Copenhagen Airport
Copenhagen Airport, Kastrup (Danish: Københavns Lufthavn, Kastrup, pronounced [kʰøpm̩ˈhɑwns ˈlɔftˌhɑwˀn ˈkʰæˌstʁɔp]; IATA: CPH, ICAO: EKCH) is the main international airport serving Copenhagen, Denmark, the rest of Zealand, the Øresund Region, and a large part of southern Sweden including Scania. It is the largest airport in the Nordic countries with close to 30.3 million passengers in 2019 and one of the oldest international airports in Europe. It is the third-busiest airport in Northern Europe, and the busiest for international travel in Scandinavia.[3]
Copenhagen Airport, Kastrup Københavns Lufthavn, Kastrup | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | Københavns Lufthavne | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Copenhagen, Denmark and Malmö, Sweden | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Kastrup, Tårnby, Copenhagen, Denmark | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 5 m / 17 ft | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 55°37′05″N 012°39′22″E | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | cph.dk | ||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||
 CPH Location within Denmark | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2019) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
The airport is located on the island of Amager, 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) south of Copenhagen city centre, and 24 kilometres (15 mi) west of Malmö city centre, which is connected to Copenhagen via the Øresund Bridge. The airport covers an area of 11.8 square kilometres (4.6 sq mi).[4] Most of the airport is situated in the municipality of Tårnby, with a small portion in the city of Dragør.
The airport is the main hub out of three used by Scandinavian Airlines and is also an operating base for Sunclass Airlines and Norwegian Air Shuttle. Copenhagen Airport handles around 60 scheduled airlines, and has a maximum operation capability of 83 operations/hour, and a total of 108 jet bridges and remote parking stands. Unlike other Scandinavian airports, most of the airport's passengers are international. In 2015, 6.1% of passengers travelled to and from other Danish airports, 83.5% to/from other European airports, and 10.4% were intercontinental passengers.[5] The airport is owned by Københavns Lufthavne, which also operates Roskilde Airport. The airport employs 1,700 people (not including employees in shops, restaurants, etc.).[6]
Copenhagen Airport was originally called Kastrup Airport, since it is located in the small town of Kastrup, now a part of the Tårnby municipality. The formal name of the airport is still Copenhagen Airport, Kastrup, to distinguish it from Roskilde Airport, whose formal name is Copenhagen Airport, Roskilde.
History
The airport was inaugurated 20 April 1925 and was one of the first civil airports in the world. It consisted of a large, impressive terminal built of wood, a couple of hangars, a balloon mast, a hydroplane landing stage and a few grassy meadows that could be used as runways. The grass on the runways was kept short by sheep, which were shepherded away before take-offs and landings. From 1932 to 1939, takeoffs and landings increased from 6,000 to 50,000 and passenger number increased to 72,000. Between 1936 and 1939, a new terminal was built, considered one of the finest examples of Nordic functionalism. The terminal was designed by Vilhelm Lauritzen, who was considered a pioneer among architects, in terms not only of architecture and construction, but also of service and passenger comfort.[7]
In the years of World War II, the Copenhagen airport was closed for civil operations except for periodic flights to destinations in Sweden, Germany, and Austria. In the summer of 1941 the first hard-surface runway opened. It was 1,400 metres (4,600 ft) long and 65 metres (213 ft) wide. When World War II ended in May 1945, Copenhagen had the most modern international airport in Europe, because the airport remained untouched by actual acts of war.
On 1 August 1947, Scandinavian Airlines (SAS) was founded, an important event for the Copenhagen Airport, as Copenhagen was to be the main hub for the airline. Traffic increased rapidly in the first years SAS operated. On 26 January 1947, a KLM Douglas DC-3 "Dakota" crashed at the airport after stopping en route to Stockholm. 22 people on board died, including the Swedish prince Gustav Adolf and the American opera singer Grace Moore. In 1948 Copenhagen airport was third largest airport in Europe with 150 daily takeoffs and almost 300,000 passengers for the year. The airport continued its rapid growth. The terminal was expanded several times and new hangars were erected.
