Kowie Railway 4-4-0T
The Kowie Railway 4-4-0T of 1882 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.
| Kowie Railway 4-4-0T | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Kowie Railway 4-4-0T Grahamstown | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 1882, two 4-4-0 American type tank locomotives entered passenger service on the private Kowie Railway which was under construction between Port Alfred and Grahamstown.[1]
The Kowie Railway
The private Kowie Railway between Port Alfred and Grahamstown was built and operated by three successive private enterprises, all of which ran into financial difficulties.[2]
In 1881, the Government of the Cape of Good Hope passed a Bill to authorise the London-based Grahamstown and Port Alfred Railway Company to construct a railway from Port Alfred to Grahamstown. The contract for construction was awarded to Pauling & Co. and the first sod was officially turned on 21 October 1881.[2][3][4]
The surveyed route of the line crossed the Kowie River at Blaauwkrantz, where a high bridge needed to be constructed. It had been estimated that the line would be completed by the end of 1883, but since the construction of the Blaauwkrantz Bridge delayed progress, the 43-mile long (69-kilometre) line was only partially opened to traffic from Port Alfred as far as Blaauwkrantz on 24 December 1883. Here, passengers had to disembark and complete the journey to Grahamstown on the post cart.[2][3][4]
On 1 October 1884, the bridge was completed and opened to traffic. The Kowie Railway linked up with the Cape Government Railways at Grahamstown on 11 November 1884.[3]
Manufacturer
In 1882, two 4-4-0 American type tank locomotives, with works numbers 294 and 295, were delivered from Hunslet Engine Company to the Grahamstown and Port Alfred Railway Company. The locomotives were acquired for passenger working and were named Grahamstown and Bathurst respectively. They were designed for wood-burning and were equipped with large American-style balloon smokestacks which incorporated spark arresters.[1][4]
Liquidation
Partly as a result of the difficulties experienced with harbour development at Port Alfred, the Grahamstown and Port Alfred Railway Company soon experienced financial difficulties and was forced into liquidation in 1887. In 1888, a group of Grahamstown residents formed a syndicate and took over the operation of the line to Port Alfred until 1895, when they sold out to the Kowie Railway Company.[2]
The Kowie Railway was never prosperous. After the Cape Government eventually abandoned its attempts at harbour development at Port Alfred in 1898 due to the continuous silting up of the Kowie River, the line's financial difficulties increased. Track maintenance was neglected and the situation was aggravated by a series of minor accidents.[1]
The Blaauwkrantz disaster
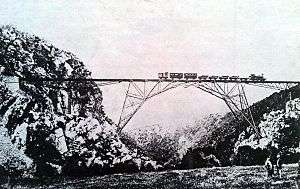
The Kowie Railway's death blow came on 22 April 1911. A mixed train from Port Alfred, made up of six goods trucks, three passenger carriages and a guard's van, came to grief when one of the goods trucks derailed on the Blaauwkrantz Bridge and, with the three carriages and the guard's van, plunged into the ravine 200 feet (61 metres) below. Of the 55 passengers, 31 were killed and 23 seriously injured. The resultant claims against the Kowie Railway Company forced it into bankruptcy.[1][2][3][5]
South African Railways
On 1 April 1913, the line was taken over by the Union Government and became part of the South African Railways. The two passenger locomotives, along with the two goods engines Port Alfred and Kowie, and three Cape 4th Class 4-6-0TT locomotives which had been purchased from the Cape Government Railways around 1904, remained in service on this line until they were scrapped.[1][2]
References
- Holland, D.F. (1971). Steam Locomotives of the South African Railways. 1: 1859–1910 (1st ed.). Newton Abbott, Devon: David & Charles. p. 80-83. ISBN 978-0-7153-5382-0.
- The South African Railways - Historical Survey. Editor George Hart, Publisher Bill Hart, Sponsored by Dorbyl Ltd., Published c. 1978, pp. 12-13.
- Heritage Portal: The Port Alfred to Grahamstown Railway Archived 6 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1943). The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter II - The Cape Government Railways (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, November 1943. pp. 811-812, 818.
- The Port Alfred Kowie Railway 1883-1913