Mapuche language
Mapuche or Mapudungun[6] (from mapu 'land' and dungun 'speak, speech') is an Araucanian language related to Huilliche spoken in south-central Chile and west central Argentina by the Mapuche people (from mapu 'land' and che 'people'). It is also spelled Mapuzugun and Mapudungu. It was formerly known as Araucanian,[6] the name given to the Mapuche by the Spaniards; the Mapuche avoid it as a remnant of Spanish colonialism.
| Mapuche | |
|---|---|
| Mapudungun | |
| Native to | Chile, Argentina |
| Ethnicity | 1.7 million Mapuche[1][2] |
Native speakers | 260,000 (2007)[3] |
Araucanian
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Galvarino (Chile)[4] Padre Las Casas, Chile |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | arn |
| ISO 639-3 | arn |
| Glottolog | mapu1245[5] |
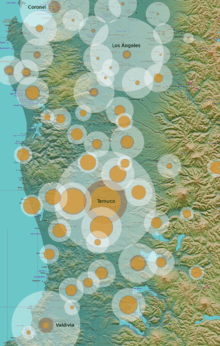 Core region of mapuche population 2002 by counties.
Orange: rural Mapuche; Dark: urban Mapuche; White: non-Mapuche inhabitants Surfaces of circles are adjusted to 40 inhabitants/km2. | |
Mapudungun is not an official language of Chile or Argentina and has received virtually no government support throughout its history. It is not used as a language of instruction in either country’s educational system despite the Chilean government's commitment to provide full access to education in Mapuche areas in southern Chile. There is an ongoing political debate over which alphabet to use as the standard alphabet of written Mapudungun. There are approximately 144,000 native speakers in Chile and another 8,400 in west central Argentina.
Only 2.4% of urban speakers and 16% of rural speakers use Mapudungun when speaking with children, and only 3.8% of speakers aged 10–19 years in the south of Chile (the language’s stronghold) are "highly competent" in the language.[7]
Speakers of Chilean Spanish who also speak Mapudungun tend to use more impersonal pronouns when speaking Spanish.[8]
Name
Depending on the alphabet, the sound /tʃ/ is spelled ⟨ch⟩ or ⟨c⟩, and /ŋ/ as ⟨g⟩ or ⟨ng⟩. The language is called either the "speech (d/zuŋun) of the land (mapu)" or the "speech of the people (tʃe)". An ⟨n⟩ may connect the two words. There are thus several ways to write the name of the language:
| Alphabet | Mapu with N | Mapu without N | Che/Ce |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ragileo | Mapunzugun[9] | Mapuzugun | Cezugun |
| Unified | Mapundungun | Mapudungun | Chedungun |
| Azümchefe | Mapunzugun | Mapuzugun | Chezugun |
| Wirizüŋun | Mapunzüŋun | Mapuzüŋun | Chezüŋun |
History
Prehistory
Moulian et al. (2015) argue that the Puquina language influenced Mapuche language long before the rise of the Inca Empire.[10] This areal linguistic influence may have arrived with a migratory wave arising from the collapse of the Tiwanaku Empire around 1000 CE.[10][11]
There is a more recent lexical influence from the Quechuan languages (pataka 'hundred', warangka 'thousand') associated with the Inca Empire and from Spanish.
