List of terrorist incidents
The following is a list of terrorist incidents that have not been carried out by a state or its forces (see state terrorism and state-sponsored terrorism). Assassinations are listed at List of assassinated people.
| Terrorism | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
|
By ideology
|
|||||||
|
Structure |
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
Terrorist groups |
|||||||
|
Adherents |
|||||||
|
Response to terrorism
|
|||||||
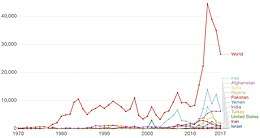
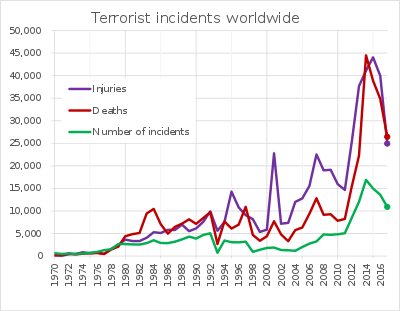
Terrorism deaths per year by country
Definitions of terrorism vary, so incidents listed here are restricted to those that are notable and described as "terrorism" by a consensus of reliable sources.
Pre-1800
Scholars dispute what might be called terrorism in earlier periods. The modern sense of terrorism emerged in the mid-19th century.[3]
| Date | Type | Dead | Injured | Location | Details | Perpetrator | Part of |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 November 1605 | Attempted bombing | 0 | 0 | Gunpowder Plot: A group of English Catholics led by Robert Catesby plotted to bomb the House of Lords in order to kill King James I, with the goal of installing his nine-year-old daughter Princess Elizabeth as the Catholic head of state. The explosives beneath the House of Lords were discovered a day before their planned detonation, and the conspirators were either killed in a battle at Holbeche House or executed for treason. | Robert Catesby and co-conspirators |
1800–1899
| Date | Type | Dead | Injured | Location | Details | Perpetrator | Part of |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 July 1835 | Shooting | 18 | 22 (+1) | Giuseppe Marco Fieschi used a volley gun to attack the royal entourage of King Louis-Philippe of France during the annual review of the National Guard as part of a revolutionary plot. Fieschi was badly injured when four of the weapon's barrels exploded and was captured soon after. He was executed with co-conspirators Pierre Morey and Theodore Pépin on 19 February 1836. | Giuseppe Marco Fieschi | ||
| 14 April 1865 | Assassination, shooting, killing | 1 | 8 (+1) | President Abraham Lincoln was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth at Ford's Theatre in Washington D.C. Booth's co-conspirators were to launch simultaneous attacks on Vice President Andrew Johnson and Secretary of State William H. Seward, but Seward's attacker failed to kill him and Johnson's lost his nerve. Booth was killed after a 12-day manhunt, and several of his co-conspirators were later arrested and executed. | John Wilkes Booth and co-conspirators | American Civil War | |
| 1865–1877 | Murders | c. 3,000 | Several | c. 3,000 Freedmen and their Republican Party allies are killed by the Ku Klux Klan and well-organized campaigns of violence by other local whites in a campaign of terrorist violence that weakened the reconstructionist governments in the Southern United States and helped re-establish legitimized segregation.[4][5] | Ku Klux Klan | Reconstruction Era | |
| 13 December 1867 | Prison escape | 12 | 120 | The "Clerkenwell Outrage": a bomb exploded next to a wall of Clerkenwell Prison as an attempt to abet the escape of an arms dealer. | Fenian Society | ||
| 28 December 1870 | Attempted Assassination | 1 | 0 | Attack to General Juan Prim, Prime Minister of Spain. He died two days later after the injuries. | Political adversaries | ||
| 1880 | Attempted Assassination | 0 | 0 | Attempted assassination of General Mikhail Loris-Melikov. | Anarchists (suspected) | ||
| 1881 | Assassination by Bombing | 2 | 12 | Assassination of Alexander II of Russia. | Narodnaya Volya | ||
| 1881-5 | Bombing | 0 (+3) | 98 | Fenian dynamite campaign. | Irish Republican Brotherhood | ||
| 1884 | Assassination | 2 | 0 | Assassination of Colonel Soudekine, Chief of Police. | Nihilist movement | ||
| 4 May 1886 | Bombing | 7 (+4) | 160+ | Haymarket Affair. A peaceful rally in Haymarket, Chicago, Illinois, was disrupted when a bomb was detonated as police were dispersing the public demonstration. | FOTLU | ||
| 23 July 1892 | Assassination attempt | 0 | 1 (+1) | Alexander Berkman, a Russian expatriate, attempted to assassinate Henry Clay Frick, an American industrialist, financier, and art patron, in Pittsburgh. Berkman was arrested and Frick survived. Berkman claims inspiration from the Haymarket Affair. | Alexander Berkman | ||
