Timeline of Malaysian history
This is a timeline of Malaysian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Malaysia and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of Malaysia.
2nd century
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 200 | Gangga Negara was founded by a son of Merong Mahawangsa.
Hikayat Merong Mahawangsa (Jawi: حكاية مروڠ مهاوڠسا ) or The Kedah Annals is an ancient work of Malay literature which chronicles the bloodline of Merong Mahawangsa and the foundation of the Kedah, a state in Malaysia. |
| The reign of the ancient Hindu Malay kingdom of Langkasuka began. |
The first research into the Beruas kingdom was conducted by Colonel James Low in 1849, and a century later by H.G. Quaritch Wales. According to the Museum and Antiquities Department, both researchers agreed that the Gangga Negara kingdom existed between 100 and 1000 CE,[1] but could not ascertain the exact site. For years, villagers had unearthed artefacts believed to be from the ancient kingdoms, most of which are at present displayed at the Beruas Museum, including a 128-kilogram (282 lb) cannon, swords, kris, coins, tin ingots, pottery from the Ming Dynasty and various eras, and large jars. They can be dated back to the 5th and 6th century.[2] Through these artefacts, it has been postulated that Pengkalan (Ipoh), Kinta Valley, Tanjung Rambutan, Bidor and Sungai Siput were part of the kingdom. Artefacts also suggest that the kingdom's centre might have shifted several times. Gangga Negara was renamed to Beruas after the establishment of Islam there.
4th century
5th century
6th century
7th century
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 630 | The Kedah Kingdom was founded by Maharaja Derbar Raja of Bandar Abbas. |
| 700 | The ancient kingdom of Srivijaya began to influence Maritime Southeast Asia.
Between the 7th and the 13th century, much of the Malay peninsula was under the Buddhist Srivijaya empire. The site of Srivijaya's centre is thought be at a river delta in eastern Sumatra, based near what is now Palembang. For over six centuries the Maharajahs of Srivijaya ruled a maritime empire that became the main power in the archipelago. The empire was based around trade, with local kings (dhatus or community leaders) swearing allegiance to the central lord for mutual profit.[3] |
| The reign of Pan Pan ended. |
8th century
9th century
11th century
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1100 | The reign of Gangga Negara ended. |
12th century
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1136 | Phra Ong Mahawangsa converted to Islam and founded the Kedah Sultanate, so ending the practice of Hinduism in the dynasty. |
13th century
| Year | Event |
|---|
14th century
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1400 | The reign of Langkasuka end |
15th century
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1402 | The Malacca Kingdom was founded by Parameswara. |
| 1405 | Chinese admiral Zheng He reached Malacca, establishing and strengthening diplomatic ties between Ming China and Malacca Sultanate. |
| 1445 | Tun Perak led the Malaccan army to victory by defeating Siamese invaders. As a result, he was made bendahara in 1456. |
| 1450 | The Sulu Sultanate reached its peak by extending its rule to the eastern part of North Borneo. |
16th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1511 | 15 August | The city of Malacca comes under Portuguese rule after falling to an army led by Alfonso de Albuquerque.
Sultan Mahmud Shah of Malacca made several attempts to retake the capital. He rallied support from his ally the Sultanate of Demak in Java, that in 1511 agreed to send naval forces to assist the effort to retake Malacca. Led by Pati Unus, the Sultan of Demak, the combined Malay–Javan efforts failed and were fruitless. The Portuguese retaliated and forced the sultan to flee to Pahang. Later, the sultan sailed to Bintan Island and established a new capital there. With a base established, the sultan rallied the disarrayed Malay forces and organised several attacks and blockades against the Portuguese's position. Frequent raids on Malacca caused the Portuguese severe hardship. In 1521 the second Demak campaign to assist the Malay Sultan to retake Malacca was launched, however once again failed with the cost of the Demak Sultan's life. He was later remembered as Pangeran Sabrang Lor or the Prince who crossed (the Java Sea) to North (Malay Peninsula). The raids helped convince the Portuguese that the exiled sultan's forces must be silenced. A number of attempts were made to suppress the Malay forces, but it wasn't until 1526 that the Portuguese finally razed Bintan to the ground. The sultan then retreated to Kampar in Riau, Sumatra where he died two years later. He left two sons named Muzaffar Shah and Alauddin Riayat Shah. |
| 1528 | The Johor Sultanate was founded by Alauddin Riayat Shah, son of Sultan Mahmud Shah of Malacca, and crowned Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah II.
