House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (Dutch: Huis van Oranje-Nassau, pronounced [ˈɦœys fɑn oːˌrɑɲə ˈnɑsʌu]),[1] is the current reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the politics and government of the Netherlands and Europe especially since William the Silent organized the Dutch revolt against Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) led to an independent Dutch state.
| House of Orange-Nassau | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Parent house | House of Nassau |
| Country | Netherlands, United Kingdom, Ireland, Luxembourg, Orange, Nassau |
| Etymology | Orange, France & Nassau, Germany |
| Founded | 1544 |
| Founder | William the Silent |
| Current head | Willem-Alexander of the Netherlands (in cognatic line) |
| Titles |
|
| Estate(s) | Netherlands |
| Dissolution | 1962 (in agnatic line; last male dynast died in 1890) |
Several members of the house served during this war and after as stadtholder ("governor"; Dutch: stadhouder) during the Dutch Republic. However, in 1815, after a long period as a republic, the Netherlands became a monarchy under the House of Orange-Nassau.
The dynasty was established as a result of the marriage of Henry III of Nassau-Breda from Germany and Claudia of Châlon-Orange from French Burgundy in 1515. Their son René inherited in 1530 the independent and sovereign Principality of Orange from his mother's brother, Philibert of Châlon. As the first Nassau to be the Prince of Orange, René could have used "Orange-Nassau" as his new family name. However, his uncle, in his will, had stipulated that René should continue the use of the name Châlon-Orange. History knows him therefore as René of Châlon. After the death of René in 1544, his cousin William of Nassau-Dillenburg inherited all of his lands. This "William I of Orange", in English better known as William the Silent, became the founder of the House of Orange-Nassau.[2]:10
The House of Nassau
Nassau Castle was founded around 1100 by Dudo, Count of Laurenburg, the founder of the House of Nassau. In 1120, Dudo's sons and successors, Counts Rupert I and Arnold I, established themselves at Nassau Castle, taking for themselves the title "Count of Nassau". In 1255 the Nassau possessions were split between Walram and Otto, the sons of Count Henry II. The descendants of Walram were known as the Walram Line, and they became Dukes of Nassau and, in 1890, Grand Dukes of Luxembourg. This line also included Adolph of Nassau, who was elected King of the Romans in 1292. The descendants of Otto became known as the Ottonian Line, and they inherited parts of the County of Nassau, as well as properties in France and the Netherlands.

The House of Orange-Nassau stems from the younger Ottonian Line. The first of this line to establish himself in the Netherlands was John I, Count of Nassau-Dillenburg, who married Margareta of the Marck. The real founder of the Nassau fortunes in the Netherlands was John's son, Engelbert I. He became counsellor to the Burgundian Dukes of Brabant, first to Anton of Burgundy, and later to his son Jan IV of Brabant. He also would later serve Philip the Good. In 1403, he married the Dutch noblewoman Johanna van Polanen and so inherited lands in the Netherlands, with the Barony of Breda as the core of the Dutch possessions and the family fortune.[3]:35
A nobleman's power was often based on his ownership of vast tracts of land and lucrative offices. It also helped that much of the lands that the House of Orange-Nassau controlled sat under one of the commercial and mercantile centers of the world (see below under Lands and Titles. The importance of the family grew throughout the 15th and 16th centuries as they became councilors, generals and stadholders of the Habsburgs (see armorial of the great nobles of the Burgundian Netherlands and List of Knights of the Golden Fleece). Engelbert II of Nassau served Charles the Bold and Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, who had married Charles's daughter Mary of Burgundy. In 1496, he was appointed stadtholder of Flanders and by 1498 he had been named President of the Grand Conseil. In 1501, Maximilian named him Lieutenant-General of the Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands. From that point forward (until his death in 1504), Engelbert was the principal representative of the Habsburg Empire to the region. Hendrik III of Nassau-Breda was appointed stadtholder of Holland and Zeeland by Charles of Ghent in the beginning of the 16th century. Hendrik was succeeded by his son René of Châlon-Orange in 1538, who had inherited the title of Prince of Orange and the principality of that name from his maternal uncle Philibert of Chalon. René died prematurely on the battlefield in 1544. His possessions, including the principality and title, passed by his will as sovereign prince to his paternal cousin, William I of Orange. From then on, the family members called themselves "Orange-Nassau."[2]:8[3]:37[4]:vol3,pp3–4[5]:37,107,139
The Dutch rebellion

Although Charles V pretended to resist the Protestant Reformation, he ruled the Dutch territories wisely with moderation and regard for local customs, and he did not persecute his Protestant subjects on a large scale. His son Philip II inherited his antipathy for the Protestants but not his moderation. Under the reign of Philip, a true persecution of Protestants was initiated and taxes were raised to an outrageous level. Discontent arose and William of Orange (with his vague Lutheran childhood) stood up for the Protestant (mainly Calvinist) inhabitants of the Netherlands. Things went badly after the Eighty Years' War started in 1568, but luck turned to his advantage when Protestant rebels attacking from the North Sea captured Brielle, a coastal town in present-day South Holland in 1572. Many cities in Holland began to support William. During the 1570s he had to defend his core territories in Holland several times, but in the 1580s the inland cities in Holland were secure. William of Orange was considered a threat to Spanish rule in the area and was assassinated in 1584 by a hired killer sent by Philip.[4]:vol3,p177[5]:216[7]
William was succeeded by his second son Maurits, a Protestant who proved an excellent military commander. His abilities as a commander and the lack of strong leadership in Spain after the death of Philip II (1598) gave Maurits excellent opportunities to conquer large parts of the present-day Dutch territory.[4]:vol 3,pp243–253[8] In 1585 Maurits was elected stadtholder of the Provinces of Holland and Zealand as his father's successor and as a counterpose to Elizabeth's delegate, the Earl of Leicester. In 1587 he was appointed captain-general (military commander-in-chief) of the armies of the Dutch Republic. In the early years of the 17th century there arose quarrels between stadtholder and oligarchist regents—a group of powerful merchants led by Johan van Oldebarnevelt—because Maurits wanted more powers in the Republic. Maurits won this power struggle by arranging the judicial murder of Oldebarnevelt.[5]:421–432,459[8]
Expansion of dynastic power

Maurits died unmarried in 1625 and left no legitimate children. He was succeeded by his half-brother Frederick Henry (Dutch: Frederik Hendrik), youngest son of William I. Maurits urged his successor on his deathbed to marry as soon as possible. A few weeks after Maurits's death, he married Amalia van Solms-Braunfels. Frederick Henry and Amalia were the parents of a son and several daughters. These daughters were married to important noble houses such as the house of Hohenzollern, but also to the Frisian Nassaus, who were stadtholders in Friesland. His only son, William, married Mary, Princess Royal and Princess of Orange, the eldest daughter of Charles I of Scotland and England. These dynastic moves were the work of Amalia.[2]:72–74[9]:61
Exile and resurgence
Frederick Henry died in 1647 and his son succeeded him. As the Treaty of Munster was about to be signed, thereby ending the Eighty Years' War, William tried to maintain the powers he had in wartime as military commander. These would necessarily be diminished in peacetime as the army would be reduced, along with his income. This met with great opposition from the regents. When Andries Bicker and Cornelis de Graeff, the great regents of the city of Amsterdam refused some mayors he appointed, he besieged Amsterdam. The siege provoked the wrath of the regents. William died of smallpox on November 6, 1650, leaving only a posthumous son, William III (*November 14, 1650). Since the Prince of Orange upon the death of William II, William III, was an infant, the regents used this opportunity to leave the stadtholdership vacant. This inaugurated the era in Dutch history that is known as the First Stadtholderless Period.[10] A quarrel about the education of the young prince arose between his mother and his grandmother Amalia (who outlived her husband by 28 years). Amalia wanted an education which was pointed at the resurgence of the House of Orange to power, but Mary wanted a pure English education. The Estates of Holland, under Jan de Witt and Cornelis de Graeff, meddled in the education and made William a "child of state" to be educated by the state. The doctrine used in this education was keeping William from the throne. William became indeed very docile to the wishes of the regents and the Estates.[9][10]
The Dutch Republic was attacked by France and England in 1672. The military function of stadtholder was no longer superfluous, and with the support of the Orangists, William was restored, and he became the stadtholder. William successfully repelled the invasion and seized royal power. He became more powerful than his predecessors from the Eighty Years' War.[9][10] In 1677, William married his cousin Mary Stuart, the daughter of the future king James II of England. In 1688, William embarked on a mission to depose his Catholic father-in-law from the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland. He and his wife were crowned the King and Queen of England on April 11, 1689. With the accession to the thrones of the three kingdoms, he became one of the most powerful sovereigns in Europe, and the only one to defeat Louis XIV of France.[9] William III died childless after a riding accident on March 8, 1702, leaving the main male line of the House of Orange extinct, and leaving Scotland, England and Ireland to his sister-in-law Queen Anne.

