Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (Italian: Granducato di Toscana; Latin: Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was a central Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Duchy of Florence.[2] The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population of the Grand Duchy was about 1,815,000 inhabitants.[3]
Grand Duchy of Tuscany | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1569–1801 1814–1859 1859–1860 | |||||||||||||||||||
Anthem: "La Leopolda" | |||||||||||||||||||
.png) The Grand Duchy of Tuscany in 1815. | |||||||||||||||||||
.jpg) Northern Italy in 1815. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Florence | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Italian | ||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Unitary absolute monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Grand Duke | |||||||||||||||||||
• 1569–1574 | Cosimo I de' Medici (first) | ||||||||||||||||||
• 1859–1860 | Ferdinand IV (last) | ||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||
| 27 August 1569 | |||||||||||||||||||
• End of Medici rule | 9 July 1737 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 21 March 1801 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 9 June 1815 | |||||||||||||||||||
• Deposition of the Habsburgs | 16 August 1859 | ||||||||||||||||||
• Merged to form the United Provinces of Central Italy | 8 December 1859 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 22 March 1860 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||
• 1801 | 1,096,641[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Tuscan lira (to 1826) Tuscan fiorino (1826–1859) | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Initially, Tuscany was ruled by the House of Medici until the extinction of its senior branch in 1737. While not as internationally renowned as the old republic, the grand duchy thrived under the Medici and it bore witness to unprecedented economic and military success under Cosimo I and his sons, until the reign of Ferdinando II, which saw the beginning of the state's long economic decline. It peaked under Cosimo III.[4]
Francis Stephen of Lorraine, a cognatic descendant of the Medici, succeeded the family and ascended the throne of his Medicean ancestors. Tuscany was governed by a viceroy, Marc de Beauvau-Craon, for his entire rule. His descendants ruled, and resided in, the grand duchy until its end in 1859, barring one interruption, when Napoleon Bonaparte gave Tuscany to the House of Bourbon-Parma (Kingdom of Etruria, 1801–7). Following the collapse of the Napoleonic system in 1814, the grand duchy was restored. The United Provinces of Central Italy, a client state of the Kingdom of Sardinia, annexed Tuscany in 1859. Tuscany was formally annexed to Sardinia in 1860, as a part of the unification of Italy, following a landslide referendum, in which 95% of voters approved.[5]
Medici Period
Foundation
In 1569, Cosimo de' Medici had ruled the Duchy of Florence for 32 years. During his reign, Florence purchased the island of Elba from the Republic of Genoa (in 1548),[6] conquered Siena (in 1555)[7] and developed a well-equipped and powerful naval base on Elba. Cosimo also banned the clergy from holding administrative positions and promulgated laws of freedom of religion, which were unknown during his time.[8] Cosimo also was a long-term supporter of Pope Pius V, who in the light of Florence's expansion in August 1569 declared Cosimo Grand Duke of Tuscany, a title unprecedented in Italy.[6]
The international reaction to Cosimo's elevation was bleak. Queen Catherine of France, though herself a Medici, viewed Cosimo with the utmost disdain.[9] Rumours circulated at the Viennese court that had Cosimo as a candidate for King of England.[10] Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor and his cousin King Philip II of Spain reacted quite angrily, as Florence was an Imperial fief and declared Pius V's actions invalid. However, Maximilian eventually confirmed the elevation with an Imperial diploma in 1576.[11]
During the Holy League of 1571, Cosimo fought against the Ottoman Empire, siding with the Holy Roman Empire. The Holy League inflicted a crushing defeat against the Ottomans at the Battle of Lepanto.[12] Cosimo's reign was one of the most militaristic Tuscany had ever seen.
