Psycholeptic
In pharmacology, a psycholeptic is a medication which produces a calming effect upon a person.[1] Such medications include barbiturates, benzodiazepines, nonbenzodiazepines, phenothiazines, opiates/opioids, carbamates, ethanol, 2-methyl-2-butanol, cannabinoids (in some classifications), some antidepressants, neuroleptics, and some anticonvulsants. Many herbal medicines may also be classified as psycholeptics (e.g. kava)
Not to be confused with Psychoanaleptic.
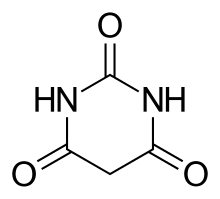
Barbiturate
The psycholeptics are classified under N05 in the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System.
See also
References
- editors, Q. Alan Xu, Timothy L. Madden; Madden, Timothy L. (2012). LC-MS in drug bioanalysis. New York: Springer. p. 352. ISBN 9781461438281. Retrieved 10 January 2017.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Psycholeptics. |
| 5-HT1AR agonists | |
|---|---|
| GABAAR PAMs |
|
| Gabapentinoids (α2δ VDCC blockers) | |
| Antidepressants |
|
| Sympatholytics (Antiadrenergics) |
|
| Others | |
| |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.