As result of Inca rule there was some Mapudungun–Imperial Quechua bilingualism among Mapuches of Aconcagua Valley at the arrival of the Spanish in the 1530s and 1540s.[12]
The finding of many Chono toponyms in Chiloé Archipelago, where Veliche, a variant of Mapuche language has been dominant suggest Mapuche language displaced Chono language there prior to the arrival of the Spanish in the mid-16th century.[13] A theory postulated by chronicler José Pérez García holds the Cuncos settled in Chiloé Island in Pre-Hispanic times as consequence of a push from more northern Huilliches who in turn were being displaced by Mapuches.[14]
Spanish–Mapuche bilingualism in colonial times
As the 16th and 17th century Central Chile was becoming a melting pot for uprooted indigenous peoples[15] it has been argued that Mapuche, Quechua and Spanish coexisted there, with significant biligualism, during the 17th century.[16] However the indigenous language that has influenced Chilean Spanish the most is Quechua rather than Mapuche.[16]
In colonial times many Spanish and mestizo spoke Mapuche language. For example in the 17th century many soldiers at the Valdivian Fort System were bilingual.[17]
During the 17th and 18th centuries most of Chiloé Archipelago's population was bilingual and according to John Byron many Spaniards preferred to use the local Huilliche language because they considered it more beautiful.[18] Around the same time, Governor Narciso de Santa María complained that Spanish settlers in the islands could not speak Spanish properly, but could speak Veliche, and that this second language was more used.[19]
Further decline
Mapudungun was once the only language spoken in central Chile. The sociolinguistic situation of the Mapuche has changed rapidly. Now, nearly all of Mapuche people are bilingual or monolingual in Spanish. The degree of bilingualism depends on the community, participation in Chilean society, and the individual's choice towards the traditional or modern/urban way of life.[20]
Dialects
| Dialect sub-groups | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cladogram showing the closeness of Mapuche dialect sub-groups based on shared features according to Robert A. Croese. Dialect sub-groups are roughly ordered from their geographical distribution from north to south.[21] |
Linguist Robert A. Croese divides Mapudungun into eight dialectal sub-groups (I-VIII). Sub-group I is centered in Arauco Province, Sub-group II is the dialect of Angol, Los Ángeles and the middle and lower Bío Bío River. Sub-group III is centered around Purén. In the areas around Lonquimay, Melipeuco and Allipén River dialect sub-group IV is spoken. Sub-group V is spoken at the coast of Araucanía Region including Queule, Budi Lake and Toltén.
Temuco is the epicenter of the Mapuche territory today.[22] Around Temuco, Freire and Gorbea the sub-group VI is spoken. Group VII is spoken in Valdivia Province plus Pucón and Curarrehue. The last "dialect" sub-group is VIII which is the Huilliche language spoken from Lago Ranco and Río Bueno to the south and is not mutually intelligible with the other dialects.[21]
These can be grouped in four dialect groups: north, central, south-central and south. These are further divided into eight sub-groups: I and II (northern), III–IV (central), V-VII (south-central) and VIII (southern). The sub-groups III-VII are more closely related to each other than they are to I-II and VIII. Croese finds these relationships as consistent, but not proof, with the theory of origin of the Mapuche proposed by Ricardo E. Latcham.[21]
The Mapudungun spoken in the Argentinean provinces of Neuquen and Rio Negro is similar to that of the central dialect group in Chile, while the Ranquel (Ranku ̈lche) variety spoken in the Argentinean province of La Pampa is closer to the northern dialect group.[23]
Phonology
Prosody
Mapudungun has partially predictable, non-contrastive stress. The stressed syllable is generally the last one if it is closed (awkán 'game', tralkán 'thunder'), and the one before last if the last one is open (rúka 'house', lóngko 'head'). There is no phonemic tone.
Vowels
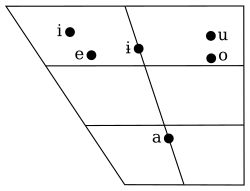
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | ɨ | o |
| Open | a |
- Sadowsky et al. transcribe the vowels with ⟨ɪ, ɘ, ʊ, ë, ö, ɐ̝⟩.[24] This article follows the traditional transcription ⟨i, ɨ, u, e, o, a⟩.