The Perak Sultanate was founded by Sultan Muzaffar Shah, son of Sultan Mahmud Shah of Malacca. |
17th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1613 | Triangular war: War between Portuguese in Malacca, Aceh Sultanate and Johor Empire. | |
| 1641 | The Sejarah Melayu composed by Tun Sri Lanang | |
| 1641 | The Dutch and their local allies conquered Malacca from the Portuguese. | |
| 1660 | Kedah was undered Thai sovereignty. | |
| 1666 | Johor-Jambi War: War broke out between Johor and Jambi. |
18th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1704 | Sultan cedes the lands East of Marudu Bay to the Sultan of Sulu. | |
| 1723 | State of Pasir Besar renamed Luak Johol. | |
| 1725 | Paduka Sri Sultan Zainal-Abidin I, younger son of Tun Habib 'Abdu'l-Majid bin Mat Ali invested as Sultan by his nephew, Sultan Sulaiman Badr ul-'Alam Shah of Johor | |
| 1750 | Luak Sungai Ujong founded. Luak Gunung Pasir founded, under the suzerainty of Rembau. Luak Ulu Muar founded, under the suzerainty of Johol. Luak Jempol founded, under suzerainty of Jelebu. Luak Inas (also called Jelai) founded. | |
| 1773 | Negeri Sembilan (a confederation of nine states) established. | |
| 1775 | Luak Teraci founded, under the suzerainty of Sungai Ujong. | |
| 1775 | Paduka Sri Sultan Long Yunus expelled Long Muhammad and became Raja of Kelantan installed by his father-in-law Sultan Mansur Shah I of Trengganu. |
19th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1819 | Thomas Stamford Raffles arrived and signed a treaty with Sultan Hussein Shah of Johor, on behalf of the British East India Company, to develop the southern part of Singapore as a British trading post. | |
| 1820 | Ghee Hin Kongsi and Hai San Secret Society, 2 secret societies in Singapore and Malaya was established. | |
| 1824 | March | The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 was signed by the United Kingdom and the Netherlands to address issues regarding trade rights in the Spice Islands. |
| 1826 | The Burney Treaty was signed between Thailand and the United Kingdom, partitioning the northern Malay states between the two countries. | |
| The Straits Settlements were established as part of the territories controlled by the British East India Company. | ||
| 1831 | August | Naning War: The opposition of Dol Said to British taxation policy in Naning led to the Naning War. Dol Said's force defeated 150 British soldiers led by Captain Wyllie. |
| 1834 | February | Naning War: Dol Said surrenders to British forces in return for an official pardon, effectively ending the Naning War. |
| 1841 | 18 August | The Kingdom of Sarawak was established by Sir James Brooke after a grant of independence from the Sultanate of Brunei. |
| 1843 | 4 June | A war expedition established by Sir James Brooke to attack the Rentap and the Dayak Iban tribe at Saribas begins. |
| 1853 | Alan Lee, officer in charge of another fort at Nanga Lingga, Sri Aman was defeated and killed by Rentap forces. | |
| 1857 | 1857 Chinese Uprising: Liu Shan Bang, leader of the gold miners in Pangkalan Tebang started a rebellion against the White Rajahs in Bau, Sarawak. | |
| 1861 | July | First Larut War: arguments over control of watercourse to mines escalated and led members of the Hai San Society to drive the members of the Ghee Hin society out of Kamunting.[4][5][6][7] |
| 1865 | Second Larut War: started by a gambling quarrel in June of that year between members of Ghee Hin Kongsi and Hai San Secret Society. | |
| 1867 | Klang War: Raja Mahadi challenged Raja Abdullah for authority over Klang. | |
| 1 April | The Straits Settlements came under direct British control as a crown colony. | |
| 1863 | Rentap's fortress at Nanga Skrang was successfully infiltrated by the attacking party of Tuan Muda Charles Brooke and Rentap ultimately retired from the war. | |
| 1871 | Third Larut War: began by an affair between Ghee Hin and Hai San and conflict between the succession for the next Sultan of Perak between Raja Abdullah and Raja Ismail. | |
| Tristram Speedy sailed to the Straits Settlements in Malaya and became superintendent of police on the island of Penang. | ||