The second stadtholderless era
The regents found that they had suffered under the powerful leadership of King William III and left the stadtholderate vacant for the second time. As William III died childless in 1702 the principality became a matter of dispute between Prince John William Friso of Nassau-Dietz of the Frisian Nassaus and King Frederick I of Prussia, who both claimed the title Prince of Orange. Both descended from Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange. The King of Prussia was his grandson through his mother, Countess Luise Henriette of Nassau. Frederick Henry in his will had appointed this line as successor in the case the main House of Orange-Nassau would die out. John William Friso was a great-grandson of Frederick Henry (through Countess Albertine Agnes of Nassau, another daughter) and was appointed heir in William III's will. The principality was captured by the forces of King Louis XIV of France under François Adhémar de Monteil, Count of Grignan, in the Franco-Dutch War in 1672, and again in August 1682. With the Treaty of Utrecht that ended the wars of Louis XIV, the territory was formally ceded to France by Frederick I in 1713.[3]:1 John William Friso drowned in 1711 in the Hollands Diep near Moerdijk, and he left his posthumously born son William IV, Prince of Orange. That son succeeded at that time his father as stadtholder in Friesland (as the stadtholderate had been hereditary in that province since 1664), and Groningen. William IV was proclaimed the stadtholder of Guelders, Overijssel, and Utrecht in 1722. When the French invaded Holland in 1747, William IV was appointed stadtholder in Holland and Zeeland also. The stadtholderate was made hereditary in both the male and the female lines in all provinces at the same time.[2] :148–151,170
The end of the stadtholderate
William IV died in 1751, leaving his three-year-old son, William V, as the stadtholder. Since William V was still a minor, the regents reigned for him. He grew up to be an indecisive person, a character defect which would come to haunt William V his whole life. His marriage to Wilhelmina of Prussia relieved this defect to some degree. In 1787, Willem V survived an attempt to depose him by the Patriots (anti-Orangist revolutionaries) after the Kingdom of Prussia intervened. When the French invaded Holland in 1795, William V was forced into exile, and he was never to return alive to Holland.[2]:228–229[4]:vol5,289
After 1795, the House of Orange-Nassau faced a difficult period, surviving in exile at other European courts, especially those of Prussia and England. Following the recognition of the Batavian Republic by the 1801 Oranienstein Letters, William V's son William VI renounced the stadtholdership in 1802. In return, he received a few territories like the Free Imperial City of Dortmund, Corvey Abbey and Diocese of Fulda from First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte of the French Republic (Treaty of Amiens), which was established as the Principality of Nassau-Orange-Fulda.[11] William V died in 1806.[12]
The Monarchy (since 1815)
| Dutch Royalty House of Orange-Nassau |
|---|
 |
| King William I |
|
Children Grandchildren
|
| King William II |
|
Children Grandchildren |
| King William III |
|
Children Grandchildren |
| Queen Wilhelmina |
|
Children Grandchildren |
| Queen Juliana |
|
Children Grandchildren
|
| Queen Beatrix |
|
Children Grandchildren
|
| King Willem-Alexander |
|
Children |
A new spirit: the United Kingdom of the Netherlands
After a repressed Dutch rebel action, Prussian and Cossack troops drove out the French in 1813, with the support of the Patriots of 1785. A provisional government was formed, most of whose members had helped drive out William V 18 years earlier. However, they were realistic enough to realize that any new government would have to be headed by William V's son, William Frederick (William VI). All agreed that it would be better in the long term for the Dutch to restore William themselves rather than have him imposed by the allies.[2]:230