- In stressed syllables, /i, u/ are near-close [ɪ, ʊ], whereas the mid /e, o/ are centralized close-mid [ë, ö]. The open vowel is realized as a raised open central [ɐ], making it sound closer to [ɜ] than to [ä]. Unstressed vowels are more close [i, u, ɪ, ʊ, ə] (though unstressed /e, o/ are still somewhat more open than stressed /i, u/). Utterance-final unstressed vowels are generally devoiced or even elided when they occur after voiceless consonants, sometimes even after voiced consonants.[25]
- Traditionally, /ɨ/ has been described as a close central vowel with an unstressed mid central allophone. According to Sadowsky et al., the vowel is close-mid [ɘ] when stressed and near-close [ɨ̞] when unstressed, patterning phonetically with the mid series.[26]
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Postalveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | (n̪) | n | ɲ | ŋ | |||
| Stop | p | (t̪) | t | tʃ | ʈʂ | k | ||
| Fricative | f | θ | s | ʃ | ɣ | |||
| Approximant | central | ɻ | j | w | ||||
| lateral | (l̪) | l | ʎ | |||||
- /m, p/ are bilabial, whereas /f/ is labiodental.[7]
- The dental series /n̪, t̪, l̪/ is phonetically interdental and occurs only in some dialects.[27]
- Utterance-final coronal laterals /l̪, l/ may be devoiced and fricated: [ɬ̪, ɬ]. [28]
- The plosives may be aspirated. It is often the case with the main allophone of /k/ ([k]). Its fronted allophone [c] is less frequently aspirated, as is the alveolar /t/. When it comes to the dental /t̪/ as well as the bilabial /p/, aspiration is even rarer.[29]
- Some speakers realize /ʈʂ/ as apical postalveolar, either an affricate or an aspirated plosive.[28]
- /ɻ/ has been traditionally classified as an approximant; however, Sadowsky et al. prefer to classify it as a fricative [ʐ] as that is the predominant variant in their sample. Other possible variants include a lateral approximant [ɭ] and, in post-nuclear position, a voiceless fricative [ʂ].[30]
- /j/ may be realized with frication: [ʝ].[28]
- Among the velar consonants, /w/ is labialized. Before front vowels, /ŋ, k, ɣ/ are fronted to [ŋ˖, c, ɣ˖~ʝ].[27]
Orthography

The Mapuche had no writing system before the Spanish arrived, but the language is now written with the Latin script. Although the orthography used in this article is based on the Alfabeto Mapuche Unificado, the system used by Chilean linguists and other people in many publications in the language, the competing Ragileo, Nhewenh and Azumchefi systems all have their supporters, and there is still no consensus among authorities, linguists and Mapuche communities. The same word can look very different in each system, with the word for "conversation or story" being written either gvxam, gytram, or ngütram, for example.[31]
Microsoft lawsuit
In late 2006, Mapuche leaders threatened to sue Microsoft when the latter completed a translation of their Windows operating system into Mapudungun. They claimed that Microsoft needed permission to do so and had not sought it.[32][33] The event can be seen in the light of the greater political struggle concerning the alphabet that should become the standard alphabet of the Mapuche people.
Morphology
- Mapuche is an agglutinative language.[34] The word order of Mapudungun is flexible, but a topic–comment construction is common. The subject (agent) of a transitive clause tends to precede the verb, and the object tends to follow (A–V–O order); the subject of an intransitive clause tends to follow the verb (V–S order).[20]
- Most complex verb formations in Mapudungun are constructed with five or six morphemes.[35]
- Nouns are grouped in two classes, animate and inanimate. For example, pu is a plural indicator for animate nouns and yuka as the plural for inanimate nouns. Chi (or ti) can be used as a definite animate article, as in chi wentru 'the man' and chi pu wentru for 'the men'. The number kiñe 'one' serves as an indefinite article. Subjects and objects use the same case.[36]
- There are, for personal pronouns, three persons and three numbers: iñche 'I', iñchiw 'we (2)', iñchiñ 'we (more than 2)'; eymi 'you', eymu 'you (2)', eymün 'you (more than 2)'; fey 'he/she/it', feyengu 'they (2)', feyengün 'they (more than 2)'.
- Possessive pronouns are related to the personal forms: ñi 'my; his, her; their', yu 'our (2)', iñ 'our (more than 2)'; mi 'your', mu 'your (2)', mün 'your (more than 2)'. They are often found with a particle ta, which does not seem to add anything specific to the meaning: tami 'your'.
- Interrogative pronouns include iney 'who', chem 'what', chumül 'when', chew 'where', chum(ngechi) 'how' and chumngelu 'why'.
