London Borough of Newham
The London Borough of Newham /ˈnjuːəm/ (![]()
London Borough of Newham | |
|---|---|
London borough | |
 Coat of arms Council logo | |
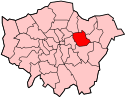
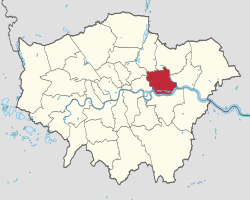 Newham shown within Greater London | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | London |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Created | 1 April 1965 |
| Admin HQ | East Ham |
| Government | |
| • Type | London borough council |
| • Body | Newham London Borough Council |
| • Leadership | Mayor and Cabinet (Labour) |
| • Executive mayor | Rokhsana Fiaz (Labour) |
| • London Assembly | Unmesh Desai (Labour) AM for City and East |
| • MPs | Lyn Brown (Labour) Stephen Timms (Labour) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 13.98 sq mi (36.22 km2) |
| Area rank | 289th (of 317) |
| Population (mid-2019 est.) | |
| • Total | 353,134 |
| • Rank | 20th (of 317) |
| • Density | 25,000/sq mi (9,700/km2) |
| • Ethnicity[1] | 16.7% White British 0.7% White Irish 0.2% White Gypsy or Irish Traveller 11.4% Other White 1.3% White & Black Caribbean 1.1% White & Black African 0.9% White & Asian 1.3% Other Mixed 13.8% Indian 9.8% Pakistani 12.1% Bangladeshi 1.3% Chinese 6.5% Other Asian 12.3% Black African 4.9% Black Caribbean 2.4% Other Black 1.1% Arab 2.3% Other |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| Postcodes | |
| Area code(s) | 020 |
| ONS code | 00BB |
| GSS code | E09000025 |
| Police | Metropolitan Police |
| Website | http://www.newham.gov.uk |
The name Newham reflects its creation and combines the compass points of the old borough names.
It is 5 miles (8 km) east of the City of London, north of the River Thames. Newham was one of the six host boroughs for the 2012 Summer Olympics and contains most of the Olympic Park including the London Stadium. The local authority is Newham London Borough Council.
The borough's motto, from its coat of arms, is "Progress with the People". The coat of arms was derived from that of the County Borough of West Ham, while the motto is a translation of the County Borough of East Ham's Latin "Progressio cum Populo".[2]
History
The borough was formed by merging the former area of the Essex county borough of East Ham and the county borough of West Ham as a borough of the newly formed Greater London, on 1 April 1965 – these in turn were successors to the ancient civil and ecclesiastical parishes of East Ham and West Ham. Green Street and Boundary Road mark the former boundary between the two. North Woolwich also became part of the borough (previously being in the Metropolitan Borough of Woolwich, south of the river Thames in the County of London) along with a small area west of the River Roding which had previously been part of the Municipal Borough of Barking. Newham was devised for the borough as an entirely new name.[3]
Ham(me): Pre-partition origins
The area of the modern borough was at one time occupied by a territory called 'Ham'.
The first known written use of the term, as 'Hamme', is in an Anglo-Saxon charter of 958, and again in the 1086 Domesday Book as Hame. It is formed from Old English 'hamm' and means 'a dry area of land between rivers or marshland', referring to the location of the settlement within boundaries formed by the rivers Lea, Thames and Roding and their marshes.[4]
These natural boundaries suggest that Little Ilford, North Woolwich and areas of the parish of Barking west of the Roding are likely to have been part of Ham(me).
The territory was subdivided into the more familiar West and East Ham sometime in the 12th century, with the earliest recorded distinction being as 'Westhamma' in 1186. It could be speculated that the partition arose as a result of population increase resulting from economic prosperity delivered by the construction of Bow Bridge over the Lea and the creation of Stratford Langthorne Abbey.
North Woolwich was removed from Ham at an earlier date, in the aftermath of the Norman Conquest but it is unclear when Little Ilford and western Barking were transferred, and it is not known for sure that they were part of Ham.
