in 1903.[1]
- South West Africa Southern – The Lüderitz–Keetmanshoop line in 1908.[1]
The 1850s
The 1860s
1860
1862
- New lines opened:
- Cape Western – Cape Town to Stellenbosch on 1 May.
- The first 7 ft (2,134 mm) gauge locomotive arrives in South Africa when the Table Bay Harbour Board acquires a single broad gauge locomotive, builder or appearance unknown, for excavation and breakwater construction work.[6]
1863
- New lines opened:
- Cape Western – Stellenbosch to Wellington on 4 November.
- The Cape Town and Green Point Tramway introduces horse-drawn trams from Adderley Street to Green Point.
1869
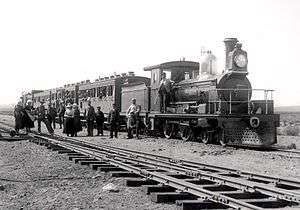
- The first rails of the Namaqualand Railway from Port Nolloth to O'okiep are laid.[2]
The 1870s
1870
1871
- New lines opened:[2]
- Namaqualand – Port Nolloth to Muishondfontein on 18 February.
- The first 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) gauge locomotives arrive in South Africa.
1872
- The Cape Government Railways is established and takes over the operation of all public railways in the Colony, consisting of altogether 63 route miles of track from Cape Town via Stellenbosch to Wellington and via Salt River to Wynberg.[10][11]
1873
- New lines opened:
- Namaqualand – Muishondfontein to Kookfontein.[2]
- The first 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) Cape gauge locomotives arrive in South Africa.
1874
- The railway line from Port Elizabeth to Uitenhage is partially opened.
1875
- New lines opened:[4]
- Cape Midland – Port Elizabeth to Addo on 26 July and Swartkops to Uitenhage on 22 September.
- Cape Western – Wellington to Wolseley on 3 November.
1876
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – East London to Blaney on 18 December.
- Cape Midland – Addo to Sand Flats on 1 April.
- Cape Western – Wolseley to Worcester on 16 June and Bellville to Muldersvlei on 14 September.
- Namaqualand – Kookfontein to O'okiep on 1 January.[2]
- The ship Memento sinks off East London with two Cape 2nd Class 2-6-2TT locomotives for the Eastern System.
- Construction begins on the Cape Town Central Station as hub to the Cape Government Railways.
- The Hex River tunnel on the railway line between Osplaas and Matroosberg is completed.[12]
- Construction begins on the Cape gauge railway line from Durban to Pietermaritzburg in Natal.
1877
- New lines opened:[4]
- Cape Eastern – Blaney to King William's Town and to Kei Road, both on 1 May.
- Cape Midland – Uitenhage to Glenconnor on 1 May and Sand Flats to Alicedale on 27 May.
- Cape Western – Worcester to Kleinstraat on 7 November and Kraaifontein to Malmesbury on 12 November.
1878
1879
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – Döhne to Cathcart on 3 November.
- Cape Midland – Mount Stewart to Graaff-Reinet on 26 August, and Alicedale to Grahamstown on 3 September and to Middleton on 17 September.
- Cape Western – Koup to Fraserburg Road on 11 August.
- Natal – Pinetown to Botha's Hill in March and Avoca to Verulam on 1 September.
The 1880s
1880
- New lines opened:[13]
- Cape Eastern – Cathcart to Queenstown on 5 May.
- Cape Midland – Middleton to Cookhouse on 2 March.
- Cape Western – Fraserburg Road to Beaufort West on 5 February.
- Natal – Rossburgh to Isipingo on 1 February and Botha's Hill to Pietermaritzburg on 1 December.[1]
1881
1882
- New lines opened:
- Cape Western – Wynberg to Muizenberg on 15 December.
1883
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – Queenstown to Sterkstroom on 15 October.
- Cape Midland – Cradock to Colesberg on 16 October.
- Cape Western – Muizenberg to Kalkbaai on 5 May and Beaufort West to Victoria West Road on 14 May.
1884
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – Sterkstroom to Molteno on 16 September.
- Cape Midland – Noupoort to De Aar on 31 March, to link with the Cape Western.
- Cape Western – Victoria West Road to Oranjerivier on 3 November.
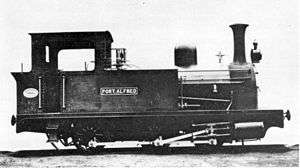
- Kowie – Port Alfred to Grahamstown on 1 December.
- Natal – Pietermaritzburg to Merrivale in May.