- Mapudungu uses particles, which is a small group of morphemes that enable the speaker to express how they feel about what they have said. Examples include chi (doubt), am (surprise), nga (regret), llemay (certainty), chemay (amazement), chiam (wonder), amfe (exclamation). There are also more complicated particles such as kay, which suggest the information about to be said is in contrast to what was just said. Another complex particle is may, which is used when the speaker expects to get a positive reaction from what they are saying. One particle, anchi, refers to the subject of the sentence, and an example would be "chem anchi?" which translates to what [is] that (pointed out)?[37]
- "An inflection can be added to a noun with -mew or -mu. This suffix can refer to time, place, cause or comparison.[22] "An example of this is the sentence
Mesa-mew müle-y ti mamüllü ñi müle-n mi tukupu-a-l.
table-loc be-ind/3sS the wood poss be-noml 2s.poss use-nrld-noml
‘On the table is the wood that you should use.’ [38]
- Numbers from 1 to 10 are as follows: 1 kiñe, 2 epu, 3 küla, 4 meli, 5 kechu, 6 kayu, 7 regle, 8 pura, 9 aylla, 10 mari; 20 epu mari, 30 küla mari, 110 (kiñe) pataka mari. Numbers are extremely regular in formation, which is comparable to Chinese and Wolof, or to constructed languages such as Esperanto.
- Verbs can be finite or non-finite (non-finite endings: -n, -el, -etew, -lu, -am, etc.), are intransitive or transitive and are conjugated according to person (first, second and third), number (singular, dual and plural), voice (active, agentless passive and reflexive-reciprocal, plus two applicatives) and mood (indicative, imperative and subjunctive). In the indicative, the present (zero) and future (-(y)a) tenses are distinguished. There are a number of aspects: the progressive, resultative and habitual are well established; some forms that seem to mark some subtype of perfect are also found. Other verb morphology includes an evidential marker (reportative-mirative), directionals (cislocative, translocative, andative and ambulative, plus an interruptive and continuous action marker) and modal markers (sudden action, faked action, immediate action, etc.). There is productive noun incorporation, and the case can be made for root compounding morphology.
- "Spanish loan verbs have generally been adapted into Mapudungu in the third person singular form. An example is the Mapudungu verb for "to be able" is "pwede," and the Spanish translation for "he can" is "puede."[22]
The indicative present paradigm for an intransitive verb like konün 'enter' is as follows:
| Number | ||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | ||
| Person | First | konün
( ← kon-n) |
koniyu
( ← kon-i-i-u) |
koniyiñ
( ← kon-i-i-n) |
| Second | konimi
( ← kon-i-m-i) |
konimu
( ← kon-i-m-u) |
konimün
( ← kon-i-m-n) | |
| Third | koni
( ← kon-i-0-0) |
koningu
( ← kon-i-ng-u) |
koningün
( ← kon-i-ng-n) | |
What some authors have described as an inverse system (similar to the ones described for Algonquian languages) can be seen from the forms of a transitive verb like pen 'see'. The 'intransitive' forms are the following:
| Number | ||||
| Singular | Dual | Plural | ||
| Person | First | pen
( ← pe-n) |
peyu
( ← pe-i-i-u) |
peiñ
( ← pe-i-i-n) |
| Second | peymi
( ← pe-i-m-i) |
peymu
( ← pe-i-m-u) |
peymün
( ← pe-i-m-n) | |
| Third | pey
( ← pe-i-0-0) |
peyngu
( ← pe-i-ng-u) |
peyngün
( ← pe-i-ng-n) | |
The 'transitive' forms are the following (only singular forms are provided here):
| Agent | ||||
| First | Second | Third | ||
| Patient | First | pewün
( ← pe-w-n) |
peen
( ← pe-e-n) |
peenew
( ← pe-e-n-mew) |
| Second | peeyu
( ← pe-e-i-u) |
pewimu
( ← pe-w-i-m-u) |
peeymew
( ← pe-e-i-m-i-mew) | |
| Third | pefiñ
( ← pe-fi-n) |
pefimi
( ← pe-fi-i-m-i) |
DIR pefi / INV peeyew / REFL pewi
( ← pe-fi-i-0-0 / pe-e-i-0-0-mew / pe-w-i-0-0) | |
When a third person interacts with a first or second person, the forms are direct (without -e) or inverse (with -e); the speaker has no choice. When two third persons interact, two different forms are available: the direct form (pefi) is appropriate when the agent is topical (the central figure in that particular passage). The inverse form (peenew) is appropriate when the patient is topical. Thus, chi wentru pefi chi domo means 'the man saw the woman' while chi wentru peeyew chi domo means something like 'the man was seen by the woman'. However, that it is not a passive construction; the passive would be chi wentru pengey 'the man was seen; someone saw the man'. Therefore, a better translation may be 'it was the woman who saw the man' or 'the woman was the one who saw the man'.
