Outline of Malaysia
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Malaysia:
.svg.png)
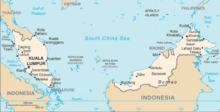
Malaysia is a sovereign country located on the Malay Peninsula and a northern portion of the Island of Borneo in Southeast Asia.[1] Malaysia comprises thirteen states and three federal territories with a total land area of 329,847 square kilometres (127,355 sq mi).[2] The capital of Malaysia is Kuala Lumpur, while Putrajaya is the seat of the federal government.
The population stands at over 25 million.[1] The country is separated into two regions—Peninsular Malaysia and Malaysian Borneo—by the South China Sea.[1] Malaysia borders Thailand, Indonesia, Singapore, Brunei, the Philippines,[1] and Vietnam. The country is located near the equator and experiences a tropical climate.[1]
Malaysia is headed by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong and politically led by a Prime Minister.[3][4] The government is closely modeled after the Westminster parliamentary system.[5]
General reference
- Pronunciation: /məˈleɪʒə/ or /məˈleɪziə/
- Common English country name: Malaysia
- Official English country name: Malaysia
- Common endonym(s): Malaysia
- Official endonym(s): Malaysia
- Adjectival(s): Malaysian
- Demonym(s): Malaysians
- Etymology: Name of Malaysia
- International rankings of Malaysia
- ISO country codes: MY, MYS, 458
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:MY
- Internet country code top-level domain: .my
History of Malaysia
Events and treaties
- Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824
- Burney Treaty
- Anglo-Siamese Treaty of 1909
- Battle of Malaya
- Sandakan Death Marches
- Brunei Revolt
- Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation
- May 13 incident
- Mat Salleh Rebellion
Small area histories
Politics of Malaysia
- Form of government: Federal constitutional elective monarchy and parliamentary democracy
- Capital of Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur
- Flag of Malaysia
- Elections in Malaysia
- Political parties in Malaysia
- National Front (Barisan Nasional)
- United Malays National OrganisationN1 (UMNO)
- Malaysian Chinese Association (MCA)
- Malaysian Indian Congress (MIC)
- Malaysian People's Movement Party (Gerakan)
- People's Progressive Party (PPP)
- United Traditional Bumiputera Party (PBB)
- Sarawak United People's Party (SUPP)
- Sabah Progressive Party (SAPP)
- Sabah United PartyN2 (PBS)
- Liberal Democratic Party (LDP)
- United Sabah People's Party (PBRS)
- United Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Organisation (UPKO)
- Sarawak Progressive Democratic Party (SPDP)
- Sarawak People's Party (PRS)
- Pact of Hope (Pakatan Harapan)
- People's Justice Party (Keadilan; PKR)
- Democratic Action Party (DAP)
- National Trust Party (AMANAH)
- Parti Pribumi Bersatu Malaysia (BERSATU; PBBM)
- Pan-Malaysian Islamic PartyN3 (PAS)
- Malaysian People's Party (PRM)
- Socialist Party of Malaysia (PSM)
- Malaysian Democratic Party (MDP)
- National Front (Barisan Nasional)
- Yang di-Pertuan Agong (King of Malaysia)
- Civil Service in Malaysia
Branches of the government of Malaysia
Executive branch of the government of Malaysia
- Head of state: Yang di-Pertuan Agong, Muhammad V
- Head of government: Prime Minister of Malaysia, Mahathir Mohamad
- Cabinet of Malaysia
- Ministries of Malaysia
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Education
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- Ministry of Higher Education
- Ministry of Internal Security (Malaysia)
- Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation
- Ministry of Women, Family and Community Development
- Ministry of the Federal Territories
Legislative branch of the government of Malaysia
Judicial branch of the government of Malaysia
Courts of Malaysia
- Federal Court of Malaysia
- Court of Appeal of Malaysia
- High Courts of Malaysia
- Syariah Court
Foreign relations of Malaysia
- Diplomatic missions in Malaysia
- Diplomatic missions of Malaysia
International organisation membership
Malaysia is a member of:[1]
|
|
Law and order in Malaysia
Military of Malaysia
Military of Malaysia
- Command
- Commander-in-chief: Supreme Commander of the Malaysian Armed Forces, Muhammad V of Kelantan
- Chief of Defence Forces: General (Jen) Tan Sri Zulkifli Zainal Abidin
- Forces
- Army of Malaysia
- Navy of Malaysia
- Air Force of Malaysia
- Malaysian Special Operations Force
- Military history of Malaysia
Geography of Malaysia
- Malaysia is: a megadiverse country
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Eurasia (both on the mainland and offshore)
- Time zone: Malaysian Standard Time = ASEAN Common Time (UTC+08)
- Extreme points of Malaysia
