British Pakistanis
British Pakistanis (Urdu: پاکستانی نژاد برطانوی; also known as Pakistani British people or Pakistani Britons) are citizens or residents of the United Kingdom whose ancestral roots lie in Pakistan. This includes people born in the UK who are of Pakistani descent and Pakistani-born people who have migrated to the UK. The majority of British Pakistanis originate from the Azad Kashmir and Punjab regions, with a smaller number from other parts of Pakistan including Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Balochistan.
پاکستانی نژاد برطانوی | |
|---|---|
| Total population | |
Northern Ireland: 1,091 (2011) 1.86% of the UK's population (2011)[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| West Midlands, Greater London, Yorkshire and the Humber, North West England | |
| Languages | |
| English (British and Pakistani) · Urdu · Potohari, Mirpuri · Punjabi · Kashmiri · Pashto · Saraiki · Sindhi · Balochi · others | |
| Religion | |
| Islam (Sunni, Shi'ite, Sufism Minority: Christianity · Hinduism · Sikhism · others | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Overseas Pakistani · British Asian · British Indian · British Bangladeshi · British Afghan |
The UK is home to the largest Pakistani community in Europe, with the population of British Pakistanis exceeding 1.17 million based on the 2011 census. British Pakistanis are the second-largest ethnic minority population in the United Kingdom and also make up the second-largest sub-group of British Asians. In addition, they are one of the largest overseas Pakistani communities, similar in number to the Pakistani diaspora in Saudi Arabia.[2][3]
Due to the historical relations between the two countries, immigration to the UK from the region which is now Pakistan began in small numbers in the mid-19th century. During the mid-nineteenth century, parts of what is now Pakistan came under the British Raj and people from those regions served as soldiers in the British Indian Army and some were deployed in other parts of the British Empire. However, it was following the Second World War, the break-up of the British Empire and the independence of Pakistan, that Pakistani immigration to the United Kingdom increased, especially during the 1950s and 1960s. This was made easier as Pakistan was a member of the Commonwealth.[4] Pakistani immigrants helped to resolve labour shortages in the British steel, textile and engineering industries. Doctors from Pakistan were recruited by the National Health Service in the 1960s.[5]
The British Pakistani population has grown from about 10,000 in 1951 to over 1.1 million in 2011.[1][6] The vast majority of these live in England, with a sizable number in Scotland and smaller numbers in Wales and Northern Ireland. The most diverse Pakistani population is in London which comprises Punjabis, Mirpuri Kashmiris, Pashtuns, Sindhis, Muhajirs, Saraikis, Baloch and others.[2][7]
The majority of British Pakistanis are Muslim; around 90 per cent of those living in England and Wales at the time of the 2011 UK Census stated their religion was Islam.[8][9] The majority are Sunni Muslims, with a significant minority of Shia Muslims. The UK also has one of the largest overseas Christian Pakistani communities; the 2011 census recorded around 17,000 Christian Pakistanis living in England and Wales, around 1 per cent of the Pakistani population of England and Wales.
Since their settlement, British Pakistanis have had diverse contributions and influence on British society, politics, culture, economy and sport. Whilst social issues include high relative poverty rates among the community according to the 2001 census,[10] significant progress has been made in recent years, with the 2011 Census showing British Pakistanis as having amongst the highest levels of home ownership in Britain.[11]
Traditionally, many British Pakistanis have been self-employed, with many working in the transport industry or in family-run businesses of the retail sector.[2]
History
| Part of a series on |
| British Pakistanis |
|---|
| History |
| Category |
| Demographics |
|
Pakistani communities · Bradford Pakistani community of London |
| Languages |
| Urdu · others |
| Culture |
|
Balti (food) · Balti Triangle British Punjabi writers Discrimination |
| Religion |
| Islam in England |
| Notables |
|
List of British Pakistanis English people of Pakistani descent Scottish people of Pakistani descent Welsh people of Pakistani descent Northern Irish people of Pakistani descent |
| Related topics |
|
Pakistan – United Kingdom relations Britons in Pakistan British Asian 2001 Oldham race riots 2001 Bradford riots |
Pre-Independence
The earliest period of Asian migration to Britain has not been ascertained. It is known that Romani (Gypsy) groups such as the Romanichal and Kale arrived in the region during the Middle Ages, having originated from, what is now, North India and Pakistan and traveled westward to Europe via Southwest Asia around 1000 CE, intermingling with local populations over the course of several centuries.[12][13][14]
Immigration from what is now Pakistan to the United Kingdom began long before the independence of Pakistan in 1947. Muslim immigrants from Kashmir, Punjab, Sindh, the North-West Frontier and Balochistan as well as other parts of South Asia, arrived in the British Isles as early as the mid-seventeenth century as employees of the East India Company, typically as lashkars and sailors in British port cities.[15][16] These immigrants were often the first Asians to be seen in British port cities and were initially perceived as indolent due to their reliance on Christian charities.[17] Despite this, most early Pakistani immigrants married local white British women because there were few South Asian women in Britain at the time.[18]
During the colonial era, Asians continued coming to Britain as seamen, traders, students, domestic workers, cricketers, political officials and visitors, and some of them settled in the region.[19] South Asian seamen sometimes settled after ill treatment or being abandoned by ship masters.[20][21]
Many early Pakistanis came to the UK as scholars and studied at major British institutions, before later returning to British India. An example of such a person is Muhammad Ali Jinnah, the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah came to the UK in 1892 and started an apprenticeship at Graham's Shipping and Trading Company. After completing his apprenticeship, Jinnah joined Lincoln's Inn where he trained as a barrister. At 19, Jinnah became the youngest person from South Asia to be called to the bar in Britain.[22]
British interwar period
Most early Pakistani settlers (then part of the British India Empire) and their families moved from port towns to the Midlands, as Britain declared war on Germany in 1939. Many of these Kashmiris, Punjabis and Sindhis worked in the munition factories of Birmingham. After the war, most of these early settlers stayed on in the region and took advantage of an increase in the number of jobs.[23] These settlers were later joined by the arrival of their families to Britain.[24]
In 1932, the Indian National Congress survey of 'all Indians outside India' (Which Pakistani regions were then part of) estimated that there were 7,128 Indians in the United Kingdom.[25]
There were 832,500 Muslim Indian soldiers in 1945; most of these recruits were from what is now Pakistan.[26] These soldiers fought alongside the British Army during the First and Second World Wars, particularly in the latter, during the Battle of France, the North African Campaign and the Burma Campaign. Many contributed to the war effort as skilled labourers, including as assembly-line workers in the aircraft factory at Castle Bromwich, Birmingham, which produced Spitfire fighters.[26] Most returned to the South Asia after their service, although many of these former soldiers returned to Britain in the 1950s and 1960s to fill labour shortages.
Post-Independence
Following the Second World War, the break-up of the British Empire and the independence of Pakistan, Pakistani immigration to the United Kingdom increased, especially during the 1950s and 1960s. Many Pakistanis came to Britain following the turmoil during the partition of India and the subsequent independence of Pakistan; among them were those who migrated to Pakistan upon displacement from India, and then migrated to the UK, thus becoming secondary migrants.[27] Migration was made easier as Pakistan was a member of the Commonwealth of Nations.[4] Pakistanis were invited by employers to fill labour shortages which arose after the Second World War.
As Commonwealth citizens, they were eligible for most British civic rights. They found employment in the textile industries of Lancashire and Yorkshire, manufacturing in the West Midlands, and car production and food processing industries of Luton and Slough. It was common for Pakistani employees to work on night shifts and at other less-desirable hours.[28]
Many Mirpuris began emigrating from Pakistan after the completion of Mangla Dam in Mirpur, Azad Kashmir, in the late 1950s led to the destruction of hundreds of villages. Up to 5,000 people from Mirpur (five per cent of the displaced)[29] left for Britain, while others were allotted land in neighbouring Punjab or used monetary compensation to resettle elsewhere in Pakistan.[27] The displaced Mirpuris were given legal and financial assistance by the British contractor which had built the dam.[30] Those from unaffected areas of Pakistan, such as the Punjab, also immigrated to Britain to help fill labour shortages. Punjabis began to leave Pakistan in the 1960s. They worked in the foundries of the English Midlands, and a significant number also settled in Southall in West London.[31]
During the 1960s, a considerable number of Pakistanis also arrived from urban areas. Many of these people were qualified teachers, doctors, and engineers.[28] They had a predisposition to settle in London due to its greater economic opportunities compared to the Midlands or the North of England.[28] Most medical staff from Pakistan were recruited in the 1960s and almost all worked for the National Health Service.[32] At the same time, the number of Pakistanis coming as workers declined.[27]
In addition, there was a stream of migrants from East Pakistan (now Bangladesh).[24][33] During the 1970s, many East African Asians, most of whom already held British passports because they were brought to Africa by British colonialists, entered the UK from Kenya and Uganda. Idi Amin chose to expel all Ugandan Asians in 1972 because of the perception that they were responsible for the country's economic stagnation.[34] The Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962 and Immigration Act 1971 largely restricted any further primary immigration to the UK, although family members of already-settled immigrants were allowed to join their relatives.[35]
The early Pakistani workers who entered the UK came with the intent of staying and working temporarily and eventually returning home. However, this changed into permanent family immigration since the 1962 Act, as well as due to socio-economic circumstances and the future of children which most families saw in Britain.[27]
When the UK experienced deindustrialisation in the 1970s, many British Pakistanis became unemployed. The change from the manufacturing sector to the service sector was difficult for ethnic minorities and white Britons alike, especially for those with little academic education. The Midlands and North of England were areas which were heavily reliant on manufacturing industries and the effects of deindustrialisation continue to be felt in these areas.[36] As a result, increasing numbers of British Pakistanis have resorted to self-employment. National statistics from 2004 show that one in seven British Pakistani men work as taxi drivers, cab drivers or chauffeurs.[37]
Demographics
Population
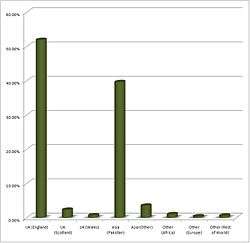
In the 2011 UK Census, 1,174,983 residents classified themselves as ethnically Pakistani (excluding people of mixed ethnicity), regardless of their birthplace with 1,112,212 of these living in England.[1] The equivalent figure in the 2001 UK Census was 747,285, an increase of 427,000 over 10 years.[39]
Of those Pakistanis living in England, Wales and Scotland in 2001, 55 per cent were born in the UK, 36.9 per cent in Pakistan and 3.5 per cent elsewhere in Asia.[38] According to estimates by the Office for National Statistics, the number of people born in Pakistan living in the UK in 2013 was 502,000.[40]
The Ministry of Overseas Pakistanis of the Pakistan government estimates that 1.26 million Pakistanis eligible for dual nationality live in the UK, constituting well over half of the total number of Pakistanis in Europe.[6][41]
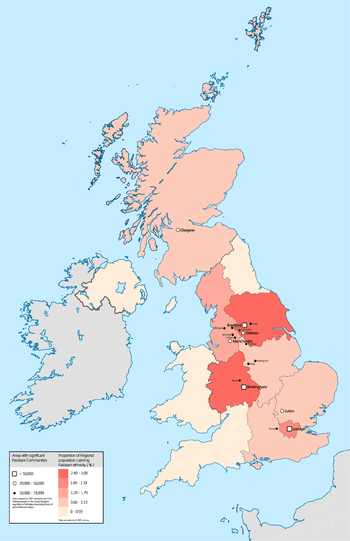
The majority of British Pakistanis are from the Azad Kashmir and Punjab areas of Pakistan,[7] with Azad Kashmiris making up the largest and Punjabis making up the second largest portion. A high proportion of the members of Pakistani communities in the West Midlands and the North originated in Azad Kashmir.[42]
Large communities from Azad Kashmir can be found in Birmingham, Bradford, Oldham and the surrounding northern towns.[7] Luton and Slough have the largest Mirpuri Kashmiri communities in the south of England, while a large proportion of Punjabis also reside in the south.[28] There is also a small Pakistani Pashtun population in the UK.[43]