1885
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – Molteno to Aliwal North on 2 September.
- Cape Western – Oranjerivier to Kimberley on 28 November.
- Natal – Merrivale to Estcourt on 21 December.
1887
1889
- New lines opened:
- Cape Western – Eerste River to Somerset West on 21 October.
- Namaqualand – Braakpits Junction to Flat Mine on 23 April.[2]
- Natal – Ladysmith to Glencoe on 4 September.[13]
The 1890s
1890
- New lines opened:
- Cape Midland – Colesberg Junction to Norvalspont on 17 December.
- Cape Western – Somerset West to Sir Lowry's Pass Village on 1 February, Kalkbaai to Simon's Town and Kimberley to Vryburg, both on 1 December.
- Free State – Norvalspont to Bloemfontein on 17 December.
- Natal – Glencoe to Talana on 28 March and to Newcastle on 15 May.
- Transvaal – Braamfontein to Springs on 13 October and to Roodepoort on 17 November.
1891
- New lines opened:
- Natal – Newcastle to Charlestown on 7 April.
- Transvaal – Roodepoort to Krugersdorp on 10 February and Mozambique border near Komatipoort to Malelane on 28 December.
1892
- New lines opened:[14]
- Cape Eastern – Dreunberg Junction to Bethulie Bridge on 21 May.
- Cape Midland – Rosmead to Stormberg Junction on 8 February, to link with the Cape Eastern.
- Free State – Bloemfontein to Vaal River Bridge on 7 May, Bethulie Bridge to Springfontein on 21 May and Natal-Free State border to Harrismith on 12 July.
- Natal – Danskraal to Natal-Free State border on 12 July.
- Transvaal – Malelane to Nelspruit on 20 June and Vaal River Bridge to Germiston on 15 September.
1894
1895
- New lines opened:
- Natal – Charlestown to Natal-Transvaal border on 1 December.
- Transvaal – Natal-Transvaal border to Union Junction near Alberton on 15 December, linking Natal to Transvaal.
- The railways of the Cape Colony, Natal, the Orange Free State, the South African Republic and southern Mozambique are all linked at Union Junction near Alberton on 15 December.[14]
1896
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – Sterkstroom to Indwe on 1 February.
- Transvaal – Kaapmuiden to Barberton on 1 April and Krugersdorp to Frederikstad on 2 November.
- Cape Town's first electric tram service begins operating along Adderley Street to Mowbray Hill.
1897
- New lines opened:
- Cape Midland – Rosmead to Middelburg on 1 October.
- Cape Western – Mafeking to Ramatlabama at the Bechuanaland Protectorate border on 13 March.
- Natal – Isipingo to Park Rynie on 1 December, Verulam to Tongaat on 3 December and Thornville to Richmond on 15 December.
- Transvaal – Frederikstad to Klerksdorp on 3 August.
- The Pretoria-Pietersburg Railway purchases a 4-6-0T locomotive named Portuguese from Mozambique.[10]
1898
- New lines opened:
- Cape Midland – Middelburg to Graaff-Reinet on 3 March and Bamboo Junction to Cape Collieries.
- Free State – Theunissen to Winburg on 1 November.
- Namaqualand – Garracoop Junction to Nababeep on 15 October.[2]
- Natal – Clairwood to Wests in Durban on 13 June and Tongaat to Tugela on 1 December.[14]
- Transvaal – Pretoria to Potgietersrus on 1 October.
1899
- New lines opened:[15]
- Cape Central – Roodewal to Swellendam on 12 April.
- Free State – Wolwehoek to Heilbron on 31 January.
- Natal – Pietermaritzburg to New Hanover on 25 October.
- Transvaal – Potgietersrus to Pietersburg on 1 May.
- Walvis Bay - Walvis Bay to Plum.
The 1900s
1900
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – Bowker's Park to Tarkastad on 5 December.
- Natal – New Hanover to Greytown on 25 July, Park Rynie to Umzinto and Kelso Junction to Mtwalume, both on 8 August.
1901
- New lines opened:
- Cape Western – Malmesbury to Moorreesburg on 9 September.
- Natal – Stanger to Kearsney on 13 March and Mtwalume to North Shepstone on 27 July.
- The electric tramline in Cape Town is extended from Sea Point to Camps Bay.
1902
- New lines opened:
- Cape Midland – Cookhouse to Somerset East and Klipplaat to Willowmore, both on 1 August.
- Cape Western – Sir Lowry's Pass Village to Caledon on 1 August and Moorreesburg to Eendekuil on 15 November.
