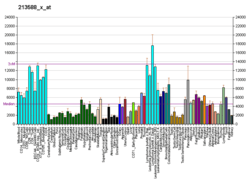
60S ribosomal protein L14
60S ribosomal protein L14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL14 gene.[5][6]
Function
Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a ribosomal protein that is a component of the 60S subunit. The protein belongs to the L14E family of ribosomal proteins. It contains a basic region-leucine zipper (bZIP)-like domain. The protein is located in the cytoplasm. This gene contains a trinucleotide (GCT) repeat tract whose length is highly polymorphic; these triplet repeats result in a stretch of alanine residues in the encoded protein. Transcript variants utilizing alternative polyA signals and alternative 5'-terminal exons exist but all encode the same protein. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes of this gene dispersed through the genome.[6]
Interactions
RPL14 has been shown to interact with PHLDA1.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000188846 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025794 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Tanaka M, Tanaka T, Harata M, Suzuki T, Mitsui Y (March 1998). "Triplet repeat-containing ribosomal protein L14 gene in immortalized human endothelial cell line (t-HUE4)". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 243 (2): 531–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.8125. PMID 9480843.
- "Entrez Gene: RPL14 ribosomal protein L14".
- Hinz T, Flindt S, Marx A, Janssen O, Kabelitz D (May 2001). "Inhibition of protein synthesis by the T cell receptor-inducible human TDAG51 gene product". Cell. Signal. 13 (5): 345–52. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00141-3. PMID 11369516.
External links
- Human RPL14 genome location and RPL14 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Wool IG, Chan YL, Glück A (1996). "Structure and evolution of mammalian ribosomal proteins". Biochem. Cell Biol. 73 (11–12): 933–47. doi:10.1139/o95-101. PMID 8722009.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Dave VP, Larché M, Rencher SD, Koop BF, Hurwitz JL (1994). "Restricted usage of T-cell receptor V alpha sequence and variable-joining pairs after normal T-cell development and bone marrow transplantation". Hum. Immunol. 37 (3): 178–84. doi:10.1016/0198-8859(93)90183-2. PMID 8244780.
- Li SH, McInnis MG, Margolis RL, Antonarakis SE, Ross CA (1993). "Novel triplet repeat containing genes in human brain: cloning, expression, and length polymorphisms". Genomics. 16 (3): 572–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1232. PMID 8325628.
- Aoki M, Koranyi L, Riggs AC, Wasson J, Chiu KC, Vaxillaire M, Froguel P, Gough S, Liu L, Donis-Keller H (1996). "Identification of trinucleotide repeat-containing genes in human pancreatic islets". Diabetes. 45 (2): 157–64. doi:10.2337/diabetes.45.2.157. PMID 8549859.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Reddy PH, Stockburger E, Gillevet P, Tagle DA (1998). "Mapping and characterization of novel (CAG)n repeat cDNAs from adult human brain derived by the oligo capture method". Genomics. 46 (2): 174–82. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.5044. PMID 9417904.
- Hinz T, Flindt S, Marx A, Janssen O, Kabelitz D (2001). "Inhibition of protein synthesis by the T cell receptor-inducible human TDAG51 gene product". Cell. Signal. 13 (5): 345–52. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00141-3. PMID 11369516.
- Uechi T, Tanaka T, Kenmochi N (2001). "A complete map of the human ribosomal protein genes: assignment of 80 genes to the cytogenetic map and implications for human disorders". Genomics. 72 (3): 223–30. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6470. PMID 11401437.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H, Mann M, Lamond AI (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Yoshihama M, Uechi T, Asakawa S, Kawasaki K, Kato S, Higa S, Maeda N, Minoshima S, Tanaka T, Shimizu N, Kenmochi N (2002). "The human ribosomal protein genes: sequencing and comparative analysis of 73 genes". Genome Res. 12 (3): 379–90. doi:10.1101/gr.214202. PMC 155282. PMID 11875025.
- Odintsova TI, Müller EC, Ivanov AV, Egorov TA, Bienert R, Vladimirov SN, Kostka S, Otto A, Wittmann-Liebold B, Karpova GG (2004). "Characterization and analysis of posttranslational modifications of the human large cytoplasmic ribosomal subunit proteins by mass spectrometry and Edman sequencing". J. Protein Chem. 22 (3): 249–58. doi:10.1023/A:1025068419698. PMID 12962325.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, Ong SE, Lyon CE, Lamond AI, Mann M (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.