Up to 250,000 Pakistanis come to the UK each year, for work, visit or other purposes.[44] Likewise, up to 270,000 British citizens travel to Pakistan each year, mainly to visit family.[44][45] Excluding British citizens of Pakistani descent, the number of individuals living in the UK with a Pakistani passport was estimated at 188,000 in 2017; this made Pakistan the eighth most common non-British nationality in the UK.[46] Pakistan International Airlines flies to several UK airports, providing air linkages between Pakistan and the UK,[47] while British Airways resumed its flights to Pakistan in 2019.[48]
Demographer Ceri Peach has estimated the number of British Pakistanis in the 1951 to 1991 censuses. He back-projected the ethnic composition of the 2001 census to the estimated minority populations during previous census years. The results are as follows:
| Year | Population (rounded to nearest 1,000)[49] |
|---|---|
| 1951 (estimate) | 10,000 |
| 1961 (estimate) | 25,000 |
| 1971 (estimate) | 119,000 |
| 1981 (estimate) | 296,000 |
| 1991 (estimate) | 477,000 |
| 2001 (actual) | 747,000 |
| 2011 (actual) | 1,175,000[1] |
Population distribution
At the time of the 2011 UK Census, the distribution of people describing their ethnicity as Pakistani was as follows:[1]
| Region | Number of British Pakistanis | Percentage of total British Pakistani population | British Pakistanis as percentage of region's population | Significant Communities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| England | 1,112,282 | 94.7% | 2.10% | |
| North East England | 19,831 | 1.69% | 0.76% | Newcastle-Upon-Tyne - 2.4%
Middlesbrough - 5.0% Stockton-On-Tees - 1.7% |
| North West England | 189,436 | 16.12% | 2.69% | Manchester - 8.5%
Rochdale - 10.5% Oldham - 10.0% Blackburn With Darwen - 12.0% Pendle - 17.1% |
| Yorkshire and the Humber | 225,892 | 19.23% | 4.28% | Bradford - 20.4%
Kirklees - 9.9% Calderdale - 6.8% Sheffield - 4.0% Leeds - 3.0% |
| East Midlands | 48,940 | 4.17% | 1.08% | Derby - 5.9%
Nottingham - 5.5% Leicester - 2.4% |
| West Midlands | 227,248 | 19.34% | 4.06% | Birmingham - 13.5%
Walsall - 5.3% Stoke-On-Trent - 4.2% Dudley - 3.3% Sandwell - 4.5% East Staffordshire - 4.9% |
| East of England | 66,270 | 5.64% | 1.13% | Luton - 14.4%
Peterborough - 6.6% Watford - 6.7% |
| London | 223,797 | 19.05% | 2.74% | London Borough of Waltham Forest - 10.2%
London Borough of Newham - 9.8% London Borough of Redbridge - 11.1% |
| South East England | 99,246 | 8.45% | 1.15% | Slough - 17.7%
Wycombe - 7.6% Woking - 5.7% Crawley - 4.3% Reading - 4.5% |
| South West England | 11,622 | 0.99% | 0.22% | Bristol - 1.6% |
| Wales | 12,229 | 1.04% | 0.40% | Cardiff - 1.8%
Newport - 2.1% |
| Scotland | 49,381 | 4.24% | 0.93% | Glasgow - 3.8%
Edinburgh - 1.2% |
| Northern Ireland | 1,091 | 0.09% | 0.06% | Belfast - 0.09% |
| Total UK | 1,174,983 | 100% | 1.86% |
London
Greater London has the largest Pakistani community in the United Kingdom. The 2011 census recorded 224,000 British Pakistanis living in London.[50] However, it only forms 2.7 per cent of London's population, which is significantly lower than certain other British cities despite their lower overall Pakistani population. This population is made up of Punjabis, Mirpuris, Pashtuns, Sindhis, Muhajirs and Baloch.[51] This mix comparably makes the British Pakistani community of London more diverse than other communities in the UK, whereas a high proportion of Pakistani communities in the West Midlands and the North came from Azad Kashmir.[28]
The largest concentrations are in East London,[51] with the largest communities found in places including Ilford, Leyton, Walthamstow, Newham borough and Barking. Significant communities can also be found in the boroughs of Brent, Ealing and Hounslow in West London and Wandsworth and Croydon in South London.[52]
A considerable number of Pakistanis have set up their own businesses, often employing family members.[51] Today, a fifth of Pakistani Londoners are self-employed.[51] Businesses such as grocery stores and newsagents are common, while later arrivers commonly work as taxi drivers or chauffeurs.[51]
Well-known British Pakistanis from London include Sadiq Khan, the mayor of London; Anwar Pervez, whose Earl's Court grocery store expanded into the Bestway chain with a turnover of £2 billion,[53] and the playwright and author Hanif Kureishi.[54]
Birmingham
Birmingham has the second largest Pakistani community in the United Kingdom. The 2011 census recorded that there were 144,627 Pakistanis living in Birmingham, making up 13.5 per cent of the city's total population.[1]
The largest concentrations are in inner city Birmingham and areas such as Sparkhill, Small Heath, Bordesley Green, Balsall Heath, Aston, Ward End, Lozells, Nechells, Alum Rock and Washwood Heath. Wealthy middle-class Pakistanis tend to live in Hall Green and Yardley.[55][56]
The majority of "Brummie" Pakistanis can trace their roots to Azad Kashmir, with large minorities from Punjab and more recently, Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa. The BBC sitcom Citizen Khan is set among the Pakistani community of Sparkhill, described as "the capital of British Pakistan."
Bradford
The 2011 Census recorded 106,614 Pakistanis in Bradford. This was 20.4 per cent of the total population.[1]
The majority of British Pakistanis in Bradford can trace their roots to the Mirpur District of Azad Kashmir.[57]
Glasgow
Pakistanis make up the largest 'visible' ethnic minority in Scotland, representing nearly one third of the non-white ethnic minority population.[58] The 2011 census recorded 22,405 Pakistanis in Glasgow, 3.78% of the city's total population.[59]
There are large Pakistani communities throughout the city, notably in the Pollokshields area of South Glasgow, where there are said to be some "high standard" Pakistani takeaways and Asian fabric shops.[60] The majority came from the central Punjab part of Pakistan, including Faisalabad and Lahore.[61]
A survey by the University of Glasgow found that Scottish Pakistanis felt more Scottish than English people living there, and that their preferred political party was the Scottish National Party.[62] Glaswegian Humza Yousaf, of the SNP, who has served as the Minister for Transport and the Islands in the devolved Scottish Government since 18 May 2016, is of partly Pakistani descent.
Manchester

Pakistanis are the largest ethnic minority in Manchester, where they made up 3.8 per cent of the inner city's population in 2001.[63] Large Pakistani populations are also to be found in the Greater Manchester boroughs of Oldham and Rochdale, where they constituted 4.1 and 5.5 per cent of the population, respectively.[63]
In 2011, the ethnic Pakistani population of Manchester City had risen to 42,904, or 8.5% of the city's total population.[64] In the wider area of Greater Manchester, there were 130,012 people of Pakistani ethnicity, or 4.8 per cent of the population.[65] With greater prosperity, a recent trend has seen some of Manchester's Asian community move out of the inner city into more spacious suburbs, though British Pakistanis in Oldham and Rochdale remain less transient due to lower economic opportunities in these towns.[31]
A significant number of Manchester-based Pakistani business families have moved down the A34 road to live in the affluent Heald Green area.[66] Academics have associated the suburban movement of Pakistani-origin Muslims in Manchester with the formation of "gilded ghettoes" in the sought-after commuter suburbs of Cheshire.[31]
In 2018, Manchester was the venue for a fundraising telethon held to help crowdfund a major dam project in Pakistan.[67]
Nottingham
The 2011 census recorded 16,771 British Pakistanis in Nottingham which formed 5.5% of the city's population.[65]
There are a number of areas where Pakistanis have businesses and a number of 'Curry mile' streets as in Radford Road, Alfreton Road and Sneinton Dale Road. Within Bobbersmill and Forest Fields areas, Pakistanis are 17.4% of the total population.[68]
Leeds
The 2011 census recorded 22,492 Pakistanis, 3% of the Leeds population.[69] The districts of Beeston, Harehills and Hyde Park are home to significant Pakistani populations.
Religion
The majority of Pakistanis in the UK (over 90%) are Muslims. The largest proportion of these belong to the Sunni branch of Islam, with a significant minority belonging to the Shia branch.[7] Other notable sects include Ahmadiyya (whose spiritual leader, Mirza Masroor Ahmad, is based in London)[70] and Sufism. Mosques, community centres and religious youth organisations play an integral part in British Pakistani social life.[71]
Pakistanis account for 38 per cent of all Muslims in England and Wales.[8] This figure varies from a high of 71 per cent in Yorkshire and The Humber to a low of 21.5 per cent in Greater London. In England and Wales, there are around 17,000 Pakistani Christians, and slightly fewer Hindus, Sikhs, Zoroastrians (mainly Parsis)[72] and others.
The overall religious breakdown of British Pakistanis living in England and Wales in 2011 was:
| Religion | Percentage of British Pakistani population in England and Wales[8] |
|---|---|
| 91.46% | |
| Not stated | 5.16% |
| 1.52% | |
| None | 1.07% |
| 0.34% | |
| 0.29% | |
| 0.06% | |
| Other religion | 0.05% |
| 0.04% |
Languages
Most British Pakistanis speak English, and those who were born in the UK consider British English to be their first language. Pakistani English is spoken by first-generation and recent immigrants. Urdu, the national language of Pakistan, is understood and spoken by many British Pakistanis at a native level, and is the fourth-most commonly spoken language in the UK.[73][74] Urdu is taught in some secondary schools and colleges for GCSEs and A Levels.[75] It is also offered in madrassas along with Arabic.[76][77] According to Sajid Mansoor Qaisrani Urdu language periodicals of 1990s published in UK used to exclusively focus on South Asian issues, sans any relevance to British society.[78] Coverage of local British issues and problems of local Pakistanis in UK used to be very less.[78] Beyond Pakistani youth's interest in identifying with ethnic and religious identity, Urdu language was of little use to them in finding suitable employment opportunities.[78]
As the majority of Pakistanis in Britain are from Azad Kashmir and Punjab, some common languages spoken amongst Pakistanis in Britain are Punjabi, Potohari, Mirpuri and Hindko, which are closely related dialects of Punjabi.[79] Other Punjabi dialects are also spoken in Britain, making Punjabi the third-most commonly spoken language.[73][80]
Other significant Pakistani languages spoken include Pashto, Saraiki, Sindhi, Balochi and a minority of others. The number of speakers of such languages (as a primary language) in the United Kingdom, based on an Ethnologue report, are shown below. These languages are not only spoken by British Pakistanis, but also by other groups such as British Indians, British Afghans or British Iranians.[81]
| Primary language | Speakers |
|---|---|
| Punjabi | 573,500 |
| Urdu | 400,000 |
| Pashto | 162,000 |
| Memoni | 140,000 |
| Kashmiri | 115,000 |
| Saraiki | 30,000 |
| Sindhi | 25,000 |
| Balochi | NA |
Diaspora
Many British Pakistanis have emigrated from the UK, establishing a diaspora of their own. There are around 80,000 Britons in Pakistan,[82][83] a substantial number of whom are British Pakistanis who have resettled in Pakistan. The town of Mirpur in Azad Kashmir, where the majority of British Pakistanis hail from, has a large expatriate population of resettled British Pakistanis and is dubbed "Little England".[84][85][86]
Other British Pakistanis have migrated elsewhere to Europe, North America, the Middle East, Asia and Australia. Dubai, UAE remains a popular destination for British Pakistani expatriates to live in, mainly because of its modern lifestyle and work opportunities, Muslim culture, and convenient location between the UK and Pakistan.[87]
Pakistanis in Hong Kong were given full British citizenship in 1997 during the handover of Hong Kong, when it ceased to be a British colony, so as to prevent them being made stateless.[88] Previously, as Hong Kong residents, they held the status of British Overseas Territories citizens.[89][90]
Culture

Pakistan's Independence Day is celebrated on 14 August of each year in large Pakistani-populated areas of various cities, including Green Street in Newham, London, and the Curry mile in Manchester. Pakistani Muslims also observe the month of Ramadan and mark the Islamic festivals of Eid al-Adha and Eid al-Fitr.[91]
The annual Birmingham Eid Mela attracts more than 20,000 British Pakistanis to celebrate the festival of Eid. The Eid Mela also welcomes Muslims of other ethnic backgrounds. International and UK Asian musicians help celebrate the nationwide Muslim community through its culture, music, food and sport.[92]
Green Street in East London hosts Europe's "first Asian shopping mall".[93] A number of high-end Pakistani fashion and other retail brands have opened stores in the UK.[94][95]
Cuisine
Pakistani and South Asian cuisines are highly popular in Britain and have nurtured a largely successful food industry. The cuisine of Pakistan is strongly related to North Indian cuisine, coupled with an exotic blend of Arabic, Afghan, Central Asian, Persian and Turkish flavours.[96] The Pakistani language Urdu is also a mixture of Arabic, Persian and Turkish,[97] which shows and reflects the unity between the linguistic and culinary aspects of Pakistani culture. Mirpuri cuisine and Punjabi cuisine are well represented in Britain, reflecting the ethnic backgrounds of the Pakistanis who live in Britain.
