Prisoner of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a non-combatant—whether a military member, an irregular military fighter, or a civilian—who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.[lower-alpha 1]

Belligerents hold prisoners of war in custody for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons, such as isolating them from enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishing them, prosecuting them for war crimes, exploiting them for their labour, recruiting or even conscripting them as their own combatants, collecting military and political intelligence from them, or indoctrinating them in new political or religious beliefs.[1]
Ancient times

For most of human history, depending on the culture of the victors, enemy combatants on the losing side in a battle who had surrendered and been taken as prisoners of war could expect to be either slaughtered or enslaved.[2] Early Roman gladiators could be prisoners of war, categorised according to their ethnic roots as Samnites, Thracians, and Gauls (Galli).[3] Homer's Iliad describes Greek and Trojan soldiers offering rewards of wealth to opposing forces who have defeated them on the battlefield in exchange for mercy, but their offers are not always accepted; see Lycaon for example.
Typically, victors made little distinction between enemy combatants and enemy civilians, although they were more likely to spare women and children. Sometimes the purpose of a battle, if not of a war, was to capture women, a practice known as raptio; the Rape of the Sabines involved, according to tradition, a large mass-abduction by the founders of Rome. Typically women had no rights, and were held legally as chattels.[4]
In the fourth century AD, Bishop Acacius of Amida, touched by the plight of Persian prisoners captured in a recent war with the Roman Empire, who were held in his town under appalling conditions and destined for a life of slavery, took the initiative in ransoming them by selling his church's precious gold and silver vessels and letting them return to their country. For this he was eventually canonized.[5]
Middle Ages and Renaissance

During Childeric's siege and blockade of Paris in 464, the nun Geneviève (later canonised as the city's patron saint) pleaded with the Frankish king for the welfare of prisoners of war and met with a favourable response. Later, Clovis I liberated captives after Genevieve urged him to do so.[6]
Many French prisoners of war were killed during the Battle of Agincourt in 1415.[7] This was done in retaliation for the French killing of the boys and other non-combatants handling the baggage and equipment of the army, and because the French were attacking again and Henry was afraid that they would break through and free the prisoners to fight again.
In the later Middle Ages, a number of religious wars aimed to not only defeat but eliminate their enemies. In Christian Europe, the extermination of heretics was considered desirable. Examples include the 13th century Albigensian Crusade and the Northern Crusades.[8] When asked by a Crusader how to distinguish between the Catholics and Cathars once they'd taken the city of Béziers, the Papal Legate Arnaud Amalric famously replied, "Kill them all, God will know His own".[lower-alpha 2]
Likewise, the inhabitants of conquered cities were frequently massacred during the Crusades against the Muslims in the 11th and 12th centuries. Noblemen could hope to be ransomed; their families would have to send to their captors large sums of wealth commensurate with the social status of the captive.
In feudal Japan, there was no custom of ransoming prisoners of war, who were for the most part summarily executed.[9]
.jpg)
The expanding Mongol Empire was famous for distinguishing between cities or towns that surrendered, where the population were spared but required to support the conquering Mongol army, and those that resisted, where their city was ransacked and destroyed, and all the population killed. In Termez, on the Oxus: "all the people, both men and women, were driven out onto the plain, and divided in accordance with their usual custom, then they were all slain".[10]
The Aztecs were constantly at war with neighbouring tribes and groups, with the goal of this constant warfare being to collect live prisoners for sacrifice.[11] For the re-consecration of Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan in 1487, "between 10,000 and 80,400 persons" were sacrificed.[12][13]
During the early Muslim conquests, Muslims routinely captured large number of prisoners. Aside from those who converted, most were ransomed or enslaved.[14][15] Christians who were captured during the Crusades were usually either killed or sold into slavery if they could not pay a ransom.[16] During his lifetime, Muhammad made it the responsibility of the Islamic government to provide food and clothing, on a reasonable basis, to captives, regardless of their religion; however if the prisoners were in the custody of a person, then the responsibility was on the individual.[17] The freeing of prisoners was highly recommended as a charitable act. On certain occasions where Muhammad felt the enemy had broken a treaty with the Muslims, he ordered the mass execution of male prisoners, such as the Banu Qurayza. Females and children of this tribe were divided up as ghanima (spoils of war) by Muhammad.[18]
Modern times

The 1648 Peace of Westphalia, which ended the Thirty Years' War, established the rule that prisoners of war should be released without ransom at the end of hostilities and that they should be allowed to return to their homelands.[19]
There also evolved the right of parole, French for "discourse", in which a captured officer surrendered his sword and gave his word as a gentleman in exchange for privileges. If he swore not to escape, he could gain better accommodations and the freedom of the prison. If he swore to cease hostilities against the nation who held him captive, he could be repatriated or exchanged but could not serve against his former captors in a military capacity.
European settlers captured in North America
Early historical narratives of captured colonial Europeans, including perspectives of literate women captured by the indigenous peoples of North America, exist in some number. The writings of Mary Rowlandson, captured in the brutal fighting of King Philip's War, are an example. Such narratives enjoyed some popularity, spawning a genre of the captivity narrative, and had lasting influence on the body of early American literature, most notably through the legacy of James Fenimore Cooper's The Last of the Mohicans. Some Native Americans continued to capture Europeans and use them both as labourers and bargaining chips into the 19th century; see for example John R. Jewitt, an Englishman who wrote a memoir about his years as a captive of the Nootka people on the Pacific Northwest coast from 1802 to 1805.
French Revolutionary wars and Napoleonic wars
The earliest known purposely built prisoner-of-war camp was established at Norman Cross, England in 1797 to house the increasing number of prisoners from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. The average prison population was about 5,500 men. The lowest number recorded was 3,300 in October 1804 and 6,272 on 10 April 1810 was the highest number of prisoners recorded in any official document. Norman Cross was intended to be a model depot providing the most humane treatment of prisoners of war. The British government went to great lengths to provide food of a quality at least equal to that available to locals. The senior officer from each quadrangle was permitted to inspect the food as it was delivered to the prison to ensure it was of sufficient quality. Despite the generous supply and quality of food, some prisoners died of starvation after gambling away their rations. Most of the men held in the prison were low-ranking soldiers and sailors, including midshipmen and junior officers, with a small number of privateers. About 100 senior officers and some civilians "of good social standing", mainly passengers on captured ships and the wives of some officers, were given parole d'honneur outside the prison, mainly in Peterborough although some further afield in Northampton, Plymouth, Melrose and Abergavenny. They were afforded the courtesy of their rank within English society. During the Battle of Leipzig both sides used the city's cemetery as lazaret and prisoner camp for around 6000 POWs who lived in the vaults and used the coffins for firewood. Food was scarce and prisoners resorted to eating horses, cats, dogs or even human flesh. The bad conditions inside the graveyard contributed to a city-wide epidemic after the battle.[20][21]
Prisoner exchanges
The extensive period of conflict during the American Revolutionary War and Napoleonic Wars (1793–1815), followed by the Anglo-American War of 1812, led to the emergence of a cartel system for the exchange of prisoners, even while the belligerents were at war. A cartel was usually arranged by the respective armed service for the exchange of like-ranked personnel. The aim was to achieve a reduction in the number of prisoners held, while at the same time alleviating shortages of skilled personnel in the home country.
American Civil War
At the start of the civil war a system of paroles operated. Captives agreed not to fight until they were officially exchanged. Meanwhile, they were held in camps run by their own army where they were paid but not allowed to perform any military duties.[22] The system of exchanges collapsed in 1863 when the Confederacy refused to exchange black prisoners. In the late summer of 1864, a year after the Dix–Hill Cartel was suspended; Confederate officials approached Union General Benjamin Butler, Union Commissioner of Exchange, about resuming the cartel and including the black prisoners. Butler contacted Grant for guidance on the issue, and Grant responded to Butler on 18 August 1864 with his now famous statement. He rejected the offer, stating in essence, that the Union could afford to leave their men in captivity, the Confederacy could not.[23] After that about 56,000 of the 409,000 POWs died in prisons during the American Civil War, accounting for nearly 10% of the conflict's fatalities.[24] Of the 45,000 Union prisoners of war confined in Camp Sumter, located near Andersonville, Georgia, 13,000 (28%) died.[25] At Camp Douglas in Chicago, Illinois, 10% of its Confederate prisoners died during one cold winter month; and Elmira Prison in New York state, with a death rate of 25% (2,963), nearly equalled that of Andersonville.[26]
Amelioration
During the 19th century, there were increased efforts to improve the treatment and processing of prisoners. As a result of these emerging conventions, a number of international conferences were held, starting with the Brussels Conference of 1874, with nations agreeing that it was necessary to prevent inhumane treatment of prisoners and the use of weapons causing unnecessary harm. Although no agreements were immediately ratified by the participating nations, work was continued that resulted in new conventions being adopted and becoming recognized as international law that specified that prisoners of war be treated humanely and diplomatically.
Hague and Geneva Conventions
Chapter II of the Annex to the 1907 Hague Convention IV – The Laws and Customs of War on Land covered the treatment of prisoners of war in detail. These provisions were further expanded in the 1929 Geneva Convention on the Prisoners of War and were largely revised in the Third Geneva Convention in 1949.
Article 4 of the Third Geneva Convention protects captured military personnel, some guerrilla fighters, and certain civilians. It applies from the moment a prisoner is captured until he or she is released or repatriated. One of the main provisions of the convention makes it illegal to torture prisoners and states that a prisoner can only be required to give their name, date of birth, rank and service number (if applicable).
The ICRC has a special role to play, with regards to international humanitarian law, in restoring and maintaining family contact in times of war, in particular concerning the right of prisoners of war and internees to send and receive letters and cards (Geneva Convention (GC) III, art.71 and GC IV, art.107).
However, nations vary in their dedication to following these laws, and historically the treatment of POWs has varied greatly. During World War II, Imperial Japan and Nazi Germany (towards Soviet POWs and Western Allied commandos) were notorious for atrocities against prisoners of war. The German military used the Soviet Union's refusal to sign the Geneva Convention as a reason for not providing the necessities of life to Soviet POWs; and the Soviets similarly killed Axis prisoners or used them as slave labour. The Germans also routinely executed Western Allied commandos captured behind German lines per the Commando Order. North Korean and North and South Vietnamese forces[27] routinely killed or mistreated prisoners taken during those conflicts.
Qualifications