Cosimo experienced several personal tragedies during the later years of his reign. His wife, Eleanor of Toledo, died in 1562, along with four of his children due to a plague epidemic in Florence. These deaths were to affect him greatly, which, along with illness, forced Cosimo to unofficially abdicate in 1564. This left his eldest son, Francesco, to rule the duchy. Cosimo I died in 1574 of apoplexy, leaving a stable and extremely prosperous Tuscany behind him, having been the longest ruling Medici yet.[13]
Francesco and Ferdinando I
Francesco had little interest in governing his realm, instead participating in scientific experiments.[11] The administration of the state was delegated to bureaucrats. He continued his father's Austrian/Imperial alliance, cementing it by marrying Johanna of Austria.[14] Francesco is best remembered for dying on the same day as his second wife, Bianca Cappello, spurring rumours of poisoning.[14] He was succeeded by Ferdinando de' Medici, his younger brother, whom he loathed.[14]
Ferdinando eagerly assumed the government of Tuscany.[15] He commanded the draining of the Tuscan marshlands, built a road network in Southern Tuscany, and cultivated trade in Livorno.[16] To augment the Tuscan silk industry, he oversaw the planting of Mulberry trees along the major roads (silk worms feed on Mulberry leaves).[15] He shifted Tuscany away from Habsburg[17] hegemony by marrying the first non-Habsburg candidate since Alessandro de' Medici, Duke of Florence, Christina of Lorraine, a granddaughter of Catherine de' Medici. The Spanish reaction was to construct a citadel on their portion of the island of Elba.[16] To strengthen the new Tuscan alliance, he married the deceased Francesco's younger daughter, Marie, to Henry IV of France. Henry explicitly stated that he would defend Tuscany from Spanish aggression, but later reneged.[16] Ferdinando was forced to marry his heir, Cosimo, to Archduchess Maria Maddalena of Austria to assuage Spain (where Maria Maddalena's sister was the incumbent Queen consort).[16] Ferdinando sponsored a Tuscan colony in America, with the intention of establishing a Tuscan settlement in the area of what is now French Guiana. Despite all of these incentives to economic growth and prosperity, the population of Florence, at dawn of the 17th century, was a mere 75,000 souls, far smaller than the other capitals of Italy: Rome, Milan, Venice, Palermo and Naples.[18] Francesco and Ferdinando, due to lax distinction between Medici and Tuscan state property, are thought to be wealthier than their ancestor, Cosimo de' Medici, the founder of the dynasty.[19] The Grand Duke alone had the prerogative to exploit the state's mineral and salt resources. The fortunes of the Medici were directly tied to the Tuscan economy.[19]
Ferdinando, despite no longer being a cardinal, exercised much influence at successive Papal conclaves; elections which chose the Pope, the head of the Catholic Church. In 1605, Ferdinando succeeded in getting his candidate, Alessandro de' Medici, elected as Pope Leo XI. Leo XI died less than a month later, but fortunately for the Medici his successor Pope Paul V was also pro-Medici.[20] Ferdinando's pro-Papal foreign policy, however, had drawbacks. Tuscany was overcome with religious orders, all of whom were not obliged to pay taxes. Ferdinando died in 1609, leaving an affluent realm; however, his inaction in international affairs drew Tuscany into the provincial yolk of politics.
Cosimo II and Ferdinando II

Ferdinando's elder son, Cosimo, mounted the throne following his death. Like his uncle, Francesco I, government held no appeal for him, and Tuscany was ruled by his ministers.[21] Cosimo II's twelve-year reign was punctuated by his contented marriage with Maria Maddalena and his patronage of astronomer Galileo Galilei.