The popular Balti dish has its roots in Birmingham, where it was believed to have been created by a Pakistani immigrant of Balti origin in 1977. The dish is thought to have borrowed native tastes from the northern Pakistani region of Baltistan in Kashmir.[98] In 2009, the Birmingham City Council attempted to trademark the Balti dish to give the curry Protected Geographical Status alongside items such as luxury cheese and champagne.[99] The area of Birmingham where the Balti dish was first served is known locally as the "Balti Triangle" or "Balti Belt".[100][101]
Chicken tikka masala has long been amongst the nation's favourite dishes, and is claimed to have been invented by a Pakistani chef in Glasgow, though its origins remain disputed.[102][103] There has been support for a campaign in Glasgow to obtain European Union Protected Designation of Origin status for it.[104]
Pakistanis are well represented in the British food industry. Many self-employed British Pakistanis own takeaways and restaurants. "Indian restaurants" in the North of England are almost entirely Pakistani owned.[105] According to the Food Standards Agency, the South Asian food industry in the UK is worth £3.2 billion, accounting for two thirds of all eating out, and serving about 2.5 million British customers every week.[106] Mirpuri and Punjabi origin curry sauces are sold in British supermarkets by British Pakistani entrepreneurs such as Manchester-born Nighat Awan. Awan's Asian food business, Shere Khan, has made her one of the richest women in Britain.[107]
Successful fast-food chains founded by British Pakistanis include Chicken Cottage[108] and Dixy Chicken.[109]
Sports
The expansion of the British Empire led to cricket being played overseas.[110] Cricket is a core part of Pakistani sporting culture and is often played by British Pakistanis for leisure and recreation.[111] Aftab Habib, Usman Afzaal, Kabir Ali, Owais Shah, Sajid Mahmood, Adil Rashid, Amjad Khan, Ajmal Shahzad, Moeen Ali, Zafar Ansari and Saqib Mahmood have played cricket for England.[112][113] Similarly, Asim Butt, Omer Hussain, Majid Haq, Qasim Sheikh and Moneeb Iqbal have represented Scotland. Prior to playing for England, Amjad Khan represented Denmark, the country of his birth. Imad Wasim became the first Welsh-born cricketer to represent Pakistan.[114][115] Former Pakistani cricketer Azhar Mahmood moved his career to England and became a naturalised British citizen.[116] There are several other British Pakistanis, as well as cricketers from Pakistan, who play English county cricket.[117][118]
Many young British Pakistanis find it difficult to make their way to the highest level of playing for England, despite much talent around the country. Many concerns about this have been documented although the number of British Pakistanis making progress in representing England is on the rise.[119]
The Pakistan national cricket team enjoys a substantial following among British Pakistanis, with the level of support translating to the equivalent of a home advantage whenever the team tours the UK. The "Stani Army" are a group consisting of British Pakistanis who follow the team especially when they play in the UK. The Stani Army are seen as the "rival" fan club to India's "Bharat Army".[120][121][122][123][124] England and Pakistan share a long cricketing relationship, often characterised by rivalries.[125][126]
Football is also widely followed and played by many young British Pakistanis (see British Asians in association football). Many players in the Pakistan national football team are British-born Pakistanis who became eligible to represent the country due to their Pakistani heritage. Zesh Rehman is a football defender who briefly played for Fulham F.C., becoming the first British Asian to play in the Premier League, before also playing for the English national U-18, U-19 and U-20 football teams until eventually opting for Pakistan.
Other notable British Pakistani footballers include Adnan Ahmed, Amjad Iqbal, Atif Bashir, Iltaf Ahmed, Kashif Siddiqi, Reis Ashraf, Shabir Khan and Usman Gondal. Hockey and polo are commonly played in Pakistan, with the former being a national sport, but these sports are not as popular among British Pakistanis, possibly due to the urban lifestyles which the majority of them embrace. Imran Sherwani was a hockey player of Pakistani descent who played for the English and Great Britain national field hockey teams.[127]
Adam Khan is a race car driver from Bridlington, Yorkshire. He represents Pakistan in the A1 Grand Prix series. Khan is currently the demonstration driver for the Renault F1 racing team.[128] Ikram Butt was the first South Asian to play international rugby for England in 1995.[129] He is the founder of the British Asian Rugby Association and the British Pakistani rugby league team, and has also captained Pakistan. Amir Khan is the most famous British Pakistani boxer. He is the current WBA World light welterweight champion and 2004 Summer Olympics silver medalist.[130] Matthew Syed was a table tennis international, and the English number one for many years.[131] Lianna Swan is a swimmer who has represented Pakistan in several events.[132]
Literature
A number of British Pakistani writers are notable in the field of literature. They include Tariq Ali, Kamila Shamsie, Nadeem Aslam, Mohsin Hamid and others.[133]
Through their publications, diaspora writers have developed a body of work that has come to be known as Pakistani English literature.
Ethnicity and cultural assimilation
A report conducted by The University of Essex found that British Pakistanis identify with 'Britishness' more than any other Britons. The study is one of several recent studies that have found that Pakistanis in Britain express a strong sense of belonging in Britain. The report showed that 90% of Pakistanis feel a strong sense of belonging in Britain compared to 84% of white Britons.[134]
English Pakistanis tend to identify much more with the United Kingdom than with England, with 63% describing themselves in a Policy Exchange survey as exclusively "British" and not "English" in terms of nationality, and only 15% saying they were solely English.[135]
Azad Kashmiris
Around 70% of all British Pakistanis trace their origins to the region of Mirpur in Azad Kashmir, northeastern Pakistan, including the towns of Dadyal, Chakswari, Islamgarh, Khari Sharif, Prahi, Bajjar and surrounding villages. Some also originate from the neighbouring districts of Bagh, Muzaffarabad, Rawalakot, Neelum, Bhimber and Kotli.[23][136][137] Pahari-Potwari dialects, spoken natively by Mirpuri immigrants, figure as the most commonly spoken languages of the British Pakistani community after English. Whilst these people may identify as "Kashmiris", most of them are not ethnic Kashmiris; rather, their native regions came under the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir in 1846.
The first generation migrant Mirpuris were not highly educated, and being from rural settlements, had little or no experience of urban living in Pakistan.[3] Migration from Mirpur and its adjacent areas started soon after the second world war as the majority of the male population of this area and the Potohar region worked in the British armed forces, as well as to fill labour shortages in industry. But the mass migration phenomenon accelerated in the 1960s, when, for improving water supply, the Mangla Dam project was built in the area, flooding the surrounding farmlands. Up to 5,000 people from Mirpur (five per cent of the displaced) resettled in Britain. The British contractor undertaking the project provided assistance to the displaced Mirpuris.
More Mirpuris joined their relatives in Britain after availing government compensation and liberal migration policies. Cities with large concentration of Mirpuris are Manchester, Bradford, Birmingham, Leeds and Luton.[23] Today, there are an estimated 700,000 people from Azad Kashmir residing in the UK.[23]
Mirpur was considered to be a conservative district in the 1960s, and life in its rural villages like most of the South Asian countries, was dominated by rigid hierarchies. Economic boom brought dramatic changes to the area after its residents started migrating to Europe, especially the UK, bolstering remittances. Families in Pakistan tend to be close knit and the guiding influence behind everything from marriage to business.[138] These Asian cultural values have clashed with British ones, which tend to be more free thinking and independent. Mirpuri migrants lived in some of the most segregated areas of Britain, and their children attended the most segregated schools.[139]
The British government has made attempts to improve community cohesion by nurturing a sense of shared or collective national identity. One programme designed to encourage greater social mixing includes the busing of students of Pakistani origin to "white schools" in an attempt to bridge the divide between the British Pakistani and white British ethnic groups.[140]
The Mirpuri community has made significant economic progress over the years. In almost all the major UK cities there is a sizeable Mirpuri business community which owns take aways, restaurants, shops and taxi bases to small and medium-sized manufacturing units, legal and financial firms. On the other hand, after the economic hardships faced by the first generation Mirpuri immigrants, their third and fourth generations are moving fast in the new fields of science, technology, arts and social sciences with higher number of youth taking admissions in different universities.
The Mirpuri expatriate community has made notable progress in UK politics and a sizeable number of MPs, councillors, lord mayors and deputy mayors are representing the community in different constituencies.[137] The 2005 Kashmir earthquake caused widespread losses in Azad Kashmir, affecting many British Pakistanis.[23]
Many Mirpuri have named their businesses after the Pakistani region. One of the largest companies incorporating such a name is Kashmir Crown Bakeries, which is a food-making business based in Bradford. The company is a major local employer and is the largest Asian food manufacturer in Europe.[141] The owner, Mohammed Saleem, claims that combining traditional Mirpuri baking methods with vocational British training has given his baking business a multimillion-pound turnover.[142]
Punjabis
Punjabis make up the second-largest sub-group of British Pakistanis, estimated to make up a third of that group.[143] With an equally large number from Indian Punjab, two thirds of all British Asians are of Punjabi descent, and they are the largest Punjabi community outside of South Asia,[143] resulting in Punjabi being the third-most commonly spoken language in the UK.[73][80]
People who came from the Punjab area have integrated much more easily into British society because the Punjab is a mostly prosperous part of Pakistan.[144] Early Punjabi immigrants to Britain tended to have more higher education credentials[31] and found it easier to assimilate because many already had a basic knowledge of the English language (speaking Pakistani English). Research by Teesside University has found that the British Punjabi community of late has become one of the most highly educated and economically successful ethnic minorities in the UK.[145]
Most Pakistani Punjabis living in the UK can trace their roots to the irrigated farms and urban conurbations of northern and central Punjab, including Jhelum, Faisalabad, Sahiwal, Jhang, Toba Tek Singh, Gujar Khan, Kallar Syedan, Attock, Bewal, Chiniot, Chakwal, Sui Cheemian, Sargodha, Gujrat, Sialkot and Gujranwala[3][146] while more recent immigrants have also arrived from large cities such as Lahore, urban Faisalabad, Islamabad-Rawalpindi and Multan. Additionally, many Muslim Punjabis entered the UK from Kenya and Uganda in the 1970s.[147] These workers were brought to Africa by British colonialists, therefore most held British passports. British Punjabis are commonly found in the south of England, the Midlands and the major cities in the north (with smaller minorities in former mill towns in Lancashire and Yorkshire).
Pashtuns
Pakistani Pashtuns (Pathans) in the United Kingdom originate from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in northwestern Pakistan. A number of estimates exist on the Pashtun population in the UK. Ethnologue estimates that there are up to 87,000 native Pashto-speakers in the UK; this figure also includes Afghan immigrants belonging to the Pashtun ethnicity.[148] Another report shows that there are over 100,000 Pashtuns in Britain, making them the largest Pashtun community in Europe.[149]
Major Pashtun settlement in the United Kingdom can be dated over the course of the past five decades. There is a British Pashtun Council which has been formed by the Pashtun community in the UK.
