Mesalazine
Mesalazine, also known as mesalamine or 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), is a medication used to treat inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.[1] It is generally used for mildly to moderately severe disease.[1] It is taken by mouth or rectally.[1] The formulations which are taken by mouth appear to be similarly effective.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Asacol, Lialda, Pentasa, others[1] |
| Other names | mesalamine, 5-aminosalicylic acid, 5-ASA, Mesalazine (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a688021 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, rectal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | orally: 20–30% absorbed rectally: 10–35% |
| Metabolism | Rapidly & extensively metabolised intestinal mucosal wall and the liver |
| Elimination half-life | 5 hours after initial dose. At steady state 7 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.745 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
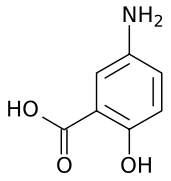
| Formula | C7H7NO3 |
| Molar mass | 153.137 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 283 °C (541 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Common side effects include headache, nausea, abdominal pain, and fever.[1] Serious side effects may include pericarditis, liver problems, and kidney problems.[1][3] Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding appears safe.[3] In people with a sulfa allergy certain formulations may result in problems.[1] Mesalazine is an aminosalicylate and anti-inflammatory.[1][3] It works by direct contact with the intestines.[1]
Mesalazine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1987.[1][4] It is available as a generic medication and sold under many brand names worldwide.[5][1] In 2017, it was the 246th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions.[6][7]
Medical uses
It is used to treat inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.[1] It is generally used for mildly to moderately severe disease.[1] It is taken by mouth or rectally.[1] The formulations which are taken by mouth appear to be similarly effective.[3]
Side effects
There are no data on use in pregnant women, but the drug does cross the placenta and is excreted in breast milk. The drug should not be used in children under two,[8] people with kidney disease,[8] or people who are allergic to aspirin.[8]
Side effects are primarily gastrointestinal but may also include headache; GI effects include nausea, diarrhea and abdominal pain. There have been scattered reports of various problems when the oral form is used, including: problems caused by myelosuppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia, and thrombocytopenia), as well as hair loss, peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, liver problems, myocarditis and pericarditis, allergic and fibrotic lung reactions, lupus erythematosus-like reactions and rash (including urticaria), drug fever, interstitial nephritis and nephrotic syndrome, usually reversible on withdrawal. Very rarely, use of mesalazine has been associated with an exacerbation of the symptoms of colitis, Stevens Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme.[8]
Chemistry
Mesalazine is the active moiety of sulfasalazine, which is metabolized to sulfapyridine and mesalazine.[9] It is also the active component of the prodrug balsalazide along with the inert carrier molecule 4-aminobenzoyl-beta-alanine.[10]
References
- "Mesalamine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists.
- "Mesalamine Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 18 September 2018. Retrieved 30 December 2019.
- British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 39–41. ISBN 9780857113382.
- "Asacol HD- mesalamine tablet, delayed release". DailyMed. 15 April 2018. Retrieved 30 December 2019.
- "ANDA Approval Reports - 2017 First Generic Drug Approvals". Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 8 April 2019.
- "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Mesalamine - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Asacol 400mg MR Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 14 April 2016. Retrieved 30 December 2019.
- Lippencott's Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology, 4th Ed. Finkel, Cubeddu and Clark
- Drugs & Therapy Properties 2003 Oct; Vol 19, No. 10
External links
- "Mesalamine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.