To be entitled to prisoner-of-war status, captured persons must be lawful combatants entitled to combatant's privilege—which gives them immunity from punishment for crimes constituting lawful acts of war such as killing enemy combatants. To qualify under the Third Geneva Convention, a combatant must be part of a chain of command, wear a "fixed distinctive marking, visible from a distance", bear arms openly, and have conducted military operations according to the laws and customs of war. (The Convention recognizes a few other groups as well, such as "[i]nhabitants of a non-occupied territory, who on the approach of the enemy spontaneously take up arms to resist the invading forces, without having had time to form themselves into regular armed units".)
Thus, uniforms and badges are important in determining prisoner-of-war status under the Third Geneva Convention. Under Additional Protocol I, the requirement of a distinctive marking is no longer included. francs-tireurs, militias, insurgents, terrorists, saboteurs, mercenaries, and spies generally do not qualify because they do not fulfill the criteria of Additional Protocol 1. Therefore, they fall under the category of unlawful combatants, or more properly they are not combatants. Captured soldiers who do not get prisoner of war status are still protected like civilians under the Fourth Geneva Convention.
The criteria are applied primarily to international armed conflicts. The application of prisoner of war status in non-international armed conflicts like civil wars is guided by Additional Protocol II, but insurgents are often treated as traitors, terrorists or criminals by government forces and are sometimes executed on spot or tortured. However, in the American Civil War, both sides treated captured troops as POWs presumably out of reciprocity, although the Union regarded Confederate personnel as separatist rebels. However, guerrillas and other irregular combatants generally cannot expect to receive benefits from both civilian and military status simultaneously.
Rights
Under the Third Geneva Convention, prisoners of war (POW) must be:
- Treated humanely with respect for their persons and their honor
- Able to inform their next of kin and the International Committee of the Red Cross of their capture
- Allowed to communicate regularly with relatives and receive packages
- Given adequate food, clothing, housing, and medical attention
- Paid for work done and not forced to do work that is dangerous, unhealthy, or degrading
- Released quickly after conflicts end
- Not compelled to give any information except for name, age, rank, and service number[28]
In addition, if wounded or sick on the battlefield, the prisoner will receive help from the International Committee of the Red Cross.[29]
When a country is responsible for breaches of prisoner of war rights, those accountable will be punished accordingly. An example of this is the Nuremberg and Tokyo Trials. German and Japanese military commanders were prosecuted for preparing and initiating a war of aggression, murder, ill treatment, and deportation of individuals, and genocide during World War II.[30] Most were executed or sentenced to life in prison for their crimes.
U.S. Code of Conduct and terminology
The United States Military Code of Conduct was promulgated in 1955 via Executive Order 10631 under President Dwight D. Eisenhower to serve as a moral code for United States service members who have been taken prisoner. It was created primarily in response to the breakdown of leadership and organization, specifically when U.S. forces were POWs during the Korean War.
When a military member is taken prisoner, the Code of Conduct reminds them that the chain of command is still in effect (the highest ranking service member eligible for command, regardless of service branch, is in command), and requires them to support their leadership. The Code of Conduct also requires service members to resist giving information to the enemy (beyond identifying themselves, that is, "name, rank, serial number"), receiving special favors or parole, or otherwise providing their enemy captors aid and comfort.
Since the Vietnam War, the official U.S. military term for enemy POWs is EPW (Enemy Prisoner of War). This name change was introduced in order to distinguish between enemy and U.S. captives.[31][32]
In 2000, the U.S. military replaced the designation "Prisoner of War" for captured American personnel with "Missing-Captured". A January 2008 directive states that the reasoning behind this is since "Prisoner of War" is the international legal recognized status for such people there is no need for any individual country to follow suit. This change remains relatively unknown even among experts in the field and "Prisoner of War" remains widely used in the Pentagon which has a "POW/Missing Personnel Office" and awards the Prisoner of War Medal.[33][34]
World War I


.jpg)
During World War I, about eight million men surrendered and were held in POW camps until the war ended. All nations pledged to follow the Hague rules on fair treatment of prisoners of war, and in general the POWs had a much higher survival rate than their peers who were not captured.[35] Individual surrenders were uncommon; usually a large unit surrendered all its men. At Tannenberg 92,000 Russians surrendered during the battle. When the besieged garrison of Kaunas surrendered in 1915, 20,000 Russians became prisoners. Over half the Russian losses were prisoners as a proportion of those captured, wounded or killed. About 3.3 million men became prisoners.[36]
The German Empire held 2.5 million prisoners; Russia held 2.9 million, and Britain and France held about 720,000, mostly gained in the period just before the Armistice in 1918. The US held 48,000. The most dangerous moment for POWs was the act of surrender, when helpless soldiers were sometimes mistakenly shot down. Once prisoners reached a POW camp conditions were better (and often much better than in World War II), thanks in part to the efforts of the International Red Cross and inspections by neutral nations.
There was however much harsh treatment of POWs in Germany, as recorded by the American ambassador to Germany (prior to America's entry into the war), James W. Gerard, who published his findings in "My Four Years in Germany". Even worse conditions are reported in the book "Escape of a Princess Pat" by the Canadian George Pearson. It was particularly bad in Russia, where starvation was common for prisoners and civilians alike; a quarter of the over 2 million POWs held there died.[37] Nearly 375,000 of the 500,000 Austro-Hungarian prisoners of war taken by Russians perished in Siberia from smallpox and typhus.[38] In Germany, food was short, but only 5% died.[39]
The Ottoman Empire often treated prisoners of war poorly. Some 11,800 British soldiers, most of them Indians, became prisoners after the five-month Siege of Kut, in Mesopotamia, in April 1916. Many were weak and starved when they surrendered and 4,250 died in captivity.[40]
During the Sinai and Palestine campaign 217 Australian and unknown numbers of British, New Zealand and Indian soldiers were captured by Ottoman Empire forces. About 50% of the Australian prisoners were light horsemen including 48 missing believed captured on 1 May 1918 in the Jordan Valley. Australian Flying Corps pilots and observers were captured in the Sinai Peninsula, Palestine and the Levant. One third of all Australian prisoners were captured on Gallipoli including the crew of the submarine AE2 which made a passage through the Dardanelles in 1915. Forced marches and crowded railway journeys preceded years in camps where disease, poor diet and inadequate medical facilities prevailed. About 25% of other ranks died, many from malnutrition, while only one officer died.[41][42]
The most curious case came in Russia where the Czechoslovak Legion of Czechoslovak prisoners (from the Austro-Hungarian army): they were released in 1917, armed themselves, briefly culminating into a military and diplomatic force during the Russian Civil War.
Release of prisoners

