Methyldichlorophosphine
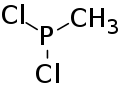
Methyldichlorophosphine (alternatively known as dichloro(methyl)phosphane and methyl phosphonous dichloride) is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula CH3Cl2P. It is a colorless, corrosive, flammable, and highly reactive liquid with a pungent odor. It is also extremely toxic if inhaled, can cause burns upon contact with the skin and eyes, and releases fumes of hydrochloric acid in moist environments.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dichloro(methyl)phosphane | |
| Other names
Methyl phosphonous dichloride, Dichloromethylphosphine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UN number | 2845 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3Cl2P | |
| Molar mass | 116.91 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Methyldichlorophosphine belongs to the group of halophosphines, which are used as intermediates in the production of plant protection agents, stabilizers for plastics, and catalysts. It is a precursor of the herbicide Glufosinate. It is also used in the production of flameproofing compounds.[2]
Methyldichlorophosphine has a number of potential uses, but it is often used in the manufacture of nerve agents. When reacted with sulfuryl chloride it produces methylphosphonic acid dichloride, a direct chemical precursor to the nerve agents sarin, soman, and VX.
References
- Pubchem. "Dichloro(methyl)phosphane". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (7th ed.), 2007, doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_545.pub2