The boundary between West and East Ham was drawn from the now lost Hamfrith Waste and Hamfrith Wood in the north (then the southernmost parts of Epping Forest which extended as far south as the Romford Road at that time), along Green Street down to the small, similarly lost, natural harbour known as Ham Creek.
The formation of the modern borough in 1965 saw the merger of West and East Ham, together with North Woolwich and Barking west of the River Roding (Little Ilford had become part of East Ham as part of earlier local government reorganisations). This reorganisation effectively re-established the earlier territory of Ham.
Governance
Unlike most English districts, its council is led by a directly elected mayor of Newham. From 2002 to 2009 one of the councillors had been appointed as the "civic ambassador" and performed the civic and ceremonial role previously carried out by the mayor. The post has been discontinued.[5]
At the borough elections held in 2014, the Labour Party won all 60 of the seats on the Council. Sir Robin Wales was re-elected as the borough's Executive Mayor with 61% of the first preference votes cast.
In 2018, Robin Wales was deselected as the Labour Party mayoral candidate. Rokhsana Fiaz was elected in the position of Executive Mayor, also for the Labour party.[6]
Demography
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 8,875 | — |
| 1811 | 11,166 | +25.8% |
| 1821 | 13,005 | +16.5% |
| 1831 | 15,553 | +19.6% |
| 1841 | 17,758 | +14.2% |
| 1851 | 24,875 | +40.1% |
| 1861 | 69,355 | +178.8% |
| 1871 | 113,835 | +64.1% |
| 1881 | 158,314 | +39.1% |
| 1891 | 259,155 | +63.7% |
| 1901 | 338,506 | +30.6% |
| 1911 | 442,158 | +30.6% |
| 1921 | 448,081 | +1.3% |
| 1931 | 454,096 | +1.3% |
| 1941 | 377,508 | −16.9% |
| 1951 | 313,837 | −16.9% |
| 1961 | 271,858 | −13.4% |
| 1971 | 235,496 | −13.4% |
| 1981 | 209,131 | −11.2% |
| 1991 | 221,146 | +5.7% |
| 2001 | 243,737 | +10.2% |
| 2011 | 307,984 | +26.4% |
| Source: A Vision of Britain through time, citing Census population | ||
Newham has the youngest overall population and one of the lowest indigenous White British populations in the country according to the 2011 UK Census. The borough has the second-highest percentage of Muslims in the UK, after the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, at 32%. A 2017 report from Trust for London and the New Policy Institute found that 36% of local employees in Newham are in low paid work; the highest percentage of any London borough. Newham also has a 37% poverty rate, which is the second-highest rate in London.[7]
When using Simpson's Diversity Index on 10 aggregated ethnic groups, the 2001 UK Census identified Newham as the most ethnically diverse district in England and Wales, with 9 wards in the top 15.[8] However, when using the 16 ethnic categories in the Census so that White Irish and White Other ethnic minorities are also included in the analysis, Newham becomes the second-most ethnically diverse borough[9] with six out of the top 15 wards, behind Brent with 7 out of the top 15 wards.