| 1873 | Tristram Speedy commanded a body of Indian troops to restore order in Larut, a Malayan mining district, for the Menteri (Chief Minister) Ngah Ibrahim. | |
| Civil war break out in Seremban between the forces of Dato' Kelana and Dato' Shahbandar due to dissatisfaction about their rights to collect taxes and ownership and control of the mines. British sided with Dato' Kelana defeated its opposition and Sungai Ujong successfully felt to the hand of British forces. | ||
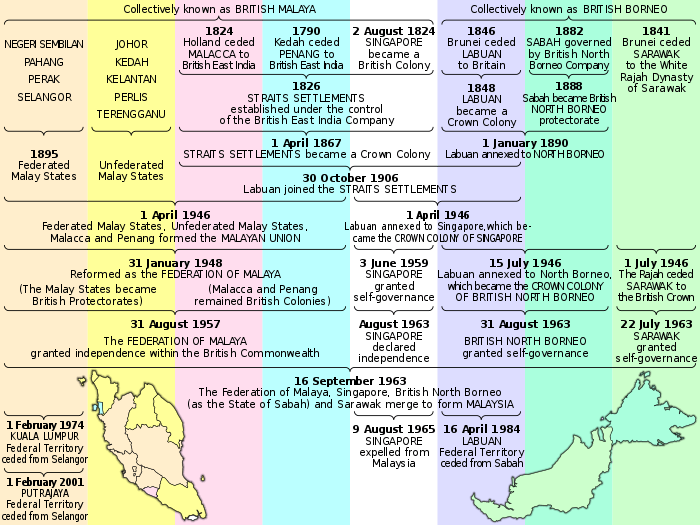
| 1874 | 20 January | The Pangkor Treaty of 1874 signalled official British involvement in the policies of the Malays, and the establishment of British Malaya. |
| 1875 | 2 November | James W. W. Birch, the first Resident of Perak was assassinated by local Malay chief, Dato Maharajalela and his follower, Seputum in Pasir Salak. |
| 7 November | Perak War: The sultan of Upper Perak and other local chiefs attempted to end foreign influence in the region and remove the British administrator James W.W. Birch. | |
| 1876 | 21 July | Following the trial held in 1875 between 14 and 22 December in Matang, Perak, Abdullah Muhammad Shah II of Perak and Ngah Ibrahim were exiled to the Seychelles. |
| 1877 | 20 January | Lela Pandak Lam was executed by hanging in Taiping. |
| 1879 | 25 October | Jementah Civil War: Tengku Alam Shah refused to place Muar under the temporary administration of Sultan Abu Bakar of Johor. |
| 1882 | North Borneo became a British protectorate under the sovereign North Borneo Chartered Company. | |
| 1887 | Terengganu Inscription Stone was discovered by villagers at a steep sloping riverbank of Tersat river, Kampung Buluh, Kuala Berang, Hulu Terengganu. | |
| 1895 | Selangor, Perak, Negeri Sembilan and Pahang joined to become the Federated Malay States, a federation of British protectorates. | |
| 1896 | Mat Salleh Rebellion: Disputes between locals and the British North Borneo Company led to rebellion. | |
| 1900 | September | Chinese leader, Wong Nai Siong and his party started recruiting villagers from Fujian to immigrate to Sibu, Sarawak. |
20th century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1909 | 10 March | The Anglo-Siamese Treaty of 1909 was signed by the United Kingdom and Thailand, effectively dissecting the northern Malay states. |
| 1914 | 28 October | Battle of Penang: The German cruiser SMS Emden sank two Allied warships in the Strait of Malacca. |
| 1915 | William Kellie Smith, a Scottish planter started the construction project of Kellie's Castle in Batu Gajah, Perak. | |
| 1922 | Haji Abdul Rahman Limbong represented one of the 43 farmers being put to trial in a court for doing farming without permission. | |
| 1928 | Haji Abdul Rahman Limbong assembled about 1,000 people in Kampung Buluh, to launch their resistance to get the British out of their state. Several police stations were attacked were made in Kuala Berang. | |
| 1941 | 7 December | Attack on Pearl Harbor: Japan opened hostilities with the Allies and their colonies. |
| 8 December | Japanese occupation of Malaya: Japanese forces invaded and began the occupation of British Malaya. | |
| 16 December | Japanese occupation of British Borneo: Japanese forces invaded and began the occupation of British Borneo. | |
| 10 December | The British battleship HMS Prince of Wales and the battlecruiser HMS Repulse were sunk by Japanese bombers. | |
| 1942 | 14 January | Battle of Muar: The last major battle of the Malayan campaign was fought. |
| 23 January | Parit Sulong Massacre: Allied soldiers were massacred by Japanese forces. | |
| 9 February | Battle of Singapore: The Japanese crossed the Strait of Johor in inflatable boats and landed in Singapore. | |
| 13 February | Battle of Pasir Panjang: A Malay regiment led by Lieutenant Adnan bin Saidi fought bravely against the Japanese at Pasir Panjang Ridge. | |
| 18 October | Kedah became the Thai possession of Syburi. | |
| 1945 | January | Sandakan Death Marches: Cruel marches began which were forced by Japan. |