- Free State – Bloemfontein to Sannaspos on 1 May.
- Natal – Tugela to Mhlatuze on 18 July.
1903
- New lines opened:
- Cape Central – Swellendam to Riversdale on 19 February.
- Cape Eastern – King William's Town to Middledrift on 14 December.
- Cape Midland – Cookhouse to Adelaide and Willowmore to Le Roux, both on 14 December.
- Cape Western – Kalbaskraal to Hopefield on 28 February.
- Free State – Sannaspos to Thaba 'Nchu on 22 March and Harrismith to Aberfeldy on 1 April.
- Natal – Mhlatuze to Somkele on 17 September and Talana to Lucas Meyer on 12 November.
- Transvaal – India Junction to India Junction to Driehoek (avoiding line) on 27 April and to New Canada on 1 November.
1904
- New lines opened:[16]
- Cape Eastern – Indwe to Xalanga on 17 August, Amabele to Komga on 7 September and Middledrift to Adelaide on 17 October.
- Cape Midland – Le Roux to Oudtshoorn on 1 March.
- Cape Western – Maitland to Ottery on 1 February, Paarl to Franschhoek on 7 June and Ceres Road to Artois in December.
- Free State – Thaba 'Nchu to Modderpoort on 15 June and Hamilton to Tempe on 1 September.
- Natal – Pietermaritzburg to Elandskop on 3 November.
- Transvaal – Langlaagte to Vereeniging on 15 December.
1905
- New lines opened:[16]
- Cape Eastern – Xalanga to Elliot on 18 May, Komga to Eagle on 1 November and Aliwal North to Lady Grey on 2 November.
- Cape Midland – Humewood Road to Humansdorp on 1 November.
- Cape Western – Hutchinson to Pampoenpoort on 1 May, De Aar to Prieska on 19 September, Cape Town to Sea Point on 1 December and Van der Stel to Strand on 16 December.
- Free State – Springfontein to Jagersfontein on 1 February, Aberfeldy to Bethlehem on 1 March, Modderpoort to Ladybrand on 16 December, Marseilles to Maseru in Basutoland on 18 December, and Dover to Parys on 22 December.
- Natal – Elandskop to Donnybrook on 1 November.
- Transvaal – Rayton to Cullinan on 27 March, Klerksdorp to Vierfontein, Free State on 1 August and Springs to Breyten on 20 December.
1906
- New lines opened:[16]
- Cape Central – Riversdale to Voorbaai on 22 January.
- Cape Eastern – Elliot to Maclear on 29 August and Eagle to Butterworth on 17 December.
- Cape Midland – Port Elizabeth to Humewood Road on 1 April, Humansdorp to Misgund on 1 December and Valley Junction to Walmer on 15 December.
- Cape Western – Pampoenpoort to Carnarvon on 1 August.
- Free State – Jagersfontein to Fauresmith on 6 February and Bethlehem to Kroonstad on 21 June.
- Natal – Donnybrook to Creighton on 16 May and Ennersdale to Loskop on 1 June.
- Transvaal – Orkney to Fourteen Streams on 6 April, regauged from Pienaarsrivier to Settlers on 21 June, Apex to Witbank on 26 December, Pretoria North to Rustenburg on 27 December and Nancefield to Pimville.
1907
- New lines opened:[17]
- Cape Midland – Knysna to Templeman on 14 July and Mosselbaai to George on 25 September.
- Cape Western – Misgund to Avontuur on 1 January and Mafeking to Buurman's Drift on 16 May.[11]
- Free State – Modderpoort to Bethlehem on 2 July.[17]
- Natal – Estcourt to Weenen on 18 April, Loskop to Winterton on 15 May and North Shepstone to South Shepstone on 2 September.
- Transvaal – Breyten to Ermelo on 13 March and Krugersdorp to Zeerust on 5 July.
1908
- New lines opened:
- Cape Eastern – West Bank, Buffalo Harbour to Chiselhurst on 4 January.[11]
- Cape Western – Milnerton to Ascot on 28 May.[17]
- Free State – Hamilton to Beaconsfield on 8 April.
- Natal – Esperanza to Donnybrook on 3 June.
- Transvaal – Machadodorp to Breyten on 6 February.
1909
- New lines opened:[17]
- Cape Midland – Barkly Bridge to Alexandria on 18 May.
- Natal – Creighton to Riverside in the Eastern Cape on 4 February and Vryheid East to Hlobane on 1 April.
The 1910s
1910
- New lines opened:[17]
- Eastern Cape – By the Natal Government Railways from Riverside to Malenge in the Eastern Cape on 21 March.
- Natal – Utrecht Junction to Utrecht on 27 April.
- Transvaal – Belfast to Lydenburg on 29 April, Komatipoort to Newington on 15 May and Dunswart to Cranbourne on 4 July.
