Kowie Railway 0-6-0T
The Kowie Railway 0-6-0T of 1882 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.
| Kowie Railway 0-6-0T Kowie Railway 4-4-0T 1884 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
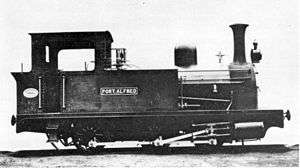 Kowie Railway 0-6-0T Port Alfred, as built | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 1882, two 0-6-0 tank locomotives entered service on the private Kowie Railway which was being constructed between Port Alfred and Grahamstown. Both locomotives were rebuilt to a 4-4-0T wheel arrangement in 1884.[1][2]
The Kowie Railway
The private Kowie Railway line from Port Alfred to Grahamstown was built and operated by three successive private enterprises. Early in 1881, the Government of the Cape of Good Hope passed a Bill to authorise the London-based Grahamstown and Port Alfred Railway Company to construct a railway from Port Alfred northwestwards to Grahamstown. The company was established with a capital of £200,000 and, since the railway was to link Grahamstown with the harbour at Port Alfred, the Government undertook to subsidise it to the extent of £500,000.[1][2][3]
The greatest challenge to overcome during the building of the railway was the construction of the Blaauwkrantz Bridge across the Kowie River, which delayed progress. In 1882, the 43-mile long (69-kilometre) railway was partially opened to traffic as far as Blaauwkrantz. The line was only completed to Grahamstown and opened to traffic on 3 December 1884. The track had approximately 6% of 1 in 40 (2½%) and 30% of 1 in 50 (2%) gradients.[2][3]
Manufacturer
On 22 May 1882, two 0-6-0 tank locomotives for the Grahamstown and Port Alfred Railway Company, built by Hunslet Engine Company with works numbers 277 and 278, were landed at Port Alfred off the SS Rothesay. The locomotives were acquired for goods working and were named Port Alfred and Kowie respectively.[1][2]
Modification
In 1884, both locomotives were rebuilt to 4-4-0 tank locomotives. The necessary parts and equipment for the conversion were supplied by Hunslet and the rebuilding took place at Port Alfred. It involved the removal of the leading coupled wheels, extending the frame in front of the smokebox and the installation of a four-wheeled leading bogie.[1]
Liquidations
Partly as a result of the delays which occurred during the Kowie Harbour development at Port Alfred due to the continuous silting up of the Kowie River, the Grahamstown and Port Alfred Railway Company soon suffered financial difficulties and was forced into liquidation in 1887.[3]
A group of Grahamstown residents formed a syndicate in 1888 and took over the operation of the line to Port Alfred until 1895, when they sold out to the Kowie Railway Company.[3]
South African Railways
Following a major disaster when a passenger train derailed on the Blaauwkrantz Bridge in 1911, the resultant claims against the Kowie Railway Company led to its bankruptcy. On 1 April 1913, the line and the locomotives were taken over by the Union Government and became part of the South African Railways. The two locomotives remained in service on this line until they were scrapped.[1][2][3]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kowie Railway 0-6-0T. |
- Holland, D.F. (1971). Steam Locomotives of the South African Railways. 1: 1859–1910 (1st ed.). Newton Abbott, Devon: David & Charles. p. 80-83. ISBN 978-0-7153-5382-0.
- Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1943). The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter II - The Cape Government Railways (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, November 1943. pp. 811-812, 818.
- The South African Railways - Historical Survey. Editor George Hart, Publisher Bill Hart, Sponsored by Dorbyl Ltd., Published c. 1978, pp. 12-13.