At the invitation of the provisional government, William Frederick returned to the Netherlands on November 30. This move was strongly supported by the United Kingdom, which sought ways to strengthen the Netherlands and deny future French aggressors easy access to the Low Countries' Channel ports. The provisional government offered William the crown. He refused, believing that a stadholdership would give him more power. Thus, on December 6, William proclaimed himself hereditary sovereign prince of the Netherlands—something between a kingship and a stadholdership. In 1814, he was awarded sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands and the Prince-Bishopric of Liège as well. On March 15, 1815 with the support of the powers gathered at the Congress of Vienna, William proclaimed himself King William I. He was also made grand duke of Luxembourg, and (to assuage French sensitivity by distancing the title from the now-defunct principality) the title 'Prince of Orange' was changed to 'Prince of Oranje'.[13] The two countries remained separate despite sharing a common monarch. William had thus fulfilled the House of Orange's three-century quest to unite the Low Countries.[4]:vol5,398
As king of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, William tried to establish one common culture. This provoked resistance in the southern parts of the country, which had been culturally separate from the north since 1581. He was considered an enlightened despot.[4]:vol5,399
The Prince of Orange held rights to Nassau lands (Dillenburg, Dietz, Beilstein, Hadamar, Siegen) in central Germany. On the other hand, the King of Prussia, Frederick William III—brother-in-law and first cousin of William I, had beginning from 1813 managed to establish his rule in Luxembourg, which he regarded as his inheritance from Anne, Duchess of Luxembourg who had died over three centuries earlier. At the Congress of Vienna, the two brothers-in-law agreed to a trade—Frederick William received William I's ancestral lands while William I received Luxembourg. Both got what was geographically nearer to their center of power.[4]:vol5,392
In 1830, most of the southern portion of William's realm—the former Austrian Netherlands and Prince-Bishopric—declared independence as Belgium. William fought a disastrous war until 1839 when he was forced to settle for peace. With his realm halved, he decided to abdicate in 1840 in favour of his son, William II. Although William II shared his father's conservative inclinations, in 1848 he accepted an amended constitution that significantly curbed his own authority and transferred the real power to the States General. He took this step to prevent the Revolution of 1848 from spreading to his country.[4]:vol5,455–463
William III and the threat of extinction
William II died in 1849. He was succeeded by his son, William III. A rather conservative, even reactionary man, William III was sharply opposed to the new 1848 constitution. He continually tried to form governments that were dependent on his support, even though it was prohibitively difficult for a government to stay in office against the will of Parliament. In 1868, he tried to sell Luxembourg to France, which was the source of a quarrel between Prussia and France.[4]:vol5,483
William III had a rather unhappy marriage with Sophie of Württemberg, and his heirs died young. This raised the possibility of the extinction of the House of Orange-Nassau. After the death of Queen Sophie in 1877, William remarried, to Emma of Waldeck and Pyrmont in 1879. One year later, Queen Emma gave birth to their daughter and the royal heiress, Wilhelmina.[4]:vol5,497–498
A modern monarchy
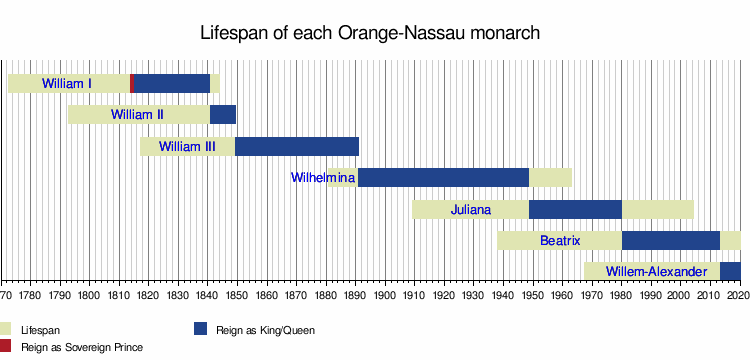
Wilhelmina was queen of the Netherlands for 58 years, from 1890 to 1948. Because she was only 10 years old in 1890, her mother, Emma of Waldeck and Pyrmont, was the regent until Wilhelmina's 18th birthday in 1898. Since females were not allowed to hold power in Luxembourg, due to Salic law, Luxembourg passed to the House of Nassau-Weilburg, a collateral line to the House of Orange-Nassau. For a time, it appeared that the Dutch royal family would die with Wilhelmina. Her half-brother, Prince Alexander, had died in 1884, and no royal babies were born from then until Wilhelmina gave birth to her only child, Juliana, in 1909. The Dutch royal house remained quite small until the later 1930s and the early 1940s, during which Juliana gave birth to four daughters. Although the House of Orange died out in its male line with the death of Queen Wilhelmina, the name "Orange" continues to be used by the Dutch royalty[4]:vol5,507–508 and as evidenced in many patriotic songs, such as "Oranje boven".
The Netherlands remained neutral in World War I, during her reign, and the country was not invaded by Germany, as neighboring Belgium was.[14]
Nevertheless, Queen Wilhelmina became a symbol of the Dutch resistance during World War II. The moral authority of the Monarchy was restored because of her rule. After 58 years on the throne as the Queen, Wilhelmina decided to abdicate in favour of her daughter, Juliana. Juliana had the reputation of making the monarchy less "aloof", and under her reign the Monarchy became known as the "cycling monarchy". Members of the royal family were often seen bicycling through the cities and the countryside under Juliana.[14]
A royal marriage policy quarrel occurred starting in 1966 when Juliana's eldest daughter, the future Queen Beatrix, decided to marry Claus von Amsberg, a German diplomat. The marriage of a member of the royal family to a German was quite controversial in the Netherlands, which had suffered under Nazi German occupation in 1940–45. This reluctance to accept a German consort probably was exacerbated by von Amsberg's former membership in the Hitler Youth under the Nazi regime in his native country, and also his following service in the German Wehrmacht. Beatrix needed permission from the government to marry anyone if she wanted to remain heiress to the throne, but after some argument, it was granted. As the years went by, Prince Claus was fully accepted by the Dutch people. In time, he became one of the most popular members of the Dutch monarchy, and his death in 2002 was widely mourned.[14]
On April 30, 1980, Queen Juliana abdicated in favor of her daughter, Beatrix. In the early years of the twenty-first century, the Dutch monarchy remained popular with a large part of the population. Beatrix's eldest son, Willem-Alexander, was born on April 27, 1967; the first immediate male heir to the Dutch throne since the death of his great-granduncle, Prince Alexander, in 1884. Willem-Alexander married Máxima Zorreguieta, an Argentine banker, in 2002; the first commoner to ever marry an heir apparent to the Dutch throne. They are parents of three daughters: Catharina-Amalia, Alexia, and Ariane. After a long struggle with neurological illness, Queen Juliana died on March 20, 2004, and her husband, Prince Bernhard, died on December 1 of that same year.[14]
Upon Beatrix's abdication on April 30, 2013, the Prince of Orange was inaugurated as King Willem-Alexander, becoming the Netherlands' first male ruler since 1890. His eldest daughter, Catharina-Amalia, as heiress apparent to the throne, became Princess of Orange in her own right.[14]
Net worth
Unlike other royal houses, there has always been a separation in the Netherlands between what was owned by the state and used by the House of Orange in their offices as monarch, or previously, stadtholder, and the personal investments and fortune of the House of Orange.
As monarch, the King or Queen has use of, but not ownership of, the Huis ten Bosch as a residence and Noordeinde Palace as a work palace. In addition, the Royal Palace of Amsterdam is also at the disposal of the monarch (although it is only used for state visits and is open to the public when not in use for that purpose), as is Soestdijk Palace (which is open to the public and not in official use at all at this time).[15] The crown jewels, comprising the crown, orb and sceptre, Sword of State, royal banner, and ermine mantle have been placed in the Crown Property Trust. The trust also holds the items used on ceremonial occasions, such as the carriages, table silver, and dinner services.[16] The Royal House is also exempt from income, inheritance, and personal tax.[17][18]
The House of Orange has long had the reputation of being one of the wealthier royal houses in the world, largely due to their business investments in Royal Dutch Shell, Philips Electronics company, KLM-Royal Dutch Airlines, and the Holland-America Line. How significant these investments are is a matter of conjecture, as their private finances, unlike their public stipends as monarch, are not open to public scrutiny.[19]
As late as 2001, the fortune of the Royal Family was estimated by various sources (Forbes magazine) at $3.2 billion. Most of the wealth was reported to come from the family's longstanding stake in the Royal Dutch/Shell Group. At one time, the Oranges reportedly owned as much as 25% of the oil company; their stake is in 2001 was estimated at a minimum of 2%, worth $2.7 billion on the May 21 cutoff date for the Billionaires issue. The family also was estimated to have a 1% stake in financial services firm ABN-AMRO.[20][21]
The royal family's fortune seems to have been hit by declines in real estate and equities after 2008. They were also rumored to have lost up to $100 million when Bernard Madoff's Ponzi scheme collapsed, though the royal house denies the allegations.[22] In 2009, Forbes estimated Queen Beatrix's wealth at US$300 million.[23] This could also have been due to splitting the fortune between Queen Beatrix and her 3 sisters, as there is no right of the eldest to inherit the whole property. A surge in export revenue, recovery in real estate and strong stock market have helped steady royal family's fortunes, but uncertainty over the new government and future austerity measures needed to bring budget deficits in line may dampen future prospects. In July 2010, Forbes magazine estimated her net worth at $200 million[19] This estimate was unchanged in April 2011.[24]
Stadtholderate under the House of Orange-Nassau
| Name | Lifespan | Reign start | Reign end | Notes | Family | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
William I
| 24 April 1533 – 10 July 1584 (aged 51) | 1559 | 1584 | Stadtholder[25] | Orange-Nassau |  |
Maurice
| 14 November 1567 – 23 April 1625 (aged 57) | 1585 | 1625 | Stadtholder,[26] son of William I | Orange-Nassau |  |
Frederick Henry
| 29 January 1584 – 14 March 1647 (aged 63) | 1625 | 1647 | Stadtholder,[27] son of William I | Orange-Nassau |  |
William II
| 27 May 1626 – 6 November 1650 (aged 24) | 14 March 1647 | 6 November 1650 | Stadtholder,[28] son of Frederick Henry | Orange-Nassau |  |
William III
| 4 November 1650 – 8 March 1702 (aged 51) | 4 July 1672 | 8 March 1702 | Stadtholder,[29] son of William II[30] | Orange-Nassau | _(lighter).jpg) |
William IV
| 1 September 1711 – 22 October 1751 (aged 40) | 1 September 1711 (under the regency of Marie Louise until 1731) | 22 October 1751 | Hereditary Stadtholder of the United Netherlands,[31] son of John William Friso | Orange-Nassau |  |