In 1954, Scandinavian Airlines begins the world's first trans-polar route, flying initially to Los Angeles. The route proved to be a publicity coup, and for some years Copenhagen became a popular transit point for Hollywood stars and producers flying to Europe – also the airport handled 11,000 tonnes of freight per year. In 1956, the airport handled 1 million passengers per year and won the award for the world's best airport. The runways were lengthened and fitted with technically advanced equipment.
.jpg)
By 10 May 1960, when the new airport terminal (now Terminal 2) was inaugurated, the daily number of jet operations had increased to 28, and still traffic kept on growing. The large new airport terminal soon became too small, and in 1969 yet another huge expansion programme was launched. Domestic traffic was relocated to a new domestic terminal (the eastern part of Terminal 1). The (current) international terminal was supplemented with a new pier (C) and a separate arrivals hall (the building between Terminals 2 and 3). A new control tower and 3,600 metres (11,800 ft) of additional runways allowed take-offs and landings to take place at the same time. When the comprehensive expansion was completed in 1972, the number of take-offs and landings exceeded 180,000 and there were more than eight million passengers.[8]
Throughout the 1970s, airport traffic continued to grow, but the airport was not expanded further. A new large airport located at the island of Saltholm (with a connecting bridge to Denmark and Sweden) was on the drawing board. It would be a huge investment, and the proposal was evaluated thoroughly by many experts. In 1980, however, the Danish parliament instead decided to expand the capacity of Copenhagen airport to 20–22 million passengers by the year 2000. This solution was far cheaper than building a new airport and because the new types of aircraft were less noisy, an airport on Saltholm did not offer a decisive environmental gain. In 1973 the airport handled 8 million passengers per year. The third (long) runway opened and the dual runway system (04L/22R-04R/22L) opened, strongly expanding the starts and landings capacity.
The expansion of the airport began in 1982, after the necessary period of planning. The intention was not to build Europe's largest airport, but to build transit passengers' favourite airport. A stay at the airport was supposed to be an integral part of the travel experience. Efficiency and precision were obvious demands, but focus was also on generating an oasis where international travellers could relax: beautiful architecture, Scandinavian design, and pleasant, light, and comfortable surroundings with plenty of shops, restaurants, and other facilities providing enjoyment and pleasure. The new cargo terminal was built in the eastern area of the airport.
A number of important construction projects were completed in 1998: a pier connecting the domestic and international terminals; a new arrivals hall; new modern baggage handling facilities; an underground railway station with two large underground parking facilities with 2400 spaces opens; and above it all the spacious and impressive delta-shaped terminal (Terminal 3) with 17 million passengers capacity. The first stage of the new Pier D was completed in the spring of 1999.[9]
On 1 July 2000 the Øresund Bridge opened which connects Denmark and Sweden by motorway and train. In 2001 the five-star Hilton hotel opened with 382 rooms. In 2006 for the first time in its history Copenhagen airport exceeded 20 million passengers and reached 20,900,000 passengers. In October 2007 the metro station opened, connecting the airport to the Copenhagen Metro. A new control tower opened in 2008 by Naviair as part of a major renovation of the ATC system. Airport officials announced plans to build a new low-cost terminal at the facility. On 31 October 2010 the new low cost terminal CPH Go opened by easyJet.[10] In 2013 the airport handled a new record of 24,067,030 passengers. In 2014 CPH announced plans to increase capacity to 40 million passengers per year.[11]
From late 2015, the airport became the first in Scandinavia to have a regularly scheduled A380 service after Emirates started operating the plane for its Copenhagen route.[12][13]
Facilities
Terminals
Copenhagen Airport has two terminals for check-in, Terminals 2 and 3, which handle all flights and share a common airside passenger concourse as well as the arrivals section which houses customs and baggage claim and is physically located in Terminal 3. The airside is reached through a common security check located between Terminal 2 and Terminal 3.