British Pashtuns have continued to maintain ties with Pakistan over the years, taking keen interest in political and socioeconomic developments in northwestern Pakistan.[149] Many Pashtun families came from cities such as Peshawar, Mardan, Swat, Kohat and Nowshera. There are also smaller communities from other parts of Pakistan, such as Punjabi-Pashtuns from Attock.[30]
Baloch
There is a small Baloch community in the UK, originating from the Balochistan province of southwestern Pakistan and neighbouring regions.[150] There are many Baloch associations and groups active in the UK, including the Baloch Students and Youth Association (BSYA),[151][152] Baloch Cultural Society, Baloch Human Rights Council (UK) and others.[153]
Some Baloch political leaders and workers are based in the UK, where they found exile.[154][155][156][157]
Muhajirs
There are over 400,000 Urdu-speakers in the UK,[81] some of whom are Muhajirs.[150] Muhajirs originally migrated from present-day India to Pakistan following the partition of British India in 1947. Most of them settled in Pakistan's largest city, Karachi, where they form the demographic majority. Many Muhajir Pakistanis later migrated to Britain, effecting a secondary migration.[27]
Altaf Hussain, leader of the Muttahida Qaumi Movement (MQM)—the largest political party in Karachi, with its roots lying in the Muhajir community—has been based in England in self-imposed exile since 1992. He is controversially regarded to have virtually "ruled" and "remotely governed" Karachi from his residence in the north London suburb of Edgware.[158][159]
Others
There is also a Pakistani Hazara community in the UK, concentrated particularly in Milton Keynes, northeastern London, Southampton and Birmingham. A Persian-speaking community originating from central Afghanistan. They migrated to the UK from Quetta and its surroundings, which is historically home to the large Hazara population in Pakistan.[160][161][162]
Health and social issues
Health
Pakistanis together with Bangladeshis in the UK have poor health by many measures, for instance there is a fivefold rate of diabetes.[163]
Pakistani men have the highest rate of heart disease in the UK.[164]
Sexual health
British Pakistanis, male and female, on average claim to have had only one sexual partner. The average British Pakistani male claims to have lost his virginity at the age of 20, the average female at 22, giving an average age of 21. 3.2 per cent of Pakistani males report that they have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), compared to 3.6 per cent of Pakistani females.[165]
Cultural norms regarding issues such as chastity and marriage have resulted in British Pakistanis having a substantially older age for first intercourse, lower number of partners, and lower STI rates than the national average.[165]
Cousin marriages and health risks
Research in Birmingham in the 1980s suggested that 50-70% of marriages within the Pakistani community were consanguineous.[166] Such consanguinity can double the likelihood of a child suffering from a birth defect from 3% to 6%.[167] Children born to closely related Pakistani parents had an autosomal recessive condition rate of 4% compared to 0.1% for the European group.[166]
Cousin marriages or marriages within the same tribe and clan are common in some parts of South Asia, including rural areas of Pakistan.[168] A major motivation is to preserve patrilineal tribal identity.[169] The tribes to which British Pakistanis belong include Jats, Ahirs, Gujjars, Awans, Arains, Rajputs and several others, all of whom are spread throughout Pakistan and north India. As a result, there are some common genealogical origins within these tribes.[170]
Some Mirpuri British Pakistanis view cousin or in-tribe marriages as a way of preserving this ancient tribal tradition and maintaining a sense of brotherhood, an extension of the biradri system which underpins community support networks.[150][171]
Most British Pakistanis prefer to marry within their own ethnic group,[172] and in 2009, it was estimated that six in ten British Pakistanis choose a spouse from Pakistan.[44]
Forced marriage
According to the British Home Office, 38 per cent of the cases of forced marriage investigated in 2014 involved families of Pakistani origin. This was the highest nationality, followed by Indians and Bangladeshis.[173] The Home Office estimates that 79% of cases involved female victims and 21% involved male victims.[173]
Sixty per cent of the Pakistani forced marriages handled by the British High Commission assistance unit in Islamabad are linked to the small towns of Bhimber and Kotli and the city of Mirpur in Azad Kashmir.[174]
According to 2017 data by the Forced Marriage Unit (FMU), a joint effort between the Home Office and the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, of the 439 callers related to Pakistan, 78.8% were female and 21.0% were male, 13.7% were under the age of 15 and another 13.0% were aged 16–17. Over 85% of the cases dealt with by the FMU were dealt with entirely in the UK, preventing the marriage before it could take place. Victims were in some cases forced to sponsor a visa for the spouse.[175]
Education
Data from the 2011 census shows that 25% of British Pakistanis in England and Wales hold degree level qualifications, in comparison to 26% of White British people. This has increased since 1991, when the figures for both groups holding a degree were 7% and 13%, respectively.[176][177]
The younger generation of British Pakistanis tends to be more educationally qualified than the older generation.[177] 26% of British Pakistanis in England and Wales did not have qualifications, compared to 24% of White British people, making them of one of the least qualified major groups.[177][178]
Secondary education
Pakistani pupils perform slightly below the national average when measured by the proportion of pupils gaining grade 4 or above in English and Maths GCSEs.[179] The British Pakistani GCSE pass rates does not distinguish the differences in achievement around the country, and Pakistani pupils have greater regional fluctuations than other groups.[28] For example, in 2015, Pakistani pupils from London were achieving above the results for White British pupils regionally and nationally. 73.9% of Pakistani pupils in London achieved five or more A*-C grades, compared to the White British London average of 69.5% in London and 65.9% across England and Wales.[180]
In the London borough of Croydon, 79.7% of Pakistani pupils gained five or more A*-C grades, compared to an average of 77.8% of Indian pupils and 71.3% of White British pupils.[180] These nationwide differences are the result of differences in material circumstances, social class, and migration histories of the different communities which make up British Pakistanis.[28]
In 2012, 46.5% of Pakistani students in England who were eligible for free school meals achieved five or more A*-C GCSE grades including English and mathematics. This figure is 10.2% higher than the national average of 36.3%.[181]
| Percentage achieving Grade 4/C or above in English and Mathematics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pakistani pupils | All pupils | |
| 2013/14 | 53.4% | 58.9% |
| 2014/15 | 53.6% | 59.2% |
| 2015/16 | 58.1% | 63.0% |
| 2016/17 | 60.1% | 63.9% |
| 2017/18 | 61.3% | 64.2% |
| 2018/19 | 62.2% | 64.6% |
There are several Muslim schools which also cater to British Pakistani pupils.[184][185]
Higher education
According to the Office for National Statistics, there were 249,508 graduates of Pakistani descent in 2017, an increase from 185,827 in 2011.[186][187] In 2017, approximately 16,480 British Pakistani students were admitted to university, almost a two-fold increase from 8,460 in 2006.[188]
51% of British Pakistanis choose to continue their studies at the university level. This is higher than the rate for White British (38%), Black Caribbean (41%), Mixed (40%), and lower than the rate for Indians (75%) and Bangladeshis (53%).[189]
The higher education drop out rate among British Pakistanis may be due to lower individualism where the family influences the individuals career choices, as well as high expectations which lead to higher failure rate due to individual interest not matching with the forced selection of the career. Secondly a lack of role models in higher education within the family also one of the reasons.[190]
Science and mathematics are the most popular subjects at A level and degree level among the youngest generation of British Pakistanis, as they begin to establish themselves within the field.[191]
In addition, there are over 10,000 Pakistani international students who enrol and study at British universities and educational institutions each year.[44][192] There are numerous student and cultural associations formed by Pakistani pupils studying at British universities.
Since 2008, thousands of British Pakistani graduates in Britain have been forced to work for low wages due to the rising unemployment and recession in the country. The majority of graduates attended post-1992 universities and graduated without experience. More than 20,000 British Pakistani students who graduated in 2012 were still without jobs six months after graduating. Moreover, an increasing number of university graduates are opting for low-paying minimum wage positions. In 2011 alone, some 10,270 graduates found work as labourers, couriers, office juniors, hospital porters, waiters, bar staff, cleaners, road sweepers and school dinner servers. This was almost double the number in 2008 before the UK recession struck.[193]
Language education
Urdu courses are available in the UK and can be studied at GCSE and A level.[75][194] Urdu degrees are offered in a couple of British universities and institutes, while several others are also hoping to offer courses in Urdu, open to established speakers as well as beginners, in the future.[195][196][197][198]
The Punjabi language is also offered at GCSE and A Level,[199] and taught as a course by two universities: SOAS[200] and King's College London.[201] Pashto is presently taught at SOAS and King's College London as well.[202]
Economics

Location has had a great impact on the success of British Pakistanis. The existence of a North-South divide leaves those in the north of England economically depressed, although there is a small concentration of more highly educated Pakistanis living in the suburbs of Greater Manchester and the West Midlands, as some Pakistani immigrants have taken advantage of the trading opportunities and entrepreneurial environment which exist in major UK cities.[206] But material deprivation and under-performing schools of the inner city have impeded social mobility for many Mirpuris.[206]
British Pakistanis based in large cities have found making the transition into the professional middle class easier than those based in peripheral towns. This is due to the fact that cities like Birmingham, Manchester, Leeds, Liverpool, Newcastle, Glasgow and Oxford have provided a more economically encouraging environment than the small towns in Lancashire and Yorkshire.[31]
On the other hand, the decline in the British textile boom brought about economic disparities for Pakistanis who worked and settled in the smaller mill towns following the 1960s, with properties failing to appreciate enough and incomes having shrunk.[172]
Most of the initial funds for entrepreneurial activities were historically collected by workers in food processing and clothing factories.[207] The funds were often given a boost by wives saving "pin money" and interest-free loans which were exchanged between fellow migrants. By the 1980s, British Pakistanis began dominating the ethnic and halal food businesses, Indian restaurants, Asian fabric shops, and travel agencies.[206] Other Pakistanis secured ownership of textile manufacturing or wholesale businesses and took advantage of cheap family labour. The once multimillion-pound company Joe Bloggs has such an origin.
Clothing imports from Southeast Asia began to affect the financial success of these mill-owning Pakistanis in the 1990s. However, some Pakistani families based in the major cities managed to buck this trend by selling or renting out units in their former factories.[206]
In the housing rental market, Pakistani landlords first rented out rooms to incoming migrants, who were mostly Pakistani themselves. As these renters settled in Britain and prospered to the point where they could afford to buy their own homes, non-Asian university students became the main potential customers to these landlords. By 2000, several British Pakistanis had established low-cost rental properties throughout England.[206] Aneel Mussarat is an example of a property millionaire. His company, MCR Property Group, specialises in renting apartments to university students in Manchester and Liverpool.
British Pakistanis are most likely to live in owner-occupied Victorian terraced houses of the inner city.[208] In the increasing suburban movement amongst Pakistanis living in Britain,[209] this trend is most conspicuous among children of Pakistani immigrants.[210] Pakistanis tend to place a strong emphasis on owning their own home and have one of the highest rates of home ownership in the UK at 73 per cent, slightly higher than that of the white British population.[211]
Many first generation British Pakistanis have invested in second homes or holiday homes in Pakistan.[212] They have purchased houses next to their villages and sometimes even in more expensive cities, such as Islamabad and Lahore. Upon reaching the retirement age, a small number hand over their houses in Britain to their offspring and settle in their second homes in Pakistan.[206] This relocation multiplies the value of their British state pensions. Investing savings in Pakistan has limited the funding available for investing in their UK businesses. In comparison, other migrant groups, such as South Asian migrants from East Africa, have benefited from investing only in Britain.[206]
Economic status
Statistics from the 2011 census show that Pakistani communities in England particularly in the North and the Midlands, are disproportionately affected by low pay, unemployment and poverty.[213][214] Thirty-two per cent of British Pakistanis live in a deprived neighbourhood, compared to 10 per cent for England overall.[215] Consequently, many fall within the welfare net.[216] In Scotland however, Pakistanis were less likely to live in a deprived area than the average.[217] Conversely, there were around 100 British Pakistani millionaires in 2001, representing a variety of industries.[218][219] Sir Anwar Pervez, owner of one of the UK's largest companies, the Bestway group,[220] is the richest British Pakistani and also among the UK's 50 richest people, with assets exceeding £1.5 billion.[221]
In addition, several wealthy Pakistanis including prominent politicians own millions of pounds' worth of assets and properties in the UK, such as holiday homes.[222][223][224][225] In 2017, 19.8 per cent of Pakistani secondary school students were eligible for free school meals, compared to 13.1 per cent of White British pupils. Amongst pupils in Key Stage 1, 14.1 per cent of both Pakistani and White British children were eligible for FSM.[226]
A 2020 report by the Runnymede Trust found that British Pakistani households have an estimated median total wealth of £127,000, placing them in third place out of the major ethnic groups in the UK.[227] The statistics show the following:
| Ethnic group | Median total wealth |
|---|---|
| White British | £282,000 |
| Indian | £266,000 |
| Pakistani | £127,000 |
| Black Caribbean | £89,000 |
| Other Asian | £50,000 |
| Bangladeshi | £28,000 |
| Black African | £28,000 |
Employment

According to the 2011 Census:[228]
| Economic Activity | All | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employed | 49% | 68% | 32% |
| Self-Employed | 24% | 30% | 10% |
| Economically Inactive | 41% | 24% | 60% |
Data from the 2011 Census shows that British Pakistanis had one of the lowest employment rates amongst other ethnic groups and a lower than average employment rate in all regions of England and Wales, reported at 49%. The statistics also showed that Pakistanis had one of the highest rates of unemployment at 12%.