William V
| 8 March 1748 – 9 April 1806 (aged 58) | 22 October 1751 | 9 April 1806 | Hereditary Stadtholder of the United Netherlands, son of William IV, succeeded by his son King William I (-> Principality of the Netherlands (1813–1815) | Orange-Nassau |  |
Stadtholderate under the House of Nassau
Note:[32]
| Name | Lifespan | Reign start | Reign end | Notes | Family | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
John VI
| 22 November 1536 – 8 October 1606 (aged 69) | 1578 | 1581 | Stadtholder,[33] brother of William I | Nassau |  |
William Louis
| 13 March 1560 – 31 May 1620 (aged 60) | 1584 | 1620 | Stadtholder,[34] son of John VI | Nassau |  |
| Ernest Casimir I | 22 December 1573 – 2 June 1632 (aged 58) | 1620 | 1632 | Stadtholder,[35] son of John VI | Nassau | .jpg) |
| Henry Casimir I | 21 January 1612 – 13 July 1640 (aged 28) | 1632 | 1640 | Stadtholder,[36] son of Ernest Casimir I | Nassau |  |
| William Frederick | 7 August 1613 – 31 October 1664 (aged 51) | 1640 | 1664 | Stadtholder,[37] son of Ernest Casimir I | Nassau | _Governor_of_Frisia_1664.jpg) |
| Henry Casimir II | 18 January 1657 – 25 March 1696 (aged 39) | 18 January 1664 | 25 March 1696 | Hereditary Stadtholder,[38] son of William Frederick | Nassau |  |
| John William Friso | 4 August 1687 – 14 July 1711 (aged 23) | 25 March 1696 | 14 July 1711 | Hereditary Stadtholder,[39] son of Henry Casimir II, succeeded by his son William IV of Orange-Nassau, Hereditary Stadtholder of the United Netherlands (-> Stadtholderate under the House of Orange-Nassau | Nassau, Orange-Nassau | _by_Lancelot_Volders.jpg) |
Principality of the Netherlands (1813–1815)
| Name | Lifespan | Reign start | Reign end | Notes | Family | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| William I | 24 August 1772 – 12 December 1843 (aged 71) | 6 December 1813 | 16 March 1815 | Raised Netherlands to status of kingdom in 1815, son of Stadtholder William V | Orange-Nassau | %2C_souverein_vorst_der_Verenigde_Nederlanden%2C_later_koning_der_Nederlanden_Rijksmuseum_SK-A-1519.jpeg) |
Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–present)
| Name | Lifespan | Reign start | Reign end | Notes | Family | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| William I | 24 August 1772 – 12 December 1843 (aged 71) | 16 March 1815 | 7 October 1840 | Son of the last Stadtholder William V | Orange-Nassau |  |
| William II | 6 December 1792 – 17 March 1849 (aged 56) | 7 October 1840 | 17 March 1849 | Son of William I | Orange-Nassau |  |
| William III | 17 February 1817 – 23 November 1890 (aged 73) | 17 March 1849 | 23 November 1890 | Son of William II | Orange-Nassau | %2C_koning_der_Nederlanden%2C_Nicolaas_Pieneman%2C_1856_-_Rijksmuseum.jpg) |
| Wilhelmina | 31 August 1880 – 28 November 1962 (aged 82) | 23 November 1890 | 4 September 1948 | Daughter of William III | Orange-Nassau |  |
| Juliana | 30 April 1909 – 20 March 2004 (aged 94) | 4 September 1948 | 30 April 1980 | Daughter of Wilhelmina | Orange-Nassau (House of Mecklenburg) |  |
| Beatrix | 31 January 1938 | 30 April 1980 | 30 April 2013 | Daughter of Juliana | Orange-Nassau (House of Lippe) |  |
| Willem-Alexander | 27 April 1967 | 30 April 2013 | Son of Beatrix | Orange-Nassau (House of Amsberg) |  |
The Royal Family and the Royal House
A distinction is made in the Netherlands between the royal family and the Royal House.
The royal family is the Orange-Nassau family.
However, not every member of the family is also a member of the Royal House. By Act of Parliament, the members of the Royal House are:[14]
- the monarch (King or Queen);
- the former monarch (on abdication);
- the members of the royal family in the line of succession to the throne, limited to the second degree of sanguinity reckoned from the reigning monarch;
- H.R.H. Princess Margriet of the Netherlands, (for whom an exception was made);
- the spouses of the above.
Members of the Royal House lose their membership and designation as prince or princess of the Netherlands if they lose the membership of the Royal House on the succession of a new monarch (not being in the second degree of sanguinity to the monarch anymore), or marry without the consent of the Dutch Parliament. For example, this happened with Prince Friso in 2004, when he married Mabel Wisse Smit. This is written down in the law of membership of the Royal House, 2002.[40]
Family tree
The lineage of the House of Nassau can be traced back to the 10th century.
The following family tree is compiled from Wikipedia and the reference cited in the note[41]
| Dudo of Laurenburg (German: Dudo) (ca. 1060 – ca. 1123) was Count of Laurenburg in 1093 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rupert I of Nassau (German: Ruprecht) (ca. 1090 – ca. 1154) was from 1123 co-Count of Laurenburg later title himself 1st Count of Nassau | Arnold I, Count of Laurenburg (died ca. 1148) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rupert II (German: Ruprecht) Count of Laurenburg (1154–1158)(died ca. 1159) | Walram I of Nassau (French: Valéran) (ca. 1146–1198) was the first (legally titled) Count of Nassau (1154–1198) | Henry (Heinrich) I co-Count of Nassau (1160 – August 1167) | Rupert III, the Bellicose German: Ruprecht der Streitbare (died 1191) co-Count of Nassau (1160–1191) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Henry (Heinrich) II, the Rich Count of Nassau (1180–1251) | Rupert (Ruprecht) IV Count of Nassau (1198–1230) Teutonic Knight (1230–1240) | Herrmann (d after 3 December 1240) Canon of Mainz Cathedral | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Walram II of Nassau (ca. 1220 – 1276) the WALRAMIAN Branch present-day rulers of Luxembourg descend from him | Rupert (Ruprecht) V d. before 1247 Teutonic Knight (1230–1240) | Otto I of Nassau (reigned ca. 1247 – 1290) the OTTONIAN branch the present-day rulers of the Netherlands descend from him | John (ca. 1230 – 1309) Bishop-Elect of Utrecht (1267–1290) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adolf (ca. 1255–1298) King of Germany (1292–1298) | Henry (d. 1343) Count of Nassau in Siegen | Emich (d. 7 June 1334) Count of Nassau in Hadamar extinct 1394 | John (d. 1328) Count Nassau in Dillenburg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ruprecht (+ 1304) | Gerlach I, Count of Nassau-Wiesbaden (bef 1288 +1361) | Walram III Count of Nassau-Wiesbaden | Otto II (c. 1305 – 1330/1331) Count of Nassau-Dillenburg | Henry (1307–1388) Count of Nassau-Beilstein ext. 1561 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adolph (1307 +1370) Count of Nassau in Wiesbaden-Idstein ext 1605 | John I (1309 +1371) Count of Nassau-Weilburg | Rupert 'the Bellicose' (c. 1340 +1390) Count of Nassau-Sonnenberg | John I (1340 +1416) Count of Nassau-Dillenburg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Philip I 1368 +1429) Count of Nassau in Weilburg,Saarbrücken, etc. | Adolph (1362 +1420) Count of Nassau-Dillenburg-Dietz | John II "The Elder" (c.1365 +1443) | Engelbert I (c. 1370/80 +1442) Count of Nassau, Baron of Breda founder of the Netherlands Nassaus | John III "The Younger" (+1430) Count of Nassau in Siegen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Philip II (1418 +1492) Count of Nassau-Weilburg | John II (1423 +1472) Count of Nassau-Saarbrücken ext. 1574 | John IV (Jan) (1410, +1475) Count of Nassau-Dillenburg-Dietz | Henry II (1414 +1450) Count of Nassau-Dillenburg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| John III (1441 +1480) Count of Nassau-Weilburg | Philip (1443–1471) Count of Nassau-Weilburg | Engelbert II the Valorious (1451 +1504) Count of Nassau and Vianden, Baron of Breda(fr), Lek, Diest, Roosendaal en Nispen and Wouw | John V (1455 +1516) Count of Nassau in Dillenburg, Siegen, Hadamar, Herborn, Vianden, Dietz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| From here descends the House of Nassau-Weilburg and the Grand Ducal Family of Luxembourg (see below also)' | From here descends the House of Orange-Nassau (see below also) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A detailed family tree can be found here.[42] A detailed family tree of the House of Orange-Nassau from the 15th century can be found on the Dutch Wikipedia at Dutch monarchs family tree.
A summary family tree of the House of Orange-Nassau[43] from the joining of the house of Nassau-Breda/Dillenburg and the House of Châlon-Arlay-Orange to the end of the Dutch Republic is shown below. The family spawned many famous statesmen and generals, including two of the acknowledged "first captains of their age", Maurice of Nassau and the Marshal de Turenne.
The house of Orange-Nassau was relatively unlucky in establishing a hereditary dynasty in an age that favoured hereditary rule. The Stuarts and the Bourbons came to power at the same time as the Oranges, the Vasas and Oldenburgs were able to establish a hereditary kingship in Sweden and Denmark, and the Hohenzollerns were able to set themselves on a course to the rule of Germany. The House of Orange was no less gifted than those houses, in fact, some might argue more so, as their ranks included some the foremost statesmen and captains of the time. Although the institutions of the United Provinces became more republican and entrenched as time went on, William the Silent had been offered the countship of Holland and Zealand, and only his assassination prevented his accession to those offices. This fact did not go unforgotten by his successors.[2]:28–31,64,71,93,139–141
_-_Four_generations_Princes_of_Orange_-_William_I%2C_Maurice_and_Frederick_Henry%2C_William_II_and_William_III_-_1662-1666.jpg)
The Prince of Orange was also not just another noble among equals in the Netherlands. First, he was the traditional leader of the nation in war and in rebellion against Spain. He was uniquely able to transcend the local issues of the cities, towns and provinces. He was also a sovereign ruler in his own right (see Prince of Orange article). This gave him a great deal of prestige, even in a republic. He was the center of a real court like the Stuarts and Bourbons, French speaking, and extravagant to a scale. It was natural for foreign ambassadors and dignitaries to present themselves to him and consult with him as well as to the States General to which they were officially credited. The marriage policy of the princes, allying themselves twice with the Royal Stuarts, also gave them acceptance into the royal caste of rulers.[44]:76–77,80
Besides showing the relationships among the family, the tree above then also points out an extraordinary run of bad luck. In the 211 years from the death of William the Silent to the conquest by France, there was only one time that a son directly succeeded his father as Prince of Orange, Stadholder and Captain-General without a minority (William II). When the Oranges were in power, they also tended to settle for the actualities of power, rather than the appearances, which increasingly tended to upset the ruling regents of the towns and cities. On being offered the dukedom of Gelderland by the States of that province, William III let the offer lapse as liable to raise too much opposition in the other provinces.[44]:75–83