| June | Sandakan Death Marches: The death marches came to an end. | |
| 27 June | Battle of North Borneo: A battle was fought between the Australians and Japanese. | |
| 14 August | Japan surrendered, leaving a power vacuum. | |
| 5 September | The British returned and established a military administration in the Straits Settlements. | |
| 23 September | Kedah and the three other states were returned to the British. | |
| 1946 | 1 April | The Straits Settlements were dissolved and replaced by the Malayan Union, conceived to unify the Malay Peninsula under a single government. |
| 8 February | Charles Vyner Brooke declared that the Sarawak Supreme Council agreed on the cession of Sarawak to British. | |
| 1 July | British officially declared Sarawak as Crown Colony of Sarawak | |
| 1948 | 31 January | Opposition from Malay nationalists forced the Malayan Union to disband in favour of the Federation of Malaya, which restored the symbolic positions of the rulers of the Malay states. |
| 18 June | Sungai Siput Incident: Rubber plantations and tin mines in Malaya were destroyed by Communists, leading the British to declare a state of emergency. | |
| 16 July | Death of Lau Yew: British security forces clashed with those of the Malayan Communist Party resulting in the death of one of their key leaders, Lau Yew.[8] | |
| 1949 | 8 October | The University of Malaya was established following the merger of Raffles College and King Edward Medical College. |
| 3 December | Rosli Dhobi and several members from Rukun 13 orchestrated the assassination of the Governor of Sarawak, Sir Duncan Stewart in Sibu. | |
| 1950 | 23 February | Bukit Kepong Incident: An armed encounter took place between Communists and the police. |
| 1951 | 6 October | Assassination of Sir Henry Gurney: British High Commissioner Sir Henry Gurney was killed by members of the Malayan Communist Party in Fraser's Hill. |
| 1956 | 18 January | A constitutional conference proposed the appointment of the Reid Commission to devise a constitution for a fully self-governing and independent Federation of Malaya. |
| 8 February | Baling Talks: An talk between representative of the government of Malaya and Malayan Communist Party to resolve the Malayan Emergency situation. Tan Cheng Lock, David Marshall and Tunku Abdul Rahman represented the government whereas Chin Peng, Rashid Maidin and Chen Tien represented the communists. However, the talks were unsuccessful because the surrender terms were not acceptable to the Malayan Communist Party. | |
| 1957 | 21 February | The Reid Commission submitted its working draft to a Working Committee. |
| 31 July | Independence of the Federation of Malaya | |
| 15 August | The new Federal Constitution was passed by the Federal Legislative Council. | |
| 31 August | Formal independence of the Federation of Malaya was achieved. | |
| 1961 | 27 May | Malayan Prime Minister Tunku Abdul Rahman proposed a merger between Singapore, Malaya, North Borneo and Sarawak. |
| 1962 | 17 January | Cobbold Commission: The Cobbold Commission, was a Commission of Enquiry set up to determine whether the people of North Borneo (now Sabah) and Sarawak supported the proposal to create the Federation of Malaysia consisting of Malaya, Brunei, Singapore, North Borneo, and Sarawak. |
| 1962 | 8 December | Brunei Revolt: A revolt led by Yassin Affandi began coordinated attacks on oil installations, police stations and government facilities around the protectorate. |
| 1963 | 20 January | Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation: Indonesian Foreign Minister Subandrio announced that Indonesia would pursue a policy of konfrontasi with the Federation of Malaysia, North Borneo and Sarawak. |
| 9 July | The Malaysia Agreement was signed by the governments of the United Kingdom, Malaya, Singapore, North Borneo and Sarawak. | |
| 31 July | Manila Accord was signed by the governments of Malaya (now Malaysia), Indonesia and, Philippines. | |
| 16 September | Malaysia established. Singapore, Sabah, Sarawak and Malaya merged to form Malaysia. | |
| 1965 | May | Lee Kuan Yew began campaigning for a Malaysian Malaysia. |