- High: Gunung Kinabalu 4,095 m (13,435 ft)
- Low: South China Sea and Indian Ocean 0 m
- Land boundaries: 2,669 km
-
- Coastline: 4,675 km
- Peninsular Malaysia 2,068 km
- East Malaysia 2,607 km
- Coastline: 4,675 km
- Population of Malaysia: 27,730,000 - 43rd most populous country
- Area of Malaysia: 329,847 km² - 66th largest country
- Atlas of Malaysia
- Malaysian Standard Time
Environment of Malaysia
- Climate of Malaysia
- Environmental issues in Malaysia
- List of ecoregions in Malaysia
- Renewable energy in Malaysia
- Protected areas of Malaysia
- National parks of Malaysia
- Wildlife of Malaysia
Natural geographic features of Malaysia
Regions of Malaysia
- West Malaysia (Peninsula Malaysia)
- East Malaysia (Malaysian Borneo)
Administrative divisions of Malaysia
Administrative divisions of Malaysia
States of Malaysia
States of Malaysia
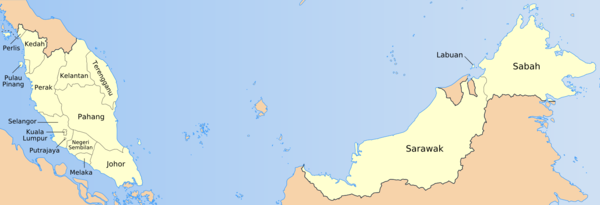
Malaysia has 13 states:
Federal territories of Malaysia
Malaysia also has three federal territories, which are governed directly by the federal government of Malaysia:
Districts of Malaysia
Districts of Malaysia
Municipalities of Malaysia
Municipalities of Malaysia
- Cities of Malaysia
- Capital of Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur
- State capitals of Malaysia
- Cities, by population
Economy and infrastructure of Malaysia
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 38th (thirty-eighth)
- Agriculture in Malaysia
- Accounting in Malaysia
- Banking in Malaysia
- Banks in Malaysia
- National Bank of Malaysia
- Islamic banking
- Currency of Malaysia: Ringgit
- Communications in Malaysia
- Companies of Malaysia
- Energy in Malaysia
- Health care in Malaysia
- Mining in Malaysia
- Science and technology in Malaysia
- Poverty in Malaysia
- Malaysia Stock Exchange
- Telecommunications in Malaysia
- Tourism in Malaysia
- Transport in Malaysia
- Airports in Malaysia
- Rail transport in Malaysia
- Roads in Malaysia
- Water supply and sanitation in Malaysia
Economic plans and policies
Demography of Malaysia
- Languages of Malaysia
- Malaysian citizenship
- Healthcare in Malaysia
Religion
Ethnicities
- Bumiputra
- Malaysian Malay
- Malaysian Chinese
- Malaysian Indian
Culture of Malaysia
|
|
|
Art in Malaysia
- Art in Malaysia
- Cinema of Malaysia
- Literature of Malaysia
- Music of Malaysia
- Television in Malaysia
Education in Malaysia
- Ministry of Education
- Ministry of Higher Education
- Malaysian Qualifications Framework
- List of schools in Malaysia
- List of post-secondary institutions in Malaysia
- List of universities in Malaysia
- Issues in Malaysian Education
- Standardised examinations
- Ujian Pencapaian Sekolah Rendah (UPSR)
- Pentaksiran Tingkatan Tiga (PT3)
- Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (SPM)
- Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia (STPM)
See also
| Malay language edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
- Index of Malaysia-related articles
- List of international rankings
- List of Malaysia-related topics
- Malay units of measurement
- Member state of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Asia
- Outline of geography
Notes
- ^ UMNO was deregistered in 1988 and the Prime Minister of Malaysia formed a new party known as United Malays National Organisation (Baru) on February 16, 1988. The term "Baru" or "New" was removed by a constitutional amendment on July of the same year.
- ^ The United Sabah Party (Parti Bersatu Sabah) was a member of Barisan Nasional from its establishment in 1985 until its withdrawal from the coalition in 1990. The party rejoined the coalition in 2002.[6]
- ^ The Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party entered a coalition with the former Alliance Party in 1972 and subsequently joined the Barisan Nasional coalition when it was founded in 1974. It withdrew from the coalition in 1977.[7]
References
- "Malaysia". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 2, 2009. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- Article 1. Constitution of Malaysia.
- Article 33. Constitution of Malaysia.
- Article 43. Constitution of Malaysia.
- The Federation of International Trade Associations. General Information of Malaysia. Retrieved December 7, 2007.
- "Parti Bersatu Sabah (PBS)". MalaysiaToday.com. 2008-06-05. Archived from the original on December 1, 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-24.
- Hooker, M. B. (1983). Islam in South-East Asia. Boston: Brill Archive. pp. 203–204. ISBN 90-04-06844-9.
External links
- Government
- myGovernment Portal – Malaysian Government Portal
- Office of the Prime Minister of Malaysia
- Department of Statistics Malaysia
- Maps
- Overviews and Data