Health
In 2018, Newham had the lowest life expectancy and the highest rate of heart disease of all London boroughs together with the London Borough of Tower Hamlets.[10]
In 2019, the BBC reported that Newham had the highest rate of tuberculosis in the UK at 107 per 100000 population, which was higher than Rwanda (69) and Iraq (45) according to WHO figures from 2013. More than 80% of TB cases in London occur in people born abroad. The UK average was 13.[11]
| Ethnic Group | 2001[12] | 2011[13] | 2016 (Projection)[14] | 2020 (Estimate)[15] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Percentage (%) | Number | % | |
| White: British | 82,390 | 33.78% | 51,516 | 16.73% | 13.5% | 47,858 | 13.2 |
| White: Irish | 3,231 | 1.32% | 2,172 | 0.71% | 0.7% | 2,835 | 0.8 |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | 462 | 0.15% | – | - | - | ||
| White: Other | 10,509 | 4.31% | 35,066 | 11.39% | 12.6% | 49,660 | 13.7 |
| White: Total | 96,130 | 39.42% | 89,216 | 28.97% | 26.8% | 100,353 | 27.5% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | 29,597 | 12.14% | 42,484 | 13.79% | 15.0% | 53,917 | 14.8 |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | 20,644 | 8.46% | 30,307 | 9.84% | 10.4% | 35,777 | 9.8% |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | 21,458 | 8.80% | 37,262 | 12.10% | 12.4% | 45,259 | 12.4% |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | 2,349 | 0.96% | 3,930 | 1.28% | 1.4% | 5,984 | 1.6% |
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | 7,603 | 3.12% | 19,912 | 6.47% | 6.6% | 24,134 | 6.6% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | 81,651 | 33.48% | 133,895 | 43.47% | 46.1% | 165,071 | 45.3% |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | 17,931 | 7.35% | 15,050 | 4.89% | 4.4% | 14,837 | 4.1% |
| Black or Black British: African | 31,982 | 13.11% | 37,811 | 12.28% | 11.2% | 40,439 | 11.1% |
| Black or Black British: Other Black | 2,740 | 1.12% | 7,395 | 2.40% | 2.6% | 9,533 | 2.6% |
| Black or Black British: Total | 52,653 | 21.59% | 60,256 | 19.56% | 18.3% | 64,809 | 17.8% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | 2,986 | 1.22% | 3,957 | 1.28% | – | 4,108 | 1.1% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | 1,657 | 0.68% | 3,319 | 1.08% | – | 4,013 | 1.1% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | 1,652 | 0.68% | 2,677 | 0.87% | – | 4,127 | 1.1% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | 1,953 | 0.80% | 3,992 | 1.30% | – | 6,035 | 1.7% |
| Mixed: Total | 8,248 | 3.38% | 13,945 | 4.53% | 4.9% | 18,283 | 5.0% |
| Other: Arab | 3,523 | 1.14% | – | 4,732 | 1.3% | ||
| Other: Any other ethnic group | 7,149 | 2.32% | – | 10,317 | 2.8% | ||
| Other: Total | 5,209 | 2.14% | 10,672 | 3.47% | 3.9% | 15,049 | 4.1% |
| BAME: Total | 147,761 | 60.58% | 218,768 | 71.03% | 260,680 | 72.9% | |
| Total | 243,891 | 100.00% | 307,984 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 364,346 | 100.00% |
Newham has the lowest percentage of White British residents of all of London's boroughs. The White British proportion of the population fell from 33.8% in 2001 to 16.7% in 2011; this decrease of 37.5 percentage points is the largest of any local authority in England and Wales between the two censuses.[16][17] The joint-lowest wards with White British population are Green Street East and Green Street West, both having 4.8% – the third-lowest behind Southall Broadway and Southall Green in Ealing. East Ham North follows closely, at 4.9%.[18]
People of White British ancestry nevertheless remain the largest single ethnic group in the borough. The largest non-White British ethnic groups are Indian (14%), African (12%), Bangladeshi (12%) and Pakistani (10%). Newham has had a large Indian community for many decades. The ethnic group to increase the most in number since 1991 is the Bangladeshi community.[19]
Religion
Religion in Newham as of 2011.
Education
A 2017 report by Trust for London and the New Policy Institute finds that the GCSE attainment gap between advantaged and disadvantaged pupils in Newham is the 4th best out of 32 London boroughs.[20]
Schools and colleges
The Borough is the education authority for the district providing education in a mix of Foundation, community and voluntary aided schools.[21] The borough also owns and operates Debden House, a residential adult education college in Loughton, Essex, and is home to the Rosetta Art Centre, a dedicated visual art organisation which delivers courses at its base in Stratford and produces participatory art projects, programmes and initiatives. The Essex Primary School in Sheridan Road with over 900 pupils is one of the biggest primary schools in London.
University
The University of East London has two campuses in Newham:
- the Stratford Campus, at Stratford
- the Docklands Campus, next to the regenerated Royal Albert Dock
Birkbeck Stratford is a collaboration between Birkbeck, University of London and UEL to increase participation in adult learning. This is based on the UEL/Birkbeck shared campus, USS (University Square Stratford), in the centre of Stratford.
