Iuticosaurus
Iuticosaurus (meaning "Jute lizard") is a genus of titanosaur sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of the Isle of Wight.[1] Two species have been named: I. valdensis and I. lydekkeri.[2] I. valdensis was found in the Wessex Formation and I. lydekkeri in the younger Upper Greensand.
| Iuticosaurus | |
|---|---|
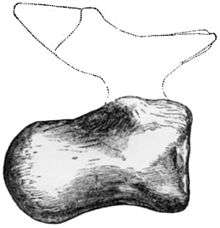 | |
| Lectotype caudal vertebra of I. valdensis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Infraorder: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Genus: | †Iuticosaurus le Loeuff e.a., 1993 |
| Type species | |
| †Iuticosaurus valdensis (von Huene, 1929) | |
| Other species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
History and taxonomy
In 1887 Richard Lydekker described two sauropod tail vertebrae found by William D. Fox near Brook Bay on Wight, BMNH R146a and BMNH 151, and referred them to the genus Ornithopsis, despite indicating their similarity to Titanosaurus, because the tail of Ornithopsis was unknown.[3] On reading the paper to the Geological Society of London, Lydekker was criticised by Harry Govier Seeley and John Hulke for his choice and in 1888 he referred to the fossils as Titanosaurus sp. a, Titanosaurus sp. b being a third vertebra, BMNH 32390.[4]
In 1929 Friedrich von Huene named both taxa as full species. The first became Titanosaurus Valdensis, the specific name referring to the Wealden, the second Titanosaurus Lydekkeri, its specific name honouring Lydekker.[5] By present convention both specific names would be spelled as T. valdensis and T. lydekkeri respectively.
In 1993 Jean le Loeuff redescribed the material and named a separate genus: Iuticosaurus, the generic name referring to the Jutes who settled the island in the fifth century and established a Jute dynasty in the sixth century. Le Loeuff made Iuticosaurus valdensis the type species, and chose BMNH 151 as the lectotype. Another vertebra, BMNH R 1886, was referred by him to this species. The second species, though formally named by him as Iuticosaurus lydekkeri, he considered a nomen dubium.[2]
Description
Iuticosaurus was probably similar to Titanosaurus. It measured 15 to 20 metres (49–65 feet) long.[2]
Classification
Most researchers have concluded that both species of Iuticosaurus cannot be distinguished from other titanosaurs and are therefore nomina dubia.
References
- Iuticosaurus on DinoWight
- J. le Loeuff, E. Buffetaut, M. Martin, V. Martin & H. Tong, 1993, "Découverte d'Hadrosauridae (Dinosauria, Ornithischia) dans le Maastrichtien des Corbières (Aude, France)", Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série II 316: 1023-1029
- Lydekker, R., 1887, "On certain dinosaurian vertebrae from the Cretaceous of India and the Isle of Wight", Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London 43: 157–160
- Lydekker, R., 1888, Catalogue of fossil reptilia and Amphibia in the British Museum. Pt. I. Containing the orders Ornithosauria, Crocodilia, Dinosauria, Squamata, Rhynchocephalia, and Proterosauria, British Museum of Natural History, London, 309 pp
- Huene, F. v. 1929, "Los saurisquios y ornitisquios del Cretáceo Argentino", Anales del Museo de La Plata (series 3) 3: 1–196