At the end of the war in 1918 there were believed to be 140,000 British prisoners of war in Germany, including thousands of internees held in neutral Switzerland.[43] The first British prisoners were released and reached Calais on 15 November. Plans were made for them to be sent via Dunkirk to Dover and a large reception camp was established at Dover capable of housing 40,000 men, which could later be used for demobilisation.
On 13 December 1918, the armistice was extended and the Allies reported that by 9 December 264,000 prisoners had been repatriated. A very large number of these had been released en masse and sent across Allied lines without any food or shelter. This created difficulties for the receiving Allies and many released prisoners died from exhaustion. The released POWs were met by cavalry troops and sent back through the lines in lorries to reception centres where they were refitted with boots and clothing and dispatched to the ports in trains.
Upon arrival at the receiving camp the POWs were registered and "boarded" before being dispatched to their own homes. All commissioned officers had to write a report on the circumstances of their capture and to ensure that they had done all they could to avoid capture. Each returning officer and man was given a message from King George V, written in his own hand and reproduced on a lithograph. It read as follows:[44]
The Queen joins me in welcoming you on your release from the miseries & hardships, which you have endured with so much patience and courage.
During these many months of trial, the early rescue of our gallant Officers & Men from the cruelties of their captivity has been uppermost in our thoughts.
We are thankful that this longed for day has arrived, & that back in the old Country you will be able once more to enjoy the happiness of a home & to see good days among those who anxiously look for your return.
George R.I.
While the Allied prisoners were sent home at the end of the war, the same treatment was not granted to Central Powers prisoners of the Allies and Russia, many of whom had to serve as forced labour, e.g. in France, until 1920. They were released after many approaches by the ICRC to the Allied Supreme Council.[45]
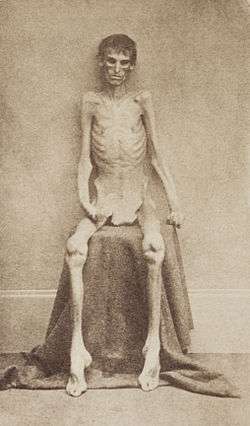
World War II
.jpg)
Historian Niall Ferguson, in addition to figures from Keith Lowe, tabulated the total death rate for POWs in World War II as follows:[46][47]
Percentage of
POWs that DiedSoviet POWs held by Germans 57.5% German POWs held by Yugoslavs 41.2% German POWs held by Soviets 35.8% American POWs held by Japanese 33.0% American POWs held by Germans 1.19% German POWs held by Eastern Europeans 32.9% British POWs held by Japanese 24.8% German POWs held by Czechoslovaks 5.0% British POWs held by Germans 3.5% German POWs held by French 2.58% German POWs held by Americans 0.15% German POWs held by British 0.03%
Treatment of POWs by the Axis
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, which had signed but never ratified the 1929 Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War,[48] did not treat prisoners of war in accordance with international agreements, including provisions of the Hague Conventions, either during the Second Sino-Japanese War or during the Pacific War, because the Japanese viewed surrender as dishonorable. Moreover, according to a directive ratified on 5 August 1937 by Hirohito, the constraints of the Hague Conventions were explicitly removed on Chinese prisoners.[49]
Prisoners of war from China, the United States, Australia, Britain, Canada, India, the Netherlands, New Zealand, and the Philippines held by Japanese imperial armed forces were subject to murder, beatings, summary punishment, brutal treatment, forced labour, medical experimentation, starvation rations, poor medical treatment and cannibalism.[50] The most notorious use of forced labour was in the construction of the Burma–Thailand Death Railway. After 20 March 1943, the Imperial Navy was under orders to execute all prisoners taken at sea.
After the Armistice of Cassibile, Italian soldiers and civilians in East Asia were taken as prisoners by the Japanese armed forces and subject to the same conditions as other POWs.[51]
According to the findings of the Tokyo Tribunal, the death rate of Western prisoners was 27.1%, seven times that of POWs under the Germans and Italians.[52] The death rate of Chinese was much higher. Thus, while 37,583 prisoners from the United Kingdom, Commonwealth, and Dominions, 28,500 from the Netherlands, and 14,473 from the United States were released after the surrender of Japan, the number for the Chinese was only 56.[53] The 27,465 United States Army and United States Army Air Forces POWs in the Pacific Theater had a 40.4% death rate.[54] The War Ministry in Tokyo issued an order at the end of the war to kill all surviving POWs.[55]
No direct access to the POWs was provided to the International Red Cross. Escapes among Caucasian prisoners were almost impossible because of the difficulty of men of Caucasian descent hiding in Asiatic societies.[56]
Allied POW camps and ship-transports were sometimes accidental targets of Allied attacks. The number of deaths which occurred when Japanese "hell ships"—unmarked transport ships in which POWs were transported in harsh conditions—were attacked by US Navy submarines was particularly high. Gavan Daws has calculated that "of all POWs who died in the Pacific War, one in three was killed on the water by friendly fire".[57] Daves states that 10,800 of the 50,000 POWs shipped by the Japanese were killed at sea[58] while Donald L. Miller states that "approximately 21,000 Allied POWs died at sea, about 19,000 of them killed by friendly fire."[59]
Life in the POW camps was recorded at great risk to themselves by artists such as Jack Bridger Chalker, Philip Meninsky, Ashley George Old, and Ronald Searle. Human hair was often used for brushes, plant juices and blood for paint, and toilet paper as the "canvas". Some of their works were used as evidence in the trials of Japanese war criminals.
Female prisoners (detainees) at Changi prisoner of war camp in Singapore, bravely recorded their defiance in seemingly harmless prison quilt embroidery.[60]
Research into the conditions of the camps has been conducted by The Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine.[61]
 Troops of the Suffolk Regiment surrendering to the Japanese, 1942
Troops of the Suffolk Regiment surrendering to the Japanese, 1942 Many US and Filipino POWs died as a result of the Bataan Death March, in May 1942
Many US and Filipino POWs died as a result of the Bataan Death March, in May 1942 Water colour sketch of "Dusty" Rhodes by Ashley George Old
Water colour sketch of "Dusty" Rhodes by Ashley George Old Australian and Dutch POWs at Tarsau, Thailand in 1943
Australian and Dutch POWs at Tarsau, Thailand in 1943
 U.S. Navy nurses rescued from Los Baños Internment Camp, March 1945
U.S. Navy nurses rescued from Los Baños Internment Camp, March 1945 Allied prisoners of war at Aomori camp near Yokohama, Japan waving flags of the United States, Great Britain, and the Netherlands in August 1945.
Allied prisoners of war at Aomori camp near Yokohama, Japan waving flags of the United States, Great Britain, and the Netherlands in August 1945. Canadian POWs at the Liberation of Hong Kong
Canadian POWs at the Liberation of Hong Kong Malnourished Australian POWs forced to work at the Aso mining company, August 1945.
Malnourished Australian POWs forced to work at the Aso mining company, August 1945. POW art depicting Cabanatuan prison camp, produced in 1946
POW art depicting Cabanatuan prison camp, produced in 1946 Australian POW Leonard Siffleet captured at New Guinea moments before his execution with a Japanese shin gunto sword in 1943.
Australian POW Leonard Siffleet captured at New Guinea moments before his execution with a Japanese shin gunto sword in 1943. Captured soldiers of the British Indian Army executed by the Japanese.
Captured soldiers of the British Indian Army executed by the Japanese.
Germany
French soldiers
After the French armies surrendered in summer 1940, Germany seized two million French prisoners of war and sent them to camps in Germany. About one third were released on various terms. Of the remainder, the officers and non-commissioned officers were kept in camps and did not work. The privates were sent out to work. About half of them worked for German agriculture, where food supplies were adequate and controls were lenient. The others worked in factories or mines, where conditions were much harsher.[62]
Western Allies' POWs
Germany and Italy generally treated prisoners from the British Commonwealth, France, the US, and other western Allies in accordance with the Geneva Convention, which had been signed by these countries.[63] Consequently, western Allied officers were not usually made to work and some personnel of lower rank were usually compensated, or not required to work either. The main complaints of western Allied prisoners of war in German POW camps—especially during the last two years of the war—concerned shortages of food.

Only a small proportion of western Allied POWs who were Jews—or whom the Nazis believed to be Jewish—were killed as part of the Holocaust or were subjected to other antisemitic policies. For example, Major Yitzhak Ben-Aharon, a Palestinian Jew who had enlisted in the British Army, and who was captured by the Germans in Greece in 1941, experienced four years of captivity under entirely normal conditions for POWs.[64]

However, a small number of Allied personnel were sent to concentration camps, for a variety of reasons including being Jewish.[65] As the US historian Joseph Robert White put it: "An important exception ... is the sub-camp for U.S. POWs at Berga an der Elster, officially called Arbeitskommando 625 [also known as Stalag IX-B]. Berga was the deadliest work detachment for American captives in Germany. 73 men who participated, or 21 percent of the detachment, perished in two months. 80 of the 350 POWs were Jews." Another well-known example was a group of 168 Australian, British, Canadian, New Zealand and US aviators who were held for two months at Buchenwald concentration camp;[66] two of the POWs died at Buchenwald. Two possible reasons have been suggested for this incident: German authorities wanted to make an example of Terrorflieger ("terrorist aviators") or these aircrews were classified as spies, because they had been disguised as civilians or enemy soldiers when they were apprehended.
Information on conditions in the stalags is contradictory depending on the source. Some American POWs claimed the Germans were victims of circumstance and did the best they could, while others accused their captors of brutalities and forced labour. In any case, the prison camps were miserable places where food rations were meager and conditions squalid. One American admitted "The only difference between the stalags and concentration camps was that we weren't gassed or shot in the former. I do not recall a single act of compassion or mercy on the part of the Germans." Typical meals consisted of a bread slice and watery potato soup which, however, was still more substantial than what Soviet POWs or concentration camp inmates received. Another prisoner stated that "The German plan was to keep us alive, yet weakened enough that we wouldn't attempt escape."[67]
As Soviet ground forces approached some POW camps in early 1945, German guards forced western Allied POWs to walk long distances towards central Germany, often in extreme winter weather conditions.[68] It is estimated that, out of 257,000 POWs, about 80,000 were subject to such marches and up to 3,500 of them died as a result.
Italian POWs
In September 1943 after the Armistice, Italian officers and soldiers that in many places waited for clear superior orders, were arrested by Germans and Italian fascists and taken to German internment camps in Germany or Eastern Europe, where they were held for the duration of World War II. The International Red Cross could do nothing for them, as they were not regarded as POWs, but the prisoners held the status of "military internees". Treatment of the prisoners was generally poor. The author Giovannino Guareschi was among those interned and wrote about this time in his life. The book was translated and published as "My Secret Diary". He wrote about the hungers of semi-starvation, the casual murder of individual prisoners by guards and how, when they were released (now from a German camp), they found a deserted German town filled with foodstuffs that they (with other released prisoners) ate.. It is estimated that of the 700,000 Italians taken prisoner by the Germans, around 40,000 died in detention and more than 13,000 lost their lives during the transportation from the Greek islands to the mainland.[69]
Eastern European POWs
Germany did not apply the same standard of treatment to non-western prisoners, especially many Polish and Soviet POWs who suffered harsh conditions and died in large numbers while in captivity.
Between 1941 and 1945 the Axis powers took about 5.7 million Soviet prisoners. About one million of them were released during the war, in that their status changed but they remained under German authority. A little over 500,000 either escaped or were liberated by the Red Army. Some 930,000 more were found alive in camps after the war. The remaining 3.3 million prisoners (57.5% of the total captured) died during their captivity.[71] Between the launching of Operation Barbarossa in the summer of 1941 and the following spring, 2.8 million of the 3.2 million Soviet prisoners taken died while in German hands.[72] According to Russian military historian General Grigoriy Krivosheyev, the Axis powers took 4.6 million Soviet prisoners, of whom 1.8 million were found alive in camps after the war and 318,770 were released by the Axis during the war and were then drafted into the Soviet armed forces again.[73] By comparison, 8,348 Western Allied prisoners died in German camps during 1939–45 (3.5% of the 232,000 total).[74]