The University of East London had formed a partnership with the United States Olympic Committee which resulted in the United States Olympic Team using University of East London campuses as training bases during the London 2012 Olympic and Paralympic Games.[22]
Places of interest

Community
- The Hub, a community resource centre built by the local community, in Star Lane, E16, featuring up to the minute "green" features
- Grassroots, also built by the local community and another innovative green resource centre built by the community. Grassroots is in Memorial Recreation Ground, E15
- Rosetta Art Centre, situated in walking distance to Grassroots, also in E15
Libraries
Newham has ten libraries (Beckton, Canning Town, Custom House, East Ham, Green Street, Manor Park, North Woolwich, Plaistow, Stratford and Forest Gate).[23]
Museums
- North Woolwich Old Station Museum. Closed in 2008.[24]
- Three Mills, a mill complex on the east bank of the River Lea. A trading site for nearly a thousand years, the House Mill was built in 1776 and was (and remains) the country's largest tide mill. It has been restored and contains much of its original machinery including four large waterwheels, millstones and grain chutes.
Markets
There are a number of local markets in the Borough, including Queens Market, which the Council is controversially seeking to redevelop. These proposals are being fought by Friends of Queens Market.
Parks and open spaces
80 hectares within the borough are designated as part of the Metropolitan Green Belt.
Performance

- Stratford Circus Arts Centre, a community arts venue which presents theatre, dance, music, circus and comedy from around the world for communities in Newham and East London. The organisation works with schools and local groups in Newham to provide classes, workshops and outreach opportunities. Stratford Circus Arts Centre partners with Newham Council for Every Child a Theatre Goer which invites every year 6 child to a performance at the venue
- Theatre Royal Stratford East
- St Mark's Church, Silvertown The church was designed by Samuel Saunders Teulon. It was built between 1861 and 1862 after a cholera epidemic swept the district and local clergy appealed through the columns of The Times for funds to provide an architectural, as well as spiritual, beacon for the area. It is now the home of the Brick Lane Music Hall.
Shopping and exhibitions
- Queen's Market – an historic street market
- ICC London – ExCeL – International Conference Centre
- Gallions Reach Shopping Park
- East Shopping Centre – Europe's first purpose-built boutique Asian shopping centre
- Green Street – a shopping street mostly catering for the Asian community[25]
- Stratford Centre
- Westfield Shopping Centre, Stratford – The largest Westfield Shopping Centre in Europe.
Sport
- Newham was one of the six host boroughs for the 2012 Summer Olympics.
- West Ham United F.C. play its home matches at the London Stadium (formally the Olympic Stadium) in Stratford.
- Newham Dockers Rugby League club that train and play out of East London Rugby Club, competing in the London Premier League
- The Newham and Essex Beagles Athletics Club has its headquarters at the Terence McMillan Stadium, part of Newham Leisure Centre, in Plaistow.
- Clapton F.C., a non-league football club, plays in Forest Gate.
- London APSA F.C. a non-league football club, plays in Plaistow.