The common airside passenger concourse is divided into piers, called A, B, C, D and F.[14] Pier A and B are for flights inside Schengen only. Pier C is mostly for flights outside Schengen. Pier D is mostly for flights inside Schengen. The newest section, CPH Go, now called Pier F, dedicated to low-cost carriers opened in October 2010. So far, EasyJet, Transavia and Ryanair are the only airlines operating from this facility. An all new Terminal 4 has been discussed, but replaced by plans to expand the current facilities in appropriate increments.[15] Copenhagen Airport says passengers have easy transfer possibilities.[16]
Previously all domestic flights departed from Terminal 1, but from 29 March 2015 all departures have been collected in Terminals 2 and 3,[17][18] and Pier C was expanded with another jetbridge at DKK 10M to facilitate the Emirates Airbus A380 to Dubai from December 2015,[19][20] which was the first 2-class A380 carrying 615 passengers.[13][21]
A new pier, to be called Pier E, is under construction and will be fully finished in 2020.[22]
 Welcome sign
Welcome sign- Check-in desks at Terminal 2
- Exterior of Terminal 3
 Baggage claim inside Terminal 3
Baggage claim inside Terminal 3
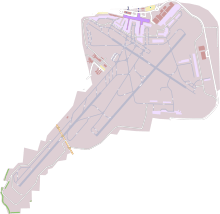
Runways
Despite the short distance to the city centre, approaches to, and departures from, the airport are above water due to the heading of the dual parallel runway system (04R/22L & 04L/22R). Those runways point to the Øresund strait, close in both directions. The supplementary runway (30/12) oriented perpendicular to the main runways also has its approach or departure over Øresund in one direction. In the opposite direction, the 30/12 runway has noise restrictions as flight happens close over residential areas.[23] Other advantages are the low altitude of the airport and absence of hills and high buildings below the approach directions. In case of fog, the runway 22L is equipped with an ILS of category III C system, which allows modern aircraft to land in zero sight. Runway 04R/22L was widened by 4 meters in each side at DKK 30M to accommodate the Airbus A380, as part of a general concrete renewal program of DKK 300M.[13][19][20]
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| China Cargo Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong |
| DHL Aviation | East Midlands, Leipzig/Halle, Madrid, Oslo–Gardermoen, Stockholm–Arlanda |
| Emirates SkyCargo | Atlanta, Chicago–O'Hare, Columbus–Rickenbacker,[54] Dubai–Al Maktoum,[55] Houston–Intercontinental, Los Angeles, Mexico City |
| FedEx Express | Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| LATAM Cargo Brasil | Campinas |
| West Air Sweden | Helsinki |
Statistics
Passenger numbers
handled[nb 1] |
% Change |
movements |
% Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 18,082,158 | 288,738 | ||
| 2002 | 18,253,446 | 266,896 | ||
| 2003 | 17,707,742 | 259,002 | ||
| 2004 | 19,034,557 | 272,512 | ||
| 2005 | 19,980,301 | 268,652 | ||
| 2006 | 20,877,533 | 258,354 | ||
| 2007 | 21,409,886 | 257,587 | ||
| 2008 | 21,529,857 | 264,086 | ||
| 2009 | 19,715,317 | 236,170 | ||
| 2010 | 21,501,473 | 245,635 | ||
| 2011 | 22,725,284 | 253,759 | ||
| 2012 | 23,334,939 | 242,990 | ||
| 2013 | 24,066,917 | 244,933 | ||
| 2014 | 25,627,093 | 251,799 | ||
| 2015 | 26,608,869 | 254,832 | ||
| 2016 | 29,043,287 | 265,784 | ||
| 2017 | 29,177,833 | 259,243 | ||
| 2018[57] | 30,298,531 | 266,096 | ||
| 2019[1] | 30,256,703 | 263,411 |
Busiest routes
| Rank | Airport | All passengers | Change 18/19 |
Operating airlines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Qatar Airways | |||
| 2 | Delta Air Lines, Norwegian, Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 3 | Emirates, Norwegian | |||
| 4 | Norwegian, Thai Airways | |||
| 5 | Air China, Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 6 | Air Canada | |||
| 7 | Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 8 | Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 9 | Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 10 | Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 11 | Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 12 | Singapore Airlines | |||
| 13 | Scandinavian Airlines | |||
| 14 | Air India | |||
| 15 | Scandinavian Airlines |
| Destination |
Airport(s) |
Passengers |
|---|---|---|
| Aalborg | Aalborg Airport | 890,706 |
| Bornholm | Bornholm Airport | 256,913 |
| Aarhus | Aarhus Airport | 194,782 |
| Billund | Billund Airport | 151,201 |
| Karup | Midtjyllands Airport | 148,508 |
Other facilities
The SAS traffic office resides at Copenhagen Airport South and in Dragør, Dragør Municipality together with a VIP-terminal. The VIP-terminal is actually the first terminal building, from the 1920s. It was moved about 2 km during the 1990s.