The main house of Orange-Nassau also spawned several illegitimate branches. These branches contributed to the political and economic history of England and the Netherlands. Justinus van Nassau was the only extramarital child of William of Orange. He was a Dutch army commander known for unsuccessfully defending Breda against the Spanish, and the depiction of his surrender on the famous picture by Diego Velázquez, The Surrender of Breda. Louis of Nassau, Lord of De Lek and Beverweerd was a younger illegitimate son of Prince Maurice and Margaretha van Mechelen. His descendants were later created Counts of Nassau-LaLecq. One of his sons was the famous general Henry de Nassau, Lord of Overkirk, King William III's Master of the Horse, and one of the most trusted generals of John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough. His descendants became the Earls of Grantham in England. Frederick van Nassau, Lord of Zuylestein, an illegitimate son of Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange, gave rise to the Earls of Rochford in England. The 4th earl of Rochford was a famous English diplomat and a statesman.
In 1814, William VI of Orange became King of the Netherlands. The institution of the monarch in the Netherlands is considered an office under the Dutch Constitution. There are none of the religious connotations to the office as in some other monarchies. A Dutch sovereign is inaugurated rather than crowned in a coronation ceremony. It was initially more of a crowned/hereditary presidency, and a continuation of the status quo ante of the pre-1795 hereditary stadholderate in the Republic. In practice today, the monarch has considerably less power. This summary genealogical tree shows how the current Royal house of Orange-Nassau is related:[14]
Coats of Arms