- London Lituanica, a basketball team playing in the English Basketball League
- Tomás Mac Curtain's women's GAA team train weekly at the East London Rugby Club
- Diesel Gym London a non-profit organisation and one of the UK's largest Mixed Martial Arts centres
- London Regatta Centre a charitable organisation promoting water sports such as rowing and dragon boats
Newspapers
The local newspaper is the Newham Recorder.[26]
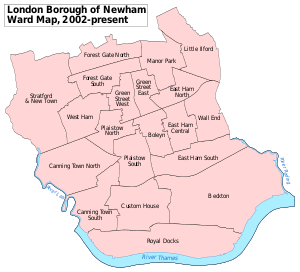
Districts

- Beckton
- Canning Town
- Custom House
- Cyprus
- East Ham
- East Village
- Forest Gate
- Little Ilford
- Manor Park
- Maryland
- Mill Meads
- North Woolwich (/ˈwʊlɪtʃ/ or /ˈwʊlɪdʒ/)
- Plaistow (/ˈplɑːstoʊ/)
- Plashet
- Silvertown
- Stratford
- Stratford City
- Stratford Marsh
- Stratford New Town
- Temple Mills
- Upton
- Upton Park
- Wallend
- West Ham
Parishes
The borough is covered by the following ecclesiastical parishes of the Church of England:
- Parish of the Divine Compassion, Plaistow and North Canning Town
- St Martin's Church, Plaistow
- St Mary's Church, Plaistow
- St Philip and St James Church, Plaistow
- St Matthias' Church, Canning Town
- St Luke's Church, Canning Town
- Church of the Ascension, Victoria Docks
- St John's Church, North Woolwich
- St Mark's Church, Beckton
- Parish of East Ham, Holy Trinity
- St George's and St Ethelbert's Church, East Ham
- St Paul's Church, East Ham
- Little Ilford
- St Barnabas, Little Ilford
- Emmanuel Forest Gate, with St Peter's, Upton Cross
- St Mark's Church, Forest Gate
- St Saviour and St James, Forest Gate
- St Margaret with St Columba, Leytonstone
- St Paul and St James, Stratford
- St John with Christchurch, Stratford
- All Saints Church, West Ham
Transport
Since the 1980s, public transport in Newham has undergone many upgrades and improvements are still continuing to this day. The Jubilee Line Extension was completed in 1999, including new or improved stations at Canning Town, West Ham and Stratford. The Docklands Light Railway opened in 1987 and has undergone many extensions since, predominantly serving Newham and the neighbouring borough of Tower Hamlets. The DLR network compensates for Newham's lack of tube stations, of which there are only 6, in comparison with other London boroughs. It was extended to serve London City Airport, as well as Stratford International station in 2011 after its High Speed 1 link opened in late 2009. The Crossrail scheme will also improve rail connections to several stations as it heads through the borough on an east west axis. As a result of all the recent developments, the borough contains one of only two airports located within the Greater London boundary and currently the only railway station outside of central London that is served by high speed rail.
List of stations
- Abbey Road DLR station
- Beckton DLR station
- Beckton Park DLR station
- Cyprus DLR station
- Canning Town station – Jubilee line and DLR
- Custom House for ExCeL DLR station
- East Ham tube station – District and Hammersmith & City lines
- Forest Gate railway station – TfL Rail
- Gallions Reach DLR station
- King George V DLR station
- London City Airport DLR station
- Manor Park railway station – TfL Rail
- Maryland railway station – TfL Rail
- Plaistow tube station – District and Hammersmith & City lines
- Pontoon Dock DLR station
- Prince Regent DLR station
- Royal Albert DLR station
- Royal Victoria DLR station
- Star Lane DLR station
- Stratford station – Abellio Greater Anglia, TfL Rail, c2c, Jubilee and Central lines, London Overground and DLR
- Stratford High Street DLR station
- Stratford International station – Southeastern, DLR
- Pudding Mill Lane DLR station
- Upton Park tube station – District and Hammersmith & City lines
- Wanstead Park railway station – London Overground
- West Ham station – c2c, Jubilee, District and Hammersmith & City lines, and DLR
- West Silvertown DLR station
- Woodgrange Park railway station – London Overground
Travel to work
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were: underground, metro, light rail, tram, 23.0% of all residents aged 16–74; driving a car or van, 7.6%; bus, minibus or coach, 7.6%; train, 7.2%; on foot, 4.1%; work mainly at or from home, 1.4%; bicycle, 1.0%.[27]
River services
Cable car
International services
- Dutchflyer rail-sea service via Stratford station to the Netherlands
- London City Airport
- Stratford International station (No Eurostar trains stop)[28]
Bus routes
London Buses routes 5, 25, 58, 69, 86, 97, 101, 104, 108, 115, 147, 158, 173, 238, 241, 257, 262, 276, 300, 308, 309, 323, 325, 330, 339, 366, 376, 388, 425, 473, 474, 541, D8, W19, School buses routes 673, 678 and Night route N8, N15, N86, N205, N550 and N551.[29]
Freedom of the Borough
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the Borough of Newham.