Around 60% of British Pakistani women were economically inactive and 15% were unemployed in 2011.[229] Amongst older employed Pakistani women, many work as packers, bottlers, canners, fillers, or sewing machinists.[37] Pakistani women have recently begun to surge into the labour market.[230]
Latest figures from the Office for National Statistics show that British Pakistanis are far more likely to be self-employed than any other ethnic group, at 25%.[231]
The latest available data from the Labour Force Survey show that in the fourth quarter of 2019, the employment rate for British Pakistanis stood at 57% and unemployment rates were 7%.[232]
According to General Medical Council statistics, 14,213 doctors from Pakistan are registered in the UK,[233] and 2,100 dentists of Pakistani ethnicity were registered with the General Dental Council as of 2017.[234] Pakistani-origin doctors make up 4.6 per cent of all doctors in the UK[233] and Pakistan is one of the largest source countries of foreign young doctors in the UK.[235]
Social class
The majority of British Pakistanis are considered to be working or middle class.[236] According to the 2011 Census, 16.5 per cent of Pakistanis living in England and Wales were in managerial or professional occupations, 19.3 per cent in intermediate occupations, and 23.5 per cent in routine or manual occupations. The remaining 24.4 per cent and 16.3 per cent were classified under never worked or long-term unemployed and full-time students.[237]
Whilst British Pakistanis living in the Midlands and the North are more likely to be unemployed or suffer from social exclusion,[28] some Pakistani communities in London and the south-east are said to be "fairly prosperous".[42] It was estimated that, in 2001, around 45 per cent of British Pakistanis living in both inner and outer London were middle class.[238]
Media
Cinema
Notable films that depict the lives of British Pakistanis include My Beautiful Laundrette, which received a BAFTA award nomination, and the popular East is East which won a BAFTA award, a British Independent Film Award and a London Film Critics' Circle Award. The Infidel looked at a British Pakistani family living in East London.[239] The Infidel depicted religious issues and the identity crisis facing a young member of the family. The film Four Lions also looked at issues of religion and extremism. It followed British Pakistanis living in Sheffield in the North of England. The sequel to East is East, called West is West was released in the UK on 25 February 2011.[240]
Citizen Khan is a sitcom developed by Adil Ray which is based on a British Pakistani family in Sparkhill, Birmingham, dubbed the "capital of British Pakistan."[241] The soap opera EastEnders also features many British Pakistani characters.[242] Pakistani Lollywood films have been screened in British cinemas.[243][244] Indian Bollywood films are also shown in British cinemas and are popular with many second generation British Pakistanis and British Asians.[245]
Television
BBC has news services in Urdu and Pashto.[246][247] In 2005, the BBC showed an evening of programmes under the title "Pakistani, Actually". The programmes offered an insight into the lives of Pakistanis living in Britain and some of the issues faced by the community.[248][249] The executive producer of the series said, "These documentaries provide just a snapshot of contemporary life among British Pakistanis—a community who are often misunderstood, neglected or stereotyped."[248]
The Pakistani channels of GEO TV, ARY Digital and many others are available to watch on subscription. These channels are based in Pakistan and cater to the Pakistani diaspora, as well as anyone of South Asian origin. They feature news, sports and entertainment, with some channels broadcast in Urdu/Hindi.
Mishal Husain is a newsreader and presenter for the BBC of Pakistani descent.[250] Saira Khan hosts the BBC children's programme Beat the Boss. Martin Bashir is a Christian Pakistani[251] who worked for ITV, then American Broadcasting Company, before becoming BBC News Religious Affairs correspondent in 2016.
Radio
The BBC Asian Network is a radio station available across the entire UK and is aimed at Britons of South Asian origin under 35 years of age.[252] Apart from this popular station, there are many other national radio stations for or run by the British Pakistani community, including Sunrise and Kismat Radios of London.
Regional British Pakistani stations include Asian Sound of Manchester, Radio XL and Apni Awaz of Birmingham and Sunrise Radio Yorkshire which based in Bradford.[253] These radio stations generally run programmes in a variety of South Asian languages.
Print
The Pakistani newspaper the Daily Jang has the largest circulation of any daily Urdu-language newspaper in the world.[254] It is sold at several Pakistani newsagents and grocery stores across the UK. Urdu newspapers, books and other periodical publications are available in libraries which have a dedicated Asian languages service.[255] Examples of British-based newspapers written in English include the Asian News (published by Trinity Mirror) and the Eastern Eye. These are free weekly newspapers aimed at all British Asians.[256][257]
British Pakistanis involved in print media include Sarfraz Manzoor, who is a regular columnist for The Guardian,[258] one of the largest and most popular newspaper groups in the UK. Anila Baig is a feature writer at The Sun, the biggest-selling newspaper in the UK.[259]
Politics
British Pakistanis are represented in politics at all levels. In 2019 there were fifteen British Pakistani MPs in the House of Commons.[260] Notable members have included Shadow Secretary of State for Justice Sadiq Khan[261] and Home Secretary, Sajid Javid,[262] described by The Guardian as a 'rising star' in the Tory party.[263] The Guardian stated that "The treasury minister is highly regarded on the right and would be the Tories' first Muslim leader." Whereas The Independent have stated that Javid could become the next Chancellor of the Exchequer.[264] Ahead of the 2019 UK general election there were a record number of British Pakistanis contesting UK polls.[265]
Notable British Pakistanis in the House of Lords include Minister for Faith and Communities and former Chairman of the Conservative Party Sayeeda Warsi,[266] Tariq Ahmad,Nazir Ahmed,[267][268] and Qurban Hussain.[269] Mohammad Sarwar of the Labour Party was the first Muslim member of the British parliament, being elected for Glasgow in 1997 and serving till 2010.[270] In 2013, Sarwar quit British politics and returned to Pakistan, where he joined the government and briefly served as the Governor of Punjab.[271] Other politicians in Pakistan known to have held dual British citizenship include Rehman Malik,[272] Ishrat-ul-Ibad Khan,[273] and some members of the Pakistani national and provincial legislative assemblies.[274][275]
In 2007, 257 British Pakistanis were serving as elected councillors or mayors in Britain.[276] British Pakistanis make up a sizeable proportion of British voters and are known to make a difference in elections, both local and national.[277] They are much more active in the voting process, with 67 per cent voting in the last general elections of 2005, compared to just over 60 per cent for the whole country.[278]
Apart from their involvement in domestic politics, the British Pakistani community also maintains keen focus on the politics of Pakistan and has served as an important soft power prerogative in historical, cultural, economic and bilateral relations between Pakistan and the United Kingdom.[279][280] Major Pakistani political parties such as the Pakistan Muslim League (N),[281] Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf,[282] Pakistan Peoples Party,[283] Muttahida Qaumi Movement[284] and others have political chapters and support in the UK.
Some of the most influential names in Pakistani politics are known to have studied, lived or exiled in the UK.[285] London in particular has long served as a hub of Pakistani political activities overseas.[285][286][287][288] The British Mirpuri community has a strong culture of diaspora politics, playing a significant role in advocating the settlement of the Kashmir conflict and raising awareness of human rights issues in Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir.[289][290][291] Much of Pakistani lobbying and intelligence operations in the UK are focused on this key diaspora issue.[292]
Labour Party
The Labour Party has traditionally been the natural choice for many British Pakistanis. The Labour Party are also said to be more dependent on votes from British Pakistanis than the Conservative Party.[293] British Pakistani support for Labour reportedly fell because of party's decision to take part in the Iraq War,[294] when a substantial minority of Muslim voters switched from Labour to the Liberal Democrats.[295] A 2005 poll carried out by ICM showed that 40 per cent of British Pakistanis intended to vote for Labour, compared to 5 per cent for the Conservative Party and 21 per cent for the Liberal Democrats.[296] However, according to survey research, 60 per cent of Pakistani voters voted Labour in the subsequent general election, held in 2010[297] and this figure rose to more than 90 per cent in the 2017 general election.[295]
High-profile British Pakistani politicians within the Labour Party include Shahid Malik and Lord Nazir Ahmed, who became the first Muslim life peer in 1998.[298] Sadiq Khan became the first Muslim cabinet minister in June 2009, after being invited to accept the post by former Prime Minister Gordon Brown.[299] Anas Sarwar served as an MP for Glasgow Central between 2010 and 2015. Shabana Mahmood is the current Labour Chief Secretary to the Treasury.
Conservative Party

Some commentators have argued that the Conservative Party has become increasingly popular with some British Pakistanis, as they become more affluent.[301] However, analysis of a representative sample of ethnic Pakistani voters in the 2010 general election from the Ethnic Minority British Election Study shows that 13 per cent of them voted Conservative, compared to 60 per cent Labour and 25 per cent Liberal Democrat.[297]
The proportion of British Pakistanis voting Conservative fell in the 2015 and 2017 general elections.[295] Michael Wade, Chairman of the Conservative Friends of Pakistan, has argued that while polls have showed that only one third of British Pakistani men would never vote Conservative, "the fact is that the Conservative Party has not been successful in reaching out to the British Pakistani community; and so they, in turn, have not looked to the Conservative Party as the one that represents their interests".[302]
The Conservative Friends of Pakistan aims to develop and promote the relationship between the Conservative Party, the British Pakistani community and Pakistan.[303] David Cameron opened a new gym aimed at British Pakistanis in Bolton after being invited by Amir Khan in 2009.[304] Cameron also appointed Tariq Ahmad, Baron Ahmad of Wimbledon, a Mirpuri-born politician, a life peerage. Multi-millionaire Sir Anwar Pervez, who claims to have been born Conservative,[305] has donated large sums to the party.[306][307] Sir Anwar's donations have entitled him to become a member of the influential Conservative Leader's Group.[308]
Shortly after becoming the Conservative Party leader, Cameron spent two days living with a British Pakistani family in Birmingham.[309] He said that the experience taught him about the challenges of cohesion and integration.[309]
Sajjad Karim is a Member of the European Parliament. He represents North West England through the Conservative Party. In 2005, Karim became the founding Chairman of the European Parliament Friends of Pakistan Group. He is also a member of the Friends of India and Friends of Bangladesh groups.[310] Rehman Chishti became the new Conservative Party MP for Gillingham and Rainham.[311] Sayeeda Warsi was promoted to Chairman of the Conservative Party by the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom shortly after the 2010 UK general election. Warsi was the shadow minister for community cohesion when the Conservatives were in opposition. She is the first Muslim and first Asian woman to serve in a British cabinet. Both of Warsi's grandfathers served with the British Army in the Second World War.[312]
Others
In the 2003 Scottish Parliament elections, Scottish Pakistani voters supported the Scottish National Party (SNP) more than the average Scottish voter.[62] The SNP is a centre-left civil nationalist party that campaigns for the independence of Scotland from the United Kingdom. SNP candidate Bashir Ahmad was elected to the Scottish Parliament to represent Glasgow at the 2007 election, becoming the first Member of the Scottish Parliament to be elected with a Scottish Asian background.[313]
Salma Yaqoob is the former leader of the left-wing, anti-Zionist Respect Party. The small party has seen success in areas such as Sparkbrook in Birmingham and Newham in London, where there are large Pakistani populations. Qassim Afzal is a senior Liberal Democrat politician of Pakistani origin. In 2009 he accompanied the then Deputy Prime Minister of the United Kingdom to meetings with Pakistan's President, Asif Ali Zardari.[314]
Contemporary issues
Discrimination
The chance of a Pakistani being racially attacked in a year is greater than 4 per cent—the highest rate in the country, along with British Bangladeshis—though this has come down from 8 per cent a year in 1996.[315] The term "Paki" is often used as a racist slur to describe Pakistanis and can also be directed towards non-Pakistani South Asians. There have been some attempts by the youngest generation of British Pakistanis to reclaim the word and use it in a non-offensive way to refer to themselves, though this remains controversial.[316]
In 2001 riots occurred in Bradford. Two reasons given for the riots were social deprivation and the actions of extreme right wing groups such as the National Front (NF).[317] The Anti-Nazi League held a counter protest to a proposed march by the NF leading to clashes between police and the local South Asian population, with the majority of those being involved being of Pakistani descent.[318][319]
Paki-bashing
Starting in the late 1960s,[320] and peaking in the 1970s and 1980s, violent gangs opposed to immigration took part in frequent attacks known as "Paki-bashing", which targeted and assaulted Pakistanis and other South Asians.[321] "Paki-bashing" was unleashed after Enoch Powell's inflammatory Rivers of Blood speech in 1968,[320] and peaked during the 1970s–1980s, with the attacks mainly linked to far-right fascist, racist and anti-immigrant movements, including the white power skinheads, the National Front, and the British National Party (BNP).[322][323]
These attacks were usually referred to as either "Paki-bashing" or "skinhead terror", with the attackers usually called "Paki-bashers" or "skinheads".[320] According to Robert Lambert, "influential sections of the national and local media" did "much to exacerbate" anti-immigrant and anti-Pakistani rhetoric.[323] The attacks were also fuelled by systemic failures of state authorities, which included under-reporting of racist attacks, the criminal justice system not taking racist attacks seriously, and racial harassment by police.[320]
Notable people
See also
Related Pakistanis
- British Mirpuri
- Pakistani community of London
- Overseas Pakistani
- Pakistanis in France
- Pakistanis in Ireland
- Pakistanis in the Netherlands
Related groups
- British Asian
- British Bangladeshi
- British Indian
- British Sri Lankans
- Afghans in the United Kingdom
- List of British Muslims
Arts and entertainment
Other
- Pakistan–United Kingdom relations
- Islam in the United Kingdom
- Britons in Pakistan
Notes
- This census figure may not include people of partial Pakistani ancestry.
