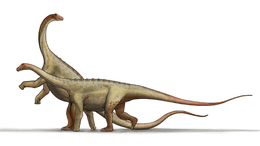Leinkupal
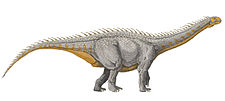
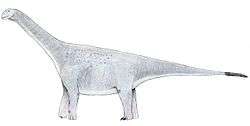
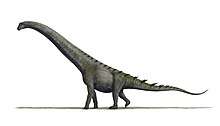
Leinkupal is a genus of diplodocine sauropod known from the Early Cretaceous (Late Berriasian to Early Valanginian stage) of the Bajada Colorada Formation, southeastern Neuquén Basin in the Neuquén Province of Argentina. It contains a single species, Leinkupal laticauda.[1]
| Leinkupal | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Cervical and dorsal vertebrae | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | †Sauropodomorpha |
| Clade: | †Sauropoda |
| Family: | †Diplodocidae |
| Subfamily: | †Diplodocinae |
| Genus: | †Leinkupal Gallina et al., 2014 |
| Type species | |
| †Leinkupal laticauda Gallina et al., 2014 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
History of discovery


In 2010 and 2012, at Picún Leufu in Neuquén Province, remains were uncovered of several types of sauropods. One of these was a diplodocoid new to science.[1]
In 2014, the type species Leinkupal laticauda was named and described by Pablo Gallina, Sebastián Apesteguía, Alejandro Haluza and Juan Canale. The generic name combines the Mapudungun lein, "vanishing", and kupal, "family", in reference to Leinkupal being the last, or youngest, known species of the Diplodocidae. The specific name is derived from Latin, latus, "wide", and cauda, "tail", in reference to the broad caudal vertebrae.[1]
The holotype, MMCH-Pv 63-1, was found in a layer of the Bajada Colorado Formation dating from the Berriasian–Valanginian. It consists of a front tail vertebra. As paratypes were assigned: MMCH-Pv 63-2/3: two front tail vertebrae; MMCH-Pv 63-4: a hind tail vertebra, MMCH-Pv 63-5: a front dorsal vertebra, MMCH-Pv 63-6: a front tail vertebra; and MMCH-Pv 63-7/8: two vertebrae of the middle tail. Additional possible material has been discovered but was not referred as its identity was uncertain.[1]
Leinkupal was a relatively small sauropod, with an estimated body length of nine metres. Several unique derived traits, or autapomorphies, could be established. The front tail vertebrae have extremely well-developed transverse processes, as long as the width of the vertebral body, expanded sideways and to below, and possessing robust reinforcing ridges on their top and bottom surfaces. The front tail vertebrae have very robust ridges running between the vertebral body and the front joint processes, the prezygapophyses. The front tail vertebrae have rear joint processes, postzygapophyses, with two paired pneumatic openings at their inner bases, opposite from the joint facets.[1]
Classification

Leinkupal was placed in the Diplodocinae within the Diplodocidae. A cladistic analysis indicated it was a possible sister species of Tornieria, discovered in Africa. As the latter genus lived much earlier, during the Late Jurassic, this would imply that the Diplodocoidea had an early origin, no later than the Middle Jurassic. The affinity between Leinkupal and Tornieria could be explained by either an early radiation of diplodocines or a later colonising of South-America from Africa. Leinkupal is the only known unequivocal diplodocid from South-America and the youngest unequivocal diplodocid globally, the only known from the Cretaceous.[1]
Cladogram of the Diplodocidae after Tschopp, Mateus, and Benson (2015).[2]
| Diplodocidae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Palaeoenvironment
Leinkupal was discovered in the Bajada Colorada Formation. This formation is composed of red and greenish brown sandstones and conglomerates of fine to coarse grain, in addition to prominent bands of tan siltstones and reddish claystones. These deposits represent a fluvial environment with braided rivers. Paleosols and channels with cross-stratification are present. Leinkupal shared its habitat with several theropods including basal tetanurans, possible deinonychosaurians, and possible abelisauroids, in addition to the dicraeosaurid sauropod Bajadasaurus.[1][3]
References
- Gallina, P. A.; Apesteguía, S. N.; Haluza, A.; Canale, J. I. (2014). "A Diplodocid Sauropod Survivor from the Early Cretaceous of South America". PLoS ONE. 9 (5): e97128. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...997128G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097128. PMC 4020797. PMID 24828328.
- Tschopp, E.; Mateus, O. V.; Benson, R. B. J. (2015). "A specimen-level phylogenetic analysis and taxonomic revision of Diplodocidae (Dinosauria, Sauropoda)". PeerJ. 3: e857. doi:10.7717/peerj.857. PMC 4393826. PMID 25870766.
- Gallina, P. A.; Apesteguía, S.; Canale, J. I.; Haluza, A. (2019). "A new long-spined dinosaur from Patagonia sheds light on sauropod defense system". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 1392. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.1392G. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-37943-3. PMC 6362061. PMID 30718633.