When Cosimo died, his oldest son, Ferdinando, was still a minor. This led to a regency of Ferdinand's grandmother, Dowager Grand Duchess Christina, and his mother, Maria Maddalena of Austria. Christina heavily relied on priests as advisors, lifting Cosimo I's ban on clergy holding administrative roles in government, and promoted monasticism. Christina dominated her grandson long after he came of age until her death in 1636.[22] His mother and grandmother arranged a marriage with Vittoria della Rovere, a granddaughter of the Duke of Urbino, in 1634. Together they had two children: Cosimo, in 1642, and Francesco Maria de' Medici, Duke of Rovere and Montefeltro, in 1660.[23]
Ferdinando was obsessed with new technology, and had several hygrometers, barometers, thermometers, and telescopes installed in the Pitti.[24] In 1657, Leopoldo de' Medici, the Grand Duke's youngest brother, established the Accademia del Cimento, which set up to attract scientists from all over Tuscany to Florence for mutual study.[25]
Tuscany participated in the Wars of Castro (the last time Medicean Tuscany proper was involved in a conflict) and inflicted a defeat on the forces of Urban VIII in 1643.[26] The treasury was so empty that when the Castro mercenaries were paid for the state could no longer afford to pay interest on government bonds. The interest rate was lowered by 0.75%.[27] The economy was so decrepit that barter trade became prevalent in rural market places.[26] The exchequer was barely adequate to cover the state's current expenditure, resulting in a complete termination of banking operations for the Medici.[28] Ferdinando II died in 1670, succeeded by his oldest surviving son Cosimo.[29]
Cosimo III

Cosimo III's reign was characterised by drastic changes and a sharp decline of the Grand Duchy. Cosimo III was of a puritan character, banning May celebrations, forcing prostitutes to pay for licenses and, beheading sodomites. He also instituted several laws censoring education[30] and introduced anti-Jewish legislation.[31] He imposed crippling taxes[32] while the country's population continued to decline. By 1705, the grand ducal treasury was virtually bankrupt, and the population of Florence had declined by approximately 50%, while the population of the entire grand duchy had decreased by an estimated 40%.[33] The once powerful navy was reduced to a pitiful state.[34]
Cosimo frequently paid the Holy Roman Emperor, his feudal overlord, high dues.[35] He sent munitions to the Emperor during the Battle of Vienna. Tuscany was neutral during the War of the Spanish Succession, partly due to Tuscany's ramshackle military; a 1718 military review revealed that the army numbered less than 3,000 men, many of whom were infirm and elderly.[36] Meanwhile, the state's capital, Florence, had become full of beggars.[37] Europe heard of the perils of Tuscany, and Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor asserted a remote claim to the grand duchy (through some Medici descent), but died before he could press the matter.
Cosimo married Marguerite Louise d'Orléans, a granddaughter of Henry IV of France and Marie de' Medici. Their union wrought a high level of discontentment, but despite the tension they had three children, Ferdinando, Anna Maria Luisa de' Medici, Electress Palatine and the last Medicean grand duke of Tuscany, Gian Gastone de' Medici. Neither of Cosimo's two sons was a suitable heir; Ferdinando was an alcoholic and epileptic, while his younger son, Gian Gastone, according to historian Paul Strathern, was not appropriate material for the role of sovereign.
Cosimo contemplated restoring the Republic of Florence,[5][38] a decision that was complicated by the Grand Duchy's feudal status: Florence was an Imperial fief, Siena a Spanish one.[5] The plan was about to be approved by the powers convened at Geertruidenberg when Cosimo abruptly added that if himself and his two sons predeceased his daughter, the Electress Palatine, she should succeed and the republic be re-instituted following her death.[39] The proposal sank, and ultimately died with Cosimo in 1723.
The last years of the Medici
Cosimo III was succeeded by his son, Gian Gastone, who, for most of his life, kept to his bed and acted in an unregal manner, rarely appearing to his subjects, to the extent that, at times, he had been thought dead. Gian Gastone would repeal his father's puritan laws.[40] In 1731, the Powers gathered at Vienna to decide who would succeed Gian Gastone. They drew up the Treaty of Vienna, which gave the grand ducal throne to Don Carlos, Duke of Parma. Gian Gastone was not as steadfast in negotiating Tuscany's future as his father was. He capitulated to foreign demands, and instead of endorsing the claim to the throne of his closest male relative, the prince of Ottajano, he allowed Tuscany to be bestowed upon Francis Stephen of Lorraine. Don Carlos became King of Naples shortly after his arrival in Florence in 1735, by the Treaty of Turin. Soon after, Francis Stephen of Lorraine became heir to the Tuscan throne. Gian Gastone had no say in events and had become quite attached to the Spanish Infante. The Tuscans despised the new occupying "Lorrainers", as they interfered with the Tuscan government, while the occupying Spaniards had not done so.[41] On July 9 1737, Gian Gastone died; the last male Medici of the Grand Ducal line.[42]
House of Habsburg-Lorraine

Francis Stephen
Francis I (as Francis Stephen became known) lived in Florence briefly with his wife, the Habsburg heiress Maria Theresa, who became Tuscany's grand duchess. Francis had to cede his ancestral Duchy of Lorraine in order to accommodate the deposed ruler of Poland, whose daughter Marie Leszczyńska became Queen of France and of Navarre in 1725. Marie's father Stanisław I of Poland ruled Lorraine as compensation for his loss of the Kingdom of Poland. Francis was reluctant to resign the duchy, but Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor (Maria Theresa's father) stated that if he didn't relinquish his rights to Lorraine, he could not marry Maria Theresa. Francis did not live in his Tuscan realm, and lived in the capital of his wife's realm, Vienna. He was elected Holy Roman Emperor in 1745. He died at Innsbruck from a stroke in 1765; his wife pledged the rest of her life to mourning him, while co-ruling with her son, and Francis' imperial successor Joseph II. Tuscany passed to another son, Leopold.[43] The administrative structure of the grand duchy itself would see little change under Francis I.