References
- "2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in the United Kingdom". Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2013. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- "Britain's Pakistani community". The Daily Telegraph. 28 November 2008. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- Werbner, Pnina (2005). "Pakistani migration and diaspora religious politics in a global age". In Ember, Melvin; Ember, Carol R.; Skoggard, Ian (eds.). Encyclopedia of Diasporas: Immigrant and Refugee Cultures around the World. New York: Springer. pp. 475–484. ISBN 0-306-48321-1.
- Satter, Raphael G. (13 May 2008). "Pakistan rejoins Commonwealth – World Politics, World". The Independent. London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Butler, Patrick (18 June 2008). "How migrants helped make the NHS". The Guardian. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Nadia Mushtaq Abbasi. "The Pakistani Diaspora in Europe and Its Impact on Democracy Building in Pakistan" (PDF). International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 August 2010. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- Department for Communities and Local Government. "The Pakistani Muslim Community in England" (PDF). Department for Communities and Local Government. pp. 5–11 (6), 36–41. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 September 2012. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
In London the community is more mixed and includes comparable numbers of Punjabis, Pathans and Kashmiris. There are also small communities of Sindhis and Balochis in London.
- "2011 Census data - religion". Retrieved 4 October 2018.
- "2011 census data – religion". The Guardian. Retrieved 29 August 2013.
- Guy Palmer; Peter Kenway (29 April 2007). "Poverty rates among ethnic groups in Great Britain". JRF. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "CoDE Housing Census Briefing" (PDF). University of Manchester. October 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 February 2014. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- Nelson, Dean (3 December 2012). "European Roma descended from Indian 'untouchables', genetic study shows". The Telegraph. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
Later, they left to flee the fall of Hindu kingdoms in what is today Pakistan, with many setting off from near Gilgit.
- Kelly, Nataly (2012). Found in Translation: How Language Shapes Our Lives and Transforms the World. Penguin. p. 48. ISBN 9781101611920.
Their roots date back to northern India and Pakistan in around 1000 CE. Invading forces pushed them from their homeland, starting a forced migration to today's Anatolia in western Turkey.
- Reed, Judy Hale (2013). Indonesian Journal of International & Comparative Law (January 2014): Socio-Political Perspectives. Institute for Migrant Rights Press. p. 179.
Roma people originated from present-day India or Pakistan and migrated over a thousand years ago to Europe and other regions of the world.
- "The First Asians in Britain". Fathom. Archived from the original on 11 April 2004. Retrieved 29 April 2010.
- "History of Islam in the UK". BBC - Religions. 7 September 2009. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- Fathom archive. "British Attitudes towards the Immigrant Community". Columbia University. Archived from the original on 3 January 2011. Retrieved 4 March 2011.
- Fisher, Michael Herbert (2006). Counterflows to Colonialism: Indian Traveller and Settler in Britain 1600–1857. Orient Blackswan. pp. 111–9, 129–30, 140, 154–6, 160–8, 172. ISBN 81-7824-154-4.
- Parekh, Bhikhu (9 September 1997). "South Asians in Britain". History Today. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- "The Goan community of London - Port communities - Port Cities". www.portcities.org.uk. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- "Find your ancestors in England & Wales Merchant Navy Crew Lists 1861-1913".
- D. N. Panigrahi, India's Partition: The Story Of Imperialism In Retreat, 2004; Routledge, p. 16
- Marco Giannangeli (10 October 2005). "Links to Britain forged by war and Partition". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- Ember, Melvin; Ember, Carol R.; Skoggard, Ian (2005). Encyclopedia of Diasporas: Immigrant and Refugee Cultures Around the World. Volume I: Overviews and Topics; Volume II: Diaspora Communities, Volume 1. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9780306483219.
- Visram, Rozina (30 July 2015). Ayahs, Lascars and Princes: The Story of Indians in Britain 1700-1947. ISBN 9781317415336.
- Sophie Hares (3 July 2009). ""Untold" story of WW2 stirs Muslim youth pride". Reuters. Retrieved 29 April 2010.
- "The Pakistani Community". BBC. 24 September 2014. Retrieved 4 October 2014.
- Robin Richardson; Angela Wood. "The Achievement of British Pakistani Learners" (PDF). Trentham Books. pp. 2, 1–17.
- "Muslims in Britain: Past And Present". Islamfortoday.com. Archived from the original on 24 March 2010. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Kinship and continuity: Pakistani families in Britain. Routledge. 2000. pp. 26–32. ISBN 978-90-5823-076-8. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Pnina Werbner. "Pakistani Migration and Diaspora Religious Politics in a Global Age" (PDF). Keele University. pp. 476–478. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- Museum of London (21 September 2004). "subject home". Museum of London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Fox, Susan (2015). The New Cockney: New Ethnicities and Adolescent Speech in the Traditional East End of London. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 9781137503992.
- Bizeck J.Phiri. "Asians: East Africa". Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- Minority Rights Group. "East African Asians". Archived from the original on 3 December 2010. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- Ethnic Minorities and Industrial Change in Europe and North America, Malcolm Cross (ed), PP: 226–250, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1992
- "National Statistics Online – Employment Patterns". Office for National Statistics. 21 February 2006. Archived from the original on 1 May 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Dobbs, Joy; Green, Hazel; Zealey, Linda, eds. (2006). Focus on Ethnicity and Religion 2006 (PDF). Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan/Office for National Statistics. pp. 30, 41. ISBN 1-4039-9328-9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 October 2006.
- "Population size: 7.9% from a non-White ethnic group". Office for National Statistics. 8 January 2004. Archived from the original on 19 June 2004. Retrieved 22 December 2010.
- "Estimated overseas-born population resident in the United Kingdom by sex, by country of birth (Table 1.4)". Office for National Statistics. 28 August 2014. Retrieved 27 April 2015. Figure given is the central estimate. See the source for 95 per cent confidence intervals.
- Cheema, Umar (12 July 2012). "Where expatriates who reach the top come from". The News. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- Instead. "The raise project". Yorkshire Forward. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "FEATURE – Support for Taliban dives among British Pashtuns | Reuters". Reuters. 10 June 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "The immigration superhighway". The Economist. 16 April 2009. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- "Foreign travel advice: Pakistan". Government of the United Kingdom. 10 August 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- Shah, Murtaza Ali (25 May 2018). "Pakistanis eighth highest number of non-British nationals living in UK". The News. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- "PIA's Network". Pakistan International Airlines. Archived from the original on 26 July 2014. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- "British Airways resumes Pakistan flights after a 10-year absence". France 24. 3 June 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
Britain is home to more than a million people of Pakistani origin, making it the largest Pakistani diaspora community in Europe.
- Peach, Ceri (2005). "Britain's Muslim population: An overview". In Abbas, Tahir (ed.). Muslim Britain: Communities under Pressure. London: Zed Books. pp. 18–30. ISBN 1-84277-449-2.
- "2011 Census: 45% of Londoners white British". BBC News. 11 December 2012.
- "Pakistani london". Renaissance London. Archived from the original on 14 September 2011. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- "London by ethnicity". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 7 February 2009. Retrieved 25 June 2009.
- Zameer Choudrey. "Bestway Group's turnover exceeds £2BN". WholesaleManager. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- Moore-Gilbert, Bart (2001). Hanif Kureishi. Manchester: Manchester University Press. pp. 1–2. ISBN 0-7190-5535-0.
- David Parker; Christian Karner. "Remembering the Alum Rock Road" (PDF). University of Nottingham. pp. 1–7. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "A Brief History of the Bangladesh Community". Birmingham City Council. 27 February 2008. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Tim Smith. "Immigration and emigration". BBC Legacies. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Scotland against racism. "Ethnicity Data". One Scotland. Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- "Scotland's Census 2011 – Table KS201SC". scotlandscensus.gov.uk. Retrieved 3 November 2015.
- "What do you know about Pollokshields?". Herald & Times Group. Archived from the original on 24 August 2011. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- "Associated Press of Pakistan ( Pakistan's Premier NEWS Agency ) – PIA inaugural flight from Glasgow to Faisalabad". App.com.pk. Archived from the original on 19 February 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Kelbie, Paul (30 October 2003). "Pakistanis living in Scotland feel more at home north of the border than the 400,000 English who live there – This Britain, UK". The Independent. London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- John Moss. "Manchester Population". Manchester 2002. Archived from the original on 17 November 2010. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- "Ethnic Group Summary: 2011 Census" (PDF). Manchester City Council. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- "Table KS201EW 2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- Asian News. "Violent racists menace affluent suburb". Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Farmer, Ben (8 June 2019). "Pakistan appeals to British diaspora in ambitious attempt to crowdfund major dam project" – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
- Services, Good Stuff IT. "Berridge - UK Census Data 2011". UK Census Data.
- "Leeds Observatory – Population". observatory.leeds.gov.uk.
- "His Holiness Mirza Masroor Ahmad, Khalifa-tul Masih V Head of the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community". Al Islam. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- Jacobson, Jessica (2006). Islam in Transition: Religion and Identity Among British Pakistani Youth. Routledge. p. 31. ISBN 9781134697106. Retrieved 9 April 2015.
- Payne, J.D. (2012). Strangers Next Door: Immigration, Migration and Mission. InterVarsity Press. p. 184. ISBN 9780830863419.
- "2011 Census: Quick Statistics". Retrieved 17 May 2014.
- "Linguistic and Ethnic Groups". U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Ager, Denis (2003). Ideology and Image: Britain and Language. Clevedon: Multilingual Matters. p. 191. ISBN 1-85359-659-0.
- William Stewart. "UK madrassas coach borderline pupils". TES Connect. Archived from the original on 17 September 2011. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- "Case study". Department for Children, Schools and Families. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Qaisrani, Sajid Mansoor (February 1990). Urdu press in Britain. Islamabad: Mashal Publications,. pp. 85, 86. ISBN 969 8094 00 8.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- "Punjabi Dialects and geographic distribution". Punjabi world. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- "Punjabi Community". The United Kingdom Parliament. Retrieved 2 November 2010
- "Ethnologue report for United Kingdom". Ethnologue.com. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Gishkori, Zahid (30 July 2015). "Karachi has witnessed 43% decrease in target killing: Nisar". The Express Tribune. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
As many as 116,308 Afghan nationals are living as immigrants in the country, higher than any other country,” Nisar told the House. Besides Afghans, 52,486 Americans, 79,447 British citizens and 17,320 Canadians are residing in the country, the interior minister added.
- "Brits Abroad". BBC News. 6 December 2006. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- Maqbool, Aleem (5 March 2012). "How city of Mirpur became 'Little England'". BBC. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- Wilkinson, Isambard (5 December 2005). "British Pakistanis bring fish and chips to Kashmir's 'Beverly Hills'". The Telegraph. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- Maqbool, Aleem (1 May 2010). "Chasing the UK vote in Pakistan's 'Little Britain'". BBC. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- Roy, Ananya; Ong, Aihwa (2011). Worlding Cities: Asian Experiments and the Art of Being Global. John Wiley & Sons. p. 170. ISBN 9781444346770. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- "Hong Kong: Indians and Pakistanis to be given full British passports". AP Archive. 22 July 2015. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- Schloss, Glenn (26 June 1997). "Pakistanis with BNO passports disowned". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- Brown, Colin (4 February 1997). "HK citizens to get full British passport rights". Independent. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- "British Pakistani Muslims in UK celebrate Eid ul Fitr with traditional zeal". Pakistan Daily. 2 October 2008. Archived from the original on 22 March 2012. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- Live, Birmingham (5 September 2011). "Thousands enjoy Eid Mela in Cannon Hill Park". birminghammail.
- Pathan, Nabila (30 March 2015). "Saris, souks and silk: Europe's 'first Asian shopping mall' opens". Al Arabiya News. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- Rehman, Maliha (30 March 2015). "The rat-race to London – Khaadi strides ahead, the others just sell lawn". The Express Tribune. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- Dar, Humayoon (15 March 2015). "Summer apparel: The evergreen lawn businesses in Pakistan". The Express Tribune. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "Pakistani society". RolaGola. Archived from the original on 15 July 2011. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- "A Brief History of Urdu". BBC Languages. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- "Birth of Birmingham's balti". BBC Legacies. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- Nick Britten (1 July 2009). "Birmingham bids to prevent curry houses elsewhere using word Balti". Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- Neil Connor. "Balti belt a wonder to behold". Trinity Mirror Midlands. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- "Welcome to the Balti Triangle". Birmingham City Council. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- http://www.shezanedinburgh.com/menu/chicken-tikka-masala/
- "Icons of England". Icons of England. Archived from the original on 2 December 2008. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- "UK Parliament Early Day Motions 2008–2009". The United Kingdom Parliament. Archived from the original on 22 December 2017. Retrieved 11 August 2010.
- The Guardian group. "Who are the British Asians?". New Statesman. Retrieved 12 April 2010.