| 9 December 1893 | Bombing | 0 | 20 | French anarchist Auguste Vaillant bombed the French Chamber of Deputies injuring 20 deputies. | Auguste Vaillant | ||
| 24 June 1894 | Assassination | 1 | 0 | French president Marie François Sadi Carnot is fatally stabbed by Italian anarchist Sante Geronimo Caserio. | Sante Geronimo Caserio | ||
| 26 August 1896 | Hijacking | 10+ | 0 | Occupation of the Ottoman Bank by Armenian separatists. A resulting anti-Armenian pogrom killed around 6,000 individuals. | Armenian Revolutionary Federation | ||
| 8 August 1893 | Attempted Assassination | 1 | 0 | Assassination of Antonio Cánovas del Castillo, Prime Minister of Spain. | Anarchists led by the Italian Michele Angiolillo | ||
1900–1929
| Date | Type | Dead | Injured | Location | Details | Perpetrator | Part of |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 July 1900 | Assassination | 1 | 0 | Gaetano Bresci, an Italian-American Anarchist, assassinated Umberto I of Italy | Gaetano Bresci | ||
| 15 April 1902 | Assassination | 1 | 0 | Minister of the Interior Dmitry Sipyagin was assassinated in the Marinsky Theatre. | Stepan Balmashov | ||
| 28 April – 1 May 1903 | Bombings | 0 (+4) | Members of the Boatmen of Thessaloníki, a Bulgarian anarchist group, carried out a series of bombings in Thessaloniki | Boatmen of Thessaloníki | |||
| 18 May 1904 | Kidnapping | 0 | 2 kidnapped | Ion Perdicaris and Cromwell Varley were kidnapped and held for ransom by bandit Mulai Ahmed er Raisuli in Morocco.[6] | Mulai Ahmed er Raisuli | ||
| 15 February 1905 | Bombing | 2 | 1+ | Assassination of Grand Duke Serge Alexandrovich Romanov by Socialist-revolutionaries. His coach driver Andrei Rudinkin was also killed. | Ivan Kalyayev | ||
| 21 July 1905 | Bombing | 26 | 58 | Yıldız assassination attempt: Attempted assassination targeting Abdul Hamid II of Ottoman Empire |
Armenian Revolutionary Federation | ||
| 31 May 1906 | Bombing | 24 | Several | Morral affair. 24 people were killed when terrorist bombed the Royal Couple, Alfonso XIII of Spain and Victoria Eugenie, on their wedding day. | Mateo del Morral | ||
| 25 August 1906 | Bombing | 28 | Several | 28 people were killed when three terrorists bombed a reception in an attempt to assassinate Pyotr Stolypin. | Union of Socialists Revolutionaries Maximalists | ||
| 11/12 July 1908 | Bombing | 1 | 23 | Night between 11 and 12 July: Bombing of the boat Amalthea where British strikebreakers lived by Anton Nilsson One was killed and 23 wounded. | Anton Nilsson | ||
| 1 October 1910 | Bombing | 21 | 105+ | Los Angeles Times bombing killed 21 people and wounded over 100 others. | Lone wolf (terrorism) | ||
| 14 September 1911 | Shooting | 1 | 0 | Assassination of Pyotyr Stolypin, Russian Prime Minister. | Dmitri Bogrov | ||
| 1912-14 | Various | 2 (+2) | 27+ (+1) | Protest campaign by militant suffragettes campaigning for women's right to vote, including acts of disruption and violence aimed at property and the public. Also included a possible second suffragette assassination attempt on Prime Minister Herbert Asquith.[7] | Women's Social and Political Union | ||
| 28
June 1914 |
Shooting | 2 | 1 | Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne. | Gavrilo Princip | ||
| 22 July 1916 | Bombing | 10 | 40 | Preparedness Day Bombing was a bombing in San Francisco, California on 22 July 1916, when the city held a parade in anticipation of the United States' entry into World War I. During the parade, a suitcase bomb was detonated, killing ten and wounding forty. | Galleanist Anarchists (suspected) | ||
| 30 July 1916 | Bombing | 4 | Hundreds | Black Tom explosion was a planned detonation of a munitions factory at Black Tom Island in the neutral United States by Imperial German Agents that killed four and injured hundreds, as well as causing millions of dollars in damages. | Imperial German Agents | ||
| 16 September 1920 | Bombing | 38 | 300 | Wall Street bombing killed 38 people and wounded 300 others.[8] | Galleanist Anarchists (suspected) | Red Scare | |
| 14 October 1920 | Bombings | 1 | 10 | In Trieste, nationalists threw six bombs at the editorial office of a Socialist newspaper, resulting in one death and ten injuries.[9] | Italian Nationalists | ||