Reform

.svg.png)
Francis' second surviving son Peter Leopold became grand duke of Tuscany and ruled the country until his brother Joseph's death. He was unpopular among his subjects, though his many reforms brought the Grand Duchy to a level of stability that had not been seen in quite a while.[43]
Leopold developed and supported many social and economic reforms. He revamped the taxation and tariff system.[43] Smallpox vaccination was made systematically available (Leopold's mother Maria Theresa had been a huge supporter on inoculation against smallpox), and an early institution for the rehabilitation of juvenile delinquents was founded. Leopold also abolished capital punishment. On 30 November 1786, after having de facto blocked capital executions (the last was in 1769), Leopold promulgated the reform of the penal code that abolished the death penalty and ordered the destruction of all the instruments for capital execution in his land. Torture was also banned.[45]
Leopold also introduced radical reforms to the system of neglect and inhumane treatment of the mentally ill. On 23 January 1774, the legge sui pazzi (law regarding the insane) was established, the first of its kind to be introduced in Europe, allowing steps to be taken to hospitalize individuals deemed insane. A few years later Leopold undertook the project of building a new hospital, the Bonifacio. He used his skill at choosing collaborators to put a young physician, Vincenzo Chiarugi, at its head. Chiarugi and his collaborators introduced new humanitarian regulations in the running of the hospital and caring for the mentally ill patients, including banning the use of chains and physical punishment, and in so doing have been recognized as early pioneers of what later came to be known as the moral treatment movement.[46]
Leopold attempted to secularize the property of the religious houses or to put the clergy entirely under the control of the government. These measures, which disturbed the deeply rooted convictions of his people and brought him into collision with the pope, were not successful.
Leopold also approved and collaborated on the development of a political constitution, said to have anticipated by many years the promulgation of the French constitution and which presented some similarities with the Virginia Bill of Rights of 1778. Leopold's concept of this was based on respect for the political rights of citizens and on a harmony of power between the executive and the legislative. However, the constitution was so radically new that it garnered opposition even from those who might have benefited from it. In 1790, Emperor Joseph II died without issue and Leopold was called to Vienna, to assume the rule of his family's Austrian dominions and become Emperor.[45] His second son Ferdinand became ruler of the Grand Duchy. Leopold himself died in 1792.
Tuscany during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
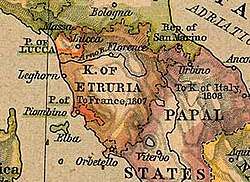
Leopold was succeeded by Ferdinand III. Ferdinand was the son of the incumbent Grand Duke, and Grand Duchess Maria Louisa. He was forced out by the French during the French Revolutionary Wars, first in 1799, and then after the Treaty of Aranjuez (1801), becoming instead Elector of Salzburg, ruling the territory of the former archbishopric. The Grand Duchy was then dissolved, and replaced by the Kingdom of Etruria under the house of Bourbon-Parma, in compensation for their loss of Duchy of Parma. In 1803, the first King of Etruria, Louis I, died and was succeeded by his infant son, Charles Louis, under the regency of his mother, Queen María Luisa.