In 2015, Boeing opened a maintenance, repair, and operations facility at CPH, as proximity to daily operations is more important than high wages when checks have to be made every 1,000 flight hours.[61]
Ground transport
Within the airport area, special airport buses depart every 15 minutes. The bus line connects all terminals and parking lot areas and uses in all 11 bus stops. The transport is free of charge for all. During a few night hours, the buses depart every 20 minutes instead.[62]
Train

The airport's station is located underneath Terminal 3 on the Øresund Railway Line.
- The station is served by trains operated by DSB Øresund as part of the Øresundståg service. These trains, running as local services between Copenhagen city centre and Helsingør, have a dense stopping pattern inside Denmark. Øresundståg also operates regional and intercity trains to destinations across the south of Sweden: Malmö, Gothenburg, Kalmar, Karlskrona, and Kristianstad.
- DSB, the Danish national rail operator, have InterCity and InterCityExpress trains calling at this station. Domestic destinations include Esbjerg, Aarhus, Aalborg and Sønderborg. DSB additionally runs trains to border cities of Germany and Sweden, such as Flensburg (Germany) and Ystad (Sweden), where a ferry connects the station to the Danish island of Bornholm.
- Swedish SJ runs several high-speed trains with daily departures between Copenhagen central station (København H) and Stockholm central station (Stockholm C) and Gothenburg (Göteborg). These trains all call at the Copenhagen Airport station (København Lufthavn/Kastrup).
Metro
Line M2 of the Copenhagen Metro links the airport with the city centre in around 15 minutes. The Metro station is two floors above the underground rail station and continues on elevated tracks until it goes underground after 5 stations. The metro trains run very frequently, in rush hours every four minutes, outside rush hours and on weekends every six minutes, and every 15/20 minutes at night.
Road
- Movia buses 5C, 35, 36 and Gråhundbus line 999 all stop at the airport; bus 888, express-bus to Jutland, also stops at the airport. Movia bus 2A stops near the airport. There are long-distance buses to Sweden and Norway operated by Swebus: 820 to Oslo via Gothenburg and 832 to Uppsala via Stockholm. GoByBus and Bus4You also operate the same routes.
- The E20 motorway runs right by the airport. The E20 uses the toll road Øresund Bridge to Sweden. The airport has 8,600 parking spaces.
Incidents and accidents

- 26 January 1947: Douglas Dakota (DC-3), PH-TCR of KLM crashed after takeoff from Copenhagen, killing all 22 on board, including Prince Gustaf Adolf of Sweden (father of present king Carl XVI Gustaf) and American singer and actress Grace Moore. The delayed KLM flight from Amsterdam had landed at Copenhagen for a routine stop before continuing to Stockholm. Soon after the Douglas DC-3 aircraft took off, it climbed to an altitude of about 50 metres (150 feet), stalled, and plummeted nose-first to the ground where it exploded on impact. The investigation showed that the crash had been caused by a forgotten elevator gust lock. Short of time, the captain never performed his checklist and took off not realising the lock was still in place. See 1947 KLM Douglas DC-3 Copenhagen accident.