The Germans officially justified their policy on the grounds that the Soviet Union had not signed the Geneva Convention. Legally, however, under article 82 of the Geneva Convention, signatory countries had to give POWs of all signatory and non-signatory countries the rights assigned by the convention.[75] Shortly after the German invasion in 1941, the USSR made Berlin an offer of a reciprocal adherence to the Hague Conventions. Third Reich officials left the Soviet "note" unanswered.[76][77] In contrast, Nikolai Tolstoy recounts that the German Government – as well as the International Red Cross – made several efforts to regulate reciprocal treatment of prisoners until early 1942, but received no answers from the Soviet side.[78] Further, the Soviets took a harsh position towards captured Soviet soldiers, as they expected each soldier to fight to the death, and automatically excluded any prisoner from the "Russian community".[79]
Some Soviet POWs and forced labourers whom the Germans had transported to Nazi Germany were, on their return to the USSR, treated as traitors and sent to gulag prison-camps.
Treatment of POWs by the Soviet Union
Germans, Romanians, Italians, Hungarians, Finns


According to some sources, the Soviets captured 3.5 million Axis servicemen (excluding Japanese) of which more than a million died.[80] One specific example is that of the German POWs after the Battle of Stalingrad, where the Soviets captured 91,000 German troops in total (completely exhausted, starving and sick) of whom only 5,000 survived the captivity.
German soldiers were kept as forced labour for many years after the war. The last German POWs like Erich Hartmann, the highest-scoring fighter ace in the history of aerial warfare, who had been declared guilty of war crimes but without due process, were not released by the Soviets until 1955, two years after Stalin died.[81]
Polish

As a result of the Soviet invasion of Poland in 1939, hundreds of thousands of Polish soldiers became prisoners of war in the Soviet Union. Thousands of them were executed; over 20,000 Polish military personnel and civilians perished in the Katyn massacre.[82] Out of Anders' 80,000 evacuees from Soviet Union gathered in the United Kingdom only 310 volunteered to return to Poland in 1947.[83]
Out of the 230,000 Polish prisoners of war taken by the Soviet army, only 82,000 survived.[84]
Japanese
After the Soviet–Japanese War, 560,000 to 760,000 Japanese prisoners of war were captured by the Soviet Union. They were captured in Manchuria, Korea, South Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands, then sent to work as forced labor in the Soviet Union and Mongolia.[85] Of them, it is estimated that between 60,000 and 347,000 died in captivity.[86][87][88][89]
Americans
There were stories during the Cold War to the effect that 23,000 Americans who had been held in German POW camps were seized by the Soviets and never repatriated. This myth had been perpetuated after the release of people like John H. Noble. Careful scholarly studies have demonstrated this is a myth based on a misinterpretation of a telegram that was talking about Soviet prisoners held in Italy.[90]
Treatment of POWs by the Western Allies
Germans




of a German General
(Front- and Backside)
During the war, the armies of Western Allied nations such as Australia, Canada, the UK and the US[91] were ordered to treat Axis prisoners strictly in accordance with the Geneva Convention.[92] Some breaches of the Convention took place, however. According to Stephen E. Ambrose, of the roughly 1,000 US combat veterans that he had interviewed, only one admitted to shooting a prisoner, saying that he "felt remorse, but would do it again". However, one-third told him they had seen US troops kill German prisoners.[93]
In Britain, German prisoners, particularly higher-ranked officers, were kept in buildings where listening devices were installed. A considerable amount of military intelligence was gained from overhearing what they thought were private casual conversations. Much of the listening was done by German refugees, in many cases Jews. Knowledge of the program was not released by the British government for half a century.[94]
Towards the end of the war in Europe, as large numbers of Axis soldiers surrendered, the US created the designation of Disarmed Enemy Forces (DEF) so as not to treat prisoners as POWs. A lot of these soldiers were kept in open fields in makeshift camps in the Rhine valley (Rheinwiesenlager). Controversy has arisen about how Eisenhower managed these prisoners[95] (see Other Losses).
After the surrender of Germany in May 1945, the POW status of the German prisoners was in many cases maintained, and they were for several years used as forced labour in countries such as the UK and France. Many died when forced to clear minefields in Norway, France etc.; "by September 1945 it was estimated by the French authorities that two thousand prisoners were being maimed and killed each month in accidents".[96][97]
In 1946, the UK had more than 400,000 German prisoners, many had been transferred from POW camps in the US and Canada. Many of these were for over three years after the German surrender used as forced labour, as a form of "reparations".[98][99] A public debate ensued in the UK, where words such as "forced labour", "slaves", "slave labour" were increasingly used in the media and in the House of Commons.[100] In 1947 the Ministry of Agriculture argued against repatriation of working German prisoners, since by then they made up 25 percent of the land workforce, and they wanted to use them also in 1948.[100]
The "London Cage", an MI19 prisoner of war facility in the UK used for interrogating prisoners before they were sent to prison camps during and immediately after World War II, was subject to allegations of torture.[101]
After the German surrender, the International Red Cross was prohibited from providing aid such as food or visiting prisoner camps in Germany. However, after making approaches to the Allies in the autumn of 1945 it was allowed to investigate the camps in the British and French occupation zones of Germany, as well as to provide relief to the prisoners held there.[102] On 4 February 1946, the Red Cross was permitted to visit and assist prisoners also in the US occupation zone of Germany, although only with very small quantities of food. "During their visits, the delegates observed that German prisoners of war were often detained in appalling conditions. They drew the attention of the authorities to this fact, and gradually succeeded in getting some improvements made".[102]
The Allies also shipped POWs between them, with for example 6,000 German officers transferred from Western Allied camps to the Sachsenhausen concentration camp that now was under Soviet Union administration.[103] The US also shipped 740,000 German POWs as forced labourers to France from where newspaper reports told of very bad treatment. Judge Robert H. Jackson, Chief US prosecutor in the Nuremberg trials, in October 1945 told US President Harry S Truman that the Allies themselves:
have done or are doing some of the very things we are prosecuting the Germans for. The French are so violating the Geneva Convention in the treatment of prisoners of war that our command is taking back prisoners sent to them. We are prosecuting plunder and our Allies are practicing it.[104][105]
Hungarians
Hungarians became POWs of the Western Allies. Some of these were, like Germans, used as forced labour in France after the cessation of hostilities.[106] After the war the POWs were handed over to the Soviets, and after the POWs were transported to the USSR for forced labour. It is called even today in Hungary malenkij robot—little work. András Toma, a Hungarian soldier taken prisoner by the Red Army in 1944, was discovered in a Russian psychiatric hospital in 2000. He was probably the last prisoner of war from World War II to be repatriated.[107]
Japanese

Although thousands of Japanese were taken prisoner, most fought until they were killed or committed suicide. Of the 22,000 Japanese soldiers present at the beginning of the Battle of Iwo Jima, over 20,000 were killed and only 216 were taken prisoner.[108] Of the 30,000 Japanese troops that defended Saipan, fewer than 1,000 remained alive at battle's end.[109] Japanese prisoners sent to camps fared well; however, some Japanese were killed when trying to surrender or were massacred[110] just after they had surrendered (see Allied war crimes during World War II in the Pacific). In some instances, Japanese prisoners were tortured by a variety of methods.[111] A method of torture used by the Chinese National Revolutionary Army (NRA) included suspending the prisoner by the neck in a wooden cage until they died.[112] In very rare cases, some were beheaded by sword, and a severed head was once used as a football by Chinese National Revolutionary Army (NRA) soldiers.[113]
After the war, many Japanese were kept on as Japanese Surrendered Personnel until mid-1947 and used as forced labour doing menial tasks, while 35,000 were kept on in arms within their wartime military organisation and under their own officers and used in combat alongside British troops seeking to suppress the independence movements in the Dutch East Indies and French Indochina.
Italians
In 1943, Italy overthrew Mussolini and became a co-belligerent with the Allies. This did not mean any change in status for Italian POWs however, since due to the labour shortages in the UK, Australia and the US, they were retained as POWs there.[114]
Cossacks
On 11 February 1945, at the conclusion of the Yalta Conference, the United States and the United Kingdom signed a Repatriation Agreement with the USSR.[115] The interpretation of this Agreement resulted in the forcible repatriation of all Soviets (Operation Keelhaul) regardless of their wishes. The forced repatriation operations took place in 1945–1947.[116]
Transfers between the Allies
The United States handed over 740,000 German prisoners to France, a signatory of the Geneva Convention. The Soviet Union had not signed the Geneva Convention. According to Edward Peterson, the U.S. chose to hand over several hundred thousand German prisoners to the Soviet Union in May 1945 as a "gesture of friendship".[117] U.S. forces also refused to accept the surrender of German troops attempting to surrender to them in Saxony and Bohemia, and handed them over to the Soviet Union instead.[118] It is also known that 6000 of the German officers who were sent from camps in the West to the Soviets were subsequently imprisoned in the Sachsenhausen concentration camp, which at the time was one of the NKVD special camp.[119][120]
Post-World War II