Etruria lasted less than a decade. By the Treaty of Fontainebleau (27 October 1807), Etruria was to be annexed by France. The negotiations had been between Spain and France, and the Etrurian regent was kept entirely in the dark, only being informed that she would have to leave her young son's kingdom on 23 November 1807. She and her court left on 10 December. On 30 May 1808, Etruria was formally annexed to France. An "Extraordinary Giunta" was placed in charge under General Jacques François Menou. Tuscany was divided into the départements of Arno, Méditerranée and Ombrone. In March 1809 a "General Government of the Departments of Tuscany" was set up, and Napoleon Bonaparte put his sister Elisa Bonaparte at its head, with the title of Grand Duchess of Tuscany.[47][48]
Tuscany restored and its final demise

The Napoleonic system collapsed in 1814, and the following territorial settlement, the Congress of Vienna, ceded the State of Presidi to a restored Tuscany. Ferdinand III resumed his rule, and died in 1824. Italian nationalism exploded in the post-Napoleonic years, leading to the establishment of secret societies bent on a unified Italy. Whence these leagues arrived in Tuscany, a concerned Ferdinand requisitioned an Austrian garrison, from his brother Emperor Francis of Austria, for the defence of the state. Ferdinand aligned Tuscany with Austria.[49]

Following Ferdinand's death, his elder son, Leopold II, succeeded him. Leopold was contemporarily acknowledged as a liberal monarch.[49] Despite his merits, his subjects dismissed him as a foreigner. His affinity for Austria was equally unpalatable. In 1847, Leopold, following the death of the then-incumbent Duchess of Parma, Marie Louise of Austria, annexed the Duchy of Lucca. (A state created solely to accommodate the House of Bourbon-Parma until they could re-assume their Parmese sovereignty). The same year, a Tuscan state council was brought into being.
In Leopold's years Italy was engulfed in popular rebellion, culminating in the Revolutions of 1848. The said revolution toppled the throne of France, and caused disarray across Europe. In Tuscany, Leopold II sanctioned a liberal constitution; and instituted a liberal ministry. Despite his attempts at acquiescence, street fighting in opposition to the regime sprang up in August, in Livorno. Leopold II lent his support to the Kingdom of Sardinia in the Austro-Sardinian War. In February 1849, Leopold II had to abandon Tuscany to Republicans and sought refuge in the Neapolitan city of Gaeta. A provisional republic was established in his stead. It was only with Austrian assistance that Leopold could return to Florence. The constitution was revoked in 1852.[49] The Austrian garrison was withdrawn in 1855.
The Second Austro-Sardinian war broke out in the summer of 1859. Leopold felt obliged to espouse Austria's cause.[50] Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia captured Tuscany in its entirety, and held it for the duration of the conflict; Leopold fled Tuscany as a result. The Peace of Villafranca allowed Leopold to return once more. Upon arrival, he abdicated in favour of his elder son, Ferdinand. Ferdinand IV's hypothetical reign didn't last long; the House of Habsburg-Lorraine was formally deposed by the National Assembly on 16 August 1859.[49]
In December 1859, the Grand Duchy was joined to the Duchies of Modena and Parma to form the United Provinces of Central Italy, which were annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia a few months later. On 22 March 1860, after a referendum that voted overwhelmingly (95%[5]) in favour of a union with Sardinia; Tuscany was formally annexed to Sardinia.[5] Italy was unified in 1870, when the remains of the Papal States were annexed in that September, deposing Pope Pius IX.