- 17 November 1957: Vickers Viscount G-AOHP of British European Airways crashed at Ballerup after the failure of three engines on approach to Copenhagen Airport. The cause was a malfunction of the anti-icing system on the aircraft.[63]
- 28 August 1971: a Malév Ilyushin Il-18, HA-MOC crashed into the sea while executing an instrument approach. The main cause of the accident was microburst, a particularly dangerous and unpredictable meteorological phenomenon. 23 passengers and the crew of nine died. Two passengers survived. The captain of the plane was World War II flying ace of the Royal Hungarian Air Force, Dezső Szentgyörgyi. He was due to retire in less than three weeks.
In fiction
Copenhagen airport is used in several Danish and other Scandinavian films. The American-German 1971 Warren Beatty and Goldie Hawn film Dollars unfolds mainly at Hamburg, but a part of the film takes place also here. Dawn Divine (portrayed by Goldie Hawn) tails a man to Copenhagen in order to establish whether he is a crook, and all scenes in Copenhagen unfold at the airport.
Notes
- Number of passengers including domestic, international and transit
References
- "CPH traffic data: Close to 30.3 million passengers in 2019". Copenhagen Airports A/S. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "EKCH – København/Kastrup" (PDF). AIP Denmark. Copenhagen: Trafikstyrelsen/Danish Transport Authority. 28 June 2012. part AD 2 – EKCH. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2012. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
- http://www.cph.dk/en/about-cph/investor/traffic-statistics/cph-more-than-24-million-travellers-in-2013-a-new-record/ Archived 2 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine – total passengers 2013 was 24,067,030 of them were 22,164,738; "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 January 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Stockholm Arlanda had 20,7 million passengers in total in 2013, but around a third are usually domestic; "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 January 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) – Oslo Gardemoen had 23,159,233 passengers in 2013. But here is usually less than half international
- "Area & Runway systems". CPH Airport. Archived from the original on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "About CPH – News". CPH Airport. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- Copenhagen Airports – Copenhagen Airports Archived 27 August 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- "The pioneer era". Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Interkontinental 1940–1972". Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Hub 1973–1999". Archived from the original on 3 January 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "The airport today 2000+". Archived from the original on 3 January 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Copenhagen Airport announces expansion plans". IceNews. 7 February 2013.
- Mutzabaugh, Ben (16 April 2015). "Emirates pushes A380 seating capacity past 600". USA Today. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- "World's largest passenger plane lands at Copenhagen Airport". Copenhagen Post. 1 December 2015.
- Copenhagen Airport Departure and Shopping Area
- "Expanding CPH". Archived from the original on 2 May 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Transferpassagerer". Archived from the original on 25 April 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Bedre forhold for indenrigs". Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Central placering af Indenrigs i CPH". Archived from the original on 24 May 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Emirates to deploy the world's biggest aircraft on its Copenhagen service Archived 9 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine" CPH press, 9 April 2015.
- "CPH: A380 er en milepæl for os Archived 17 October 2015 at the Wayback Machine" Check-in.dk, 10 April 2015.
- "Verdenspremiere i CPH på 615-sæders fly" Check-in.dk, 10 April 2015.
- CPH: Two construction projects with a price tag of DKK 1.2 billion to create additional capacity for passengers and aircrafts [sic]
- Rasmussen, Thyge. "Flytrafik som vinden blæser Archived 19 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine" with Wind rose. (English: Plane traffic as the wind blows) Danish Meteorological Institute, 17 April 2015. Retrieved: 19 April 2015.
- "Direct routes from Tallinn – airBaltic". www.airbaltic.com.