The gallery below show the coats of arms used by members of the house of Orange-Nassau. Their growing complexity and use of crowns shows how arms are used to reflect the growing political position and royal aspirations of the family. A much more complete armorial is given at the Armorial of the House of Nassau, and another one at Wapen van Nassau, Tak van Otto at the Dutch Wikipedia.
The ancestral coat of arms of the Ottonian line of the house of Nassau is shown right. Their distant cousins of the Walramian line added a red coronet to distinguish them. There is no specific documentation in the literature on the origin of the arms. The lion was always a popular noble symbol, originating as a symbol of nobility, power, and royal aspirations in western culture going all the way back to Hercules. The lion was also heavily used as a heraldic symbol in border territories and neighbouring countries of the Holy Roman Empire and France. It was in all likelihood a way of showing independence from the Holy Roman Emperor, who used an eagle in his personal arms and the King of France, who used the famous Fleur-de-lis. The lion was so heavily used in the Netherlands for various provinces and families (see Leo Belgicus) that it became the national arms of the Dutch Republic, its successor Kingdom of the Netherlands, Coat of Arms of Belgium, and Luxembourg. Blue, because of its nearness to purple, which in the northern climes tended to fade (red was the other choice), was also a popular color for those with royal aspirations. The billets could have been anything from blocks of wood to abstractions of the reenforcements holding the shield together. The fact that these were arms were very similar to those of the counts of Burgundy (Franche-Comté) did not seem to cause too much confusion.
Henry III of Nassau-Breda came to the Netherlands in 1499 as heir to his uncle, Engelbrecht II of Nassau-Breda. His and his uncle's arms are shown below. When Philbert, prince of Orange died in 1530, his sister's son René of Breda inherited the Princedom of Orange on condition that he used the name and coat of arms of the Châlon-Orange family. History knows him therefore as René of Châlon instead of as "René of Nassau-Breda." The 1st and 4th grand quarters show the arms of the Chalons-Arlay (the gold bend) princes of Orange (the bugle). The blue and gold cross is the arms of Jeanne of Geneva, who married one of the Chalons princes. The 2nd and 3rd show the quarterings of Brittany and Luxembourg-St. Pol. The inescutcheon overall is his paternal arms quartered of Nassau and Breda. William the Silent's father, William the Rich, was rich only in children. He bore the arms shown below. Clockwise from upper left they displayed the arms of Nassau (1st quarter), Katzenelenbogen (3rd quarter), Dietz (2nd quarter), Vianden (4th quarter).
 Arms of Engelbrecht II and Henry III of Nassau-Breda.[48]
Arms of Engelbrecht II and Henry III of Nassau-Breda.[48] Coat of arms of Rene of Chalons as Prince of Orange.[48]
Coat of arms of Rene of Chalons as Prince of Orange.[48] Arms of William the Rich, count of Nassau-Dillenburg.[48]
Arms of William the Rich, count of Nassau-Dillenburg.[48]
The princes of Orange in the 16th and 17th century used the following sets of arms. On becoming prince of Orange, William placed the Châlon-Arlay arms in the center ("as an inescutcheon") of his father's arms. He used these arms until 1582 when he purchased the marquisate of Veere and Vlissingen. It had been the property of Philip II since 1567, but had fallen into arrears to the province. In 1580 the Court of Holland ordered it sold. William bought it as it gave him two more votes in the States of Zeeland. He owned the government of the two towns, and so could appoint their magistrates. He already had one as First Noble for Philip William, who had inherited Maartensdijk. This made William the predominant member of the States of Zeeland. It was a smaller version of the countship of Zeeland (& Holland) promised to William, and was a potent political base for his descendants. William then added the shield of Veere and Buren to his arms as shown in the arms of Frederick Henry, William II and William III with the arms of the marquisate in the top center, and the arms of the county of Buren in the bottom center.[2]:29–30 William also started the tradition of keeping the number of billets in the upper left quarter for Nassau at 17 to symbolize the original 17 provinces of the Burgundian/Habsburg Netherlands, which he always hoped would form one united nation.
 Coat of arms of William the Silent as Prince of Orange from 1544 to 1582, and his eldest son Philip William[48]
Coat of arms of William the Silent as Prince of Orange from 1544 to 1582, and his eldest son Philip William[48] The coat of arms used by William the Silent from 1582 until his death, Frederick Henry, William II, and William III as Prince of Orange[48][48]
The coat of arms used by William the Silent from 1582 until his death, Frederick Henry, William II, and William III as Prince of Orange[48][48]
 An alternate coat of arms sometimes used by Frederick Henry, William II, and William III as Prince of Orange showing the county of Moers in the top center rather than Veere.[51]
An alternate coat of arms sometimes used by Frederick Henry, William II, and William III as Prince of Orange showing the county of Moers in the top center rather than Veere.[51] Coat of arms on expeditionary banner of William and Mary, 1688, showing the arms of William III impaled with the royal arms of England
Coat of arms on expeditionary banner of William and Mary, 1688, showing the arms of William III impaled with the royal arms of England.svg.png) Coat of arms of King William III of England as King of England.
Coat of arms of King William III of England as King of England.
When John William Friso became Prince of Orange, he used the arms below. However, he was never recognized outside of Holland and areas friendly to Holland as Prince of Orange. His son, William IV, recognized as Prince of Orange, seems to have used the original arms of William the Silent.[52] When the princes of Orange fled the Netherlands during the Batavian Republic and the Kingdom of Holland, and when France occupied the Netherlands, they were compensated by Napoleon with the Principality of Nassau-Orange-Fulda. These principalities were confiscated when Napoleon invaded Germany (1806) and William VI supported his Prussian relatives. He succeeded his father as prince of Orange later that year, after William V's death. The house of Orange-Nassau also had several illegitimate lines (see below) who based their arms on the arms of Nassau-Dillenburg.
- Arms of Johan Willem Friso as Prince of Orange.[53]
 Arms of William VI of Orange as prince of Orange-Nassau-Fulda. The bottom most shield shows clockwise from top left the principality of Fulda, the lordship of Corvey, the county of Weingarten, and the lordship of Dortmund.[52]
Arms of William VI of Orange as prince of Orange-Nassau-Fulda. The bottom most shield shows clockwise from top left the principality of Fulda, the lordship of Corvey, the county of Weingarten, and the lordship of Dortmund.[52]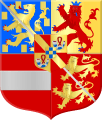
 Arms of the Louis of Nassau, Lord of De Lek and Beverweerd, natural son of Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange, and his descendants the lords of den Lek and the earls of Grantham in England[52]
Arms of the Louis of Nassau, Lord of De Lek and Beverweerd, natural son of Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange, and his descendants the lords of den Lek and the earls of Grantham in England[52] Arms of the lords of Zuylestein, natural son of Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange and his descendants the earls of Rochford in England[52]
Arms of the lords of Zuylestein, natural son of Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange and his descendants the earls of Rochford in England[52]
When William VI of Orange returned to the Netherlands in 1813 and was proclaimed Sovereign Prince of the Netherlands, he quartered the former Arms of the Dutch Republic (1st and 4th quarter) with the "Châlon-Orange" arms (2nd and 3rd quarter), which had come to symbolize Orange. As an in escutcheon he placed his ancestral arms of Nassau. When he became King in 1815, he combined the Dutch Republic Lion with the billets of the Nassau arms and added a royal crown to form the Coat of arms of the Netherlands. In 1907, Queen Wilhelmina replaced the royal crown on the lion and the shield bearers of the arms with a coronet.[54]
 Arms of the States General of the Dutch Republic. The sword symbolizes the determination to defend the nation, and the bundle of 7 arrows the unity of the 7 United Provinces of the Dutch Republic.
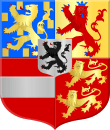
Arms of the States General of the Dutch Republic. The sword symbolizes the determination to defend the nation, and the bundle of 7 arrows the unity of the 7 United Provinces of the Dutch Republic.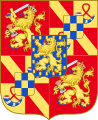 Arms of William VI as sovereign prince of the Netherlands.[48]
Arms of William VI as sovereign prince of the Netherlands.[48].svg.png) First arms of the Kingdom and Kings of the Netherlands from 1815 to 1907.[14]
First arms of the Kingdom and Kings of the Netherlands from 1815 to 1907.[14]
Wilhelmina further decreed that in perpetuity her descendants should be styled "princes and princesses of Orange-Nassau" and that the name of the house would be "Orange-Nassau" (in Dutch "Oranje-Nassau"). Only those members of the members of the Dutch Royal Family that are designated to the smaller "Royal House" can use the title of prince or princess of the Netherlands.[14] Since then, individual members of the House of Orange-Nassau are also given their own arms by the reigning monarch, similar to the United Kingdom. This is usually the royal arms, quartered with the arms of the principality of Orange, and an in escutcheon of their paternal arms.[55]
 Juliana of the Netherlands & Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms
Juliana of the Netherlands & Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms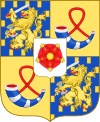 Beatrix of the Netherlands & Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms
Beatrix of the Netherlands & Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms William Alexander of the Netherlands and Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms
William Alexander of the Netherlands and Oranje-Nassau Personal Arms Arms for children of King William Alexander of the Netherlands
Arms for children of King William Alexander of the Netherlands Sons of Princess Margriet of the Netherlands, Pieter van Vollenhoven[56]
Sons of Princess Margriet of the Netherlands, Pieter van Vollenhoven[56]
As sovereign Princes, the princes of Orange used an independent prince's crown or the princely hat. Sometimes, only the coronet part was used (see, here and here). After the establishment of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, and as the principality of Orange had been incorporated into France by Louis XIV, they used the Dutch Royal Crowns. The full coats of arms of the princes of Orange, later Kings of the Netherlands, incorporated the arms above, the crown, 2 lions as supporters and the motto "Je maintiendrai" ("I will maintain"), the latter taken from the Chalons princes of Orange, who used "Je maintiendrai Chalons".[3]:35
 |
.svg.png) |
 |
|---|---|---|
Lands and Titles
Besides being sovereign over the principality of Orange, this is a partial listing of larger estates and titles that William the Silent and his heirs possessed, most enfeoffed to some other sovereign, either the King of France, the Habsburgs, or the States of the provinces of the Netherlands:
- Marquis of Veere and Vlissingen


