Perfluorinated compound
A perfluorinated compound (PFC) is an organofluorine compound containing only carbon-fluorines and C-C bonds but also other heteroatoms.
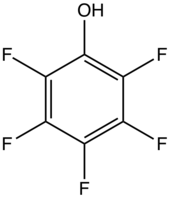
PFCs have properties that result from the presence of fluorocarbons (containing only C–F and C–C bonds) and the functional group. Common functional groups in PFCs are OH, CO2H, chlorine, O, and SO3H.
Applications
Perfluorinated compounds are used ubiquitously: For example, fluorosurfactants are widely used in the production of teflon (PTFE) and related fluorinated polymers. They confer hydrophobicity and stain-resistance to fabrics. They are components of fire-fighting foam.[1] Fluorosurfactants (PFAS) reduce surface tension by concentrating at the liquid-air interface due to the lipophobicity of polyfluorocarbons.
Chlorofluorocarbons are perfluorinated compounds that were formerly used as refrigerants (Freon) until they were implicated in ozone degradation.
Production
A common industrial method for synthesizing perflurocompounds is electrofluorination.
Examples by functional group
Perfluorinated alkyl halides
- Trifluoroiodomethane, an alkylating agent
- Pentafluoroethyl iodide, an alkylating agent
- Perfluorooctyl bromide, or perflubron, is a contrast medium for magnetic resonance imaging, computer tomography (MRI and CT) and sonography.
- It has also been used in liquid breathing.
- Dichlorodifluoromethane, refrigerant
Fluorochloroalkenes
- Chlorotrifluoroethylene, monomer
- Dichlorodifluoroethylene (three isomers), monomers
Perfluoroethers and epoxides
- Hexafluoropropylene oxide, precursor to perfluoromethyl vinyl ether (CF2=CFOCF3), a useful monomer
- whence Krytox, perfluorinated polyether used in special oils/greases
Perfluoroalcohols
- Pentafluorophenol, a moderately strong acid
Primary and secondary perfluorinated alcohols are unstable with respect to dehydrofluorination.
Perfluoroamines
- Perfluorotripentylamine (and related derivatives) are found in Fluorinert, electronic coolants.
Perfluoroketones
- Hexafluoroacetone, building block in organofluorine chemistry.
Perfluorocarboxylic acids
- Trifluoroacetic acid, a moderately strong acid useful in organic chemistry
- Heptafluorobutyric acid, a moderately strong acid that is useful in organic and analytical chemistry
- Pentafluorobenzoic acid, a moderately strong acid of interest in research community
- Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), surfactant used to make fluoropolymers such as Teflon
- Perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), surfactant in the emulsion polymerization of fluoropolymers, like PFOA.
Perfluoronitriles and isonitriles
- Trifluoromethylisocyanide, the simplest perfluorinated isonitrile.
- Trifluoromethylacetonitrile, the simplest perfluorinated nitrile
Perfluorosulfonic acids and related derivatives
- Triflic acid, a useful strong acid
- perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS) used as a replacement for PFOS in 3M's reformulated Scotchgard.
- perfluorobutane sulfonamide (FBSA), sulfonamide derivative of PFBS.
- perfluorooctanesulfonyl fluoride (POSF), precursor to PFOS-based compounds.
- perfluorooctanesulfonamide (PFOSA), used in 3M's Scotchgard formulation.
- perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), used in the semiconductor industry, 3M's former Scotchgard formulation, and 3M's former fire-fighting foam mixture.
Perfluorinated aryl borates
- Na[B(C6F5)4], salt of a weakly coordinating anion.
Environmental and health concerns
Several environmental and health concerns surrround the industrial production and use of perfluoroalkane compounds. The exceptional stability of perfluorinated compounds is desirable from the applications perspective is also a cause for environmental and health concerns.
Perfluoroalkanes
Low-boiling perfluoroalkanes are potent greenhouse gases, in part due to their very long atmospheric lifetime. The environmental concerns for perflurocompounds are similar to chlorofluorocarbons and other halogenated compounds used as refrigerants and fire suppression materials. The history of use, environmental impact, and recommendations for use are included in the Kyoto Protocol.
Fluorosurfactants
The fluorocarbons PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) and PFOS (perfluorooctane sulfonate) have both been investigated by the EU and the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) which regards them being harmful to the environment.[2] Specifically, studies found that PFOS caused "unusual and serious effects in animal toxicity tests," that it was present around the world in humans and wildlife, and that it was highly persistent in the environment.[3] (Similar concerns followed for PFOA.)
Fluorosurfactants tend to bioaccumulate, since they are extremely stable and can be stored in the bodies of humans and animals. Examples include PFOA and PFOS, frequently present in water resistant textiles and sprays conferring water resistant properties to textiles and fire-fighting foam.[2] Data from animal studies of PFOA indicate that it can cause several types of tumors and neonatal death and may have toxic effects on the immune, liver, and endocrine systems. As of 2010 data on the human health effects of PFOA were sparse.[4]
As of 2015, the U.S. Air Force had been testing 82 former and active US military installations for fluorosurfactants contained in fire fighting foam.[5] In 2015, PFCs were found in groundwater at Naval Air Station Brunswick, Maine and Grissom Air Reserve Base, Indiana, and in well water at Pease Air Force Base, New Hampshire, where 500 people including children had blood tests as part of a bio-monitoring plan through the state Department of Health and Human Services. The U.S. Department of Defense's research programs have been trying to define nature and extent of PFAS contamination at U.S. military sites, especially in groundwater.[6]
A 2018 report to Congress indicated that "at least 126 drinking water systems on or near military bases" were contaminated with PFAS compounds.[7][8]
A 2016 study found unsafe[9] levels of fluorosurfactants in 194 out of 4,864 water supplies in 33 U.S. states. Covering two-thirds of drinking water supplies in the United States, the study found thirteen states accounted for 75% of the detections. In order of frequency, these were: California, New Jersey, North Carolina, Alabama, Florida, Pennsylvania, Ohio, New York, Georgia, Minnesota, Arizona, Massachusetts, and Illinois. Firefighting foam was singled out as a major contributor.[10]
References
- Sedlak, Meg (October 2016). "Profile - Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS)" (PDF). sfei.org. San Francisco Estuary Institute. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
- US Environmental Protection Agency. "FAQ". Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Fluorinated Telomers. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- Auer, Charles, Frank Kover, James Aidala, Marks Greenwood. “Toxic Substances: A Half Century of Progress.” EPA Alumni Association. March 2016.
- Steenland, Kyle; Fletcher, Tony; Savitz, David A. (2010). "Epidemiologic Evidence on the Health Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA)". Environmental Health Perspectives. 118 (8): 1100–8. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901827. PMC 2920088. PMID 20423814.
- Associated Press (19 September 2015). "Grissom officials: Well tests show no chemical pollution". LIN Television Corporation. Retrieved 19 September 2015.
- Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP), Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (ESTCP) Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): Analytical and Characterization Frontiers webinarslides, January 28, 2016
- Lustgarten, Abrahm (2018-06-20). "Suppressed Study: The EPA Underestimated Dangers of Widespread Chemicals". ProPublica. Lisa Song, Talia Buford. Retrieved 2018-06-23.
- Associated Press (2017-07-31). "Air Force won't pay for towns' water contamination costs". Air Force Times. Retrieved 2018-06-23.
- Above the minimum reporting levels required by the EPA − 70 parts per trillion (ng/L) for PFOS and PFOA
- Unsafe levels of toxic chemicals found in drinking water for 6 million Americans Science X network, phys.org, August 9, 2016
External links
