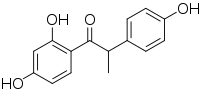
O-Desmethylangolensin
O-Desmethylangolensin (O-DMA) is a phytoestrogen. It is an intestinal bacterial metabolite of the soy phytoestrogen daidzein.[1] It produced in some people, deemed O-DMA producers, but not others.[1] O-DMA producers were associated with 69% greater mammographic density and 6% bone density.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.083 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 258.273 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H318, H400, H410 |
| P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+312, P305+351+338, P310, P330, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Frankenfeld, C. L. (2011). "O-Desmethylangolensin: The Importance of Equol's Lesser Known Cousin to Human Health". Advances in Nutrition. 2 (4): 317. doi:10.3945/an.111.000539. PMC 3125681. PMID 22332073.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