Government
Tuscany was divided into two main administrative districts: the stato nuovo (the new state) consisting of the former Republic of Siena, and the stato vecchio (the old state), the old Republic of Florence and her dependencies. The two areas were governed by separate laws. They were divided because the stato nuovo was a Spanish fief and the stato vecchio an Imperial one. Siena was ruled by a governor appointed by the grand duke. Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor proclaimed Alessandro de' Medici, ruler of Florence "for his lifetime, and after his death to be succeeded by his sons, male heirs and successors, of his body, by order of primogeniture, and failing them by the closest male of the Medici family, and likewise in succession forever, by order of primogeniture."[5]
Following the Republic's surrender in the Siege of Florence, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor issued a proclamation explicitly stating that he and he alone could determine the government of Florence.[51] On 12 August 1530, the Emperor created the Medici hereditary rulers (capo) of the Republic of Florence.[52] Pope Clement VII willed his relative Alessandro de' Medici to be the monarchical ruler of Florence, and went about requisitioning that dignity carefully; he wanted to give the impression that the Florentines democratically chose Alessandro to be their monarch.[52] In April 1532, the Pope convinced the Balía, Florence's ruling commission, to draw up a new constitution. The document in question was officiated on the 27th of that month. It formally created a hereditary monarchy, abolished the age-old signoria (elective government) and the office of gonfaloniere (titular ruler of Florence elected for a two-month term); in their place was the consigliere, a four-man council elected for a three-month term, headed by the "Duke of the Florentine Republic" (and later the Grand Duke of Tuscany). The Senate, composed of forty-eight men, chosen by the constitutional reform commission, was vested with the prerogative of determining Florence's financial, security, and foreign policies. Additionally, the senate appointed the commissions of war and public security, and the governors of Pisa, Arezzo, Prato, Voltera and Cortona and ambassadors.[53] To be eligible, one had to be male and a noble.[54] The Council of Two Hundred was a petitions court; membership was for life. This constitution was still in effect through the Medicean grand duchy, albeit the institutions decayed and powerless by the rule of Ferdinando II.[55]
Over time, the Medici acquired several territories, which included: the County of Pitigliano, purchased from the Orsini family in 1604; the County of Santa Fiora, acquired from the House of Sforza in 1633; Spain ceded Pontremoli in 1650, Silvia Piccolomini sold her estates, the Marquisate of Castiglione at the time of Cosimo I, Lordship of Pietra Santa, and the Duchy of Capistrano and the city of Penna in the Kingdom of Naples.[5] Vittoria della Rovere brought the Duchies of Montefeltro and Rovere into the family in 1631, upon her death in 1694, they passed to her younger son, Francesco Maria de' Medici. They reverted to the crown with the ascension of Gian Gastone.[56]
Gian Gastone, the last Medici, resigned the grand duchy to Francis Stephen of Lorraine. Under him, Tuscany was ruled by a viceroy, Marc de Beauvau-Craon, Prince de Craon. Francis Stephen altered the laws of succession in 1763, when he declared his second son, Leopold, heir to the grand duchy. If Leopold's line were to become extinct, it would revert to the main line. Every grand duke after Leopold resided in Florence. The grand duke Leopold II agreed to ratify a liberal constitution in 1848. The grand duke was briefly deposed by a provisional government in 1849. He was restored the same year by Austrian troops. The government was finally dissolved upon its annexation to the United Provinces of Central Italy in 1859.[5]
Flags and Coats of arms
- House of Medici
.svg.png) Flag of Grand Duchy of Tuscany
Flag of Grand Duchy of Tuscany
(1562-1737).svg.png) Naval flag
Naval flag
(1737-1749).svg.png) Coat of arms
Coat of arms
(1562-1737)
- House of Habsburg-Lorraine
 Civil flag and civil ensign
Civil flag and civil ensign
(1815-1848, 1849-1860) State flag with Lesser Coat of arms
State flag with Lesser Coat of arms
(1815-1848, 1849-1860).svg.png) State flag with Great Coat of arms
State flag with Great Coat of arms
(1765-1800, 1815–1848, 1849-1860)[44].svg.png) Flag of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany
Flag of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany
(1848-1849).svg.png) Lesser Coat of arms
Lesser Coat of arms
(1815-1848, 1849-1860) Great Coat of arms
Great Coat of arms
(1765-1800, 1815–1848, 1849-1860)[44]
See also
- History of Tuscany
- List of rulers of Tuscany
- List of Tuscan consorts
- Grand Princes of Tuscany
- Grand Princesses of Tuscany
- Line of succession to the Tuscan throne
Citations
- United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland; House of Commons, John Bowring, 1839, p 6
- Strathern, Paul: The Medici: Godfathers of the Renaissance, Vintage books, London, 2003, ISBN 978-0-09-952297-3, pp. 315–321
- commercio, Italia : Ministero di agricoltura, industria e (1862). Popolazione censimento degli antichi Stati sardi (1. gennaio 1858) e censimenti di Lombardia, di Parma e di Modena (1857-1858) pubblicati per cura del Ministero d'agricoltura, industria e commercio: Relazione generale con una introduzione storica sopra i censimenti delle popolazioni italiane dai tempi antichi sino all'anno 1860. 1.1 (in Italian). Stamperia Reale.