| 15 October 1920 | Bombings | 0 | 2 | In Milan, anarchists were responsible for throwing two bombs at a hotel holding a British delegation attending the Milan International Conference; there were two injuries.[9] | Anarchists | ||
| 8 December 1920 | Bombing | 3 | 3 | A bomb placed by a left-wing terrorist group blows up in the Romanian Senate, killing the Minister of Justice and two other senators. Likewise, President of the Senate and two Orthodox bishops were severely injured. | Max Goldstein, Leon Lichtblau and Saul Ozias | ||
| 31 May 1921 | Riot | 39-300 | 800+ | The Tulsa race riot killed at least 39 people and injured over 800.[10] | Ku Klux Klan | ||
| 13 December 1921 | Bombing | 100 | The Bolgrad palace bombing occurred when a bomb thrown by Bessarabian separatists at the Bolgrad palace, killed 100 soldiers and police officers.[11] | Bessarabian separatists | Union of Bessarabia with Romania | ||
| 31 October 1923 | Shooting | 1 | 1 | Far-right extremists shot two Jewish men as they walked across St. Stephen's Green in Dublin. One of the men was killed.[12] | Far-right extremists | ||
| 16 April 1925 | Bombing | 150 | ~500 | St Nedelya Church assault – The Bulgarian Communist Party (BCP) blew up the church's roof during the funeral service of General Konstantin Georgiev, who had been killed in a previous Communist assault on 14 April. 150 people, mainly from the country's political and military elite, were killed in the attack and around 500 were injured.[13] | Bulgarian Communist Party |
1930–1949



.svg.png)
.svg.png)



.svg.png)

1950–1969


.svg.png)


.svg.png)
.svg.png)




.svg.png)

.svg.png)








1970–present
- List of terrorist incidents in 1970
- List of terrorist incidents in 1971
- List of terrorist incidents in 1972
- List of terrorist incidents in 1973
- List of terrorist incidents in 1974
- List of terrorist incidents in 1975
- List of terrorist incidents in 1976
- List of terrorist incidents in 1977
- List of terrorist incidents in 1978
- List of terrorist incidents in 1979
- List of terrorist incidents in 1980
- List of terrorist incidents in 1981
- List of terrorist incidents in 1982
- List of terrorist incidents in 1983
- List of terrorist incidents in 1984
- List of terrorist incidents in 1985
- List of terrorist incidents in 1986
- List of terrorist incidents in 1987
- List of terrorist incidents in 1988
- List of terrorist incidents in 1989
- List of terrorist incidents in 1990
- List of terrorist incidents in 1991
- List of terrorist incidents in 1992
- List of terrorist incidents in 1993
- List of terrorist incidents in 1994
- List of terrorist incidents in 1995
- List of terrorist incidents in 1996
- List of terrorist incidents in 1997
- List of terrorist incidents in 1998
- List of terrorist incidents in 1999
- List of terrorist incidents in 2000
- List of terrorist incidents in 2001
- List of terrorist incidents in 2002
- List of terrorist incidents in 2003
- List of terrorist incidents in 2004
- List of terrorist incidents in 2005
- List of terrorist incidents in 2006
- List of terrorist incidents in 2007
- List of terrorist incidents in 2008
- List of terrorist incidents in 2009
- List of terrorist incidents in 2010
- List of terrorist incidents in 2011
- List of terrorist incidents in 2012
- List of terrorist incidents in 2013
- List of terrorist incidents in 2014
- List of terrorist incidents in 2015
- List of terrorist incidents in 2016
- List of terrorist incidents in 2017
- List of terrorist incidents in 2018
- List of terrorist incidents in 2019
- List of terrorist incidents in 2020
By country
- List of terrorist incidents in Australia
- List of terrorist incidents in Denmark
- List of terrorist incidents in France
- List of terrorist incidents in Germany
- List of terrorist incidents in Great Britain
- List of terrorist incidents in India
- List of terrorist incidents in Indonesia
- List of terrorist incidents in Iraq
- List of terrorist incidents in Mexico
- List of terrorist incidents in Norway
- List of terrorist incidents in the Netherlands
- List of terrorist incidents in North Macedonia
- List of terrorist incidents in Pakistan
- List of terrorist incidents in the Philippines
- List of terrorist incidents in Saudi Arabia
- List of terrorist incidents in Sri Lanka
- List of terrorist incidents in Syria
- List of terrorist incidents in Tunisia
- Terrorism in Austria
- Terrorism in Argentina
- Terrorism in Australia