- Count of Nassau-Dillenburg

- Katzenelnbogen




- Viscount of Antwerp
- Baron of Breda









.svg.png)


- Lord of Baarn






.svg.png)

.svg.png)






In most of the estates in the more populous provinces of Holland and Zealand, the land itself was secondary to the profit on the commerce that flowed through it.
Standards
The Dutch Royal Family also makes extensive use of royal standards that are based on their coats of arms, but not identical to them (as the British Royal Family does). Some examples from the Royal Family's website are:[14]
The standards of the ruling king or queen:
.svg.png) Royal Flag of the Netherlands (1815–1908)
Royal Flag of the Netherlands (1815–1908).svg.png) Royal Flag of the Netherlands (1908–2013)
Royal Flag of the Netherlands (1908–2013) Royal Standard of the Netherlands
Royal Standard of the Netherlands
The standards of the current sons of the former Queen, now Princess Beatrix and their wives and the Queen's husband:
.svg.png) Royal Standard of the Princes of the Netherlands (Sons of Queen Beatrix)
Royal Standard of the Princes of the Netherlands (Sons of Queen Beatrix) Standard of Claus von Amsberg as Royal consort of the Netherlands
Standard of Claus von Amsberg as Royal consort of the Netherlands Standard of Princess Maxima of the Netherlands
Standard of Princess Maxima of the Netherlands Standard of Princess Laurentien of the Netherlands
Standard of Princess Laurentien of the Netherlands
A fuller listing can be found at the Armorial de la Maison de Nassau, section Lignée Ottonienne at the French Wikipedia.
See also
For further about the Dutch Monarchy and the Dutch Royal House:
- Dutch monarchy
- House of Nassau
- Prince of Orange
- Principality of Orange
- Orange Institution
- William III of England
Traditionally, members of the Nassau family were buried in Breda; but because that city was in Spanish hands when William died, he was buried in a new crypt in the New Church, Delft. The monument on his tomb was originally very modest, but it was replaced in 1623 by a new one, made by Hendrik de Keyser and his son Pieter. Since then, most of the members of the House of Orange-Nassau, including all Dutch monarchs have been buried in that church. His great-grandson William the third, King of England and Scotland and Stadtholder in the Netherlands, was buried in Westminster Abbey
- Crypt of the House of Orange-Nassau in Delft
- Burial Monument to William the Silent
- Crypt of the Frisian Nassaus in Leeuwarden
- Crypt of the Nassau-LaLecqs in Ouderkerk aan den IJssel
- Original Crypt of Netherland Nassaus in Breda
- Crypt of Engelbrecht II van Nassau in Breda
- Crypt of the Nassau-Bergens in Bergen
- Crypt of the Nassau-Siegens in Siegen
In Robert A. Heinlein's 1956 science fiction novel Double Star, the House of Orange reigns over – but does not rule over – an empire of humanity that spans the entire Solar System.
Residences of the House of Orange
 Hotel de Nassau in Brussels painted 1658
Hotel de Nassau in Brussels painted 1658
 Noordeinde Palace, The Hague
Noordeinde Palace, The Hague Huis ten Bosch palace, The Hague
Huis ten Bosch palace, The Hague