- "Curry factfile". Food Standards Agency. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- Chris Barry. "From printing T-shirts to £30m food fortune". Manchester Evening News. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "Muslim Power List 2010". Retrieved 14 July 2013.
- "Tasty Chicken offered by the Dixy Panban Chicken Franchise". London: Franchise Business Ltd. Retrieved 14 July 2013.
- BBC World Service. "The birth and the journey through centuries". BBC. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- Stephen Brenkley (27 July 2010). "Pakistan has so much talent but we don't channel it properly". The Independent. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- Alavi, Omair (24 July 2016). "Pakistan's cricketing exports". Dawn. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- "2nd T20I, England tour of New Zealand at Wellington, Nov 3 2019". ESPN Cricinfo. Retrieved 3 November 2019.
- "Instonians sign Pakistani professional Imad Wasim". Cricket Europe. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- "Swansea-born Imad Wasim makes debut for Pakistan". BBC Sport. 19 July 2015. Retrieved 20 July 2015.
- Azhar Mahmood joins Kent, ESPNCricinfo, 22 November 2007, retrieved 20 April 2012
- Khan, Haroon (25 July 2011). "England counties are Pakistan cricketers' finishing schools". The National. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- Khan, Wasim (10 May 2018). "I was the first British born Pakistani to play professional cricket in the UK – but why are there still so few of us?". Independent. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- Westerby, John (31 May 2018). "The British Pakistanis lost to English cricket" – via www.thetimes.co.uk.
- Cox, David. "Cricket World Cup: The rise of the Bharat and Stani Armies". www.aljazeera.com.
- "BBC Radio Bristol - Desi Download, The Stani Army: UK Pakistan Cricket fans". BBC.
- Fletcher, Thomas (29 July 2011). "'Who do they cheer for?': Cricket, diaspora, hybridity and divided loyalties amongst British Asians" (PDF). International Review for the Sociology of Sport. 47 (5): 612–631. doi:10.1177/1012690211416556.
- Chaudhry, Vivek (30 May 2001). "A question of support". The uardian. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- Ehantharajah, Vithushan (June 2017). "Frenemies forever". The Cricket Monthly. Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- "The bitter cricketing history of Pakistan v England – in pictures". The Guardian. 11 January 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- Yusuf, Imran (10 October 2011). "England v Pakistan: not for the faint-hearted". Cricinfo. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- Chowdhury, Saj (2 July 2004). "Where were the Germans?". BBC News.
- LJ Hutchins. "F1: Adam Khan gets a break with Renault". Brits on Pole. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- "Trying times". Chris Arnot. 28 October 2009. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- John Moss. "Sports & Olympic Champions". Manchester UK. Archived from the original on 6 December 2010. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- "Championships". comtab.com. Commonwealth Table Tennis Federation. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
- "Lianna Swan: Flying the Flag for Pakistani Swimming". 25 July 2013. Archived from the original on 26 July 2014. Retrieved 27 July 2014.
- "Mohsin Hamid on citizenship" The Independent 25 February 2007
- Moosavi, Leon (3 July 2012). "British identity and society, Islam (News), Race issues (News), World news, Religion (News), Society, UK news". The Guardian.
- Kirkup, James (5 May 2014). "Non-white people almost 30 per cent of population by 2050". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- Maqbool, Aleem (1 May 2010). "Chasing the UK vote in Pakistan's 'Little Britain'". BBC. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- Shackle, Samira (20 August 2010). "The mosques aren't working in Bradistan". New Statesman. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- "The limits to integration", BBC News, 30 November 2006
- Samira Shackle (20 August 2010). "The mosques aren't working in Bradistan". New Statesman. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- Anthony Browne (5 May 2004). "We can't run away from it: white flight is here too". The Times. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- "The largest Asian Food Manufacturer in Europe". Kashmir Crown Bakeries. Archived from the original on 24 February 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "The History". Kashmir Crown Bakeries. Archived from the original on 24 February 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Roger Ballard; Marcus Banks (1994). Desh Pardesh: the South Asian presence in Britain. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. pp. 18, 20, 21.
- "Pakistan". National Geographic. National Geographic Society. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- Steve Taylor. "Punjabi Communities in the North East". Teesside University. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- Gilliat-Ray, Sophie (2010). Muslims in Britain. Cambridge University Press. p. 45. ISBN 9780521536882.
- "Home". Minority Rights Group.
- Lewis, M. Paul, ed. (2009), "Ethnologue report for the United Kingdom", Ethnologue: Languages of the World (16th ed.), Dallas, Texas: SIL International, retrieved 29 July 2013
- "Support for Taliban dives among British Pashtuns". Reuters. 10 June 2009. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- Childs, Peter; Storry, Michael (2013). Encyclopedia of Contemporary British Culture. Routledge. p. 386. ISBN 9781134755547.
- "Baloch youth body formed in UK". 21 July 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "Baloch students form association in UK". Daily Times. 16 July 2012. Archived from the original on 5 June 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "Balochistan: Important London Meeting For UK Baloch". Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization. 15 February 2013. Retrieved 1 June 2014.
- Shah, Murtaza Ali (28 August 2012). "Baloch diaspora pays rich tributes to Akbar Bugti". The News. Retrieved 1 June 2014.
- Butt, Qaiser (26 May 2013). "Balochistan conundrum: Khan of Kalat's return is a distant possibility". Express Tribune. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- "Family intervention?: 'Khan of Kalat's son wants to bring back exiled father'". Express Tribune. 1 April 2012. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- Shah, Murtaza Ali (10 July 2015). "Baloch leaders keep low profile in UK". The News. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- "Karachi's king over the water: Altaf Hussain of the MQM". the Guardian. 22 May 2013. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- "Altaf Hussain: Pakistan's powerful but absent politician". BBC. 3 June 2014. Retrieved 7 April 2015.
- "Daily Hansard Debate". House of Commons. 1 March 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- "Homepage". Hazara Community of Milton Keynes. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- "Pakistani Hazara campaigner fights deportation from Britain". Dawn. 16 October 2014. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- "Genetics & South Asian Populations | East London Genes & Health". www.genesandhealth.org. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- "Diabetes and heart disease in Bangladeshis and Pakistanis | East London Genes & Health". www.genesandhealth.org (in Bengali). Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- Fleming, Nic (1 April 2005). "Love league tables show link to sexual disease". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Enhanced Genetic Services Project - Evaluation Report (PDF). PHG Foundation / NHS. 2008. p. 9.
- Victoria Burchell, Victoria Burchell (8 July 2013). "Risk of birth defects from cousin marriage revealed by Bradford study". BioNews. Progress Educational Trust. Retrieved 8 July 2018.
- "Birth defects warning sparks row". BBC News. 10 February 2008. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- DeVotta, Neil (2003). Understanding Contemporary India. London: Lynne Rienner. pp. 232–237. ISBN 1-55587-958-6.
- Monika Böck; Aparna Rao (2000). Culture, Creation, and Procreation: Concepts of Kinship in South Asian Practice. Berghahn Books. pp. 81–157. ISBN 1-57181-912-6.
... Kalesh kinship is indeed orchestrated through a rigorous system of patrilineal descent defined by lineage endogamy
- Zafar Khan. "Diasporic Communities and Identity Formation". University of Luton. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- "In Britain, Bangladeshis fare better than Pakistanis". Express Tribune. 25 February 2015. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/412667/FMU_Stats_2014.pdf
- "Cry freedom – Features – TES Connect". Tes.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Forced Marriage Unit Statistics 2017 (PDF). Home Office & Foreign & Commonwealth Office. 16 March 2018. p. 12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 August 2018.
- "White British adults 'less qualified' than ethnic minorities". Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- "How are ethnic inequalities in education changing?" (PDF). Joseph Rowntree Foundation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2014. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- Paton, Graeme (10 March 2014). "White British adults 'less qualified' than ethnic minorities". ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- "Key stage 4 and multi-academy trust performance 2019 (revised)". GOV.UK.
- "2015 GCSE results in London by ethnicites - a Freedom of Information request to Department for Education". WhatDoTheyKnow. 9 April 2016.
- "Revised GCSE and equivalent results in England: academic year 2011 to 2012". Department for Education.
- "15 Indian-origin men, women in Queen's New Year's Honours list". NDTV.com.
- "Department of Geography, Cambridge » Ash Amin". www.geog.cam.ac.uk.
- "Muslim Families' Educational Experiences in England and Scotland: Final Report" (PDF). Centre for Research in Education Inclusion and Diversity. March 2013. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- "8 Muslim schools in top 50 exam league in England". The Express Tribune. 7 April 2015. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- "Data Viewer - Nomis - Official Labour Market Statistics". www.nomisweb.co.uk. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- https://www.ons.gov.uk/file?uri=/employmentandlabourmarket/peopleinwork/employmentandemployeetypes/adhocs/009099demographiceducationalandworkplacedetailsforgraduatesukapril2015tomarch2018/am201718graduates.xls
- https://www.ucas.com/file/139591/download?token=IJUQE66p
- "British Christians, Atheists Least Likely to Go to University – CP World". The Christian Post. Retrieved 19 January 2013.
- Nadeem, Rahema (2019). Achievement and Retention of British-Pakistani Students in UK Higher Education: Using Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions to Ask All the Right Questions (Applied Research International Conferences). The University of Oxford, U.K: London Institute of Skills Development. pp. 47, 48. ISBN 978-1-789728323.
- "White students 'avoid maths and science' – Education News, Education". The Independent. Archived from the original on 21 November 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Don't close the door to Asian students". Spiked. 14 April 2009. Archived from the original on 3 February 2012. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
- "Daily Times". Daily Times. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012.
- "Urdu (4645)". AQA. Archived from the original on 29 October 2014. Retrieved 21 May 2014.
- "Urdu degree 'first' for city universities". The Asian News. 6 April 2010. Archived from the original on 14 September 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Ahmad, Athar (27 March 2015). "UK's first Urdu degree offered by Manchester Metropolitan University". BBC. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "Urdu at SOAS Language Centre". SOAS. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "Urdu - King's College London". Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "AQA – Languages – GCSE – Panjabi". Archived from the original on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- "Panjabi: Languages of South Asia at SOAS: University of London". University of London. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- "King's College London - Panjabi". Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- Iqbal, Jamshed; Zaman, Amir; Ghafar, Abdul (June 2013). "Inclusion of Pashto in O'Level Cambridge Education". Department of Education, Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, Pakistan.
- Richard Ford. "Asda scores a first with Pakistani mangoes deal". The Grocer. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- Rafiq Raja. "Asian View: The joys of eating mangos". Bournemouth Echo. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- Nabanita Sircar. "Harrods & Selfridges to host Pakistani mangos". Hindustan Times. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- Encyclopedia of diasporas: immigrant and refugee cultures around the world. Springer. 2005. pp. 477–484.
- "Showing 'crap town' Luton in new light". BBC News. 4 March 2005. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- Ceri Peach. "A question of collar". Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- Phillips, D., Davis, C. and Ratcliffe, P. (2007), British Asian narratives of urban space, Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, 32: 217–234. ISSN 0020-2754
- "'Myths' threaten racial harmony, say population experts (The University of Manchester)". Manchester.ac.uk. 22 January 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Policy briefing Home ownership" (PDF). Shelter. April 2006. pp. 4–6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- Jerome Taylor (12 March 2010). "Mystery of the missing father of kidnapped boy". The Independent. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "The Poverty Site". poverty.
- http://www.ethnicity.ac.uk/medialibrary/briefingsupdated/have-ethnic-inequalities-in-employment-persisted-between-1991-2011%20(1).pdf
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 1 November 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- MacFarquhar, Neil (21 August 2006). "Pakistanis Find U.S. an Easier Fit Than Britain". The New York Times. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- http://www.gov.scot/Topics/People/Equality/Equalities/DataGrid/Ethnicity/EthPov
- "UK Pakistani Business Directory". Pakistani Business Directory. Archived from the original on 20 June 2010. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Muslims contribute 31b pounds to British economy". Pakistan Daily Times. 12 February 2007. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- Shah, Murtaza Ali (11 October 2014). "British Pakistani group acquires pharmacy business in £725m deal". The News. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- "Anwar Pervez: The Billionaire cash and carry King". Express. 21 July 2014. Retrieved 5 October 2014.
- "Shahbaz owns assets worth Rs153m in UK, Rs108m in Pakistan". Dawn. 29 January 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- Shah, Murtaza Ali (7 October 2012). "Pakistani politician buys Tony Blair's family home". The News. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "Inside Benazir Bhutto's £10 million country retreat". Telegraph. 20 June 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "Pakistani politician's London mansion becomes the talk of the town". Dawn. 30 October 2013. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "Latest percentage eligible for Free School Meals by ethnicity - a Freedom of Information request to Department for Education". WhatDoTheyKnow. 20 May 2018.