During the Korean War, the North Koreans developed a reputation for severely mistreating prisoners of war (see Crimes against POWs). Their POWs were housed in three camps, according to their potential usefulness to the North Korean army. Peace camps and reform camps were for POWs that were either sympathetic to the cause or who had valued skills that could be useful in the army and thus these enemy soldiers were indoctrinated and sometimes conscripted into the North Korean army. The regular prisoners of war were usually very poorly treated. POWs in peace camps were reportedly treated with more consideration.[121]
In 1952, the 1952 Inter-Camp P.O.W. Olympics were held during 15 and 27 November 1952, in Pyuktong, North Korea. The Chinese hoped to gain worldwide publicity and while some prisoners refused to participate some 500 P.O.W.s of eleven nationalities took part.[122] They were representative of all the prison camps in North Korea and competed in: football, baseball, softball, basketball, volleyball, track and field, soccer, gymnastics, and boxing.[122] For the P.O.W.s this was also an opportunity to meet with friends from other camps. The prisoners had their own photographers, announcers, even reporters, who after each day's competition published a newspaper, the "Olympic Roundup".[123]
Of about 16,500 French soldiers who fought at the Battle of Dien Bien Phu in French Indochina, more than 3,000 were killed in battle, while almost all of the 11,721 men taken prisoner died in the hands of the Viet Minh on death marches to distant POW camps, and in those camps in the last three months of the war.[124]
The Vietcong and the North Vietnamese Army captured many United States service members as prisoners of war during the Vietnam War, who suffered from mistreatment and torture during the war. Some American prisoners were held in the prison called the Hanoi Hilton.
Communist Vietnamese held in custody by South Vietnamese and American forces were also tortured and badly treated.[27] After the war, millions of South Vietnamese servicemen and government workers were sent to "re-education" camps where many perished.
Like in previous conflicts, there has been speculation without evidence that there were a handful of American pilots captured by the North Koreans and the North Vietnamese who were transferred to the Soviet Union and were never repatriated.[125][126][127]
Regardless of regulations determining treatment to prisoners, violations of their rights continue to be reported. Many cases of POW massacres have been reported in recent times, including 13 October massacre in Lebanon by Syrian forces and June 1990 massacre in Sri Lanka.
Indian intervention in Bangladesh liberation war in 1971 led to third Indo-Pakistan war ended up with Indian victory with India having over 90,000 Pakistani POWs.
In 1982, during the Falklands War, prisoners were well treated in general by both parties of the conflict, with military commanders dispatching 'enemy' prisoners back to their homelands in record time.[128]
In 1991, during the Persian Gulf War, American, British, Italian, and Kuwaiti POWs (mostly crew members of downed aircraft and special forces) were tortured by the Iraqi secret police. An American military doctor, Major Rhonda Cornum, a 37-year-old flight surgeon captured when her Blackhawk UH-60 was shot down, was also subjected to sexual abuse.[129]
During the 1990s Yugoslav Wars, Serb paramilitary forces supported by JNA forces killed POWs at Vukovar and Škarbrnja while Bosnian Serb forces killed POWs at Srebrenica.
In 2001, there were reports concerning two POWs that India had taken during the Sino-Indian War, Yang Chen and Shih Liang. The two were imprisoned as spies for three years before being interned in a mental asylum in Ranchi, where they spent the next 38 years under a special prisoner status.[130]
The last prisoners of Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988) were exchanged in 2003.[131]
Numbers of POWs
This article is a list of nations with the highest number of POWs since the start of World War II, listed in descending order. These are also the highest numbers in any war since the Convention Relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War entered into force on 19 June 1931. The USSR had not signed the Geneva convention.[132]
| Armies | Number of POWs held in captivity | Name of conflict |
|---|---|---|
|
World War II | |
| 5.7 million taken by Germany (about 3 million died in captivity (56–68%)) | World War II (total) | |
| 1,800,000 taken by Germany | World War II | |
| 675,000 (420,000 taken by Germany; 240,000 taken by the Soviets in 1939; 15,000 taken by Germany in Warsaw in 1944) | World War II | |
| ≈200,000 (135,000 taken in Europe, does not include Pacific or Commonwealth figures) | World War II | |
| ≈175,000 taken by Coalition of the Gulf War | Persian Gulf War | |
|
World War II | |
| ≈130,000 (95,532 taken by Germany) | World War II | |
| 90,368 taken by India & Bangladesh Liberation force (Mukti Bahini). Later released by India in accordance with the Simla Agreement. | Bangladesh Liberation War | |
| World War II |
In popular culture
Movies and Television
- 1971
- Andersonville
- Another Time, Another Place
- As Far as My Feet Will Carry Me [German: So weit die Füße tragen]
- Blood Oath
- The Bridge on the River Kwai
- The Brylcreem Boys
- The Colditz Story
- Danger Within
- The Deer Hunter
- Empire of the Sun
- Escape to Athena
- Escape from Sobibor
- Faith of My Fathers
- Grand Illusion
- The Great Escape
- The Great Raid
- Hanoi Hilton
- Hart's War
- Hogan's Heroes
- Homeland (TV series)
- Katyń
- King Rat
- Life Is Beautiful
- P.O.W.- Bandi Yuddh Ke
- The McKenzie Break
- Merry Christmas, Mr. Lawrence
- Missing in Action
- The One That Got Away
- Paradise Road
- The Purple Heart
- The Railway Man
- Rambo: First Blood Part II
- Rescue Dawn
- Schindler's List
- Slaughterhouse Five
- Some Kind of Hero
- Stalag 17
- Summer of My German Soldier
- Tea with Mussolini
- To End All Wars
- Unbroken
- Uncommon Valor
- Von Ryan's Express
- The Pianist
- The Walking Dead
- Who Goes Next?
- The Wooden Horse
Songs
- "Prisoners of War" by Funker Vogt
- "Captured" by Malevhhjjolent Creation
- "Take No Prisoners" by Megadeth
Games
See also
- KIA – Killed in Action
- MIA – Missing in Action
- WIA – Wounded in action
- 13th Psychological Operations Battalion (Enemy Prisoner of War)
- 1952 POW olympics
- American Civil War prison camps
- American Revolution prisoners of war
- Elsa Brändström, the "Angel of Siberia" for millions of German POWs in World War I
- Camps for Russian prisoners and internees in Poland (1919–1924)
- Civilian Internee
- Duty to escape
- Extermination of Soviet prisoners of war by Nazi Germany
- German Prisoners of War in the United States
- Illegal combatant
- Korean War POWs detained in North Korea
- Laws of war
- List of notable prisoners of war
- List of prisoner-of-war escapes
- Medal for civilian prisoners, deportees and hostages of the 1914-1918 Great War French medal
- Military Chaplain#Noncombatant status
- Postal censorship
- Prison escape
- Prisoner of war mail
- Prisoner of War Medal 1940–1945 Belgian award
- Rule of Law in Armed Conflicts Project (RULAC)
- Vietnam War POW/MIA issue
- World War I prisoners of war in Germany
- World War II Radio Heroes: Letters of Compassion
References
Notes
- Compare Harper, Douglas. "camouflage". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 28 October 2017. – "Captives taken in war have been called prisoners since mid-14c.; phrase prisoner of war dates from 1630s".
- According to the Dialogus Miraculorum by Caesarius of Heisterbach, Arnaud Amalric was only reported to have said that.
- see references on the pages Western Front (World War II) and North African Campaign (World War II)
Citations
- John Hickman (2002). "What is a Prisoner of War For". Scientia Militaria. 36 (2). Retrieved 14 September 2015.
- Wickham, Jason (2014) The Enslavement of War Captives by the Romans up to 146 BC, University of Liverpool PhD Dissertation. "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 May 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Wickham 2014 notes that for Roman warfare the outcome of capture could lead to release, ransom, execution or enslavement.
- "The Roman Gladiator", The University of Chicago – "Originally, captured soldiers had been made to fight with their own weapons and in their particular style of combat. It was from these conscripted prisoners of war that the gladiators acquired their exotic appearance, a distinction being made between the weapons imagined to be used by defeated enemies and those of their Roman conquerors. The Samnites (a tribe from Campania which the Romans had fought in the fourth and third centuries BC) were the prototype for Rome's professional gladiators, and it was their equipment that first was used and later adopted for the arena. [...] Two other gladiatorial categories also took their name from defeated tribes, the Galli (Gauls) and Thraeces (Thracians)."