| 7 August | Singapore and Malaysia signed a separation agreement. | |
| 9 August | The Malaysian Parliament voted to expel Singapore from the Federation. | |
| 1966 | 7 February | Exchange of notes by the government of Malaysia (formerly Malaya) and Philippines constituting an agreement relating to the implementation of the Manila Accord of 31 July 1963. |
| 1967 | February | Communist insurgency in Malaysia (1968–89): A renewed insurgency was conducted by the Malayan Communist Party against Malaysian federal security forces. |
| 1969 | 10 May | 1969 Malaysian general election: The third general election since independence was held in West Malaysia. |
| 13 May | 13 May Incident: Ethnic riots between Malays and Chinese took place in Kuala Lumpur. | |
| 14 May | A state of emergency and accompanying curfew were declared throughout the country. | |
| 16 May | The state of emergency and curfew were lifted. | |
| 1970 | Rukun Negara, the national philosophy was instituted by royal proclamation on Merdeka Day, after the May 13 Incident in 1969. | |
| 1971 | An affirmative action program known as the Malaysian New Economic Policy was launched by the Malaysian government. | |
| 1974 | 1 February | Designation of first Federal Territory. |
| 1975 | 5 August | 1975 AIA building hostage crisis: Japanese Red Army took more than 50 hostages at the AIA building, which housed several embassies. |
| 1977 | 8 November | 1977 Kelantan Emergency: The state of emergency was declared by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong (King of Malaysia) on 8 November 1977 upon the request of the federal government following a political impasse and street violence in Kelantan.[9] |
| 1979 | 21 December | Pedra Branca dispute: Singapore lodged a formal protest with Malaysia in response to a map published by Malaysia in 1979 claiming Pedra Branca. |
| 1982 | 1 January | The time zone in Peninsular Malaysia and Singapore changed to UTC+08:00 and has not changed since. |
| 1 May | The time zone in East Malaysia changed to UTC+08:00 and has not changed since. | |
| 1984 | 16 April | Labuan became a Federal Territory of Malaysia. |
| 1985 | 19 November | Memali Incident: A team of 200 policemen under orders from the Acting Prime Minister and Home Minister Musa Hitam laid siege to kampung (village) houses in Memali, near Baling in Kedah. |
| 1987 | 27 October | Operation Lalang: An operation was carried out by the Malaysian police to crack down on opposition leaders and social activists. |
| 1988 | 1988 Malaysian constitutional crisis: A series of events began which would lead to the eventual removal of the Lord President of the Federal Court. | |
| 1991 | 4 October | The Kuala Lumpur Tower official ground-breaking. |
| 1 November | The Kuala Lumpur International Airport official ground-breaking. | |
| 1993 | The Parliament passed amendments to the Constitution with the aim of stripping the royalty of legal immunity. | |
| 1 February | Kuala Lumpur International Airport construction began. | |
| 1994 | 1 January | Petronas Towers construction commenced. |
| 1996 | 1 January | Petronas Twin Towers completed. |
| Kuala Lumpur International Airport opened to public service. | ||
| 1 May | The Kuala Lumpur Tower completed. | |
| 1 June | Astro was launched as Malaysia's first subscription-based satellite television station | |
| 1997 | 1 January | Asian financial crisis: Malaysia slipped into recession. |
| 1998 | 1 January | Petronas Towers opened to public service of Aquaria KLCC, Suria KLCC and Petronas Philharmonic Hall. |
| 11 September | Opening ceremony of the 16th Commonwealth Games held in Kuala Lumpur | |
| The Kuala Lumpur National Stadium officially opened by Prime Minister Tun Doctor Mahathir Bin Mohamad. | ||
| 1999 | 29 January | Dato' Seri Anwar Ibrahim replaced by Abdullah Badawi as Deputy Prime Minister. |
21st century
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | December | Gunung Mulu National Park and Kinabalu Park became UNESCO World Heritage Sites of nature. |