1911
- New lines opened:[17]
- Cape – Eendekuil to Graafwater on 31 May and Lady Grey to Melk on 1 December, Hopefield to Bergrivier (Narrow gauge) on 21 August.
- Free State – Sannaspos to Jammerdrif on 4 September and Bethlehem to Reitz on 2 December.
- Natal – Umlaas Road to Mid Illovo on 13 April, Merrivale to Howick on 7 October and Port Shepstone to Paddock on 8 November.
- Transvaal – India Junction to Alberton on 1 March, Welverdiend to Lichtenburg on 11 May, Welgedag to Modderbee on 2 July, Ermelo to Piet Retief on 31 July, Pietersburg to Bandelierkop on 15 August and Coligny to Delareyville on 4 December.
- A passenger train from Port Alfred derails on Blaauwkrantz Bridge and plunges into the ravine below.[1][5][10][18]
1912
- New lines opened:[19]
- Cape – Wolseley to Ceres on 20 May, Malenge to Franklin on 1 August, Schoombee to Hofmeyr and Ottery to Dieprivier on 2 December, Bergrivier to Vredenburg on 16 December and Melk to Motkop on 20 December.
- Free State – Jammerdrif to Wepener on 7 February and Firham, Transvaal to Vrede on 1 May.
- Transvaal – Buurman's Drift to Ottoshoop on 15 April, Zeerust to Ottoshoop on 4 November and Newington to Tzaneen on 9 November.
- The South African Railways reclassify and renumber the rolling stock of its three constituent railways.[1][20]
1913
- New lines opened:[19]
- Cape – Butterworth to Idutywa on 15 July, George to Oudtshoorn on 6 August, Graafwater to Kleipan on 3 November, Vredenburg to Saldanha on 5 March.
- Natal – Greytown to Ahrens on 1 December and Tendeka to Piet Retief in Transvaal on 15 December.
- Free State – Arlington to Senekal on 15 May and Reitz to Marsala on 3 November.
- Transvaal – Nelspruit to Sabie on 10 November and Bandelierkop to Lilliput on 5 December.
1914
- New lines opened:[19]
- Cape – Kleipan to Birdfield on 1 January, Gamtoos to Patensie on 3 April and Caledon to Klipdale on 6 April.
- Natal – Winterton to Bergville on 5 January, Ixopo to Madonela on 2 February, Ahrens to Kranskop on 23 February and Newleigh to Estcourt deviation in September.
- Free State – Marsala to Frankfort on 4 March.
- Transvaal – Lilliput to Messina on 5 May, Sabie to Graskop on 18 May, Cranbourne to Modderbee on 25 May and Bethal to Morgenzon on 21 December.
1915
- New lines opened:[19]
- Cape – Klipdale to Protem on 30 June, Prieska to South West Border on 1 August, Birdfield to Klawer on 15 November, Motkop to New England on 29 November and Carnarvon to Williston on 1 December.
- Free State – Westleigh to Vierfontein and Fauresmith to Koffiefontein, both on 31 May.
- Natal – Dalton to Glenside on 12 April, Paddock to Izingolweni on 16 August and Schroeders to Bruyns Hill on 5 October.
- Transvaal – Tzaneen to Soekmekaar on 4 August.
- Cape (Walvisbaai) – Walvisbaai to Swakop River on 1 August.
- The SAR purchases six Rhodesian 7th Class locomotives and designate them Class 7D and Class 7B.[21]
- Thirteen Mozambican Falcon 4-4-0 locomotives are acquired to relieve engines for service in South West Africa.[22]
1916
- New lines opened:[23]
- Cape – Idutywa to Umtata on 18 September, Williston to Kootjieskolk on 2 October and Ascot to Tygerberg in November.
- Free State – Aliwal North to Zastron on 30 June and Vierfontein to Bothaville on 31 July.
- Natal – Boughton to Cedara deviation on 25 May and Donnybrook to Underberg on 24 November.
- Transvaal – Morgenzon to Amersfoort on 18 February, Volksrust to Amersfoort on 5 June and Delareyville to Pudimoe on 18 October.
1917
- New lines opened:[23]
- Natal – Izingolweni to Harding on 5 March and Gingindlovu to Eshowe on 20 June.
1918
1919
- New lines opened:[23]
- Natal – Deviation from Umlaas Road to Pentrich on 9 January.
The 1920s
1921
- New lines opened:[23]
- Transvaal – Pretoria West to Roberts Heights on 1 November.
- Natal – Booth Junction to Cato Ridge on 28 November.
1922
- New lines opened:[23]
- South West Africa – Kolmanskop to Bogenfels on 1 April.
- The South African Railways inherits all railway in South West Africa.[24]:117, 121