- Terrorism in Azerbaijan
- Terrorism in Brazil
- Terrorism in Belgium
- Terrorism in Bangladesh
- Terrorism in Bulgaria
- Terrorism in Burkina Faso
- Terrorism in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Terrorism in Colombia
- Terrorism in Croatia
- Terrorism in Canada
- Terrorism in China
- Terrorism in Chile
- Terrorism in Cyprus
- Terrorism in Denmark
- Terrorism in Egypt
- Terrorism in Ecuador
- Terrorism in Estonia
- Terrorism in France
- Terrorism in Finland
- Terrorism in Germany
- Terrorism in Greece
- Terrorism in Hungary
- Terrorism in India
- Terrorism in Indonesia
- Terrorism in Iran
- Terrorism in Iraq
- Terrorism in Italy
- Terrorism in Jamaica
- Terrorism in Kenya
- Terrorism in Kosovo
- Terrorism in Kuwait
- Terrorism in Kazakhstan
- Terrorism in Kyrgyzstan
- Terrorism in Latvia
- Terrorism in Lithuania
- Terrorism in Malaysia
- Terrorism in Morocco
- Terrorism in Myanmar
- Terrorism in Mexico
- Terrorism in Norway
- Terrorism in New Zealand
- Terrorism in Pakistan
- Terrorism in Poland
- Terrorism in Portugal
- Terrorism in the Philippines
- Terrorism in Russia
- Terrorism in Romania
- Terrorism in Syria
- Terrorism in South Africa
- Terrorism in Somalia
- Terrorism in Sudan
- Terrorism in Serbia
- Terrorism in Slovakia
- Terrorism in Sri Lanka
- Terrorism in Saudi Arabia
- Terrorism in Slovenia
- Terrorism in Spain
- Terrorism in Sweden
- Terrorism in Switzerland
- Terrorism in Turkey
- Terrorism in Tajikistan
- Terrorism in Uzbekistan
- Terrorism in Ukraine
- Terrorism in Uganda
- Terrorism in the United Arab Emirates
- Terrorism in the United Kingdom
- Terrorism in the United States
- Terrorism in Yemen
gollark: Parsing open-source SMTP port...
gollark: Deploy BLAKE2b.
gollark: We need to actuate the digital IDE form factor.
gollark: I already initialized my HTTP vertex shader array.
gollark: *Then* we'll use an exploit in your HTML/PHP7 BIOS to reverse-trilaterate your SMTP subpixel address.
See also
- State terrorism
- Domestic terrorism
- Communist terrorism
- Nuclear terrorism
- Cyber terrorism
- Economic terrorism
- Right-wing terrorism
- Terrorism in Europe
- Islamic terrorism in Europe (2014–present)
- Religious terrorism
- Islamic terrorism
- Christian terrorism
- Jewish religious terrorism
- Hindutva terrorism
- Number of terrorist incidents by country
- List of major terrorist incidents
- List of aircraft hijackings
- List of assassinated persons
- List of designated terrorist organizations
- List of events named massacres
- List of incidents of political violence in Washington, D.C.
- List of mass car bombings
- Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents
- List of marauding terrorist incidents
References
- National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism. (2018). Global Terrorism Database (globalterrorismdb_0718dist.xlsx Archived 10 July 2016 at the Wayback Machine). Retrieved from https://www.start.umd.edu/gtd University of Maryland
- National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism. (2018). Global Terrorism Database (gtd1993_0718dist.xlsx Archived 10 July 2016 at the Wayback Machine). Retrieved from https://www.start.umd.edu/gtd University of Maryland
- "BBC – History – The Changing Faces of Terrorism". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- Jonathan M. Bryant: Ku Klux Klan in the Reconstruction Era, The New Georgia Encyclopedia, 3 October 2002
- Fettman, Eric (20 January 2008). "The Bloody Shirt Terror After Appomattox by Stephen Budiansky Viking Press". New York Post. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- "PERDICARIS AND VARLEY ARE IN GRAVE DANGER; An American Resident of Tangier Tells of the Situation". The New York Times. 22 May 1904. Retrieved 5 March 2015.
- "Suffragettes, violence and militancy". The British Library. Retrieved 4 August 2020.
- "History News Service". H-net.org. Retrieved 27 March 2011.
- "BOMB WARFARE RAGING IN ITALY". The New York Times. 15 October 1920. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Austin Sarat (1 January 2009). When Law Fails: Making Sense of Miscarriages of Justice. NYU Press. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-8147-6225-7. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- "PALACE BOMBED, 100 KILLED; Bessarabian Conspirators Accused of Outrage at Bolgard". The New York Times. 14 December 1921. Retrieved 15 October 2011.