- "COSIMO III de' Medici, granduca di Toscana in "Dizionario Biografico"". www.treccani.it (in Italian). Retrieved 2020-04-25.
- François Velde (July 4, 2005). "The Grand-Duchy of Tuscany". heraldica.org. Retrieved 2009-08-19.
- Strathern, p. 340
- Strathern, p 335
- Strathern, p 375, 381.
- Frieda, Leonie: Catherine de' Medici, Orion books, London, 2005, ISBN 0-7538-2039-0, pp. 268–269
- Booth, Cecily: Cosimo I – Duke of Florence, University Press, 1921 (pre-dates use of the ISBN), p 232
- Hale, J.R.: Florence and the Medici, Orion books, London, 1977, ISBN 1-84212-456-0, p 145
- Frieda, p. 271–272
- Strathern, p. 340–341
- Hale, p 147
- Hale, p 151
- Hale, p 150
- Austria and Spain were ruled by the House of Habsburg; the two are interchangeable terms for the time period in question
- Hale, p 158
- Hale, p 160
- Hale, p 165
- Hale, p 187
- Strathern, p. 375–37, 380–381.
- Acton, p 30
- Acton, p 27
- Acton, p 38
- Hale, p 180
- Hale, p. 181.
- Strathern, p 381
- Strathern, p. 382.
- Strathern, p. 391.
- Acton, p. 140–141.
- Acton, p 185
- Strathern, p 392
- Strathern, pp. 390–391.
- Acton, p 243
- Acton, pp. 272 – 273
- Strathern, p 400
- Acton, p 254
- Acton, p 255
- Strathern, pp. 402–405
- Strathern, pp. 408–409
- Strathern, p 410
- "Leopold II (holy Roman emperor) -- Encyclopædia Britannica". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2009-10-11.
- Bandiere degli Stati italiani preunitari: Toscana.
- Woolrych, Humphry William: The history and results of the present capital punishments in England; to which are added, full tables of convictions, executions, etc, Saunders and Benning, 1832, (pre-dates use of the ISBN), p 42
- Mora, G. (1959) Vincenzo Chiarugi (1759–1820) and his psychiatric reform in Florence in the late 18th century (on the occasion of the bi-centenary of his birth) J Hist Med.
- Jackson-Laufer, Guida Myrl:Women Rulers Throughout the Ages: An Illustrated Guide, ABC-CLIO, 1999, ISBN 978-1-57607-091-8, p 142
- H. A. L. Fisher, "The French Dependencies and Switzerland", in A. Ward et al. (eds.), Cambridge Modern History, IX: Napoleon (Cambridge, 1934), p. 399.
- Catholic Encyclopaedia. "Tuscany". newadvent.org. Retrieved 18 October 2009.
- "Leopold II (grand duke of Tuscany) -- Encyclopædia Britannica". Britannica.com. Retrieved 26 September 2009.
- Hale, p 118
- Hale, 119
- Hale, p 121
- Hale, p 153
- Hale, p 178
- Acton, pp. 207–208
Bibliography
- Acton, Harold: The Last Medici, Macmillan, London, 1980, ISBN 0-333-29315-0
- Strathern, Paul: The Medici: Godfathers of the Renaissance, Vintage books, London, 2003, ISBN 978-0-09-952297-3
- Hale, J.R.: Florence and the Medici, Orion books, London, 1977, ISBN 1-84212-456-0
- Frieda, Leonie: Catherine de' Medici, Orion books, London, 2005, ISBN 0-7538-2039-0
- Booth, Cecily: Cosimo I—Duke of Florence, University Press, 1921
- Woolrych, Humphry William: The history and results of the present capital punishments in England; to which are added, full tables of convictions, executions, etc., Saunders and Benning, 1832, (pre-dates use of the ISBN)
- Jackson-Laufer, Guida Myrl: Women Rulers Throughout the Ages: An Illustrated Guide, ABC-CLIO, 1999, ISBN 978-1-57607-091-8
- Parliamentary papers, Volume 16 By the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Parliament. House of Commons – Report on the Grand Duchy of Tuscany – John Bowring – 1839

.jpg)