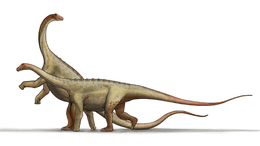Euskelosaurus
Euskelosaurus browni ("good leg lizard") is a semi-bipedal plateosaurid sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Late Triassic of South Africa and Lesotho. Fossils have only been recovered from the lower Elliot Formation in South Africa and Lesotho,[1] and in one locality in Zimbabwe.[2]
| Euskelosaurus Temporal range: Late Triassic | |
|---|---|
 | |
| E. africanus ishia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | †Sauropodomorpha |
| Family: | †Plateosauridae |
| Genus: | †Euskelosaurus |
| Species: | †E. browni |
| Binomial name | |
| †Euskelosaurus browni | |
History of Discovery
In 1863, Alfred Brown recovered fossil material consisting of limb bones and vertebrae, in the lower Elliot Formation in the southeastern Free State. In 1866, Thomas Henry Huxley first described Euskelosaurus from Brown's fossil material, and named the holotype specimen Euskelosaurus brownii after Brown.[3] Harry Seeley later described Euskelosaurus in 1894,[4] as did Friedrich von Huene in 1902. Since then, other researchers, including Robert Broom, have mentioned Euskelosaurus in their papers.[5][6][7][8][9]
Description
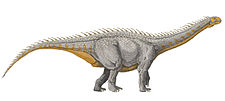
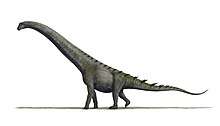
Euskelosaurus is considered to have been a large, robust member of the sauropodomorph clade. Estimates from the existing fossil material measure this dinosaur at about 10m in length. Its bones are robust and it had a graviportal limb arrangement, a key character trait of basal sauropodomorphs.[10][11][12]
Classification
While paleontologists currently consider Euskelosaurus a basal plateosaurid sauropodomorph, many paleontologists consider Euskelosaurus a “waste-basket” taxon. Its phylogenetic relationships are poorly understood and warrant further study.
References
- Gauffre, Francois-Xavier (1993). "Biochronostratigraphy of the Lower Elliot Formation, southern Africa) and preliminary results on the Maphutseng dinosaur. Saurischia: Prosauropoda) from the same Formation of Lesotho". In Lucas, Spencer G.; Morales, Michael (eds.). The Nonmarine Triassic: Bulletin 3. pp. 147–9.
- Cooper, M.R. (1980). "The first record of the prosauropod dinosaur Euskelosaurus from Zimbabwe". Arnoldia Zimbabwe. 9 (3): 1–17.
- Huxley, TH (1866). "On the remains of large dinosaurian reptiles from the Stormberg mountains, South Africa". Geological Magazine. 3: 563–4.
- Seeley, H.G. (1894). "XLI.—On Euskelesaurus Brownii (Huxley)". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 14 (83): 317–340. doi:10.1080/00222939408677811.
- Broom, R. (1911). "On the dinosaurs of the Stormberg, South Africa". Annals of the South African Museum. 7: 291–308.
- Van Heerden, J. (1979). The morphology and taxonomy of Euskelosaurus (Reptilia: Saurischia: Late Triassic) from South Africa. Nasionale Museum. OCLC 10876430.
- Welman, Johann (1999). "The basicranium of a basal prosauropod from the Euskelosaurus range zone and thoughts on the origin of dinosaurs". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 29 (1): 227–232. Bibcode:1999JAfES..29..227W. doi:10.1016/S0899-5362(99)00092-5.
- Yates, A.M. (2004). The death of a dinosaur: dismembering Euskelosaurus. Geoscience Africa. p. 715. ISBN 978-0-620-32470-0.
- Galton, Peter M. (1985). "Notes on the Melanorosauridae, a family of large Prosauropod Dinosaurs (Saurischia: Sauropodomorpha)". Geobios. 18 (5): 671–676. doi:10.1016/S0016-6995(85)80065-6.
- Durand, J.F. (2001). "The oldest juvenile dinosaurs from Africa". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 33 (3–4): 597–603. Bibcode:2001JAfES..33..597D. doi:10.1016/S0899-5362(01)00079-3.
- McPhee, Blair Wayne (2016). The South African Mesozoic: advances in our understanding of the evolution, palaeobiogeography, and palaeoecology of sauropodomorph dinosaurs (Thesis). hdl:10539/21644.
- McPhee, Blair W.; Choiniere, Jonah N. (2016). "A hyper-robust sauropodomorph dinosaur ilium from the Upper Triassic–Lower Jurassic Elliot Formation of South Africa: Implications for the functional diversity of basal Sauropodomorpha". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 123: 177–184. Bibcode:2016JAfES.123..177M. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.08.004.