References
- In isolation, van is pronounced [vɑn].
- Rowen, Herbert H. (1988). The princes of Orange: the stadholders in the Dutch Republic. Cambridge University Press.
- Grew, Marion Ethel (1947). The House of Orange. 36 Essex Street, Strand, London W.C.2: Methuen & Co. Ltd.CS1 maint: location (link)
- Blok, Petrus Johannes (1898). History of the people of the Netherlands. New York: G. P. Putnam's sons.
- Israel, Jonathan I. (1995). The Dutch Republic: Its Rise, Greatness and Fall, 1477–1806. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-873072-1. ISBN 0-19-820734-4 paperback.
- Delff, Willem Jacobsz. "De Nassauische Cavalcade". From an engraving on exhibit in the Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam. Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- Motley, John Lothrop (1855). The Rise of the Dutch Republic. Harper & Brothers.
- Motley, John Lothrop (1860). History of the United Netherlands from the Death of William the Silent to the Synod of Dort. London: John Murray.
- Geyl, Pieter (2002). Orange and Stuart 1641–1672. Arnold Pomerans (trans.) (reprint ed.). Phoenix.
- Rowen, Herbert H. (1978). John de Witt, grand pensionary of Holland, 1625–1672. Princeton University Press.
- He acquired Fulda, Corvey, Weingarten and Dortmund. He lost the possessions again after changing sides from France to Prussia in 1806 when he refused to join the Confederation of the Rhine. Cf. J. and A. Romein 'Erflaters van onze beschaving', Querido, 1979
- Hay, Mark Edward (1 June 2016). "The House of Nassau between France and Independence, 1795–1814: Lesser Powers, Strategies of Conflict Resolution, Dynastic Networks". The International History Review. 38 (3): 482–504. doi:10.1080/07075332.2015.1046387.
- Couvée, D.H.; G. Pikkemaat (1963). 1813-15, ons koninkrijk geboren. Alphen aan den Rijn: N. Samsom nv. pp. 119–139.
- "The Official Website of the Dutch Royal House in English". Archived from the original on 30 May 2013. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- (in Dutch)Wet op het Kroondomein
- "Dutch Royal House – Movable Property". Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 2008-06-29.
- (in Dutch) Constitution for the Kingdom of the Netherlands Article 40 (Dutch edition of WikiSource)
- Koninkrijksrelaties, Ministerie van Binnenlandse Zaken en. "The Constitution of the Kingdom of the Netherlands 2008". www.government.nl.
- "In Pictures: The World's Richest Royals." Forbes. 7 July 2010. 30 September 2010.
- "How Much Is Queen Elizabeth Worth?." Forbes 26 June 2001.
- "Royal Flush." Forbes 4 March 2002.
- "Monarchs and the Madoff Scandal." Forbes. 17 June 2009.
- "In Pictures: The World's Richest Royals". Forbes.com. 30 August 2007. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- "Report: The World's Richest Royals." Forbes. April 29, 2011.
- Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland and Utrecht (employed by Philip II: 1559 – 1567, employed by the States General: 1572 – 1584), Stadtholder of Friesland and Overijssel (1580–1584)
- Stadtholder of Holland and Zeeland (1585–1625), Utrecht, Guelders and Overijssel (1590–1625), Groningen (1620–1625)
- Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel (1620–1625), Groningen and Drenthe (1640–1647)
- Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, Groningen, Drenthe and Overijssel
- Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht and Overijssel (1672–1702), Guelders (1675–1702), Drenthe (1696–1702)
- William III invaded – on invitation – England and became king of England, Scotland and Ireland
- Hereditary Stadtholder of Friesland (1711–1747), Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht and Overijssel (April/May 1747 – November 1747), Stadtholder of Groningen (1718–1747), Guelders and Drenthe (1722–1747), was formally voted the first Hereditary Stadtholder of the United Provinces (1747–1751)
- Stadtholders of Friesland, Groningen and Drenthe, became the direct male line ancestor of the Republic's hereditary Stadtholders, and later of the kings of the Netherlands.
- Stadtholder of Guelders (under Philip II), architect of the Union of Utrecht
- Stadtholder of Friesland (1584–1620), Groningen (1594–1620) and Drenthe (1596–1620)
- Stadtholder of Friesland (1620–1632), Groningen and Drenthe (1625–1632)
- Stadtholder of Friesland (1632–1640), Groningen and Drenthe (1632–1640)
- Stadtholder of Friesland (1640–1664), Groningen and Drenthe (1650–1664)
- In 1675 the State of Friesland voted to make the Stadtholdership hereditary in the house of Nassau-Dietz
- Hereditary Stadtholder of Friesland (1707–1711) and Griningen (1708–1711)
- "wetten.nl – Regeling – Wet lidmaatschap koninklijk huis – BWBR0013729". wetten.overheid.nl.
- Louda, Jiri; Maclagan, Michael (December 12, 1988), "Netherlands and Luxembourg, Table 33", Heraldry of the Royal Families of Europe (1st (U.S.) ed.), Clarkson N. Potter, Inc.
- Marek, Miroslav. "Nassau index page". genealogy.euweb.cz. Retrieved 5 September 2013.
- "Official Website of the Dutch Royal House". Rijksvoorlichtingsdienst (RVD), The Hague, the Netherlands. Retrieved 2013-04-30.
- Haley, K(enneth) H(arold) D(obson) (1972). The Dutch in the Seventeenth Century. Thames and Hudson. pp. 75–83. ISBN 0-15-518473-3.
- Rietstap, Johannes Baptist (1875). Handboek der Wapenkunde. the Netherlands: Theod. Bom. p. 348.
Prins FREDERIK: Het koninklijke wapen, in 't shcildhoofd gebroken door een rooden barensteel, de middelste hanger beladen met een regtopstaanden goud pijl.
- Junius, J.H. (1894). Heraldiek. the Netherlands: Frederik Muller. p. 151.
...de tweede oon voert het koninklijk wapen gebroken door een barensteel van drie stukken met een zilveren pijl.
- Junius, J.H. (1894). Heraldiek. the Netherlands: Frederik Muller. p. 151.
...is het wapen afgebeeld van de oudste dochter van den Koning der Nederlanden. De barensteel is van keel en beladen met een gouden koningskroon.
- Rietstap, Johannes Baptist (2003). Armorial general. vol.2. Genealogical Publishing Co. p. 297. ISBN 0-8063-4811-9. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
Ecartelé : au 1. d'azur, semé de billettes d'or au lion d'or, armé et lampassé de gueules, brochant sur le tout (Maison de Nassau) ; II, d'or, au léopard lionné de gueules, arméc ouronné et lampassé d'azur (Katzenelnbogen) ; III, de gueules à la fasce d'argent (Vianden) ; IV, de gueules à deux lions passant l'un sur l'autre ; sur-le-tout écartelé, aux I et IV de gueules, à la bande d'or (Châlon), et aux II et III d'or, au cor de chasse d'azur, virolé et lié de gueules (Orange) ; sur-le-tout-du-tout de cinq points d'or équipolés à quatre d'azur (Genève) ; un écusson de sable à la fasce d'argent brochant en chef (Marquis de Flessingue et Veere); un écusson de gueules à la fasce bretessée et contre-bretessée d'argent brochant en pointe (Buren). Cimier: 1er un demi-vol cont. coupé d'or sur gueles (Chalons), 2er une ramure de cerf d'or (Orange) 3er un demi-vol de sa, ch. d'un disque de armes de Dietz. Supports: deux lions d'or, arm. et lamp. de gueles. Devise: JE MAINTIENDRAI.
- Anonymous. "Wapenbord van Prins Maurits met het devies van de Engelse orde van de Kouseband". Exhibit of a painted woodcut of Maurice's Arms encircled by the Order of the Garter in the Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam. Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- Rietstap, Johannes Baptist (1861). Armorial général, contenant la description des armoiries des familles nobles et patriciennes de l'Europe: précédé d'un dictionnaire des termes du blason. G.B. van Goor. p. 746.
a la exception de celebre prince Maurice qui portai les armes ...
- Post, Pieter (1651). "Coat of Arms as depicted in "Begraeffenisse van syne hoogheyt Frederick Hendrick"". engraving, in the collection of. Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- Rietstap, Johannes Baptist (1861). Armorial général, contenant la description des armoiries des familles nobles et patriciennes de l'Europe: précédé d'un dictionnaire des termes du blason. G.B. van Goor. p. 746.
- ""Coat of Arms as depicted on the "Familiegraf van de Oranje-Nassau's in de Grote of Jacobijnerkerk te Leeuwarden"". Familiegraf van de Oranje-Nassau's in de Grote of Jacobijnerkerk te Leeuwarden. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- "Wapens van leden van het Koninklijk Huis". Coats of Arms of the Dutch Royal Family, Website of the Dutch Monarchy, the Hague. Rijksvoorlichtingsdienst (RVD), the Hague, the Netherlands. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
Het wapen van het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden (Rijkswapen) en dat van de Koningen der Nederlanden (Koninklijk wapen) is vanaf de oprichting van het Koninkrijk in 1815 identiek. Het Wapen werd in 1907 gewijzigd en laatstelijk vastgesteld bij Koninklijk Besluit van 23 april 1980, nr. 3 (stb. 206) bij de troonsaanvaarding van Koningin Beatrix. De beschrijving van het wapenschild in het eerste artikel is dwingend voorgeschreven, de in het tweede en derde artikel beschreven uitwendige versierselen zijn facultatief. In de praktijk wordt de basisuitvoering van het wapen wel het Klein Rijkswapen genoemd. Het Koninklijk Wapen wordt sinds 1907 gekenmerkt door een gouden klimmende leeuw met gravenkroon. De blauwe achtergrond (het veld) is bezaaid met verticale gouden blokjes. De term bezaaid geeft in de heraldiek aan dat het aantal niet vaststaat, waardoor er ook een aantal niet compleet zijn afgebeeld. Het wapenschild wordt gehouden door twee leeuwen die in profiel zijn afgebeeld. Op het wapenschild is een Koningskroon geplaatst. Op een lint dat onder het wapenschild bevestigd is, staat de spreuk 'Je Maintiendrai'. Bij Koninklijk Besluit van 10 juli 1907 (Stb. 181) werd het Koninklijk Wapen, tevens Rijkswapen, aangepast. De leeuw in het schild en de schildhoudende leeuwen droegen vóór die tijd alle drie de Koninklijke kroon, maar raakten deze kwijt nu de toegevoegde purperen hermelijn gevoerde mantel, gedekt door een purperen baldakijn, een Koningskroon ging dragen. De schildhouders waren vóór 1907 bovendien aanziend in plaats van en profiel.
- "Wapens van leden van het Koninklijk Huis". Coats of Arms of the Dutch Royal Family, Website of the Dutch Monarchy, the Hague. Rijksvoorlichtingsdienst (RVD), the Hague, the Netherlands. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- Klaas. "Maurits van Vollenhoven". Article on Maurits van Vollenhoven, 18-09-2008 10:28. klaas.punt.nl. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
Literature
- Herbert H. Rowen, The princes of Orange: the stadholders in the Dutch Republic. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press, 1988.
- John Lothrop Motley, "The Rise of the Dutch Republic". New York: Harper & Brothers, 1855.
- John Lothrop Motley, "History of the United Netherlands from the Death of William the Silent to the Synod of Dort". London: John Murray, 1860.
- John Lothrop Motley, "The Life and Death of John of Barenvelt". New York & London: Harper and Brothers Publishing, 1900.
- Petrus Johannes Blok, "History of the people of the Netherlands". New York: G. P. Putnam's sons, 1898.
- Jonathan I. Israel, "The Dutch Republic: Its Rise, Greatness, and Fall, 1477–1806" Oxford University Press, 1995. ISBN 0-19-820734-4
- Pieter Geyl, "Orange and Stuart 1641–1672" Phoenix Press, 2002>
- Mark Edward Hay, ‘Russia, Britain, and the House of Nassau: The Re-Establishment of the Orange Dynasty in the Netherlands, March–November 1813’, Low Countries Historical Review 133/1, March 2018, 3–21.
- Rouven Pons (Hrsg.): Oranien und Nassau in Europa. Lebenswelten einer frühneuzeitlichen Dynastie. Historische Kommission für Nassau, Wiesbaden 2018, ISBN 978-3-930221-38-7.
External links
- Dutch Royal House – official website
- Sources about the history of Orange-Nassau in the Hessian Main State Archives, Wiesbaden
— Royal house — House of Orange-Nassau | ||
| Vacant Title last held by House of Bonaparteas ruling house of the Kingdom of Holland |
Ruling house of the Netherlands 1813– |
Succeeded by Incumbent Cadet branch of House of Mecklenburg 1948–1980 House of Lippe 1980–2013 House of Amsberg 2013 – present |
| Vacant Title last held by House of Habsburg-Lorraineas ruling house of the Duchy of Luxembourg |
Ruling house of Luxembourg 1814–1890 |
Succeeded by House of Nassau-Weilburg |
| Vacant Title last held by House of Châlon-Orangeas ruling house of the Principality of Orange |
Ruling house of the Principality of Orange 1544– |
Succeeded by Incumbent |
| Vacant Title last held by House of Habsburgas ruling house of the Spanish Netherlands |
Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic 1581–1795 |
Succeeded by Batavian Republic |
| Vacant Title last held by House of Stuartas ruling house of the Kingdom of England |
Ruling house of England 1694–1702 |
Succeeded by House of Stuart |
| Vacant Title last held by House of Stuartas ruling house of the Kingdom of Scotland |
Ruling house of Scotland 1694–1702 |
Succeeded by House of Stuart |