- Eisenberg, Bonnie; Ruthsdotter, Mary (1998). "History of the Women's Rights Movement". www.nwhp.org. Archived from the original on 12 July 2018.
- "Church Fathers: Church History, Book VII (Socrates Scholasticus)". www.newadvent.org. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- Attwater, Donald and Catherine Rachel John. The Penguin Dictionary of Saints. 3rd edition. New York: Penguin Books, 1993. ISBN 0-14-051312-4.
- "But when the outcries of the lackies and boies, which ran awaie for feare of the Frenchmen thus spoiling the campe came to the kings eares, he doubting least his enimies should gather togither againe, and begin a new field; and mistrusting further that the prisoners would be an aid to his enimies, or the verie enimies to their takers in deed if they were suffered to live, contrarie to his accustomed gentleness, commended by sound of trumpet, that everie man (upon pain and death) should uncontinentlie slaie his prisoner. When this dolorous decree, and pitifull proclamation was pronounced, pitie it was to see how some Frenchmen were suddenlie sticked with daggers, some were brained with pollaxes, some slaine with malls, others had their throats cut, and some their bellies panched, so that in effect, having respect to the great number, few prisoners were saved." : Raphael Holinshed's Chronicles of England, Scotland and Ireland, quoted by Andrew Gurr in his introduction to Shakespeare, William; Gurr, Andrew (2005). King Henry V. Cambridge University Press. p. 24. ISBN 0-521-84792-3.
- Davies, Norman (1996). Europe: A History. Oxford University Press. p. 362. ISBN 0-19-520912-5.
- Samurai, Warfare and the State in Early Medieval Japan, The Journal of Japanese Studies
- "Central Asian world cities". Faculty.washington.edu. 29 September 2007. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Meyer, Michael C. and William L. Sherman. The Course of Mexican History. Oxford University Press, 5th ed. 1995.
- Hassig, Ross (2003). "El sacrificio y las guerras floridas". Arqueología Mexicana, pp. 46–51.
- Harner, Michael (April 1977). "The Enigma of Aztec Sacrifice". Natural History. Latinamericanstudies.org. pp. 46–51.
- Crone, Patricia (2004). God's Rule: Government and Islam. Columbia University Press. pp. 371–372. ISBN 9780231132909.
- Roger DuPasquier. Unveiling Islam. Islamic Texts Society, 1992, p. 104
- Nigosian, S. A. (2004). Islam. Its History, Teaching, and Practices. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. p. 115.
- Maududi (1967), Introduction of Ad-Dahr, "Period of revelation", p. 159.
- Lings, Muhammad: His Life Based on the Earliest Sources, p. 229-233.
- "Prisoner of war", Encyclopædia Britannica
- https://reader.digitale-sammlungen.de/de/fs1/object/goToPage/bsb10604517.html?pageNo=305 (german) Rochlitz: Collected Works vol 6 (1822), description of treatment of french prisoners p. 305ff
- https://www.leipzig-lese.de/index.php?article_id=393 (german) Gravedigger Ahlemann: witness report about the Leipzig cemetery during the Battle of Leipzig.
- Roger Pickenpaugh (2013). Captives in Blue: The Civil War Prisons of the Confederacy. University of Alabama Press. pp. 57–73. ISBN 9780817317836.
- "Myth: General Ulysses S. Grant stopped the prisoner exchange, and is thus responsible for all of the suffering in Civil War prisons on both sides – Andersonville National Historic Site (U.S. National Park Service)". Nps.gov. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- Richard Wightman Fox (7 January 2008). "National Life After Death". Slate. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2012.
- "Andersonville: Prisoner of War Camp-Reading 1". Nps.gov. Retrieved 28 November 2008.
- "US Civil War Prison Camps Claimed Thousands". National Geographic News. 1 July 2003.
- "In South Vietnamese Jails". Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- "Geneva Convention". Peace Pledge Union. Retrieved 6 April 2014.
- "Story of an idea- the Film". International Committee of the Red Cross. Retrieved 6 April 2014.
- Penrose, Mary Margaret. "War Crime". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 6 April 2014.
- John Pike (12 August 1949). "FM3-19.40 Part 1 Fundamentals of Internment/Resettlement Operations Chptr 1 Introduction". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Schmitt, Eric (19 February 1991). "War in the Gulf: P.O.W.'s; U.S. Says Prisoners Seem War-Weary". The New York Times.
- Thompson, Mark (17 May 2012). "Pentagon: We Don't Call Them POWs Anymore". Time. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- "Department of Defense Instruction January 8, 2008 Incorporating Change 1, August 14, 2009" (PDF). Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- Geo G. Phillimore and Hugh H. L. Bellot, "Treatment of Prisoners of War", Transactions of the Grotius Society, Vol. 5, (1919), pp. 47–64.
- Niall Ferguson, The Pity of War. (1999) pp. 368–69 for data.
- "Disobedience and Conspiracy in the German Army, 1918–1945". Robert B. Kane, Peter Loewenberg (2008). McFarland. p.240. ISBN 0-7864-3744-8
- "375,000 Austrians Have Died in Siberia; Remaining 125,000 War Prisoner...—Article Preview—The". New York Times. 8 April 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Richard B. Speed, III. Prisoners, Diplomats and the Great War: A Study in the Diplomacy of Captivity. (1990); Ferguson, The Pity of War. (1999) Ch 13; Desmond Morton, Silent Battle: Canadian Prisoners of War in Germany, 1914–1919. 1992.
- British National Archives, "The Mesopotamia campaign", at ;
- Peter Dennis, Jeffrey Grey, Ewan Morris, Robin Prior with Jean Bou, The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History (2008) p. 429
- H.S. Gullett, Official History of Australia in the War of 1914–18, Vol. VII The Australian Imperial Force in Sinai and Palestine (1941) pp. 620–2
- The Postal History Society 1936–2011—75th anniversary display to the Royal Philatelic Society, London, p. 11
- "The Queen and technology". Royal.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 9 May 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- "Search results – Resource centre". International Committee of the Red Cross.
- Ferguson, Niall (2004), "Prisoner Taking and Prisoner Killing in the Age of Total War: Towards a Political Economy of Military Defeat", War in History, 11 (2): 148–192, doi:10.1191/0968344504wh291oa, p. 186
- Lowe, Keith (2012), Savage Continent: Europe in the aftermath of World War II, p. 122
- "International Humanitarian Law – State Parties / Signatories". Icrc.org. 27 July 1929. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Akira Fujiwara, Nitchû Sensô ni Okeru Horyo Gyakusatsu, Kikan Sensô Sekinin Kenkyû 9, 1995, p. 22
- McCarthy, Terry (12 August 1992). "Japanese troops ate flesh of enemies and civilians". The Independent. London.
- Tsuyoshi, Masuda. "Forgotten tragedy of Italian war detainees". nhk.or.jp. NHK World. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- Yuki Tanaka, Hidden Horrors, 1996, pp. 2, 3.
- Tanaka, ibid., Herbert Bix, Hirohito and the Making of Modern Japan, 2001, p. 360
- "World War II POWs remember efforts to strike against captors". The Times-Picayune. Associated Press. 5 October 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- "title=Japanese Atrocities in the Philippines". Public Broadcasting Service (PBS)
- Prisoners of the Japanese : POWs of World War II in the Pacific—by Gavin Dawes, ISBN 0-688-14370-9
- Dawes, Gavan (1994). Prisoners of the Japanese: POWs of World War II in the Pacific. Melbourne: Scribe Publications. pp. 295–297. ISBN 1-920769-12-9.
- Daws (1994), p. 297
- "Donald L. Miller "D-Days in the Pacific", p. 317"
- Hunter, Clare (2019). Threads of life : a history of the world through the eye of a needle. London: Spectre (Hodder & Stoughton). pp. 50–58. ISBN 9781473687912. OCLC 1079199690.
- Home. Captivememories.org.uk. Retrieved on 2014-05-24.
- Richard Vinen, The Unfree French: Life under the Occupation (2006) pp 183–214
- "International Humanitarian Law—State Parties / Signatories". Cicr.org. Archived from the original on 5 February 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- "Ben Aharon Yitzhak". Jafi.org.il. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- See, for example, Joseph Robert White, 2006, "Flint Whitlock. Given Up for Dead: American GIs in the Nazi Concentration Camp at Berga" Archived 11 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine (book review)
- See: luvnbdy/secondwar/fact_sheets/pow Veterans Affairs Canada, 2006, "Prisoners of War in the Second World War" and National Museum of the USAF, "Allied Victims of the Holocaust".
- Ambrose, pp 360
- "Death March from Stalag Luft 4 during WWII". www.b24.net. Retrieved 26 October 2019.
- "Le porte della Memoria". Retrieved 12 November 2006.
- Daniel Goldhagen, Hitler's Willing Executioners (p. 290)—"2.8 million young, healthy Soviet POWs" killed by the Germans, "mainly by starvation ... in less than eight months" of 1941–42, before "the decimation of Soviet POWs ... was stopped" and the Germans "began to use them as laborers".