- https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/291403/air-canada-ns20-international-operations-as-of-21may20/
- https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/276549/air-china-resumes-copenhagen-service-from-late-may-2018/ Air China resumes Copenhagen service from May 2018
- "Air Transat - Flights to Denmark". Air Transat. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- https://www.innsbruck-airport.com/media/17251/Linie_Charter_Winter_2017_18_D.3716849.pdf%5B%5D
- "Flight". apollorejser.dk.
- "Only Flight". tui.dk.
- "Bulgaria Air adds new scheduled charter routes in S19". routesonline.com. 28 March 2019.
- 2018, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Croatia Airlines adds seasonal Split – Copenhagen in S18".CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- https://dat.dk/ruter/aalborg-kobenhavn
- "Sharm El Sheikh". atlantisrejser.dk. 30 January 2018.
- Arjen Lutgendorff (25 February 2020). "EasyJet: Kopenhagen en Berlijn nieuwe bestemmingen vanaf Schiphol". traverpro.nl. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- "Svenska flygbolag – Nyheter från flyget i Sverige". www.svenskaflygbolag.com.
- "New direct route from Copenhagen to Åre Östersund Airport with easyJet". www.swedavia.com.
- 2018, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Iraqi Airways adds Basra – Copenhagen service from mid-Dec 2017".CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- 2018, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Montenegro Airlines resumes Tivat – Copenhagen in S18".CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- Liu, Jim (26 November 2019). "Norwegian S20 Short-Haul network additions". Routesonline. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- 2018, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Nouvelair Tunisie adds Scandinavia flight in S18".CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- Liu, Jim (25 May 2018). "Laudamotion adds Vienna base in W18". Routesonline. UBM (UK) Ltd. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- Liu, Jim. "Ryanair / Laudamotion S20 network consolidation as of 18JUN20". Routesonline. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- https://finalcall.travel/no/sas-flytter-london-avganger-til-lavprisflyplass/
- "Sommerprogram 2019: Seks nye destinationer og 17 nye direkte ruter fra Skandinavien" (in Danish). SAS. 8 October 2018. Archived from the original on 8 October 2018. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- Liu, Jim (9 October 2019). "SAS S20 Short-Haul network changes as of 08OCT19". routesonline.com.
- 2018, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Sichuan Airlines adds Copenhagen service from Dec 2018".CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/285619/sichuan-airlines-adds-helsinki-copenhagen-service-changes-from-sep-2019/
- "Flight". spies.dk.
- https://www.routesonline.com/news/38/airlineroute/291544/tap-air-portugal-june-august-2020-operations-as-of-31may20/
- https://airlinestravel.ro/wizz-air-anunta-8-rute-noi-de-la-bucuresti-cagliari-copenhaga-bergen-hamburg-karlsruhe-baden-baden-memmingen-santorini-si-mykonos.html
- https://www.financialmirror.com/2020/05/28/wizz-air-opens-11-new-routes-with-base-at-larnaca-airport/
- http://www.sobaka.ru/lifestyle/travel/110557#sn
- "Emirates SkyCargo adding Columbus, Ohio, to worldwide cargo route – Columbus – Columbus Business First". Columbus Business First. 5 May 2015. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Emirates SkyCargo Freighter Operations get ready for DWC move". Emirates SkyCargo. 2 April 2014.
- "Trafikstyrelsen Statistics" (in Danish). Danish Transport and Construction Agency. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- "Copenhagen Airport Statistics" (PNG). Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- "Database – Eurostat". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- "Database – Eurostat" ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 18 April 2018.
- http://stat.trafikstyrelsen.dk/
- Kristensen, Frederik Buhl (16 March 2015). "Boeing trodser det danske lønniveau og åbner værksted i København" [Boeing defies Danish wages, opens shop in Copenhagen]. Politiken. Archived from the original on 10 April 2015. Retrieved 11 April 2015.
- "Parkering i Københavns Lufthavn – Bestil online he". Archived from the original on 4 December 2014. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- "Accident description". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
External links
![]()
![]()