Language revitalization efforts
The Chilean Ministry of Education created the Office of Intercultural Bilingual Education in 1996 in an attempt to include indigenous language in education. By 2004, there were still no programs in public schools in Santiago, despite the fact that 50% of the country’s Mapuche population resides in and around the area of Santiago. 30.4% of Mapuche students never graduate eighth grade and they have high rates of poverty. Most language revitalization efforts have been in rural communities and these efforts have been received in different ways by the Mapuche population: Ortiz says some feel that teaching Mapudungu in schools will set their children behind other Chileans, which reveals that their culture has been devalued by the Chilean government for so long that, unfortunately, some Mapuche people have come to see their language as worthless, too, which is a direct and lasting impact of colonization.[39] Despite the absence of Mapudungun instruction in public schools, there are limited language course offerings at select Chilean universities, such as Pontifical Catholic University of Chile.[40]
Studies
Older works
The formalization and normalization of Mapudungun was effected by the first Mapudungun grammar published by the Jesuit priest Luis de Valdivia in 1606 (Arte y Gramatica General de la Lengva que Corre en Todo el Reyno de Chile). More important is the Arte de la Lengua General del Reyno de Chile by the Jesuit Andrés Fabrés (1765, Lima) composed of a grammar and dictionary. In 1776 three volumes in Latin were published in Westfalia (Chilidúgú sive Res Chilenses) by the German Jesuit Bernhard Havestadt. The work by Febrés was used as a basic preparation from 1810 for missionary priests going into the regions occupied by the Mapuche people. A corrected version was completed in 1846 and a summary, without a dictionary in 1864. A work based on Febrés' book is the Breve Metodo della Lingua Araucana y Dizionario Italo-Araucano e Viceversa by the Italian Octaviano de Niza in 1888. It was destroyed in a fire at the Convento de San Francisco in Valdivia in 1928.
Modern works
The most comprehensive works to date are the ones by Augusta (1903, 1916). Salas (1992, 2006) is an introduction for non-specialists, featuring an ethnographic introduction and a valuable text collection as well. Zúñiga (2006) includes a complete grammatical description, a bilingual dictionary, some texts and an audio CD with text recordings (educational material, a traditional folktale and six contemporary poems). Smeets (1989) and Zúñiga (2000) are for specialists only. Fernández-Garay (2005) introduces both the language and the culture. Catrileo (1995) and the dictionaries by Hernández & Ramos are trilingual (Spanish, English and Mapudungun).
- Gramática mapuche bilingüe, by Félix José de Augusta, Santiago, 1903. [1990 reprint by Séneca, Santiago.]
- Idioma mapuche, by Ernesto Wilhelm de Moesbach, Padre Las Casas, Chile: San Francisco, 1962.
- El mapuche o araucano. Fonología, gramática y antología de cuentos, by Adalberto Salas, Madrid: MAPFRE, 1992.
- El mapuche o araucano. Fonología, gramática y antología de cuentos, by Adalberto Salas, edited by Fernando Zúñiga, Santiago: Centro de Estudios Públicos, 2006. [2nd (revised) edition of Salas 1992.] ISBN 956-7015-41-4
- A Mapuche grammar, by Ineke Smeets, Ph.D. dissertation, Leiden University, 1989.
- Mapudungun, by Fernando Zúñiga, Munich: Lincom Europa, 2000. ISBN 3-89586-976-7
- Parlons Mapuche: La langue des Araucans, by Ana Fernández-Garay. Editions L'Harmattan, 2005, ISBN 2-7475-9237-5
- Mapudungun: El habla mapuche. Introducción a la lengua mapuche, con notas comparativas y un CD, by Fernando Zúñiga, Santiago: Centro de Estudios Públicos, 2006. ISBN 956-7015-40-6
- A Grammar of Mapuche, by Ineke Smeets. Berlin / New York: Mouton de Gruyter, 2008. ISBN 978-3-11-019558-3
Dictionaries
- Félix José de Augusta, Diccionario araucano, Santiago de Chile: Imprenta Universitaria, 1916 (Tomo primero ; Tomo segundo) [1996 reprint by Cerro Manquehue, Santiago.] ISBN 956-7210-17-9*
- María Catrileo, Diccionario lingüístico-etnográfico de la lengua mapuche. Mapudungun-español-English, Santiago: Andrés Bello, 1995.