- "Soviet Prisoners of War: Forgotten Nazi Victims of World War II". Historynet.com. Archived from the original on 30 March 2008. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Davies, Norman (2006). Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory. London: Pan Books. p. 271. ISBN 978-0-330-35212-3.
- "Report at the session of the Russian association of WWII historians in 1998". Gpw.tellur.ru. Archived from the original on 20 March 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Michael Burleigh (2000). The Third Reich—A New History. New York: Hill and Wang. pp. 512–13. ISBN 978-0-8090-9325-0.
- "Part VIII: Execution of the convention #Section I: General provisions". Retrieved 29 November 2007.
- Beevor, Stalingrad. Penguin 2001 ISBN 0-14-100131-3 p60
- James D. Morrow, Order within Anarchy: The Laws of War as an International Institution, 2014, p.218
- Nikolai Tolstoy (1977). The Secret Betrayal. Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 33. ISBN 0-684-15635-0.
- Gerald Reitlinger. The House Built on Sand. Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London (1960) ASIN: B0000CKNUO. pp. 90, 100–101.
- Rees, Simon. "German POWs and the Art of Survival". Historynet.com. Archived from the original on 19 December 2007. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- "German POWs in Allied Hands—World War II". Worldwar2database.com. 27 July 2011. Archived from the original on 12 April 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Fischer, Benjamin B., "The Katyn Controversy: Stalin's Killing Field", Studies in Intelligence, Winter 1999–2000. Archived 9 May 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "Michael Hope—"Polish deportees in the Soviet Union"". Wajszczuk.v.pl. Archived from the original on 16 February 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- "Livre noir du Communisme: crimes, terreur, répression". Stéphane Courtois, Mark Kramer (1999). Harvard University Press. p. 209. ISBN 0-674-07608-7
- "シベリア抑留、露に76万人分の資料 軍事公文書館でカード発見". Sankeishinbun. 24 July 2009. Archived from the original on 26 July 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2009.
- Japanese POW group says files on over 500,000 held in Moscow, BBC News, 7 March 1998
- UN Press Release, Commission on Human Rights, 56th session, 13 April 2000.
- POW in the USSR 1939–1956:Documents and Materials Archived 2 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine Moscow Logos Publishers (2000) (Военнопленные в СССР. 1939–1956: Документы и материалы Науч.-исслед. ин-т проблем экон. истории ХХ века и др.; Под ред. М.М. Загорулько. – М.: Логос, 2000. – 1118 с.: ил.) ISBN 5-88439-093-9
- Anne Applebaum Gulag: A History, Doubleday, April 2003, ISBN 0-7679-0056-1; page 431.Introduction online Archived 13 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine)
- Paul M. Cole (1994) POW/MIA Issues: Volume 2, World War II and the Early Cold War National Defense Research Institute. RAND Corporation, p. 28 Retrieved 18 July 2012
- Tremblay, Robert, Bibliothèque et Archives Canada, et al. "Histoires oubliées – Interprogrammes : Des prisonniers spéciaux" Interlude. Aired: 20 July 2008, 14h47 to 15h00. Note: See also Saint Helen's Island.
- Dear, I.C.B and Foot, M.R.D. (editors) (2005). "War Crimes". The Oxford Companion to World War II. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 983–9=84. ISBN 978-0-19-280670-3.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- James J. Weingartner, "Americans, Germans, and War Crimes: Converging Narratives from "the Good War" the Journal of American History, Vol. 94, No. 4. March 2008 Archived 14 November 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- How Britain’s German-born Jewish ‘secret listeners’ helped win World War II
- "Ike's Revenge?". Time. 2 October 1989. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- S. P. MacKenzie "The Treatment of Prisoners of War in World War II" The Journal of Modern History, Vol. 66, No. 3. (September 1994), pp. 487–520.
- Footnote to: K. W. Bohme, Zur Geschichte der deutschen Kriegsgefangenen des Zweiten Weltkrieges, 15 vols. (Munich, 1962–74), 1, pt. 1:x. (n. 1 above), 13:173; ICRC (n. 12 above), p. 334.
- Noam Chomsky, Edward S. Herman, "After the Cataclysm: Postwar Indochina and the Reconstruction of Imperial Ideology" (1979) pp. 35–37
- Eugene Davidsson, "The Trial of the Germans: An Account of the Twenty-Two Defendants Before the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg", (1997) pp. 518–19 "the Allies stated in 1943 their intention of using forced workers outside Germany after the war, and not only did they express the intention but they carried it out. Not only Russia made use of such labour. France was given hundreds of thousands of German prisoners of war captured by the Americans, and their physical condition became so bad that the American Army authorities themselves protested. In England and the United States, too, some German prisoners of war were being put to work long after the surrender, and in Russia thousands of them worked until the mid-50s."
- Inge Weber-Newth; Johannes-Dieter Steinert (2006). "Chapter 2: Immigration policy—immigrant policy". German migrants in post-war Britain: an enemy embrace. Routledge. pp. 24–30. ISBN 978-0-7146-5657-1. Retrieved 15 December 2009.
Views in the Media were mirrored in the House of commons, where the arguments were characterized by a series of questions, the substance of which were always the same. Here too the talk was often of slave labour, and this debate was not laid to rest until the government announced its strategy.
- Cobain, Ian (12 November 2005). "The secrets of the London Cage". The Guardian. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- Staff. ICRC in WW II: German prisoners of war in Allied hands, 2 February 2005
- Butler, Desmond (17 December 2001). "Ex-Death Camp Tells Story of Nazi and Soviet Horrors". The New York Times.
- David Lubań, "Legal Modernism", Univ of Michigan Press, 1994. ISBN 978-0-472-10380-5 pp. 360, 361
- The Legacy of Nuremberg PBS
- http://www.hungarianhistory.com/lib/francia/francia.pdf
- Thorpe, Nick. Hungarian POW identified. BBC News, 17 September 2000. Accessed 11 December 2016
- Morison, Samuel Eliot (2002) [1960]. Victory in the Pacific, 1945. Volume 14 of History of United States Naval Operations in World War II. Urbana, Illinois: University of Illinois Press. ISBN 0-252-07065-8. OCLC 49784806.
- Battle of Saipan, historynet.com
- American troops 'murdered Japanese PoWs', "American and Australian soldiers massacred Japanese prisoners of war" according to The Faraway War by Prof Richard Aldrich of Nottingham University. From the diaries of Charles Lindberg: as told by a US officer, "Oh, we could take more if we wanted to", one of the officers replied. "But our boys don't like to take prisoners." "It doesn't encourage the rest to surrender when they hear of their buddies being marched out on the flying field and machine-guns turned loose on them." On Australian soldiers attitudes Eddie Stanton is quoted: "Japanese are still being shot all over the place", "The necessity for capturing them has ceased to worry anyone. Nippo soldiers are just so much machine-gun practice. Too many of our soldiers are tied up guarding them."
- "Photos document brutality in Shanghai". CNN. 23 September 1996. Retrieved 8 June 2010.
- CNN 23 September 1996 image 2
- CNN 23 September 1996 image 3
- Insolvibile Isabella, Wops. I prigionieri italiani in Gran Bretagna, Naples, Italy, Edizioni Scientifiche Italiane, 2012, ISBN 9788849523560
- "Repatriation – The Dark Side of World War II". Fff.org. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- "Forced Repatriation to the Soviet Union: The Secret Betrayal". Hillsdale.edu. Archived from the original on 7 February 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Edward N. Peterson, The American Occupation of Germany, pp 42, 116, "Some hundreds of thousands who had fled to the Americans to avoid being taken prisoner by the Soviets were turned over in May to the Red Army in a gesture of friendship."
- Niall Ferguson, "Prisoner Taking and Prisoner Killing in the Age of Total War: Towards a Political Economy of Military Defeat" War in History 2004 11 (2) 148–192 pg. 189, (footnote, referenced to: Heinz Nawratil, Die deutschen Nachkriegsverluste unter Vertriebenen, Gefangenen und Verschleppter: mit einer übersicht über die europäischen Nachkriegsverluste (Munich and Berlin, 1988), pp. 36f.)
- "Ex-Death Camp Tells Story of Nazi and Soviet Horrors" New York Times, 17 December 2001
- Butler, Desmond (17 December 2001). "Ex-Death Camp Tells Story of Nazi and Soviet Horrors". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- "Chinese operated three types of POW camps for Americans during the Korean War". April 1997. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- Adams, (2007), p. 62.
- Adams, Clarence. (2007). An American Dream: The Life of an African American Soldier and POW who Spent Twelve Years in Communist China. Amherst & Boston. University of Massachusetts Press. ISBN 978-1-5584-9595-1, p.62
- Trap Door to the Dark Side. William C. Jeffries (2006). p. 388. ISBN 1-4259-5120-1