- "Reactionary murders in Ireland". Come Here To Me!. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- "Sofia Church Terror Attack Vie for Bulgaria Top Event". The Free Library. 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- Hughes, Matthew (2009). "The banality of brutality: British armed forces and the repression of the Arab Revolt in Palestine, 1936–39" (PDF). English Historical Review. CXXIV (507): 314–354. doi:10.1093/ehr/cep002. Archived from the original on 21 February 2016.CS1 maint: BOT: original-url status unknown (link)
- "Mad Bomber,' Now 70, Goes Free Today; Mad Bomber,' Now 70, Goes Free Today 37 Blasts Set Initials 'F.P.' Explained Institute Assailed". The New York Times. 13 December 1973. Retrieved 8 May 2010.
- "POLICE DIE IN BLAST; Timed Device Explodes After it is Taken out of Pavilion". The New York Times. 5 July 1940. Retrieved 5 March 2015.
- Clarke, Thurston. By Blood and Fire, G. P. Puttnam's Sons, New York, 1981
- Pistole, John S. (3 March 2011). "Administrator Pistole's remarks before the American Bar Association's 6th Annual Homeland Security Law Institute". TSA. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 17 August 2011.
- Larry Collins and Dominique Lapierre, 'O Jerusalem'.History Book Club. 1972. pages 191-195
- Dov Joseph, 'The Faithful City – The siege of Jerusalem, 1948'. Simon and Schuster, New York. 1960. Library of Congress number: 60-10976. page 37. 'it was possible ... (that the) drivers (were) from the more than two hundred deserters who had already joined the Arab force' (as opposed to being officially sanctioned by the British Army).
- "Pair Admits Planting Bomb That Killed 13". The Telegraph-Herald. 3 June 1949. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- Israel's Border Wars, 1949–1956, p. 309, Benny Morris, Oxford University Press, 1997
- Gilroy, Harry (22 March 1954). "Exploiting of Negev's Resources May Be Slowed by Bus Slayings; Security Moves May Act as a Brake on Developing Area Vital to Israel". The New York Times. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- Bigart, Homer (17 June 1956). "U.S. Vice Consul Is Killed By Cyprus Terrorist Bomb". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Brewers, Sam Pope (16 August 1958). "TERRORIST'S BOMB KILLS 3 IN BEIRUT". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Suniaga, Francisco (5 August 2018). "El atentado a Rómulo Betancourt". Prodavinci. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- "Violence erupts in Paarl". South African History Online. Retrieved 30 December 2017.
- Know 1 Radio.com
- "Crash Off Turkey Kills All 66 on Jet". The New York Times. 12 October 1967. Retrieved 5 March 2015.
- Aguirre, Facundo (29 September 2016). "El Operativo Cóndor en Malvinas" [The Condor Operative in Malvinas]. La Izquierda Diario (in Spanish).
- Feron, James (5 September 1968). "Fatal Bombing in Tel Aviv Stirs Mob Attack on Arabs". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- Marcus, Itamar (8 December 2016). "Rasmieh Odeh is responsible for murder of two, her accomplice tells PA TV". Palestinian Media Watch.
- Pharr, Jasper (25 January 2016). Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Terrorist on U.S. Soil. Dorrance Publishing. ISBN 9781480966468.
- "Bomb Blast at RTÉ". RTÉ Archives. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- "When loyalists bombed O'Connell". Come Here To Me!. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- "Blast in Milan Kills 13, Hurts 85; 3 More Bombs Injure 16 in Rome". The New York Times. 13 December 1969. Retrieved 5 March 2015.
External links
- U.S. National Counterterrorism Center's Worldwide Incidents Tracking System
- Fatal Terrorist Attacks in Israel since the Declaration of Principles (September 1993) to September 2000
- Assassination of Liaquat Ali Khan: Documents from the U.S. National Archives
- Terrorism Incidents at Curlie
- History of Terrorism : Timeline of Terrorist Acts – Chronology
- Thinkquest: Timeline of Terror
- Infoplease: Terrorist Attacks on Americans
- Infoplease: Terrorist Attacks (within the United States or against Americans abroad)
- Frontline : Terrorist Attacks on Americans
- PBS Frontline/New York Times "Al Qaeda's New Front" Chronology of significant plots uncovered in Europe both before and after 9/11. January 2004
- "Ephéméride Anarchiste" Listing anarchist terrorist incidents in France, or others countries. In French.
- Selected terrorist incidents worldwide, through September 2000: complied by Wm. Robert Johnston
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.