1923
- New lines opened:[23]
- Cape – Kamfersdam to Winter's Rush on 6 August and Belmont to Douglas on 9 August.
- Transvaal – Settlers to Tuinplaas on 30 October.
1924
- New lines opened:
- Cape – Klipdale to Bredasdorp on 19 April, Pinelands to Langa on 16 June, Franklin to Kokstad on 3 November, Franklin to Matatiele on 4 November, Oudtshoorn to Calitzdorp on 14 November and Touws River to Kareevlakte on 15 December.
- Free State – Wepener to Zastron on 16 April and Heilbron to Petrus Steyn on 24 July.
- South West Africa – Gobabis Junction in Windhoek to Ondekaremba on 19 September.
- Transvaal – Balfour North to Grootvlei on 1 May, Lydenburg to Steelpoort on 10 September, Naboomspruit to Singlewood on 22 September and Hercules to Schoemansville on 15 December.
1925
- New lines opened:[25]
- Cape – Kareevlakte to Ladismith on 19 October and Fort Beaufort to Katberg on 1 December.
- Free State – Senekal to Marquard on 14 October and Frankfort to Villiers on 26 November.
- Natal – Eshowe to Extension on 26 June.
- Transvaal – Rustenburg to Boshoek on 21 January, Magaliesburg to Schoemansville on 26 May, Ermelo to Lothair on 1 September, Elandshoek to Solarvale on 25 September and Nylstroom to Vaalwater on 1 October.
- The New Cape Central Railway and its line from Worcester to Voorbaai is taken over by the South African railways.
1926
- New lines opened:[25]
- Cape – Upington to Kakamas on 18 August, Addo to Sunland on 1 September, Katberg to Seymour on 19 November and Klawer to Landplaas on 8 December.
- Free State – Harrismith to Warden on 7 June.
- Natal – Mtubatuba to Candover on 15 September.
- Transvaal – Villiers, Free State to Grootvlei on 18 January and Citrus to Plaston on 22 November.
1927
- New lines opened:[25]
- Cape – Sunland to Kirkwood on 7 January, Landplaas to Bitterfontein on 27 April and Imvani to Qamata on 14 September.
- Natal – Candover to Golela, Transvaal on 4 July.
- Transvaal – Solarvale to Mount Carmel on 10 February and Makwassie to Vermaas on 1 July.
1928
- New lines opened:[25]
- Cape – Winter's Rush to Koopmansfontein on 31 January and George to Knysna on 1 May.
- Free State – Bothaville to Wesselsbron on 18 July.
- South West Africa – Ondekaremba to Seeis on 9 July.
- Transvaal – Klerksdorp to Ottosdal on 24 February, Potchefstroom to Fochville on 14 April, Brits to Beestekraal on 11 June and Singlewood to Zebediela on 2 July.
1929
- New lines opened:[25]
- Cape – Hermon to Porterville on 3 April, Ceres to Prince Alfred Hamlet on 10 April, and the line from Monument to Sea Point is uplifted on 17 April.
- Free State – Wesselsbron to Bultfontein on 16 April and Arlington to Lindley on 31 July.
- South West Africa – Seeis to Witvlei on 1 December.
- Transvaal – Boshoek to Middelwit on 12 August, Messina to Beitbridge on 31 August and Derwent to Stoffberg on 14 November.
The 1930s
1930
- New lines opened:[25][26]
- Cape – Fort Knokke to Woltemade no. 1 on 14 April, Koopmansfontein to Postmasburg on 1 November and New England to Barkly East on 10 December.
- Free State – Parys to Vredefort on 24 April and Petrus Steyn to Lindley on 14 May.
- Natal – Empangeni to Nkwalini on 19 September.
- South West Africa – Witvlei to Gobabis on 6 November.
1931
- New lines opened:[26]
- Cape – Molteno to Jamestown on 3 June.
- Natal – Chailey to Mount Alida and Greyville Cabin to Berea Road, both on 1 July.
1934
- New lines opened:[26]
- Cape – Kleinstraat to Matroosberg on 15 October.
- Transvaal – Northam Junction to Thabazimbi on 26 February, Germiston to Elsburg on 29 July and Tuinplaas to Marble Hall on 21 September.
1935
1936
- New lines opened:[26]
- Cape – Palingpan to Manganore on 15 June and Postmasburg to Lohatla on 30 June.
- Natal – Point to Congella on 1 May.
1938
- New lines opened:[27]
- Transvaal – Midway to Bank on 6 November.
The 1940s
1940
1943
- New lines opened:[27]
- Transvaal – New Canada to Phomolong on 29 January and Hercules to Koedoespoort on 7 June.
1945
- New lines opened:[27]
- Transvaal – Village Main to Faraday on 4 June.