- Esteban Erize, Diccionario comentado mapuche-español, Bahía Blanca: Yepun, 1960.
- Ana Fernández Garay, Ranquel-español/español-ranquel. Diccionario de una variedad mapuche de la Pampa (Argentina), Leiden: CNWS (Leiden University), 2001. ISBN 90-5789-058-5
- Arturo Hernández and Nelly Ramos, Diccionario ilustrado mapudungun-español-inglés, Santiago: Pehuén, 1997.
- Arturo Hernández and Nelly Ramos, Mapuche: lengua y cultura. Mapudungun-español-inglés, Santiago: Pehuén, 2005. [5th (augmented) edition of their 1997 dictionary.]
- Muñoz Urrutia, Rafael, ed. (2006). Diccionario Mapuche: Mapudungun/Español, Español/Mapudungun (2ª edición). Santiago de Chile: Editorial Centro Gráfico Ltda. ISBN 956-8287-99-X.
Mapudungun language courses
- Mapudunguyu 1. Curso de lengua mapuche, by María Catrileo, Valdivia: Universidad Austral de Chile, 2002.
- Manual de aprendizaje del idioma mapuche: Aspectos morfológicos y sintácticos, by Bryan Harmelink, Temuco: Universidad de la Frontera, 1996. ISBN 956-236-077-6
References
- "Censo Nacional de Población, Hogares y Viviendas 2010: Resultados definitivos: Serie B No 2: Tomo 1" (PDF) (in Spanish). INDEC. p. 281. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 5 December 2015.
- "2012 census". Censo.cl. Retrieved 2013-09-25.
- Mapuche at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- "Galvarino es la primera comuna de Chile en establecer el mapudungún como su idioma oficial". Radio Bío-Bío (in Spanish). 7 August 2013. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Mapudungun". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Heggarty, P.; Beresford-Jones, D. (2013). "Andes: linguistic history.". In Ness, I.; P., Bellwood (eds.). The Encyclopedia of Global Human Migration. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 401–409.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), p. 88.
- Hurtado Cubillos, Luz Marcela (2009). "La expresión de impersonalidad en el español de Chile". Cuadernos de lingüística hispánica (in Spanish). 13: 31–42.
- La Nacion (Chile) "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-08-03. Retrieved 2009-11-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Moulian, Rodrígo; Catrileo, María; Landeo, Pablo (2015). "Afines quechua en el vocabulario mapuche de Luis de Valdivia" [Akins Quechua words in the Mapuche vocabulary of Luis de Valdivia]. Revista de lingüística teórica y aplicada (in Spanish). 53 (2). doi:10.4067/S0718-48832015000200004. Retrieved January 13, 2019.
- Dillehay, Tom D.; Pino Quivira, Mario; Bonzani, Renée; Silva, Claudia; Wallner, Johannes; Le Quesne, Carlos (2007) Cultivated wetlands and emerging complexity in south-central Chile and long distance effects of climate change. Antiquity 81 (2007): 949–960
- Téllez 2008, p. 43.
- Ibar Bruce, Jorge (1960). "Ensayo sobre los indios Chonos e interpretación de sus toponimías". Anales de la Universidad de Chile. 117: 61–70.
- Alcamán, Eugenio (1997). "Los mapuche-huilliche del Futahuillimapu septentrional: Expansión colonial, guerras internas y alianzas políticas (1750-1792)" (PDF). Revista de Historia Indígena (in Spanish) (2): 29–76. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-12-28.
- "Migraciones locales y asentamiento indígena en las estancias españolas de Chile central, 1580-1650". Historia (in Spanish). 49 (1). 2016. doi:10.4067/S0717-71942016000100004.
- Hernández Salles, Arturo (1981). "Influencia del mapuche en el castellano". Documentos Lingüísticos y Literarios (in Spanish). 7: 34–44.