- Burns, Robert (29 August 1993). "Were Korean War POWs Sent to U.S.S.R? New Evidence Surfaces: Probe: Former Marine corporal spent 33 months as a prisoner and was interrogated by Soviet agents who thought he was a pilot". Los Angeles Times.
- pp 26–33 Transfer of U.S. Korean War POWs To the Soviet Union. Nationalalliance.org. Retrieved on 2014-05-24. Archived 14 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- USSR. Taskforceomegainc.org (1996-09-17). Retrieved on 2014-05-24.
- https://www.upi.com/Archives/1982/04/27/Falkland-Islands-a-gentlemans-war/9723388728000/
- "war story: Rhonda Cornum". Frontline. PBS. Retrieved 24 June 2009.
- Shaikh Azizur Rahman, "Two Chinese prisoners from '62 war repatriated", The Washington Times.
- Nazila Fathi (14 March 2003). "Threats and Responses: Briefly Noted; Iran-Iraq Prisoner Deal". New York Times. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- Clark, Alan Barbarossa: The Russian-Geran Conflict 1941–1945 p. 206, ISBN 0-304-35864-9
- Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses in the Twentieth Century, Greenhill Books, London, 1997, G. F. Krivosheev, editor (ref. Streit)
- Rüdiger Overmans: "Die Rheinwiesenlager 1945" in: Hans-Erich Volkmann (ed.): Ende des Dritten Reiches – Ende des Zweiten Weltkrieges. Eine perspektivische Rückschau. Herausgegeben im Auftrag des Militärgeschichtlichen Forschungsamtes. Munich 1995. ISBN 3-492-12056-3, p. 277
- Kurt W. Böhme: "Die deutschen Kriegsgefangenen in Jugoslawien", Band I/1 der Reihe: Kurt W. Böhme, Erich Maschke (eds.): Zur Geschichte der deutschen Kriegsgefangenen des Zweiten Weltkrieges, Bielefeld 1976, ISBN 3-7694-0003-8, pp. 42–136, 254
- "Kriegsgefangene: Viele kamen nicht zurück—Politik—stern.de<!— Bot generated title —>". Stern.de. 6 February 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
Bibliography
- John Hickman, "What is a Prisoner of War For?" Scientia Militaria: South African Journal of Military Studies. Vol. 36, No. 2. 2008. pp. 19–35.
- Full text of Third Geneva Convention, 1949 revision
- "Prisoner of War". Encyclopædia Britannica (CD ed.). 2002.
- Gendercide site
- "Soviet Casualties and Combat Losses in the Twentieth Century", Greenhill Books, London, 1997, G. F. Krivosheev, editor.
- "Keine Kameraden. Die Wehrmacht und die sowjetischen Kriegsgefangenen 1941–1945", Dietz, Bonn 1997, ISBN 3-8012-5023-7
- Bligh, Alexander. 2015. "The 1973 War and the Formation of Israeli POW Policy – A Watershed Line? ". In Udi Lebel and Eyal Lewin (eds.), The 1973 Yom Kippur War and the Reshaping of Israeli Civil–Military Relations. Washington, DC: Lexington Books (2015), 121–146.
- Bligh, Alexander. 2014. "The development of Israel's POW policy: The 1967 War as a test case", Paper presented at the Seventh Annual ASMEA Conference: Searching for Balance in the Middle East and Africa (Washington, D.C., 31 October 2014).
Primary sources
- The stories of several American fighter pilots, shot down over North Vietnam are the focus of American Film Foundation's 1999 documentary Return with Honor, presented by Tom Hanks.
- Lewis H. Carlson, WE WERE EACH OTHER'S PRISONERS: An Oral History of World War II American and German Prisoners of War, 1st Edition.; 1997, BasicBooks (HarperCollins, Inc). ISBN 0-465-09120-2.
- Peter Dennis, Jeffrey Grey, Ewan Morris, Robin Prior with Jean Bou : The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History 2nd edition (Melbourne: Oxford University Press Australia & New Zealand, 2008) OCLC 489040963.
- H.S. Gullett, Official History of Australia in the War of 1914–18, Vol. VII The Australian Imperial Force in Sinai and Palestine 10th edition (Sydney: Angus & Robinson, 1941) OCLC 220900153.
- Alfred James Passfield, The Escape Artist: An WW2 Australian prisoner's chronicle of life in German POW camps and his eight escape attempts, 1984 Artlook Books Western Australia. ISBN 0-86445-047-8.
- Rivett, Rohan D. (1946). Behind Bamboo. Sydney: Angus & Robertson. Republished by Penguin, 1992; ISBN 0-14-014925-2.
- George G. Lewis and John Mewha, History of prisoner of war utilization by the United States Army, 1776–1945; Dept. of the Army, 1955.
- Vetter, Hal, Mutine at Koje Island; Charles Tuttle Company, Vermont, 1965.
- Jin, Ha, War Trash: A novel; Pantheon, 2004. ISBN 978-0-375-42276-8.
- Sean Longden, Hitler's British Slaves. First Published Arris Books, 2006. Second Edition, Constable Robinson, 2007.
- Desflandres, Jean, Rennbahn: Trente-deux mois de captivité en Allemagne 1914–1917 Souvenirs d'un soldat belge, étudiant à l'université libre de Bruxelles 3rd edition (Paris, 1920)
Further reading
- Devaux, Roger. Treize Qu'ils Etaient: Life of the French prisoners of war at the peasants of low Bavaria (1939–1945) – Mémoires et Cultures—2007—ISBN 2-916062-51-3
- Doylem Robert C. The Enemy in Our Hands: America's Treatment of Prisoners of War From the Revolution to the War on Terror (University Press of Kentucky, 2010); 468 pages; Sources include American soldiers' own narratives of their experiences guarding POWs plus Webcast Author Interview at the Pritzker Military Library on 26 June 2010
- Gascare, Pierre. Histoire de la captivité des Français en Allemagne (1939–1945), Éditions Gallimard, France, 1967 – ISBN 2-07-022686-7.
- McGowran, Tom, Beyond the Bamboo Screen: Scottish Prisoners of War under the Japanese. 1999. Cualann Press Ltd
- Arnold Krammer, ''Nazi Prisoners of War in America 1979 Stein & Day; 1991, 1996 Scarborough House. ISBN 0-8128-8561-9.
- Bob Moore,& Kent Fedorowich eds., Prisoners of War and Their Captors in World War II, Berg Press, Oxford, UK, 1997.
- Bob Moore, and Kent Fedorowich. The British Empire and Its Italian Prisoners of War, 1940–1947 (2002) excerpt and text search
- David Rolf, Prisoners of the Reich, Germany's Captives, 1939–1945, 1998; on British POWs
- Scheipers, Sibylle Prisoners and Detainees in War , European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2011, retrieved: 16 November 2011.
- Paul J. Springer. America's Captives: Treatment of POWs From the Revolutionary War to the War on Terror (University Press of Kansas; 2010); 278 pages; Argues that the US military has failed to incorporate lessons on POW policy from each successive conflict.
- Vance, Jonathan F. (March 2006). The Encyclopedia of Prisoners of War & Internment (PDF) (Hardcover) (Second ed.). Millerton, NY: Grey House Pub, 2006. p. 800. ISBN 1-59237-120-5. |ISBN 978-1-59237-120-4 EBook ISBN 978-1-59237-170-9
- Richard D. Wiggers, "The United States and the Denial of Prisoner of War (POW) Status at the End of the Second World War", Militargeschichtliche Mitteilungen 52 (1993) pp. 91–94.
- Winton, Andrew, Open Road to Faraway: Escapes from Nazi POW Camps 1941–1945. 2001. Cualann Press Ltd.
- Harris, Justin Michael. "American Soldiers and POW Killing in the European Theater of World War II"
- United States. Government Accountability Office. DOD's POW/MIA Mission: Capability and Capacity to Account for Missing Persons Undermined by Leadership Weaknesses and Fragmented Organizational Structure: Testimony before the Subcommittee on Military Personnel, Committee on Armed Services, U.S. House of Representatives. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, 2013.
- On 12 February 2013, three American POWs gathered at the Pritzker Military Library for a webcast conversation regarding their individual experiences as POWs and the memoirs they each published:
- Rhonda Cornum – with Peter Copeland She Went to War: The Rhonda Cornum Story 1992 ISBN 9780891414636
- John Borling – a collection of his poetry Taps on the Walls: Poems from the Hanoi Hilton 2013 ISBN 9780615659053
- Donald E. Casey – To Fight for My Country, Sir!: Memoirs of a 19-year-old B-17 Navigator Shot Down in Nazi Germany 2009 ISBN 9781448669875
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Prisoners of war. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1922 Encyclopædia Britannica article "Prisoners of War". |
- Prisoners of war and humanitarian law, ICRC.
- Prisoners of War UK National Archives.
- Prisoners of War 1755–1831 UK National Archives ADM 103
- Archive of World War II memories BBC.
- Soviet Prisoners of War: Forgotten Nazi Victims of World War II HistoryNet.
- Reports made by World War I prisoners of war UK National Archives
- First hand account of being a Japanese POW. Part 1 in a series of 4 video interviews Storyvault
- German POWs and the art of survival Historical Eye
- Current status of Vietnam War POW/MIA
- Clifford Reddish. War Memoirs of a British Army Signalman as a prisoner of the Japanese
- Canada's Forgotten PoW Camps CBC Digital Archives
- German army list of Stalags
- German army list of Oflags
- Colditz Oflag IVC POW Camp
- Lamsdorf Reunited
- New Zealand PoWs of Germany, Italy & Japan New Zealand Official History
- Notes of Japanese soldier in a USSR prison camp after World War II
- German prisoners of war in Allied hands (World War II) ICRC
- World War II U.S. POW Archives
- Korean War POW Archives
- Historic films about POWs in World War I European Film Gateway
- Jewish POW swapped by Germans in World War II