1948
- New lines opened:[27]
- Free State – Whites to Odendaalsrus on 7 June.
The 1950s
1950
- New lines opened:[27]
- Transvaal – Vandyksdrif to Broodsnyersplaas on 2 October.
1951
1952
- New lines opened:[27]
- Free State – Odendaalsrus to Allanridge on 18 December.
1953
The 1960s
1965
- At least 150 are killed when a commuter train derails at the outskirts of Durban.
The 1980s
1982
1984
- The South African Railways inaugurates the MetroBlitz interurban train service between Pretoria and Johannesburg.[29]
The 1990s
1990
- South African Transport Services become Transnet and the South African Rail Commuter Corporation, with Spoornet and Metrorail as respective railway operators.
The 2000s
The 2010s
References
- The South African Railways – Historical Survey. Editor George Hart, Publisher Bill Hart, Sponsored by Dorbyl Ltd., Published c. 1978.
- Bagshawe, Peter (2012). Locomotives of the Namaqualand Railway and Copper Mines (1st ed.). Stenvalls. ISBN 978-91-7266-179-0.
- Pioneer, Little Bess & Mliss
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 181, ref. no. 200954-13
- Heritage Portal: The Port Alfred to Grahamstown Railway Archived 6 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- Table Bay Harbour construction locomotives
- The Cape Argus of 19 July 1870.
- Grace’s Guide: Henry Hughes and Company
- Dating the opening of Hughes Works
- Holland, D.F. (1971). Steam Locomotives of the South African Railways. 1: 1859–1910 (1st ed.). Newton Abbott, Devon: David & Charles. ISBN 978-0-7153-5382-0.
- Report for year ending 31st December 1909, Cape Government Railways, Section VIII – Dates of Opening and the Length of the different Sections in the Cape Colony, from the Year 1873 to 31 December 1909.
- Lewis, Charles; Pivnic, Les. "Soul of A Railway". System 1, Part 3: Wellington to Touws River, pp. 31–32. (Retrieved on 3 September 2016)
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 182, ref. no. 200954-13
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 183, ref. no. 200954-13
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 184, ref. no. 200954-13
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 185, ref. no. 200954-13
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 186, ref. no. 200954-13
- The Port Alfred Kowie Railway 1883–1913
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 187, ref. no. 200954-13
- Classification of S.A.R. Engines with Renumbering Lists, issued by the Chief Mechanical Engineer's Office, Pretoria, January 1912. (Reprinted in April 1987 by SATS Museum, R.3125-6/9/11-1000)
- Pattison, R.G. (1997). The Cape Seventh Class Locomotives (1st ed.). Kenilworth, Cape Town: The Railway History Group. ISBN 0958400946.
- Railway Modelling Scene, South Africa, May/June 1985, article written by Neill Mardell
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 188, ref. no. 200954-13
- Paxton, Leith; Bourne, David (1985). Locomotives of the South African Railways (1st ed.). Cape Town: Struik. ISBN 0869772112.
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 189, ref. no. 200954-13
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 190, ref. no. 200954-13
- Statement Showing, in Chronological Order, the Date of Opening and the Mileage of Each Section of Railway, Statement No. 19, p. 191, ref. no. 200954-13
- Middleton, John N. (2002). Railways of Southern Africa Locomotive Guide - 2002 (as amended by Combined Amendment List 4, January 2009) (2nd, Dec 2002 ed.). Herts, England: Beyer-Garratt Publications. pp. 38–39, 41, 46.
- Die Vaderland, Donderdag 12 Januarie 1984, p. 3
- "104 miners are crushed to death when an elevator carrying gold miners plunges to the bottom of a Vaal Reef mineshaft near Orkney". South African History Online. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- "Locomotive crushes 105 gold miners". The Independent. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- Fihlani, Pumza (8 June 2010). "Gautrain arrives in time for World Cup". BBC News. Retrieved 1 July 2020.