| 2001 | 1 January | The Kuala Lumpur Central Station officially opened. |
| 1 February | Putrajaya was declared as a Federal Territory Putrajaya was handed over from the Selangor state authorities. | |
| 4 March | Breakout of racial riot between Malay and Indian in Petaling Jaya, Selangor. | |
| 8 September | Opening ceremony of the 21st Southeast Asian Games held in Kuala Lumpur | |
| 2003 | 31 October | Abdullah Ahmad Badawi became the new Prime Minister of Malaysia. |
| 23 May | Pedra Branca dispute resolved. Singapore gained sovereignty over Pedra Branca; Malaysia gained sovereignty over Middle Rocks. | |
| 26 August | 2008 Permatang Pauh by-election: Marked the significant return of Anwar Ibrahim to politics after his incasceration of 10 years. Anwar won the election and was sworn into Parliament on 28 August 2008, vowing to topple the government with the help of defectors from Barisan Nasional. | |
| 12 December | Penang and Malacca City became a cultural UNESCO World Heritage Site, citing as the Historic Cities of the Straits of Malacca. | |
| 2009 | 3 February | 2009 Perak constitutional crisis: Began when three Pakatan Rakyat state legislators defected, causing a collapse of the state government. |
| 2012 | 6 July | Lenggong became a cultural UNESCO World Heritage Site. |
| 2013 | 11 February | 2013 Lahad Datu standoff: Sulu Militants' attempt to siege Lahad Datu District from Sabah, Malaysia. |
| 2014 | 27 January | Kajang Move: The attempted replacement of Khalid Ibrahim as Menteri Besar (Chief Minister) of Selangor with Anwar Ibrahim starts a political crisis. |
| 8 March | Malaysia Airlines Flight 370 disappeared. | |
| 17 July | Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 shot down over Ukraine, killing all 298 people aboard. | |
| 23 September | Kajang Move: The crisis concludes with the appointment of Parti KeADILan Rakyat Deputy President, Azmin Ali, as Menteri Besar. | |
| 2015 | 5 June | 18 people were killed in the Sabah earthquake |
| 2017 | 13 February | Kim Jong-nam assassinated at Kuala Lumpur International Airport.[10] |
| 2018 | 9 May | Barisan Nasional defeated by Pakatan Harapan, first change of governing coalition since independence. |
| 2020 | 4 February | First Malaysian infected by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)[11] |
| 24 February | Mahathir Mohamad resigns as the seventh Prime Minister of Malaysia.[12] |
References
- Research on the Early Malay Doctors 1900–1957 Malaya and Singapore, By Faridah Abdul Rashid
- John Penrose Barton; Commission of the European Communities (1987). Neutron radiography: proceedings of the second world conference, Paris, France, June 16–20, 1986. D. Reidel. ISBN 978-90-277-2495-3.
- Andaya, Barbara Watson; Andaya, Leonard Y. (1982). A History of Malaysia. London: MacMillan Press Ltd. pp. 26–28, 61, 151–152, 242–243, 254–256, 274. ISBN 0-333-27672-8.
- Notes on the Larut Disturbances by Khoo Kay Kim, A history of Perak, Sir Richard Olof Winstedt, Richard James Wilkinson, Sir William Edward Maxwell, republished by Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society, 1974, PPiv&v
- History of Malaya, 1400–1959, Joginder Singh Jessy, Jointly published by the United Publishers and Peninsular Publications, 1963, P151
- A portrait of Malaysia and Singapore, Soo Hai Ding Eing Tan, Oxford University Press, 1978, ISBN 0195807227, ISBN 9780195807226, PP78&123
- The Malayan tin industry to 1914: with special reference to the states of Perak, Selangor, Negri, Sembilan, and Pahang by Lin Ken Wong, Published for the Association for Asian Studies by the University of Arizona Press, 1965, P27
- "Malayan Emergency", Britain's Small Wars accessed 17 November 2013
- Cheah, Boon Kheng. Malaysia: The Making of a Nation. Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. p. 179. ISBN 978-981-230-175-8.
- "Kim Jong-nam killed by VX nerve agent". theguardian. 24 February 2017.
- "First Malaysian tests positive for Wuhan coronavirus | The Star Online". www.thestar.com.my. Retrieved 5 February 2020.
- "Dr Mahathir resigns". New Straits Times. 24 February 2020. Retrieved 24 February 2020.