- Urbina C., María Ximena (2017). "La expedición de John Narborough a Chile, 1670: Defensa de Valdivia, rumeros de indios, informaciones de los prisioneros y la creencia en la Ciudad de los Césares" [John Narborough expedition to Chile, 1670: Defense of Valdivia, indian rumours, information on prisoners, and the belief in the City of the Césares]. Magallania. 45 (2). doi:10.4067/S0718-22442017000200011. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- Byron, John. El naufragio de la fragata "Wager". 1955. Santiago: Zig-zag.
- Cárdenas A., Renato; Montiel Vera, Dante; Grace Hall, Catherine (1991). Los chono y los veliche de Chiloé (PDF) (in Spanish). Santiago de Chile: Olimpho. p. 277.
- Gruyter, Mouton. A Grammar of Mapuche. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter GmbH and Co., 2008. Print.
- Croese, Robert A. (1985). "21. Mapuche Dialect Survey". In Manelis Klein, Harriet; Stark, Louisa R. (eds.). South American Indian Languages: Retrospect and Prospect. Austin, Texas: University of Texas Press. pp. 784–801. ISBN 0-292-77592-X.
- (Smeets, Ineke (2008). A Grammar of Mapuche. Mouton de Gruyter.)
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), p. 87.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), p. 92.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), pp. 92–94.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), pp. 92–93.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), pp. 88–89.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), p. 91.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), p. 89.
- Sadowsky et al. (2013), p. 90.
- "LOS DIFERENTES GRAFEMARIOS Y ALFABETOS DEL MAPUDUNGUN" Archived 2013-12-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Guerra idiomática entre los indígenas mapuches de Chile y Microsoft. El Mundo / Gideon Long (Reuters), 28 November 2006
- Smeets, Ineke (2008). A Grammar of Mapuche. Mouton de Gruyter.
- (Monson et al. (2004) Data Collection and Analysis of Mapudungun Morphology for Spelling Correction. Language Technologies Institute Carnegie Mellon University)
- http://wals.info/languoid/lect/wals_code_map
- (Smeets, Ineke (2008). A Grammar of Mapuche. Mouton de Gruyter.) to the morphology section.
- (Baker, Mark C. On the Loci of Agreement: Inversion Constructions in Mapudungu. Rutgers University)
- (Ortiz, Patricio R. (2009) Indigenous Knowledge and Language: Decolonizing Culturally Relevant Pedagogy in a Mapuche Intercultural Bilingual Education Program in Chile. Canadian Journal of Indigenous Education, 32, 93-114.)
- ( http://artesycultura.uc.cl/en/creation-research/arts-projects-catalog/231-la-construccion-de-una-identidad-hibrida-en-los-escritos-de-manuel-manquilef)
Bibliography
- Aprueban alfabeto mapuche único (Oct 19, 1999). El Mercurio de Santiago.
- Campbell, Lyle (1997) American Indian languages: The historical linguistics of Native America. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-509427-1.
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos (2005) Encuesta Complementaria de Pueblos Indígenas (ECPI), 2004-2005 - Primeros resultados provisionales. Buenos Aires: INDEC. ISSN 0327-7968.
- Sadowsky, Scott; Painequeo, Héctor; Salamanca, Gastón; Avelino, Heriberto (2013), "Mapudungun", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 43 (1): 87–96, doi:10.1017/S0025100312000369
- Téllez, Eduardo (2008). Los Diaguitas: Estudios (in Spanish). Santiago, Chile: Ediciones Akhilleus. ISBN 978-956-8762-00-1.
External links
| Mapuche language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Mapudungun |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mapudungun language. |
| Look up Category:Mapudungun language in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Sound Comparisons: Mapudungun containing audio recordings and phonetic transcriptions of 37 regional varieties of Mapudungun.
- Mapudungun Vocabulary List (from the World Loanword Database)
- Mapudungun Swadesh vocabulary list (from Wiktionary's Swadesh-list appendix)
- Spanish-Mapudungun glossary
- Mapudungun-Spanish Dictionary from the U. Católica de Temuco
- Mapuche-Spanish dictionary
- Freelang Dictionary
- Audio recordings of short songs in Mapudungun with transcriptions and translations from the Mapuche Collection of Magnus Course at AILLA.
- Argentinian Languages Collection of Lucía Golluscio containing audio recordings of Mapudungun from the Archive of the Indigenous Languages of Latin America.
- Mapudungun (Intercontinental Dictionary Series)