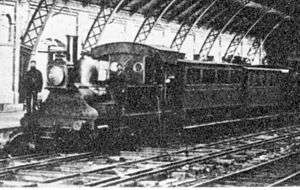


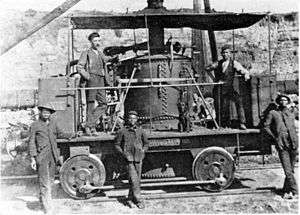
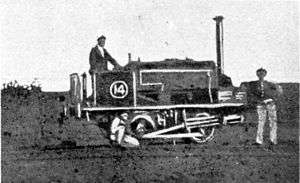

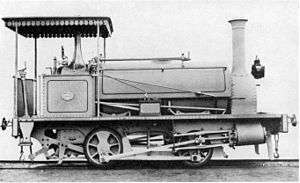
_1875_no._4.jpg)
_of_1875.jpg)
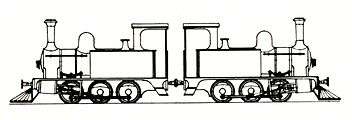



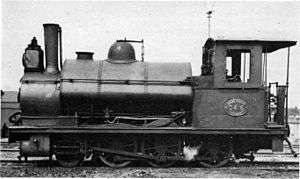
.jpg)

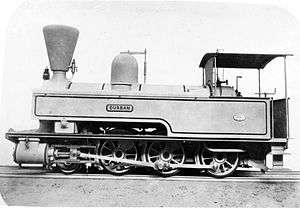



_1879.jpg)
.jpg)

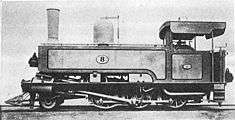

.jpg)


_1881.jpg)
_of_1882_(Wynberg_Tank).jpg)






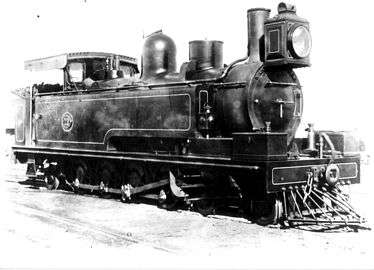
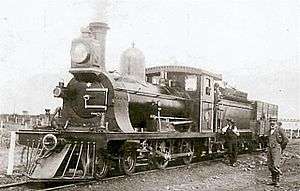

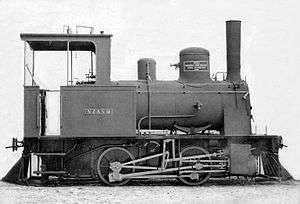


.jpg)