- https://www.runnymedetrust.org/uploads/publications/pdfs/2020%20reports/The%20Colour%20of%20Money%20Report.pdf
- "2011 Census analysis - Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- "2011 Census analysis - Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- "Asian Muslim women – All about taking part". The Economist. 22 December 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- "Coronavirus and self-employment in the UK - Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- "A09: Labour market status by ethnic group - Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- "GMC Data Explorer". www.gmc-uk.org.
- "General Dental Council FOI". General Dental Council. 2019. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- Abid, Abdul Majeed (12 October 2012). "Where have all the doctors gone?". The Friday Times. Archived from the original on 23 November 2012. Retrieved 5 March 2015.
- Gilligan, Andrew (14 January 2010). "John Denham's right: It's class, not race, that determines Britain's have-nots". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "Socioeconomic status". www.ethnicity-facts-figures.service.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- Philip Cohen (January 2008). London's Turning: The Making of Thames Gateway. London. pp. 137, 138. ISBN 978-0-7546-7063-6.
- "Omid Djalili becomes an Infidel". BBC. 23 June 2009. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- "West Is West: world exclusive clip". The Guardian. 19 October 2010. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- "Citizen Khan". BBC. Retrieved 1 November 2012.
- Rajani, Deepika (24 August 2015). "EastEnders spoiler: Shabnam prepares to leave for Pakistan after the death of her son". OK Magazine. Archived from the original on 10 October 2015. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- "Waar set to run on 23 UK screens from January 17". The Express Tribune. 14 January 2014. Retrieved 21 May 2014.
- "Bol". Filmdates.co.uk. Retrieved 21 May 2014.
- Sarfraz Manzoor (29 May 2008). "Brits in Bollywood". Retrieved 17 January 2011.
- "BBC Urdu". Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- "BBC Pashto". Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- "Beds Herts and Bucks – Read This – Luton, actually". BBC. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Luton Actually BBC2 Pakistani Actually". Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Mishal Husain, a pretty asian face of BBC". The Asians. 29 January 2010. Archived from the original on 6 October 2010. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Wells, Matt (22 January 2003). "Talk to me". The Guardian. London.
- "About the BBC". BBC. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- Sunrise Radio Yorkshire. "About Sunrise Radio". Archived from the original on 19 January 2011. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "Pakistan profile". BBC News. 11 September 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- "Asian Library Services". Manchester City Council. Archived from the original on 29 September 2011. Retrieved 17 January 2011.
- Asian News (9 August 2007). "Contact Us". Archived from the original on 22 May 2010.
- "Eastern Eye". Asian Media & Marketing Group. Archived from the original on 16 December 2010. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "Sarfraz Manzoor Profile". The Guardian. 3 June 2008. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- The Sun, Audit Bureau of Circulations. Retrieved 20 December 2010
- https://dailytimes.com.pk/519639/15-british-pakistanis-elected-as-mps-in-uk-daily-times/
- https://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/politics/justice-secretary-chris-grayling-in-uturn-defendants-on-legal-aid-will-still-be-able-to-choose-their-solicitor-8682397.html The Independent. Retrieved 4 July 2013
- Javid, Sajid (19 July 2018). "As home secretary, I'm determined to fix the Windrush injustices | Sajid Javid". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- Watt, Nicholas (31 January 2013). "Conservatives tories tory party, Boris Johnson, Michael Gove, William Hague, David Davis (Politics), George Osborne, Liam Fox, Politics". The Guardian.
- DONALD MACINTYRE (1 May 2014). "Donald Macintyre's Sketch: Hmm. Sajid Javid as Chancellor? Why not? - UK Politics - UK - The Independent". The Independent. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- "Record number of British-Pakistanis contesting UK polls". gulfnews.com.
- House of Lords Minutes of Proceedings for Tuesday 15 October 2007. House of Lords Information Office.
- "Labour peer urged support for Tories in 2005 election". New Statesman. 30 November 2006.
- "'Sterling' bounty offered for Obama, Bush". The Express Tribune. 15 April 2012.
- "The story of two Pakistani-origin Lords - The Express Tribune". 25 November 2010. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- "SARWAR, Mohammad". Who's Who 2010 online edn. Oxford University Press. November 2009. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- Buncombe, Andrew (5 August 2013). "UK's first Muslim MP Mohammad Sarwar becomes governor of Pakistan's Punjab province". The Independent. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "MPs with dual-nationality: Holding dual citizenship is no crime says Rehman Malik". The Express Tribune. 11 May 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- Foggo, Daniel (19 June 2005). "Governor claimed £244 weekly housing benefit to live in home secretly owned by his brother". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "Dual Nationality : Text of Short Order". The News. 20 September 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "Verdict on dual nationality issue: Court sends 11 legislators home". Dawn. 21 September 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- Perlez, Jane (3 August 2007). "Pakistani official tackles prejudice in Britain". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Race and politics: ethnic minorities and the British political system. Routledge. 1986. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-422-79840-2.
- Pasternicki, Adam (22 March 2010). "How Conservatives' software targets Asian voters". BBC News. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "British attitudes to the Pakistani diaspora". YouGov. 24 June 2013. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- "Pakistan, UK ought to remain positively engaged". The News. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- "Official website of Pakistan Muslim League-N UK". Pakistan Muslim League (N). Archived from the original on 4 June 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- "Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf UK". Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf. Archived from the original on 6 August 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- "Overseas organizations". Pakistan Peoples Party. Archived from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- "Muttahida Qaumi Movement UK". Muttahida Qaumi Movement. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- "East of Edgware". The Economist. 7 June 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
London has a long tradition of hosting Pakistani politicians who have left their homeland in a hurry. The usual form is for ousted leaders to set up shop in one of the city’s posher neighbourhoods, rail against the incumbent regime in Islamabad and head home in triumph when the time is right. The formula worked well for Benazir Bhutto and Nawaz Sharif (though it failed for Pervez Musharraf, a former dictator, now embroiled in a treason trial after foolishly returning last year).
- Tahir, Zulqernain (30 May 2014). "Tahirul Qadri, PML-Q leaders meet in London today in bid to form anti-govt alliance". Dawn. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
London has become the hub of Pakistan’s political activities as the Chaudhrys of Gujrat and Dr Tahirul Qadri meet there on Friday to kick off efforts to forge a ‘grand anti-government alliance’.
- Shah, Murtaza Ali (17 November 2014). "Zardari calls party meeting in London". Geo News. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- Hussain, Shahid (22 February 2007). "Benazir and Nawaz to jointly chair opposition's key London meeting". Gulf News. Retrieved 12 April 2015.
- "'Kashmir million march' to go on despite Indian efforts: Barrister Sultan". Dawn. 20 October 2014. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- "Kashmir issue: UK councillor urges resolution of dispute". The Express Tribune. 11 March 2015. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- "Kashmir 'Solidarity' Day Marked In UK". The Asians. 7 February 2015. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- Ray, Ashis (7 March 2011). "UK keeps eyes shut as ISI uses turf to hit India". Times of India. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- David Leigh (1 December 2010). "Cameron criticised radicalised Muslims: Wikileaks". The Hindu. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "War costs Labour the Muslim vote". The Muslim News. 30 May 2003. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Martin, Nicole; Khan, Omar (February 2019). "Ethnic Minorities at the 2017 British General Election" (PDF). Runnymede Trust. Retrieved 25 February 2019.
- Tom Templeton (24 April 2005). "The ethnic minority vote". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- Heath, Anthony; Khan, Omar (February 2012). "Ethnic Minority British Election Study – Key Findings" (PDF). Runnymede Trust. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- "Profile: Lord Ahmed". BBC News. 25 February 2009. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- "Tooting MP Sadiq Khan named first Muslim cabinet minister in Gordon Brown's reshuffle (From Wandsworth Guardian)". The Wandsworth Guardian. 6 June 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Sajid Javid". politics.co.uk.
- "UK | In search of the Muslim vote". BBC News. 18 April 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Michael Wade: British Pakistanis – the two-way street towards better integration". Conservative Home. 30 June 2013. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
- "Home page". Conservative Friends of Pakistan. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- "David Cameron opens Amir Khan's gym in Bolton". YouTube. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Sathnam Sanghera (21 July 2007). "Slim margins mean fat profits for the man who supplies Britain's corner shops". The Times. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- "Frontrunners in fortune". The Guardian. London. 6 March 2002. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "The top political donors". The Times. London. p. 1. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- "Conservative Party donor clubs". The Conservative Party. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- David Cameron (13 May 2007). "What I learnt from my stay with a Muslim family". The Observer. London. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- "The Conservative Party | Mr Sajjad Karim MEP". The Conservative Party. Archived from the original on 29 April 2010. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Steve Farrell (7 May 2010). "Bike-supporting Opik is election casualty". Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- Janice Turner (17 October 2009). "No garlic and silver bullets are needed for Nick Griffin". The Times. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- "First Asian MSP goes to Holyrood". BBC News. 4 May 2007. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- "Pakistan President Asif Zardari meets Liberal Democrat Leader Nick Clegg". Liberal Democrats. 27 August 2009. Archived from the original on 30 April 2010. Retrieved 10 May 2010.
- "Pakistanis are eight times more likely to be victim of a racist attack than whites – Home News, UK". The Independent. London. 4 February 2003. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- Rajni Bhatia (11 June 2007). "After the N-word, the P-word". BBC News. Retrieved 6 May 2010.
- Thomas, Paul (1 May 2009). David Waddington; Fabien Jobard; Mike King (eds.). Rioting in the UK France. Willan. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-84392-504-0.
- Chant, Sylvia H. (2011). The International Handbook of Gender and Poverty: Concepts, Research, Policy. Edward Elgar. p. 275. ISBN 978-1-84980-095-2.
- Bagguley, Paul; Yasmin Hussain (2008). Riotous Citizens: Ethnic Conflict in Multicultural Britain. Ashgate. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-7546-4627-3.
- Ashe, Stephen; Virdee, Satnam; Brown, Laurence (2016). "Striking back against racist violence in the East End of London, 1968–1970". Race & Class. 58 (1): 34–54. doi:10.1177/0306396816642997. ISSN 0306-3968. PMC 5327924. PMID 28479657.
- "In the eye of the storm". Red Pepper. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- Nahid Afrose Kabir (2012), Young British Muslims, Edinburgh University Press
- Lambert, Robert (2013). "Anti-Muslim violence in the UK: Extremist nationalist involvement and influence". In Taylor, Max; Currie, P. M.; Holbrook, Donald (eds.). Extreme Right Wing Political Violence and Terrorism. Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 40–53. ISBN 9781441140876.
Further reading
- Ali N, Ellis P and Khan Z (1996), A Time to Separate British Punjabi and British Kashmiri Identity, in Singh and Talbot (eds.) New Delhi: Manohar Publishers
- Amin, A (2002) Ethnicity and the multicultural city: living with diversity, Environment and Planning A, 34
- Amin, A (2003) Unruly strangers? The 2001 urban riots, International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 27(2)
- Anwar, M (1996) British Pakistanis: demographic, social and economic position. University of Warwick. ISBN 0-948303-59-X
- Brown, J (2006) Global South Asians: introducing the modern diaspora, Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-84456-8
- Dahya, B (1974) The nature of Pakistani ethnicity in industrial cities in Britain, Tavistock Press. ISBN 0-415-32982-5
- Kalra, V (2000) From textile mills to taxi ranks Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84014-865-7
- Giannangeli, Marco (10 October 2005). "Links to Britain forged by war and Partition". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- Imtiaz, Sharon Karima (1997). A comparative study of multilingual Pakistanis in Amsterdam and Birmingham (PDF) (PhD thesis). University of Warwick.
- Jamal, A (1998). Food consumption among ethnic minorities: the case of British-Pakistanis in Bradford, UK. Emerald Group Publishing Limited. ISSN 0007-070X
- Jamal, A (1998). Cultural diversity and its impact on businesses, in Navigation Difference: Cultural Diversity and Audience Development, Arts Council England. ISBN 0-7287-1077-3
- Kundnani, A (2001) From Oldham to Bradford: the violence of the violated Race and Class 43(2)
- Sandercock, L (2003) Cosmopolis II: mongrel cities in the twenty-first century. Continuum. ISBN 0-8264-7045-9
- Shaw, A. (1988) A Pakistani community in Britain, Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-15228-8
- Werbner, P. (2002) The migration process: Capital, gifts and offerings among British Pakistanis, Berg Publishers. ISBN 1-85973-664-5
- Yilmaz, Ihsan. (2005) Muslim Laws, Politics and Society in Modern Nation States: Dynamic Legal Pluralisms in England, Turkey, and Pakistan, Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7546-4389-0