Individuals
- Sir Jack Petchey CBE: 27 May 2010.[30]
- Mark Noble: 15 December 2016.[31]
Military Units
- G Company 7th Battalion The Rifles: 23 June 2012.[32]
See also
- List of districts in Newham
- List of schools in Newham
- Newham parks and open spaces
- Newham Sixth Form College
- Newham College of Further Education
- Stratford Circus
- Stratford, London
- Stratford City
- Thames Gateway
- Rising East
References and notes
- 2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in England and Wales, Office for National Statistics (2012). See Classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom for the full descriptions used in the 2011 Census.
- "The Civic Ambassador, The Coat of Arms". Archive.Newham.Gov.UK. Archived from the original on 2 June 2013. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- Mills, Anthony David (2001). Dictionary of London Place Names. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-280106-6
- Mills, A.D. (2001). Dictionary of London Place Names. Oxford.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 26 September 2006. Retrieved 13 December 2006.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Vote 2018: Newham mayoral election result". BBC News. 4 May 2018. Retrieved 14 May 2018.
- "London's Poverty Profile". Trust for London. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- Simpson's diversity indices by ward 1991 and 2001 – GLA Data Management and Analysis Group (page 11, Table 3)] Archived 29 May 2006 at the Wayback Machine Greater London Authority, January 2006), accessed 13 December 2006
- ":: Newham – Focus on Newham ::". 13 September 2007. Archived from the original on 13 September 2007.
- "Diabetes and heart disease in Bangladeshis and Pakistanis | East London Genes & Health". www.genesandhealth.org (in Bengali). Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- "London areas have higher TB than Iraq". 27 October 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- "Census 2001 tables". NOMIS. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- "Ethnic Group by measures". NOMIS. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- "Newham Info". www.newham.info. Archived from the original on 29 March 2018. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
- https://www.newham.info/population/. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Easton, Mark (20 February 2013). "Why have the white British left London?". BBC News. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- Archer, Graeme (22 February 2013). "Let's talk about the exodus of 600,000 whites from London". The Daily Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- "The Ethnic Cleansing of London (Part 2) – British Democrats | British Democrats". Britishdemocraticparty.org. 31 January 2013. Archived from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- "Revised document links | Centre on Dynamics of Ethnicity" (PDF). Ethnicity.ac.uk. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- "London's Poverty Profile". Trust for London. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
- Education and Learning London Borough of Newham, accessed 24 March 2008
- "2012 Partners – 2012 Office – UEL". 23 September 2010. Archived from the original on 23 September 2010.
- "Newham library services". Newham Council. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- "Decision – North Woolwich Old Station Museum Closure". Mgov.newham.gov.uk. 21 January 2009. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- "Green Street London E7 – Asian Shopping in London". Green-st.co.uk. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- Newham news, sport, leisure, property, jobs and motors Newham Recorder
- "2011 Census: QS701EW Method of travel to work, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 November 2013. Percentages are of all residents aged 16–74 including those not in employment. Respondents could only pick one mode, specified as the journey’s longest part by distance.
- "Eurostar 'will not stop' at Stratford International". BBC News. 25 May 2010.
- "Keeping London moving – Transport for London". Tfl.gov.uk. 9 November 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- https://www.newham.gov.uk/Documents/Misc/FreedomOfTheBorough.pdf
- London Borough of Newham, Newham Dockside. "Freedom of the borough for Mark Noble". www.newham.gov.uk.
- London Borough of Newham, Newham Dockside. "Freedom of the Borough awarded to G Company 7 RIFLES". www.newham.gov.uk.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to London Borough of Newham. |
- Newham London Borough Council
- Mayor of Newham
- NIMS – Statistics on Newham
- Newham Issues Forum – online local discussions
- Aston-Mansfield- charity started in 1884
- Community Links – innovative charity running community-based projects
- Newham Labour Party – website of the Labour Party in Newham
- Rising East: the journal of East London studies
- Newham Story – memories of Newham
- Local guide to Stratford, Newham
- Newham New Deal Partnership
- Newham Yaplondon Group- Local chat and discussions
- It's a Newham Thing – It's a Newham Thing