.jpg)


_F.jpg)
_ex_CGR_357-OVGS_62-CSAR_338.jpg)
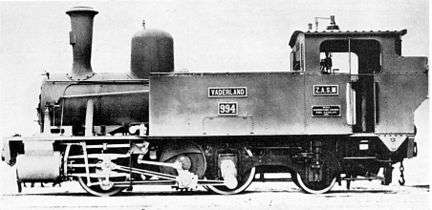

.jpg)
_ex_OVGS_88-CSAR_364.jpg)


_CGR_206.jpg)
_as_built.jpg)



_ex_CGR_665.jpg)
_ex_OVGS-CSAR_6L-3.jpg)

_ex_NCCR_4.jpg)

.jpg)

_ex_CGR.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
_ex_Zululand_Ry_1.jpg)
_NGR_38_ex_NGR_25.jpg)
.jpg)
_ex_CGR_607-547.jpg)
_ex_CGR.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
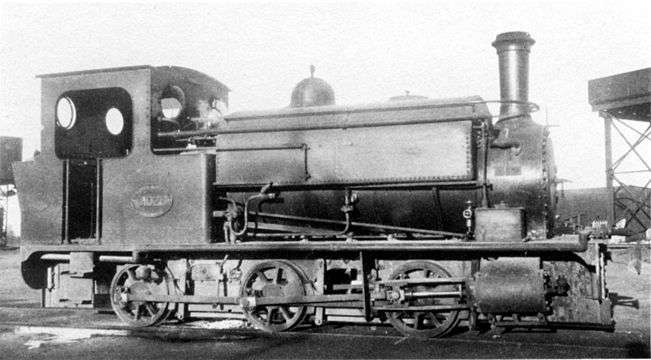



.jpg)
_ex_Zululand_Ry_2.jpg)
_NGR_Neilson_Reid_1.jpg)
_ex_CGR_538.jpg)
_ex_CGR.jpg)
_CGR_779.jpg)
_IMR-CSAR_438.jpg)
_CGR_804.jpg)
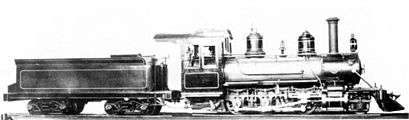
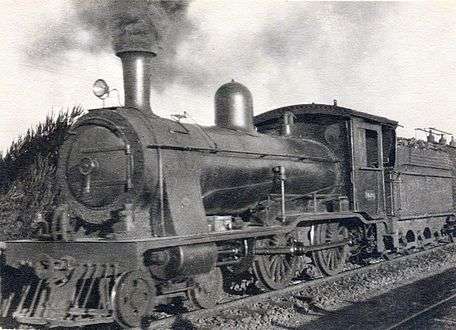


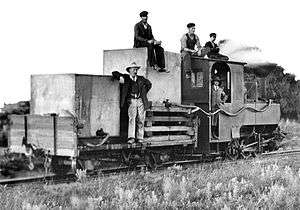
.jpg)
_CGR_903.jpg)
.jpg)
_CSAR_483.jpg)
.jpg)
_CGR_814.jpg)
_CGR_820.jpg)
_CGR_839.jpg)
_CGR_9th_Class_806.jpg)
.jpg)



_Dubs_B_250.jpg)

.jpg)
_ex_CGR.jpg)
_CGR_825.jpg)

_ex_CSAR_656.jpg)
_CSAR_721.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)





_CGR_Class_9_840_Works_4341.jpg)
_CGR_Class_10_880_Works_4375.jpg)

_ex_DSWA.jpg)

_CGR_900_3_cyl_comp.jpg)
.jpg)

_NGR_332.jpg)

.jpg)

_NGR_335.jpg)
.jpg)
_ex_CSAR_674.jpg)
.jpg)
_ex_CSAR_1002.jpg)
_NGR_337.jpg)



.jpg)
_CSAR_1023.jpg)
_CSAR_1024_b.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


_220481.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
_ex_NCCR_10.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

_a.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)

.jpg)



.jpg)


_Ex_1649.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)

_b.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
_Princess_Alice.jpg)

_Daisy.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
_Condenser.jpg)



.jpg)
_a.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

_c.jpg)


_a.jpg)
















.jpg)

.jpg)








